|
|
|
| Distribution feature of soil selenium in west Sanjiang plain and its influencing factors |
NIU Xue1( ), HE Jin1,2( ), HE Jin1,2( ), PANG Ya-Jie1, MING Yuan-Yuan1 ), PANG Ya-Jie1, MING Yuan-Yuan1 |
1. Center for Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology, China Geological Survey, Baoding 071051, China
2. Institute of Environment and Resources, Jilin University, Changchun 130026, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In recent years, precious selenium-rich land has been discovered in Sanjiang plain, Heilongjiang Province; nevertheless, studies of the distribution and the controlling factors of soil selenium content have been rarely reported. Geochemical investigation of land quality in the western part of Sanjiang plain has revealed that the surface soil in this area is mainly sufficient, without selenium poisoning. The selenium-rich soil is mainly distributed in the alluvial lacustrine low plain area between the front of Wanda Mountain and the Naoli River, and secondarily distributed in the lacustrine denudation platform in the north of Luobei County. The selenium-deficient and selenium-potential-deficient areas mainly existalong the Songhua River and the ancient course of Luobei River in Luobei area. Based on the combination of statistical correlation analysis, factor analysis, clustering analysis and the selenium spatial distribution, the authors consider that the selenium content in the surface soil of Sanjiang plain is mainly affected by the adsorption of organic matter and clay minerals in the surface soil. Oxides of iron, manganese and other elements as well as soil pH have a relatively weaker effect on selenium enrichment.The comprehensive evaluation of soil environmental quality shows that Sanjiang plain area is mostly a risk-free area, which is a precious clean land resource. Green selenium-rich agriculture can be developed by relying on selenium-rich land.
|
|
Received: 18 December 2019
Published: 01 March 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
HE Jin
E-mail: niuxue1007@163.com;hejing007105@126.com
|
|
|
|
21] redrawing)
">
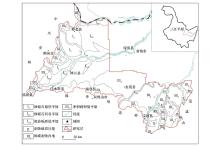
|
Study area location and geomorphological lithology sketch map
(geomorphological map basesed on Yang Xiangkui[21] redrawing)
|

| 类型 | 样品数 | 均值/10-6 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 中位数/10-6 | 标准离差 | 变异系数 | | 表层土壤 | 4287 | 0.25 | 0.06 | 2.27 | 0.23 | 0.1 | 0.39 | | 深层土壤 | 1404 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 2.03 | 0.1 | 0.07 | 0.67 |
|
Statistics of Selenium elements in surface soil and deep soil
|
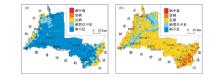
|
Distribution of selenium content in deep soil(a) and surface soil(b) in west Sanjiang plain
|

| 地貌单元 | 土壤岩性 | 样品数 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 算术平均值/10-6 | 变异系数 | | Ⅰ2 | 含泥质砂砾石 | 281 | 0.12 | 0.46 | 0.2 | 0.22 | | Ⅰ3-2 | 泥砂砾质 | 1164 | 0.09 | 0.69 | 0.2 | 0.3 | | Ⅰ3-1 | 砂砾石 | 799 | 0.06 | 0.88 | 0.23 | 0.44 | | Ⅲ2 | 粉质黏土 | 1256 | 0.06 | 0.63 | 0.28 | 0.31 | | Ⅱ | — | 20 | 0.2 | 0.51 | 0.31 | 0.23 | | Ⅲ1 | 粉质黏土 | 767 | 0.12 | 1.33 | 0.31 | 0.31 |
|
Statistics of selenium content in surface soil of geomorphic units
|

| 指标 | 成分 | | F1 | F2 | F3 | | Ni | 0.85 | 0.17 | 0.11 | | Cr | 0.83 | 0.26 | 0.09 | | V | 0.81 | 0.10 | 0.09 | | Sc | 0.81 | 0.16 | 0.27 | | Cu | 0.80 | 0.35 | 0.02 | | Ti | 0.66 | -0.06 | -0.06 | | Fe2O3 | 0.66 | 0.07 | 0.32 | | Na2O | -0.65 | -0.40 | -0.19 | | K2O | -0.58 | -0.51 | 0.26 | | Ge | 0.42 | -0.30 | 0.40 | | C | 0.16 | 0.93 | 0.00 | | Corg | 0.20 | 0.92 | 0.01 | | N | 0.28 | 0.90 | -0.01 | | S | 0.14 | 0.84 | 0.03 | | Se | 0.34 | 0.46 | -0.05 | | U | -0.04 | 0.42 | 0.39 | | Rb | 0.01 | -0.13 | 0.85 | | Tl | -0.24 | 0.02 | 0.81 | | Al2O3 | 0.26 | -0.09 | 0.76 | | Ga | 0.42 | 0.11 | 0.74 | | Be | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.73 | | Li | 0.43 | 0.24 | 0.65 | | F | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.58 |
|
Main factor load of surface soil in study area
|

