|
|
|
| Speciation of selenium in typical meadow soils in Tumed Left Banner, Inner Mongolia, China |
LIU Jin-Bao( ), XU Hong-Guo, YUAN Hong-Wei, ZHANG Xiao-Feng ), XU Hong-Guo, YUAN Hong-Wei, ZHANG Xiao-Feng |
| Geological Survey and Research Institute of Inner Mongolia, Hohhot 010020, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study determined the speciation, available content, and physicochemical properties of selenium in soils using samples of topsoil and soil column profiles from Tabusai Township, Tumed Left Banner, Inner Mongolia, China. Accordingly, this study investigated the compositions of the speciation and available content of soil selenium, as well as their influencing factors. The results indicate that: (1) the major forms of selenium in topsoil include humic acid bound, strong organic bound, and residue forms; (2) the concentration of in the humic acid bound selenium correlates positively with the cation exchange capacity (CEC) and the concentrations of organic matter, phosphorus, and potassium; the total selenium concentration correlates positively with the concentrations of humic acid bound selenium, Fe-Mn oxide bound selenium, strong organic bound selenium, and residue selenium, all of which exhibit promotion effects; (3) the sulfur concentration correlates negatively with the concentration of water-soluble selenium, demonstrating an inhibitory effect; (4) the concentrations of selenium in various forms tend to decrease from the surface layer to the deep layer; (5) the concentration of bioavailable selenium correlates positively with the total selenium concentration, organic-bound selenium, and water-soluble selenium and correlates negatively with the sulfur concentration. The soils in the study area, featuring a high concentration of water-soluble selenium and fairly high bioavailability, are suitable for planting selenium-rich agricultural products.
|
|
Received: 08 August 2022
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
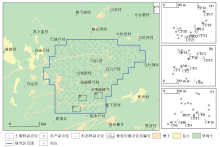
Sampling points and land type of study area
|

| 指标 | 规范要求 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | | 指标 | 规范要求 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | | 水溶态硒 | 0.005 | AFS | 0.005 | | 有效硒 | | AFS | 0.005 | | 离子交换态硒 | 0.010 | AFS | 0.010 | | 农产品硒 | 0.005 | AFS | 0.005 | | 碳酸盐结合态硒 | 0.005 | AFS | 0.005 | | 根系土硒 | 0.010 | AFS | 0.010 | | 腐殖酸结合态硒 | 0.005 | AFS | 0.005 | | pH | 0.1* | ISE | 0.1* | | 铁锰氧化物结合态硒 | 0.010 | AFS | 0.010 | | 有机质 | 0.1** | VOL | 0.02** | | 强有机结合态硒 | 0.005 | AFS | 0.005 | | CEC | 2.5*** | VOL | 2.5*** | | 残渣态硒 | 0.010 | AFS | 0.010 | | | | | |
|
Analysis methods and detection limits of selenium forms and physicochemical indexes in soil
|

| 硒形态 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 算术平均值/10-6 | 标准离差/10-6 | 变异系数 | | 水溶态硒 | 0.0073 | 0.0143 | 0.0096 | 0.0018 | 0.1920 | | 离子交换态硒 | 0.0040 | 0.0057 | 0.0049 | 0.0005 | 0.1009 | | 碳酸盐结合态硒 | 0.0037 | 0.0065 | 0.0055 | 0.0008 | 0.1503 | | 腐殖酸结合态硒 | 0.0610 | 0.1090 | 0.0824 | 0.0171 | 0.2081 | | 铁锰氧化物结合态硒 | 0.0054 | 0.0109 | 0.0071 | 0.0014 | 0.2024 | | 强有机结合态硒 | 0.0780 | 0.1550 | 0.1110 | 0.0201 | 0.1809 | | 残渣态硒 | 0.0873 | 0.2216 | 0.1343 | 0.0315 | 0.2349 | | 有效硒 | 0.0102 | 0.0190 | 0.0136 | 0.0031 | 0.2281 |
|
Statistics content of each form of selenium and effective selenium in the surface soil(n=14)
|

