|
|
|
| Distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals from dry and wet atmospheric deposition in northern Xiushan County, Chongqing |
CAI Ke-Ke1( ), ZHAO Zhi-Qiang1, MENG Li2,3, WANG Xiao-Meng1, LIU Jian1, LUO Ren-Feng1 ), ZHAO Zhi-Qiang1, MENG Li2,3, WANG Xiao-Meng1, LIU Jian1, LUO Ren-Feng1 |
1. Chongqing Geological and Mineral Resource Exploration and Development Bureau 607 Geological Team, Chongqing 400054, China
2. Chongqing Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Chongqing 401120, China
3. College of Environment and Ecology, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to determine the contents of heavy metals from dry and wet atmospheric deposition in northern Xiushan County for targeted environmental pollution prevention and control and safe farmland soil utilization. Based on the dry and wet atmospheric deposition samples continuously received from 18 sampling sites in northern Xiushan County from November 2019 to November 2020, this study tested the contents of seven heavy metal elements, including Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, and Hg. Considering the topographic features, this study analyzed the distribution patterns and sources of heavy metals from dry and wet atmospheric deposition in northern Xiushan County. Moreover, this study assessed the soil pollution caused by heavy metals from dry and wet atmospheric deposition using the geoaccumulation index method. The results show that except Hg, the other six heavy metal elements exhibited significant zoning, with their high-value deposition areas distributed primarily in the flanks and eastern segment of Chuanhegai, where their contents were much higher than the national and Chongqing's averages. In contrast, their depositional fluxes in other general deposition areas were less than the national averages by 25%. The high dry and wet atmospheric deposition in the flanks of Chuanhegai was subjected to both the mining of the lead-zinc deposit in Huayuan County in the east and the special topography. The abrupt topography increased the fluxes of the seven heavy metals in the dry and wet atmospheric deposition by 49 times. Therefore, the monitoring and assessment of environmental safety in this type of landform area should be strengthened. According to the assessment results of the geoaccumulation index method, the flanks of Chuanhegai were moderately-severely to extremely polluted by Cd, slightly-moderately polluted by Pb, and slightly-moderately to severely polluted by Zn.
|
|
Received: 29 August 2022
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
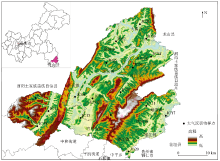
|
Study area and distribution of atmospheric dust sampling sites
|

|
Symbol diagram of heavy metal element deposition flux at various points
Note:blue points are below 25% percentile;green points are in 25%~50% percentile;orange points are in 50%~75% percentile;rose points are in 75%~90% percentile;red points are above 90% percentile
|