| F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | F7 | F8 | F9 | | 方差贡献率/% | 15.516 | 11.302 | 10.802 | 8.127 | 8.115 | 7.254 | 4.811 | 4.046 | 3.248 | | 累积方差贡献率/% | 15.516 | 26.819 | 37.621 | 45.748 | 53.862 | 61.117 | 65.927 | 69.973 | 73.221 |
|
Variance contribution rates of surface soil factor in study area
|
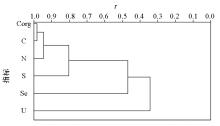
|
R-type cluster analysis of surface soil in study area
|

| 元素 | 有机质 | pH | MgO | Na2O | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | K2O | Mn | | 相关系数 | 0.425** | 0.039** | 0.124** | -0.508** | -0.013 | -0.175** | 0.017 | 0.297** | -0.512** | 0.205** |
|
Correlation coefficent between surface soli selenium content and soil physicochemical properties
|

| 等级 | 无风险区 | 风险可控 | 风险较高 | | 点数 | 4279 | 6 | 0 | | 比例/% | 99.81 | 0.19 | 0.00 |
|
Comprehensive grade statistics of soil environmental quality
|
| [1] |
中国科学院地理研究所与化学地理研究室环境与地方病组. 我国土壤表层硒含量的地理分布及其与人畜硒反应病的关系[J]. 地理研究, 1984,13(4):39-47.
|
| [1] |
Environment and Endemie Diseases Seetion,Institute of Geography and Academia Sinica. Geographical distribution of selenium content in the top soils in China and it’s association with selenium-reoponsive diseases in man and animal[J]. Geographical Research, 1984,13(4):39-47.
|
| [2] |
谭见安, 朱文郁, 李日邦, 等. 克山病与环境硒等生命元素的关系[J]. 中国地方病学杂志, 1991,10(5):269-274.
|
| [2] |
Tan J A, Zhu W Y, Li R B, et al. The relationship between Keshan disease and environmental selenium and other life elements[J]. Chinese Journal of Endemiology, 1991,10(5):269-274.
|
| [3] |
邵国璋, 关光伟. 黑龙江省土壤硒(Se)元素背景值与地方性疾病的关系[J]. 中国环境监测, 1993,9(2):61-62.
|
| [3] |
Shao G Z, Guan G W. Relation between Se background values and endemic diseases in Heilongjiang Province[J]. China Environmental Monitoring, 1993,9(2):61-62.
|
| [4] |
吕瑶瑶, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 等. 大骨节病区硒元素分布的调控机理研究——以四川省阿坝地区为例[J]. 环境化学, 2012,31(7):935-944.
|
| [4] |
Lyu Y Y, Yu T, Yang Z F, et al. Study on the regulatory mechanism of selenium distribution in Kashin-beck disease areas: A case study of aba area, Sichuan Province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2012,31(7):935-944.
|
| [5] |
Ure A M, Berrow M L. The elemental composition of soils environmental chemistry(2nd Ed)[M]. London:The Royal Socienty of Chemistry, 1982: 94-204.
|
| [6] |
王子健, 赵利华, 彭安. 低硒带土壤中硒的挥发过程研究[J]. 环境化学, 1989,8(2):7-11.
|
| [6] |
Wang Z J, Zhao L H, Peng A. Selenium evaportion from soils of Chinese Se-defficient belt[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 1989,8(2):7-11.
|
| [7] |
戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 等. 东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2015,52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [7] |
Dai H M, Gong C D, Dong B, et al. Distribution of soils selenium in the Northeast China Plain and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015,52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [8] |
刘国栋, 崔玉军, 刘立芬, 等. 土地质量地球化学平价方法研究与应用:以黑龙江省宏胜镇为例[J]. 现代地质, 2017,31(1):167-176.
|
| [8] |
Liu G D, Cui Y J, Li L F, et al. The study and application of land quality geochemical evaluation method: Illustrated by the case of Hongsheng town, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2017,31(1):167-176.
|
| [9] |
庞雅婕, 何锦, 牛雪, 等. 三江平原富Se地区地下水—土壤—农作物中Se富集规律及影响因素[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017,26(7):1137-1144.
|
| [9] |
Pang Y J, He J, Niu X, et al. Enrichment regularities and influence factors of selenium in groundwater-soil-crop seeds at a Se-rich area of the Three River Plain, China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017,26(7):1137-1144.
|
| [10] |
王甘露, 朱笑青. 贵州省土壤硒的背景值研究[J]. 环境科学研究, 2003,16(1):23-26.
|
| [10] |
Wang G L, Zhu X Q. Background value of selenium in soil of Guizhou Province[J]. Environmental Science Research, 2003,16(1):23-26.
|
| [11] |
王美珠, 章明奎. 我国部分高硒低硒土壤的成因初探[J]. 浙江大学学报:农业与生命科学版, 1996,22(1):89-93.