| 指标 | 水溶态 | 离子
交换态 | 碳酸盐
结合态 | 腐殖酸
结合态 | 铁锰氧化
物结合态 | 强有机
结合态 | 残渣态 | 可溶态 | 有机态 | 难溶态 | 三项
累加和 | | 最大值 | 3.86 | 2.03 | 2.38 | 28.01 | 2.38 | 36.21 | 44.98 | 7.82 | 60.03 | 73.55 | 93.40 | | 最小值 | 1.88 | 0.97 | 1.10 | 19.08 | 1.67 | 26.59 | 33.20 | 4.58 | 48.10 | 65.21 | 90.00 | | 平均值 | 2.76 | 1.44 | 1.61 | 23.27 | 2.01 | 31.31 | 37.60 | 5.80 | 54.58 | 68.92 | 92.19 |
|
Proportion of each form of selenium in the surface soil %
|

| 硒形态 | ZH6 | ZH10 | | 平均值/10-6 | 范围/10-6 | 所占比例/% | 平均值/10-6 | 范围/10-6 | 所占比例/% | | 水溶态 | 0.0068 | 0.0049~0.0092 | 2.76 | 0.0084 | 0.0048~0.0143 | 3.30 | | 离子交换态 | 0.0048 | 0.0040~0.0061 | 1.96 | 0.0047 | 0.0037~0.0106 | 1.85 | | 碳酸盐结合态 | 0.0056 | 0.0039~0.0066 | 2.26 | 0.0053 | 0.0047~0.0061 | 2.09 | | 腐殖酸结合态 | 0.0536 | 0.0270~0.0850 | 21.66 | 0.0613 | 0.0340~0.1090 | 23.96 | | 铁锰氧化物结合态 | 0.0050 | 0.0035~0.0084 | 2.00 | 0.0046 | 0.0025~0.0082 | 1.78 | | 强有机结合态 | 0.0879 | 0.0310~0.1550 | 35.49 | 0.0783 | 0.0380~0.1280 | 30.61 | | 残渣态 | 0.0839 | 0.0413~0.1598 | 33.88 | 0.0931 | 0.0318~0.1679 | 36.41 | | 各形态硒含量之和 | 0.2476 | 0.1179~0.4281 | 100.00 | 0.2556 | 0.1234~0.4352 | 100.00 |
|
Selenium content and proportion of each form in vertical soil profiles(n=16)
|
|
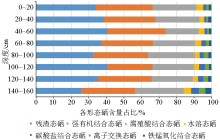
Characteristic comparison of different selenium forms in the vertical soil section CP22
|
|
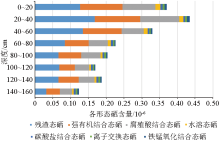
Distribution of selenium contents of various forms in the vertical soil section CP22
|

| 指标 | 水溶态硒 | 离子
交换态硒 | 碳酸盐
结合态硒 | 腐殖酸
结合态硒 | 铁锰氧化物
结合态硒 | 强有机
结合态硒 | 残渣态硒 | | 有效硒 | 0.9341** | 0.1905 | -0.0719 | 0.9701** | 0.6667 | 0.9524** | 0.7619* | | 全量硒 | 0.9461** | 0.0476 | -0.0958 | 0.9940** | 0.6667 | 1.0000** | 0.8810** | | 有机质 | 0.8253* | 0.3473 | 0.0000 | 0.8916** | 0.4671 | 0.8743** | 0.6108 | | pH值 | -0.9940** | -0.1190 | -0.0120 | -0.9461** | -0.7381* | -0.9524** | -0.7619* | | CEC | 0.1557 | 0.1429 | -0.1198 | 0.2156 | -0.2857 | 0.1905 | 0.0238 | | P | 0.9102** | 0.1667 | -0.2275 | 0.9940** | 0.6905 | 0.9762** | 0.8095* | | K | 0.9515** | 0.1205 | -0.0849 | 0.9940** | 0.6747 | 0.9880** | 0.8314* | | S | 0.7545* | 0.0238 | -0.2275 | 0.9102** | 0.5952 | 0.8810** | 0.8095* |
|
Statistical of Spearman's rank correlation coefficients (r) between soil physicochemical indicators, effective selenium, total selenium and each form of selenium in the vertical soil section CP22
|

