|
|
|
| Enrichment characteristics, source identification, and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in typical cultivated land in the mountainous area of southern Anhui Province |
YANG Yan( ), LIU Bin, XIA Fei-Qiang, CHEN Ping-Feng, ZHANG Xiang ), LIU Bin, XIA Fei-Qiang, CHEN Ping-Feng, ZHANG Xiang |
| Anhui Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Prospecting Techniques, Hefei 230022, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to explore the enrichment characteristics and origin of soil heavy metals in typical cultivated land in the mountainous area of southern Anhui province. With Ningguo City in southeastern Anhui Province as the research object, this study collected 1399 topsoil samples in the cultivated land for determining the concentrations of As, Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Cu, and Zn. Furthermore, this study conducted a health risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals using the correlation analysis, the soil environmental quality - risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land, the geoaccumulation index, the health risk index, and the positive matrix factorization (PMF) model. The results are as follows: (1) The average concentrations of As, Cr, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Cu, and Zn were 15.8×10-6, 0.41×10-6, 0.106×10-6, 31×10-6, 67×10-6, 29×10-6, 29×10-6, and 94×10-6, respectively, which were all higher than their background values in Anhui Province, except Ni. (2) The soil heavy metals generally exhibited low pollution risks, with the heavy metal concentrations of 866 soil samples lower than their risk screening values. (3) The cultivated soil was primarily polluted by Hg, Cd, and As, as indicated by the geoaccumulation index results. (4) Both non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risk levels in adults in the study area were within the acceptable ranges, as revealed by the health risk assessment results. (5) Four sources of heavy metals in the study area were identified based on the PMF model: industrial and agricultural emissions associated with human activities, atmospheric deposition, soil parent materials related to soil types, and the geological background source.
|
|
Received: 30 November 2022
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
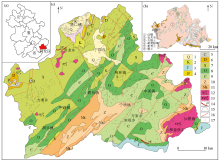
Geographical location (a),soil type (b), and sampling point distribution(c) of the study area
1—Quaternary;2—Cretaceous;3—Jurassic;4—Permian;5—Carboniferous;6—Devonian;7—Silurian;8—Ordovician;9—Cambrian;10—Tanian;11—Nanhua system;12—Yanshanian monzonitic granite;13—Yanshanian monzonitic granite porphyry;14—granite porphyry;15—stratigraphic boundary;16—fault;17—soil sampling points
|

| 元素/指标 | 分析方法 | 检出限/10-6 | 测定范围/10-6 | | As | AFS | 0.2 | 0.2~500 | | Cd | ICP-MS | 0.02 | 0.02~4.0 | | Hg | AFS | 0.0005 | 0.0005~10 | | Pb | ICP-MS | 2 | 2~2000 | | Cr | ICP-AES | 3 | 3~3500 | | Ni | ICP-AES | 0.05 | 0.05~2000 | | Cu | ICP-AES | 1 | 1~2000 | | Zn | ICP-AES | 2 | 2~3000 | | pH | ISE | 0.1* | 0.1~14.0* |
|
Analysis methods and detection limits for each element
|

| 等级 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | | Igeo | ≤0 | >0~1 | >1~2 | >2~3 | >3~4 | >4~5 | ≥5 | | 污染程度 | 无 | 无到中等 | 中等 | 中等到重度 | 重度 | 重度到极度 | 极度 |
|
Classification standard of geoaccumulation index
|

| 参数 | 含义 | 单位 | 成人 | 儿童 | | | 土壤摄入量 | mg/d | 100 | 200 | | EF | 暴露频率 | d/a | 350 | 350 | | ED | 暴露期 | a | 24 | 6 | | BW | 平均体重 | kg | 61.8 | 19.2 | | AT | 平均作用时间 | d | 9125 | 2190 | | SA | 可能接触土壤的皮肤面积 | cm2/d | 5700 | 2800 | | AF | 皮肤对土壤的吸附系数 | mg/cm2 | 0.07 | 0.2 | | ABS | 皮肤吸收率 | % | 0.1 | 0.1 | | PEF | 土壤尘产生因子 | m3/kg | 1.36′109 | 1.36′109 | | | 日空气吸入量 | m3/d | 14.5 | 7.5 |
|
Health risk assessment model exposure parameters
|