| 分区 | 样品编号 | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Hg | | 一般区 | JC01 | 0.077 | 0.935 | 1.150 | 0.550 | 2.014 | 4.765 | 0.155 | | JC02 | 0.059 | 0.948 | 0.909 | 1.597 | 1.506 | 3.664 | 0.040 | | JC03 | 0.042 | 1.067 | 1.091 | 1.179 | 1.528 | 4.723 | 0.129 | | JC04 | 0.113 | 2.505 | 1.046 | 0.628 | 1.762 | 5.096 | 0.048 | | JC05 | 0.058 | 0.679 | 0.617 | 0.441 | 1.459 | 3.689 | 0.042 | | JC06 | 0.053 | 0.656 | 0.649 | 0.492 | 1.532 | 3.131 | 0.065 | | JC07 | 0.120 | 0.766 | 1.053 | 0.433 | 2.432 | 5.658 | 0.059 | | JC08 | 0.071 | 1.371 | 1.141 | 0.788 | 5.550 | 5.516 | 0.173 | | JC09 | 0.061 | 1.353 | 1.024 | 1.653 | 1.695 | 3.753 | 0.083 | | JC13 | 0.213 | 2.043 | 3.109 | 1.558 | 4.678 | 13.765 | 0.063 | | JC14 | 0.138 | 0.784 | 1.209 | 0.459 | 2.853 | 6.769 | 0.162 | | JC15 | 0.082 | 3.491 | 1.478 | 1.041 | 3.199 | 6.476 | 0.079 | | JC18 | 0.115 | 0.837 | 1.065 | 0.341 | 3.393 | 4.935 | 0.102 | | JC20 | 0.162 | 0.643 | 0.655 | 0.352 | 2.647 | 8.851 | 0.176 | | 平均值 | 0.097 | 1.291 | 1.157 | 0.822 | 2.589 | 5.771 | 0.098 | 川河盖两翼沉
降量高值区 | JC10 | 2.500 | 40.500 | 17.200 | 14.500 | 65.400 | 108.000 | 0.138 | | JC11 | 76.100 | 388.800 | 298.400 | 237.900 | 1395.600 | 3482.200 | 0.146 | | JC16 | 0.737 | 9.689 | 8.284 | 5.076 | 21.439 | 66.948 | 0.101 | | JC17 | 1.250 | 3.530 | 3.542 | 1.621 | 15.753 | 93.506 | 0.078 | | 平均值 | 20.981 | 117.633 | 85.052 | 64.271 | 376.904 | 960.891 | 0.097 | | 全区 | 最大值 | 76.100 | 388.8 | 298.400 | 237.900 | 1395.6 | 3482.2 | 0.176 | | 最小值 | 0.042 | 0.643 | 0.617 | 0.341 | 1.459 | 3.131 | 0.024 | | 平均值 | 4.554 | 25.585 | 19.087 | 15.032 | 85.246 | 212.859 | 0.102 | | 标准差 | 17.31 | 88.54 | 67.85 | 54.14 | 318.15 | 793.58 | 0.05 | | 变异系数 | 3.81 | 3.46 | 3.55 | 3.60 | 3.73 | 3.73 | 0.45 | | 全国[19] | 平均值 | 0.71 | 18.21 | 15.55 | 7.57 | 36.72 | 147.85 | 0.07 | | 重庆主城区降水[20] | 平均值 | 0.44 | 2.9 | 13 | 2.22 | 30.25 | 76.26 | |
|
Flux of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet deposition mg·(m2·a)-1
|

| 样品编号 | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 样品编号 | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | JC01 | 0.20 | 68.0 | 27.8 | 0.08 | 34.4 | 32.6 | 84.1 | | JC13 | 0.40 | 81.2 | 32.4 | 0.24 | 33.6 | 33.9 | 99.1 | | JC02 | 0.21 | 71.1 | 28.5 | 0.06 | 34.4 | 32.1 | 89.5 | | JC14 | 0.34 | 72.9 | 28.3 | 0.57 | 34.5 | 42.8 | 95.1 | | JC03 | 0.19 | 68.6 | 25.3 | 0.07 | 33.0 | 29.8 | 86.4 | | JC15 | 0.36 | 86.7 | 26.0 | 0.21 | 33.5 | 40.7 | 95.8 | | JC04 | 0.16 | 59.2 | 19.0 | 0.07 | 25.8 | 26.3 | 69.5 | | JC18 | 0.43 | 77.9 | 29.2 | 0.55 | 32.9 | 39.9 | 102.6 | | JC05 | 0.33 | 82.3 | 29.5 | 0.17 | 34.1 | 46.9 | 88.6 | | JC20 | 0.39 | 77.6 | 32.6 | 0.17 | 39.0 | 44.0 | 104.0 | | JC06 | 0.46 | 69.5 | 27.0 | 0.30 | 30.2 | 47.6 | 90.2 | | JC10 | 0.28 | 75.2 | 28.2 | 0.09 | 34.2 | 33.7 | 85.9 | | JC07 | 0.94 | 98.1 | 50.2 | 1.46 | 49.9 | 29.1 | 122.2 | | JC11 | 0.32 | 74.0 | 47.7 | 0.07 | 34.5 | 35.7 | 87.9 | | JC08 | 0.26 | 76.1 | 28.6 | 0.35 | 35.5 | 31.1 | 84.3 | | JC16 | 0.33 | 74.5 | 46.7 | 0.07 | 39.3 | 34.9 | 89.8 | | JC09 | 0.39 | 83.0 | 26.8 | 0.23 | 32.9 | 46.0 | 94.9 | | JC17 | 0.53 | 71.4 | 32.1 | 0.22 | 34.4 | 48.8 | 94.2 |
|
The content of heavy metal elements in the soil around the atmospheric dry and wet deposition sample site 10-6
|