| 指标 | 水溶态硒 | 离子
交换态硒 | 碳酸盐
结合态硒 | 腐殖酸
结合态硒 | 铁锰氧化物
结合态硒 | 强有机
结合态硒 | 残渣态硒 | | 全量硒 | 0.4565 | 0.0330 | -0.0352 | 0.8405** | 0.8490** | 0.9493** | 0.7877** | | 有机质 | 0.1080 | 0.1716 | -0.3212 | 0.7107** | 0.5006 | 0.4273 | 0.4158 | | CEC | 0.0862 | 0.0540 | -0.3252 | 0.6108* | 0.4641 | 0.2627 | 0.2514 | | pH | 0.4823 | -0.4141 | -0.0220 | -0.1850 | 0.0077 | -0.0584 | -0.3612 | | P | 0.4724 | 0.1167 | -0.2797 | 0.6806** | 0.3742 | 0.4498 | 0.3216 | | S | -0.6615** | -0.1342 | 0.1276 | -0.2992 | -0.1808 | -0.4053 | -0.2772 | | K | 0.0796 | -0.0993 | -0.2693 | 0.5464* | 0.4237 | 0.2232 | 0.2351 | | 黏土矿物 | 0.1610 | -0.1034 | -0.2992 | 0.4224 | -0.0243 | 0.1718 | 0.1628 | | 有效硒 | 0.5254* | -0.0859 | -0.1123 | 0.4648 | 0.3322 | 0.5865* | 0.5198 |
|
Statistical of Spearman's rank correlation coefficients (r) between soil physicochemical indicators, effective selenium and each form of selenium in soils
|

| 指标 | 全量硒 | 黏土矿物 | 有机质 | pH | CEC | P | S | K | | 有效硒 | 0.6161* | 0.4129 | 0.3378 | 0.0396 | 0.0055 | 0.2511 | -0.5853* | 0.0916 |
|
Statistical of Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (r) between soil physicochemical indicators and effective selenium in soils
|

| 指标 | 水溶态硒 | 离子
交换态硒 | 碳酸盐态硒 | 腐殖酸
结合态硒 | 铁锰氧化物
结合态硒 | 强有机
结合态硒 | 残渣态硒 | 有效硒 | | 玉米籽粒硒 | 0.7289* | 0.0361 | 0.0719 | 0.0361 | -0.1818 | -0.0843 | 0.0838 | 0.8024* |
|
Statistical of Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (r) between soil selenium form, effective state and selenium content of maize seeds
|
| [1] |
Schwarz K, Foltz C M. Selenium as an integral part of factor 3 against dietary necrotic liver degeneration[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1957, 79(12):3292-3293.
|
| [2] |
Zhang X L, Ren S F, Li W C, et al. Study on correla-tion between humic acid and selenium in Kaschin-Beck disease areas[J]. Journal of Environment Sciences, 1991, 3(4):102-107.
|
| [3] |
Rotruck J T, Pope A L, Ganther H E, et al. Selenium:Biochemical role as a component of glutathione peroxidase[J]. Science, 1973, 179(4073):588-590.
|
| [4] |
Rayman M P. The argument for increasing selenium intake[J]. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society, 2002, 61(2):203-215.

|
| [5] |
李家熙, 张光第, 葛晓立, 等. 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.
|
| [5] |
Li J X, Zhang G D, Ge X L, et al. Prediction and geochemical environmental character of human selenium imbalances[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000.
|
| [6] |
陈亮, 李桃. 元素硒与人体健康[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2004, 21(3):58-59.
|
| [6] |
Chen L, Li T. Element selenium and human body health[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2004, 21(3):58-59.
|
| [7] |
Hartikainen H. Biogeochemistry of selenium and its impact on food chain quality and human health[J]. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 2005, 18(4):309-318.
|
| [8] |
Mombo S, Schreck E, Dumat C, et al. Bioaccessibility of selenium after human ingestion in relation to its chemical species and compartmentalization in maize[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2015, 38(3):869-883.