| 元素 | 参考计量RfD/mg·(kg·d)-1 | 致癌斜率SF/[mg/(kg·d)]-1 | | 经口 | 皮肤 | 呼吸 | 经口 | 皮肤 | 呼吸 | | As | 3.00×10-4 | 1.23′10-4 | 4.29′10-6 | 1.50 | 1.50 | 15.10 | | Cd | 1.00×10-3 | 2.50′10-5 | 2.86′10-6 | | | 6.30 | | Hg | 3.00×10-4 | 2.14′10-5 | | | | | | Pb | 1.40×10-3 | 5.24′10-4 | | 8.50×10-3 | | 4.20×10-2 | | Cr | 3.00×10-3 | 3.00′10-5 | 2.86′10-5 | 5.01×10-1 | 2.00′101 | 4.20′101 | | Ni | 2.00×10-2 | 5.40′10-3 | 9.00′10-5 | 1.70 | 4.25′101 | 8.40×10-1 | | Cu | 4.00×10-2 | 1.20′10-2 | | | | | | Zn | 3.00×10-1 | 6.00′10-2 | | | | |
|
RfD and SF of different heavy metal exposure pathways
|

| 参数 | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | Hg | pH | | 原始数据 | 最大值 | 326 | 95 | 94.48 | 451 | 16.06 | 225 | 292.5 | 0.650 | 8.3 | | 最小值 | 10 | 7 | 4.49 | 39 | 0.03 | 4 | 1.3 | 0.030 | 4.3 | | 中位数 | 68 | 27 | 28.20 | 91 | 0.21 | 30 | 10.6 | 0.100 | 5.4 | | 算术平均值 | 67 | 29 | 29.00 | 94 | 0.41 | 31 | 15.8 | 0.106 | 5.5 | | 标准离差 | 17.450 | 10.998 | 9.863 | 34.392 | 0.799 | 7.993 | 18.902 | 0.048 | 0.659 | | 变异系数 | 0.26 | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.37 | 1.97 | 0.26 | 1.20 | 0.46 | 0.12 | | 迭代剔除后 | 算术平均值 | 67 | 29 | 28.57 | 91 | 0.27 | 30 | 11.4 | 0.098 | 5.4 | | 标准离差 | 14.657 | 9.919 | 9.025 | 26.139 | 0.173 | 4.567 | 6.155 | 0.031 | 0.363 | | 变异系数 | 0.22 | 0.35 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.64 | 0.15 | 0.54 | 0.32 | 0.07 | | 样品数量 | 1374 | 1380 | 1383 | 1363 | 1288 | 1357 | 1276 | 1329 | 1290 | | 安徽省[11] | 算术平均值 | 66.5 | 20.4 | 29.8 | 62 | 0.097 | 26.6 | 9.0 | 0.033 | 6.4 | | 全国[17] | 算术平均值 | 66 | 25 | 27 | 71 | 0.205 | 30 | 10.3 | 0.076 | |
|
Basic statistics of heavy metals in soil
|

土壤污染
风险等级 | 样品数/件 | | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | Hg | 综合 | | 低风险 | 1398 | 1343 | 1393 | 1382 | 930 | 1396 | 1266 | 1397 | 866 | | 风险可控 | 1 | 56 | 6 | 17 | 437 | 3 | 130 | 2 | 498 | | 较高风险 | | | | | 32 | | 3 | | 35 |
|
Statistical results of cultivated land soil pollution risk levels in the study area
|

| 元素 | Igeo≤0 | 0<Igeo≤1 | 1<Igeo≤2 | 2<Igeo≤3 | 3<Igeo≤4 | 4<Igeo≤5 | Igeo>5 | | 污染程度 | 无 | 无到中等 | 中等 | 中等到重度 | 重度 | 重度到极度 | 极度 | | Cr | 99.0 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cu | 62.1 | 36.9 | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Ni | 95.4 | 4.4 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Zn | 53.4 | 44.8 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cd | 20.7 | 42.8 | 20.6 | 11.8 | 2.7 | 0.8 | 0.6 | | Pb | 93.9 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | As | 65.0 | 24.2 | 7.0 | 3.1 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 0 | | Hg | 3.4 | 51.5 | 41.0 | 4.0 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 |
|
The proportion of heavy metals in different levels of geo-accumulation index
|