| 样品编号 | 占比/% | | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | Hg | | JC10 | 1.01 | 16.30 | 6.93 | 5.84 | 26.35 | 43.51 | 0.06 | | JC11 | 1.29 | 6.61 | 5.08 | 4.05 | 23.74 | 59.23 | <0.01 | | JC16 | 0.66 | 8.63 | 7.38 | 4.52 | 19.09 | 59.63 | 0.09 | | JC17 | 1.05 | 2.96 | 2.97 | 1.36 | 13.21 | 78.39 | 0.07 | | 川河盖顶土壤 | 0.26 | 30.73 | 9.91 | 12.77 | 12.37 | 33.90 | 0.06 |
|
Proportion comparison of heavy metals between JC10、JC11、JC16、JC17 and soil of Chuanhegai
|

|
Section of atmospheric dry and wet deposition points
|

| 项目 | 地累积指数 | | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | JC10 | 3.6 | -0.2 | -0.1 | 0.7 | -0.6 | 1.5 | 0.9 | | JC11 | 4.6 | -0.8 | 0.2 | -3.1 | -0.4 | 2.0 | 2.0 | | JC16 | 2.5 | -1.6 | -0.4 | 1.0 | -1.4 | 0.6 | 0.9 | | JC17 | 4.2 | -2.1 | -0.7 | 1.5 | -2.1 | 1.1 | 2.3 |
|
Geoaccumulation index of atmospheric dry and wet deposition in two wings of Chuanhegai
|
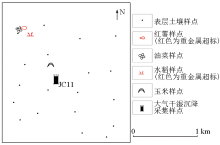
|
Surface soil and crop sample points around JC11 within 1 km
|
| [1] |
陈岳龙, 杨忠芳. 环境地球化学[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017:85-91.
|
| [1] |
Chen Y L, Yang Z F. Enviromental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Geology Press, 2017:85-86.
|
| [2] |
陈满怀, 朱永官, 董元华, 等. 环境土壤学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018:9-10.
|
| [2] |
Chen M H, Zhu Y G, Dong Y H, et al. Enviromental soil science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2018:9-10.
|
| [3] |
张乃明. 大气沉降对土壤重金属累积的影响[J]. 土壤与环境, 2001, 10(2):91-93.
|
| [3] |
Zhang N M. Effects of air settlement on heavy metal accumulation in soil[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2001, 10(2):91-93.
|
| [4] |
Goforth M R, Christoforou C S. Particle size distribution and atmospheric metals measurements in a rural area in the South Eastern USA[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2006, 356(1):217-227.

|
| [5] |
Nriagu J O. Changing metal cycles and human health[M]. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer, 1984:114-142.
|
| [6] |
熊秋林, 肖红伟, 程朋根, 等. 北京表层土壤重金属污染分布及大气沉降贡献[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(4):816-824.
|
| [6] |
Xiong Q L, Xiao H W, Cheng P G, et al. A pollution distribution of topsoil heavy metals in Beijing and its atmospheric deposition contribution[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(4):816-824.
|
| [7] |
邹天森, 康文婷, 张金良, 等. 我国主要城市大气重金属的污染水平及分布特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 2015, 28(7):1053-1061.
|
| [7] |
Zou T S, Kang W T, Zhang J L, et al. Concentrations and distribution characteristic of atmospheric heavy metals in urban areas of China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2015, 28(7):1053-1061.
|
| [8] |
戴青云, 贺前锋, 刘代欢, 等. 大气沉降重金属污染特征及生态风险研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(3):56-64.
|
| [8] |
Dai Q Y, He Q F, Liu D H, et al. Progress in research on heavy metals in atmospheric deposition:Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(3):56-64.
|
| [9] |
Mijic Z, Stojic A, Perisic M, et al. Seasonal variability and source apportionment of metals in the atmospheric deposi-tion in Belgrade[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2010, 44(30):3630-3637.