|
| [9] |
袁星荣. 硒对现代慢性疾病的预防和治疗意义[J]. 世界元素医学, 2007, 14(1/2):33-36.
|
| [9] |
Yuan X R. The significance of selenium in prevention and treatment of modern chronic diseases[J]. World Elemental Medicine, 2007, 14(1/2):33-36.
|
| [10] |
梅光泉, 应惠芳. 微量元素硒与植物有机硒化合物[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2003, 20(6):59-61.
|
| [10] |
Mei G Q, Ying H F. Trace element selenium and organic selenium compounds from plants[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2003, 20(6):59-61.
|
| [11] |
何亚琳. 环境硒与硒营养[J]. 贵州科学, 1995, 13(3):56-60.
|
| [11] |
He Y L. Environmental Se and Se nutrition[J]. Guizhou Science, 1995, 13(3):56-60.
|
| [12] |
王喜宽, 黄增芳, 王忠, 等. 内蒙古河套农业经济区多目标区域地球化学调查报告[R]. 内蒙古自治区地质调查院, 2007.
|
| [12] |
Wang X K, Huang Z F, Wang Z, et al. Report of multi-purpose regional geochemical survey in Hetao agricultural economic zone,Inner Mongolia[R]. Geological Survey Institute of Inner Mongolia, 2007.
|
| [13] |
王喜宽, 刘金宝, 孙凤霞, 等. 内蒙古呼包平原富硒耕地开发及重金属污染治理示范成果报告[R]. 内蒙古自治区地质调查院, 2019.
|
| [13] |
Wang X K, Liu J B, Sun F X, et al. Report on demonstration results of selenium-rich cultivated land development and heavy metal pollution control in Hubao Plain,Inner Mongolia[R]. Geological Survey Institute of Inner Mongolia, 2019.
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0295—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.
|
| [14] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0295—2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment[S]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016.
|
| [15] |
谭见安, 李日邦, 侯少范, 等. 环境硒与健康[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社,1989.
|
| [15] |
Tan J A, Li R B, Hou S F, et al. Environmental selenium and health[M]. Beijing: People’s Health Publishing House,1989.
|
| [16] |
周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [16] |
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [17] |
周墨, 唐志敏, 张明, 等. 赣州市水稻及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤界限值[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(4):604-609.
|
| [17] |
Zhou M, Tang Z M, Zhang M, et al. Selenium contents of rice and rhizosphere soil and threshold value of selenium-rich soil in Ganzhou of Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(4):604-609.
|
| [18] |
王惠艳, 曾道明, 郭志娟, 等. 天然富硒土地划定的富硒阈值[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1):333-342.
|
| [18] |
Wang H Y, Zeng D M, Guo Z J, et al. Selenium threshold for the delimitation of natural selenium-enriched[J]. Land Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1):333-342.
|
| [19] |
王锐, 余涛, 曾庆良, 等. 我国主要农耕区土壤硒含量分布特征、来源及影响因素[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5):359-366.
|
| [19] |
Wang R, Yu T, Zeng Q L, et al. Distribution characteristics,origin and influencing factors of soil selenium concentration of main farming areas in China[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5):359-366.
|
| [20] |
宁夏回族自治区质量技术监督局. DB64/T 1221—2016宁夏富硒农产品标准(水稻、玉米、小麦与枸杞干果)[S]. 银川: 宁夏人民教育出版社, 2016.
|
| [20] |