| 元素 | Cr | Cu | Ni | Zn | Cd | Pb | As | Hg | | Cr | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | Cu | 0.613 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | Ni | 0.743 | 0.872 | 1.000 | | | | | | | Zn | 0.371 | 0.818 | 0.769 | 1.000 | | | | | | Cd | 0.224 | 0.554 | 0.551 | 0.759 | 1.000 | | | | | Pb | 0.181 | 0.401 | 0.290 | 0.444 | 0.256 | 1.000 | | | | As | 0.273 | 0.379 | 0.348 | 0.269 | 0.170 | 0.225 | 1.000 | | | Hg | 0.116 | 0.175 | 0.136 | 0.187 | 0.125 | 0.130 | -0.019 | 1.000 |
|
Correlation analysis of heavy metal content in soil
|
|
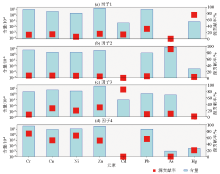
Source profiles and source contribution of soil heavy metals in the study area from PMF
|
|
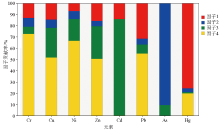
Factors profiles of heavy metals sources identified by PMF
|
|
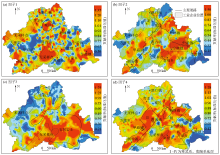
Space distribution of PMF-factors
|
| [1] |
国务院. 中共中央国务院关于做好2022年全面推进乡村振兴重点工作的意见[N/OL]. 新华社,2022-2-22. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2022-02/22/content_5675035.htm
|
| [1] |
The State Council. Opinions of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China and the State Council on doing well the key work of comprehensively promoting rural revitalization in 2022[N/OL]. Xinhua News Agency,2022-2-22. http://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2022-02/22/content_5675035.htm
|
| [2] |
中国地质调查局. 中国耕地地球化学调查报告(2015年)[EB/OL]. 北京, 2015. https://www.cgs.gov.cn/xwl/dzzl/201603/U020160726370276602662.pdf.

|
| [2] |
China Geological Survey. Report on geochemical survey of cultivated land in China 2015[EB/OL]. Beijing, 2015. https://www.cgs.gov.cn/xwl/dzzl/201603/U020160726370276602662.pdf.