|
| [10] |
赖木收, 杨忠芳, 王洪翠, 等. 太原盆地农田区大气降尘对土壤重金属元素累积的影响及其来源探讨[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(2):240-245.
|
| [10] |
Lai M S, Yang Z F, Wang H C, et al. Effects of atmospheric fallouts on heavy metal elements accumulation in soils in farmland areas in the Taiyuan basin,Shanxi,China and sources of fallouts[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(2):240-245.
|
| [11] |
丛源, 陈岳龙, 杨忠芳, 等. 北京平原区元素的大气干湿沉降通量[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(2):257-264.
|
| [11] |
Cong Y, Chen Y L, Yang Z F, et al. Dry and wet atmospheric deposition fluxes of elements in the plain area of Beijing municipality,China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(2):257-264.
|
| [12] |
汤洁, 韩维峥, 李娜, 等. 哈尔滨市城区大气重金属沉降特征和来源研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2011, 31(11):3087-3091.
|
| [12] |
Tang J, Han W Z, Li N, et al. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal element concentrations in atmospheric deposition in Harbin City,northeast China[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2011, 31(11):3087-3091.
|
| [13] |
李山泉, 杨金玲, 阮心玲, 等. 南京市大气沉降中重金属特征及对土壤环境的影响[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014, 34(1):22-29.
|
| [13] |
Li S Q, Yang J L, Ruan X L, et al. Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals and their impacts on soil environmentin in typical urban areas of Nanjing[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014, 34(1):22-29.
|
| [14] |
李萍, 薛粟尹, 王胜利, 等. 兰州市大气降尘重金属污染评价及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(3):1021-1028.
|
| [14] |
Li P, Xue L Y, Wang S L, et al. pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metal from atmospheric deposition in Lanzhou[J]. Enviromental Science, 2014, 35(3):1021-1028.
|
| [15] |
杨磊, 熊黑刚. 新疆准东煤田土壤重金属来源分析及风险评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(15):273-281.
|
| [15] |
Yang L, Xiong H G. Soil heavy metal sources analysis and risk evaluation of Zhundong coal mine in Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(15):273-281.
|
| [16] |
张国忠, 黄威, 潘月鹏, 等. 河北典型农田大气重金属干沉降通量及来源解析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2019, 27(8):1245-1254.
|
| [16] |
Zhang G Z, Huang W, Pan Y P, et al. Dry deposition flux of atmospheric heavy metals and its source apportionment in a typical farmland of Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(8):1245-1254.
|
| [17] |
江华亮, 王宗爽, 武雪芳, 等. 我国大气PM2.5中砷的污染特征、来源及控制[J]. 环境工程技术学报, 2015, 5(6):464-470.
|
| [17] |
Jiang H L, Wang Z S, Wu X F, et al. Pollution characteristics,sources and contral of arsenic in PM2.5 in China[J]. Journal of Environmental Engineering Technology, 2015, 5(6):464-470.
|
| [18] |
王增辉. 鲁西南平原区大气干湿沉降元素输入通量及来源浅析:以巨野县为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):839-846.
|
| [18] |
Wang Z H. An analysis of the input flux and source of elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of southwest plain of Shandong:A case study of Juye County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):839-846.
|
| [19] |
DZ/T 0295—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S].
|
| [19] |
DZ/T 0295—2016 Determination of land quality geochemical evaluation[S].
|
| [20] |
王梦梦, 原梦云, 苏德纯. 我国大气重金属干湿沉降特征及时空变化规律[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(11):4085-4096.
|
| [20] |
Wang M M, Yuan M Y, Su D C. Characteristics and spatial temporal variation of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet deposition of China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(11):4085-4096.