Ningxia Quality and Technical Supervision Bureau. DB64/T 1221—2016 Standard for selenium-rich agricultural products of ningxia(rice,corn,wheat and medlar dried fruit)[S]. Yinchuan: Ningxia People's Education Press, 2016.
|
| [21] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0258—2014多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250 000)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.
|
| [21] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0258—2014 Specification of multi-purpose regional geochemical survey(1∶250,000)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015.
|
| [22] |
李健, 范学臻. 农产品产地环境采样中土壤样品采集点的布设[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020(1):175,180.
|
| [22] |
Li J, Fan X Z. Layout of soil sample collection points in environmental sampling of agricultural products[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020(1):175,180.
|
| [23] |
中国地质调查局.DD 2005-03生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求(试行)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005.
|
| [23] |
China Geological Survey. DD2005-03 Technical requirements for sample analysis for eco-geochemical evaluation (trial)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2005.
|
| [24] |
王松山. 土壤中硒形态和价态及生物有效性研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012.
|
| [24] |
Wang S S. Fractionation and speciations of selenium in soil and its bioavailability[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2012.
|
| [25] |
黄春雷, 宋明义, 魏迎春, 等. 浙中典型富硒土壤区土壤硒含量的影响因素探讨[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(11):4405-4410.
|
| [25] |
Huang C L, Song M Y, Wei Y C, et al. Study on selenium contents of typical selenium-rich soil in the middle area of Zhejiang and its influencing factors[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(11):4405-4410.
|
| [26] |
周小娟, 张嫣, 祝莉玲, 等. 武汉市侏儒—消泗地区农田系统中硒的分布特征及有效性研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4):158-163,171.
|
| [26] |
Zhou X J, Zhang Y, Zhu L L, et al. Research on seleniun distribution and effectiveness in the farm system in Zhuru and Xiaosi areas,Wuhan City[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(4):158-163,171.
|
| [27] |
谭见安. 环境生命元素与克山病[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社,1996.
|
| [27] |
Tan J A. Environmental life elements and keshandisease[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press,1996.
|
| [28] |
武少兴, 龚子同, 黄标, 等. 我国土壤中的水溶态硒含量及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 中国环境科学, 1997, 17(6):522-525.
|
| [28] |
Wu S X, Gong Z T, Huang B, et al. Water-soluble selenium in main soil types of China and in relation to some soil properties[J]. China Environmental Science, 1997, 17(6):522-525.
|
| [29] |
沈燕春, 周俊. 土壤硒的赋存状态与迁移转化[J]. 安徽地质, 2011, 21(3):186-191.
|
| [29] |
Shen Y C, Zhou J. Occurrence,migration and reansformation of selenium in soil[J]. Geology of Anhui, 2011, 21(3):186-191.
|
| [30] |
Mao J D, Xing B S. Fractionation and distribution of selenium in soils[J]. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 1999, 30(17/18):2437-2447.