|
| [3] |
关连珠. 普通土壤学[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2016:366-374.
|
| [3] |
Guan L Z. General soil science[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2016:366-374.
|
| [4] |
Wang F, Guan Q, Tian J, et al. Contamination characteristics,source apportionment,and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the Hexi Corridor[J]. Catena:Giessen, 2020, 191:104573.
|
| [5] |
尹国庆, 江宏, 王强, 等. 安徽省典型区农用地土壤重金属污染成因及特征分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(1):96-104.
|
| [5] |
Yin G Q, Jiang H, Wang Q, et al. Analysis of the causes and characteristics of heavy metal pollution in agricultural land in typical areas of Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Agricultural Environmental Science, 2018, 37(1):96-104.
|
| [6] |
夏飞强, 张祥, 杨艳, 等. 安徽省宁国市土壤和农产品硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(3):585-593.
|
| [6] |
Xia F Q, Zhang X, Yang Y, et al. Selenium geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil and agricultural products in Ningguo City Anhui Province[J]. Soil, 2021, 53(3):585-593.
|
| [7] |
陶汝鹏, 吴志辉. 宁国山核桃主产区土壤肥力调查与分析[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2018, 24(18):73-75,84.
|
| [7] |
Tao R P, Wu Z H. Investigation and analysis of soil fertility in Ningguo City cathayensis main production area[J]. Anhui Agricultural Bulletin, 2018, 24(18):73-75,84.
|
| [8] |
生态环境部国家市场监督管理总局. GB 15618—2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管理标准(试行)[S].
|
| [8] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment General Administration for National Market Supervision. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk management standard for soil pollution of agricultural land[S].
|
| [9] |
李笑诺, 丁寿康, 陈卫平, 等. 土壤环境质量预警体系构建与应用[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(6):2834-2841.
|
| [9] |
Li X N, Ding S K, Chen W P, et al. Construction and application of soil environmental quality early warning system[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(6):2834-2841.
|
| [10] |
Muller G. Index of geoaccumulation in sediments of the Rhine river[J]. Geojournal, 1969, 2(3):109-118.
|
| [11] |
中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990:329-380.
|
| [11] |
China National Environmental Monitoring Centre. Background value of soil elements in China[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990:329-380.
|
| [12] |
US EPA. Supplemental guidance for developing soil screening levels for superfund sites[R]. Washington DC: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, 2002:4-24.
|
| [13] |
US EPA. Risk assessment guidance for superfound.Volume1:human health evaluation manual[R]. Washington DC: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, 1989:6-50.
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国地质矿产行业标准. DZ/T 0354—2020局部生态地球化学评价规范[S].
|
| [14] |
Geological and Mineral Industry Standards of the People 's Republic of China. DZ/T 0354—2020 Specification of local ecogeochemistry assessment[S].
|
| [15] |
环境保护部. 中国人群暴露参数手册[M]. 北京: 中国环境出版社, 2013:16-845.
|
| [15] |
Ministry of Environmental Protection. Chinese population exposure parameter manual[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2013:16-845.
|
| [16] |
Liu H, Wang H, Zhang Y, et al. Risk assessment spatial distribution and source apportionment of heavy metals in Chinese surface soils from a typically tobacco cultivated area[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2018, 25(17):16852-16863.
|
| [17] |
侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020.
|
| [17] |
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical parameters in China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020.
|
| [18] |
肖婷. 宁国市土壤pH调查及改良措施[J]. 宁夏农林科技, 2013, 54(8):46-56.
|
| [18] |
Xiao T. Soil pH survey and improvement measures in Ningguo City[J]. Ningxia Journal of Agro-Forestry Science and Technology, 2013, 54(8):46-56.
|
| [19] |
杨剑洲, 龚晶晶, 王振亮, 等. 海南岛半干旱区农用地土壤重金属富集因素、健康风险及来源识别[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10):4590-4600.
|
| [19] |
Yang J Z, Gong J J, Wang Z L, et al. Enrichment factors health risks and source identification of heavy metals in agricultural soil in semi-arid area of Hainan Island[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(10):4590-4600.
|
| [20] |
吕建树. 烟台海岸带土壤重金属定量源解析及空间预测[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(3):713-725.
|
| [20] |
Lyu J S. Quantitative source analysis and spatial prediction of soil heavy metals in Yantai coastal zone[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(3):713-725.
|
| [21] |
Liu R, Wang Q, Lu X, et al. Distribution and speciation of mercury in the peat bog of Xiaoxing'an Mountain northeastern China[J]. Environment Pollution, 2003, 124(1):39-46.

|
| [22] |
夏飞强, 张祥, 杨艳, 等. 宁国市土地质量地球化学调查与评价成果报告[R]. 安徽省地球物理地球化学勘查技术院, 2020.
|
| [22] |
Xia F Q, Zhang X, Yang Y, et al. Results report of geochemical survey and evaluation of land quality in Ningguo City[R]. Anhui Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration Technology, 2020.
|
| [23] |
王云, 魏复盛. 土壤环境元素化学[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1995:58-71.
|
| [23] |
Wang Y, Wei F S. Soil environmental element chemistry[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1995:58-71.
|
| [1] |
FAN Hai-Yin, SONG Rui-Rui, YU Lin-Song, TENG Yong-Bo, WAN Fang, ZHANG Xiu-Wen, LI Sheng-Yu, ZHAO Chuang. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of groundwater in a typical chemical industry park in northwestern Shandong, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1326-1335. |
| [2] |
WANG Hui-Yan, PENG Min, MA Hong-Hong, ZHANG Fu-Gui. Ecological risk assessment of cultivated land in typical areas with high heavy metal background values in Guizhou Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1109-1117. |
|
|
|
|