|
| [21] |
彭玉龙, 王永敏, 覃蔡清, 等. 重庆主城区降水中重金属的分布特征及其沉降量[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(7):2490-2496.
|
| [21] |
Peng Y L, Wang Y M, Qin C Q, et al. Concentrations and deposition fluxes of heavy metals in precipition in core urban areas,Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(7):2490-2496.
|
| [22] |
张夏, 刘斌, 肖柏林, 等. 重庆主城大气降尘中重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12):5288-5294.
|
| [22] |
Zhang X, Liu B, Xiao B L, et al. Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in core urban areas,Chongqing[J]. Enviromental Science, 2020, 41(12):5288-5294.
|
| [23] |
冯新斌, 陈玖斌, 付学吾, 等. 汞的环境地球化学研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(5):503-530.
|
| [23] |
Feng X B, Chen J B, Fu X W et al. Progresses on environmental geochemistry of mercury[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(5):503-530.
|
| [24] |
张龙, 林先辉, 刘俏, 等. 秀山汞矿开采对当地土水环境的影响[J]. 西南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 36(6):105-109.
|
| [24] |
Zhang L, Lin X H, Liu Q, et al. Effects of mercury mine exploitation on local soil and water environment in Xiushan[J]. Journal of Southwest China Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2011, 36(6):105-109.
|
| [25] |
王丽丽, 金囝囡, 武志宏, 等. 不同类型施工降尘中重金属污染特征及健康风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(3):1055-1065.
|
| [25] |
Wang L L, Jin J N, Wu Z H, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and associated healthrisk assessment in different types of construction dust[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(3):1055-1065.
|
| [26] |
李霞, 贾健. 复杂地形多尺度气流对城市大气污染影响的研究进展[J]. 沙漠与绿洲气象, 2016, 10(6):1-10.
|
| [26] |
Li X, Jia J. Research of the influences of the air flows on multiple scales on the transport and diffusion mechanisms of urban air pollution over the complex terrains[J]. Desert and Oasis Meteorology, 2016, 10(6):1-10.
|
| [27] |
赵西强, 王增辉, 王存龙, 等. 济南市近地表大气降尘元素地球化学特征及污染评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1):154-159.
|
| [27] |
Zhao X Q, Wang Z H, Wang C L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution assessment of near-surface atmospheric dust in Jinan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1):154-159.
|
| [28] |
刘志坚, 张绣. 银川市大气降尘重金属污染状况评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(2):316-321.
|
| [28] |
Liu Z J, Zhang X. Contamination status assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric dust falls in Yinchuan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(2):316-321.
|
| [29] |
程珂, 杨新萍, 赵方杰. 大气沉降及土壤扬尘对天津城郊蔬菜重金属含量的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(10):1835-1845.
|
| [29] |
Cheng K, Yang X P, Zhao F J. Effects of atmospheric and dust depostion on content of heavy metals in vegetables in suburbs of Tianjin[J]. Journal of Agro-Enviroment Science, 2015, 34(10):1835-1845.
|
| [30] |
章明奎, 刘兆云, 周翠. 铅锌矿区附近大气沉降对蔬菜中重金属累积的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 2010, 36(2):221-229.
|
| [30] |
Zhang M K, Liu Z Y, Zhou C. Effect of atmospheric deposition on heavy metal accumulation in vegetable crop near a lead-zinc smelt mine[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Agric. & Life Sci., 2010, 36(2):221-229.
|
| [1] |
XIAO Gao-Qiang, ZHAO Juan, CHEN Zi-Wan, SONG Xu-Feng, ZHU Neng-Gang. Delineation of areas with high geological background values of heavy metals in soils in Yunnan Province, China based on geological big data technology[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 216-227. |
| [2] |
YANG Yan, LIU Bin, XIA Fei-Qiang, CHEN Ping-Feng, ZHANG Xiang. Enrichment characteristics, source identification, and health risk assessment of soil heavy metals in typical cultivated land in the mountainous area of southern Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 255-263. |
|
|
|
|