|
| [31] |
Sharmasarkar S, Vance G F. Fractional partitioning for assessing solid-phase speciation and geochemical transformations of soil selenium[J]. Soil Science, 1995, 160(1):43-55.

|
| [32] |
何振立, 杨肖娥, 祝军, 等. 中国几种土壤中的有机硒及其分布特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 1993, 13(3):281-287.
|
| [32] |
He Z L, Yang X E, Zhu J, et al. Organic selenium and its distribution in soils[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1993, 13(3):281-287.
|
| [33] |
Rosenfeld I, Beath O A. Selenium geobotany,biochemistry,toxicity and nutrition[M]. New York: Academic Press,1964.
|
| [34] |
董广辉, 武志杰, 陈利军, 等. 土壤—植物生态系统中硒的循环和调节[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2002, 18(1):65-68.
|
| [34] |
Dong G H, Wu Z J, Chen L J, et al. Cycling and regulation of selenium in soil-plant ecosystem[J]. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 2002, 18(1):65-68.
|
| [35] |
黄淇, 成杭新, 陈出新, 等. 北京市房山区富硒土壤调查与评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(5):889-894.
|
| [35] |
Huang Q, Cheng H X, Chen C X, et al. The investigation and evaluation of selenium-rich soil in Fangshan District of Beijing City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(5):889-894.
|
| [36] |
郎春燕, 黄秀丽, 李小娇. 成都东郊稻田土壤中硒的形态的分布特征[J]. 西南农业学报, 2013, 26(2):642-646.
|
| [36] |
Lang C Y, Huang X L, Li X J. Distribution of selenium species in rice paddy soils of east suburb in Chengdu[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 26(2):642-646.
|
| [37] |
郦逸根, 徐静, 李琰, 等. 浙江富硒土壤中硒赋存形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2007, 31(2):95-109.
|
| [37] |
Li Y G, Xu J, Li Y, et al. The modes of occurrence of selenium in selenium-rich soil of Zhejiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 31(2):95-109.
|
| [38] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海东部碱性土壤中硒的形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [38] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of Se speciation of alkaline soil in eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [39] |
唐玉霞, 王慧敏, 刘巧玲, 等. 河北省麦田土壤硒的含量、形态及其有效性研究[J]. 华北农学报, 2010, 25(S):194-197.
|
| [39] |
Tang Y X, Wang H M, Liu Q L, et al. Study on the content,speciation distribution and availability of selenium in wheat field soils of Hebei[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-sinica, 2010, 25(S):194-197.
|
| [40] |
陈铭, 谭见安, 王五一. 环境硒与健康关系研究中的土壤化学与植物营养学[J]. 土壤学进展, 1994, 22(4):1-10.
|
| [40] |
Chen M, Tan J A, Wang W Y. Soil chemistry and plant nutrition in the study of the relationship between environmental selenium and health[J]. Progress in Soil Science, 1994, 22(4):1-10.
|
| [41] |
宋明义, 冯雪外, 周涛发, 等. 浙江典型富硒区硒与重金属的形态分析[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(6):960-965.
|
| [41] |
Song M Y, Feng X W, Zho T F, et al. Chemical species of heavy metals and selenium in representative Se-rich area,Zhejiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(6):960-965.
|
| [42] |
Tolu J, Di Tullo P, Le Hécho I, et al. A new methodology involving stable isotope tracer to compare simultaneously short-and long-term selenium mobility in soils[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2014, 406(4):1221-1231.

|
| [43] |
Peng Q, Guo L, Ali F, et al. Influence of Pak choi plant cultivation on Se distribution speciation and bioavailability in soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 2016, 403(1/2):331-342.

|
| [44] |
赵妍, 宗良纲, 曹丹, 等. 江苏省典型茶园土壤硒分布特性及其有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2011, 30(12):2467-2474.
|
| [44] |
Zhao Y, Zong L G, Cao D, et al. Distribution and availability of selenium in typical tea garden of Jiangsu Province,China[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2011, 30(12):2467-2474.
|
| [45] |
马友华, 丁瑞兴, 张继榛, 等. 植物体内硒和硫的相互作用[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2001, 37(2):161-166.
|
| [45] |
Ma Y H, Ding R X, Zhang J Z, et al. Interaction of selenium and sulfur in plants[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2001, 37(2):161-166.
|
| [46] |
魏然, 候青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 江西省鄱阳湖流域根系土硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(1):109-113.
|
| [46] |
Wei R, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. An analysis of speciation of selenium asits transformation and enrichment in root soil of Poyang lake basin,Jiangxi Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(1):109-113.
|
| [47] |
Dinh Q T, Wang M K, Tran T A T, et al. Bioavailability of selenium in soil-plant system and a regulatory approach[J]. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 49 (6):443-517.

|
| [1] |
BAO Feng-Qin, CHENG Hang-Xin, YONG Sheng, YANG Yu-Liang, MA Zhi-Chao, ZHAO Li-Juan. The comprehensive evaluation of farmland soil environmental quality and suggestions on the development of agriculture with distinctive local features in Tumed Left Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 487-495. |
| [2] |
HOU Jin-Kai, SONG Yan-Bin, ZHU Rui-Zhen, XIN Feng-Pei, ZHOU Jian-Chuan, LU Fu-Lan, YAO Jie. Selenium speciation in surface soil in Yaling Town, Yichuan County—Xiaodian Town,Ruyang County in Luoyang City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2): 511-517. |
|
|
|
|