|
| [11] |
Wang M Z, Zhang M K. A discussion on the cause of high-Se and low-Se soil information[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Agriculture & Life Sciences, 1996,22(1):89-93.
|
| [12] |
朱建明, 左维, 秦海波, 等. 恩施硒中毒区土壤高硒的成因:自然硒的证据[J]. 矿物学报, 2008,28(4):397-400.
|
| [12] |
Zhu J M, Zuo W, Qin H B, et al. An investigation on the source of soil Se in Yutangba,Enshi: Evidence from native selenium[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2008,28(4):397-400.
|
| [13] |
Zhu J M, Wang N, Li S H, et al. Distribution and transport of selenium in Yutangba,China: Impact of human activities[J]. Sci. Total. Environ., 2008,392(2-3):252-261.

|
| [14] |
Sun G X, Meharg A A, Li G, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in China is potentially controlled by deposition and volatilization?[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016,6:20953-20961.

|
| [15] |
Blazina T, Sun Y, Voegelin A, et al. Terrestrial selenium distribution in China is potentially linked to monsoonal climate[J]. Nature Communications, 2014,5(9):1.
|
| [16] |
魏明辉, 陈树清, 谷振飞, 等. 河北平原区表层土壤富硒成因初探[J]. 河北地质, 2012(4):29-31.
|
| [16] |
Wei M H, Chen S Q, Gu Z F, et al. The causes of rich surface soil selenium in Hebei plain[J]. Hebei Geology, 2012(4):29-31.
|
| [17] |
Uemsh C G, Subhas C G. Selenium deficiency in soils and crops and its impact on anmial and human helath[J]. Current Nutrition & Food Science, 2010,6(4):268-280.
|
| [18] |
Malisa E P. The Behaviour of selenium in geological processes[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2001,23(2):137-158.

|
| [19] |
夏学齐, 杨忠芳, 薛圆, 等. 黑龙江省松嫩平原南部土壤硒元素循环特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(5):850-858.

|
| [19] |
Xia X Q, Yang Z F, Xue Y, et al. Geochemical circling of soil Se on the southern Song-Nen Plain,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2012,26(5):850-858.

|
| [20] |
迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等, 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016,53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [20] |
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province,China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016,53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [21] |
杨湘奎, 杨文, 张烽龙, 等. 三江平原地下水资源潜力与生态环境地质调查评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2008: 5-25.
|
| [21] |
Yang X K, Yang W, Zhang F L, et al. Investigation and assessment evaluation of groundwater resources potential and eco-environment geology in Sanjiang Plain [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2008: 5-25.
|
| [22] |
徐春青, 傅有丰, 徐忠宝, 等. 黑龙江省土壤、饲料中硒的含量及其分布[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 1986,17(4):399-406.
|
| [22] |
Xu C Q, Fu Y F, Xu Z B, et al. Selenium content and distribution in soil and feed in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural College, 1986,17(4):399-406.
|
| [23] |
谭见安. 中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989: 39.
|
| [23] |
Tan J A. The atlas of endemic disease and environment of the People’s Republic of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989: 39.
|
| [24] |
何锦, 庞雅婕, 牛雪, 等. 三江平原重点富硒区 1∶5 万土地质量地球化学调查评价[R]. 中国地质调查局水文地质环境地质调查中心, 2019.
|
| [24] |
He J, Pang Y J, Niu X, et al. Geochemical survey and evaluation of 1∶50000 land quality in key selenium rich areas of Sanjiang Plain[R]. CHEGS, 2019.
|
| [25] |
向云川, 任天祥, 牟绪赞, 等. 化探资料应用技术要求[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010: 21-33.
|
| [25] |
Xiang Y C, Ren T X, Mou X Z, et al. Technical requirements for the application of geochemical data [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010: 21-33.
|
| [26] |
刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等, 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984:30-40,434-441,458-470.
|
| [26] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M, Li Z L, et al. Elemental geochemistry [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984:30-40,434-441,458-470.
|
| [27] |
安永龙, 黄勇, 张艳玲, 等, 北京房山南部地区富硒土壤生物有效性特征及来源[J]. 地质通报, 2020,39(2/3):387-398.
|
| [27] |
An Y L, Huang Y, Zhang Y L, et al. Bioavailability and source analyses of Se-enriched soil in the south of Fangshan District,Beijing[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020,39(2/3):387-399.
|
| [28] |
宋铁军. 冻融影响下水稻种植区包气带中硒的环境地球化学行为研究——以三江平原蛤蟆通河流域典型农业区为例[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2019.
|
| [28] |
Song T J. The effect of freeze-thaw action on environmental geochemistry behavior of selenium in the unsaturated zone of rice planting area—A case study of the typical agricultural area in Hamatong River Basin of Sanjiang Plain[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2019.
|
| [1] |
XUE Dong-Xu, LIU Cheng, GUO Fa, WANG Jun, XU Duo-Xun, YANG Sheng-Fei, ZHANG Pei. Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1169-1178. |
| [2] |
QUE Ze-Sheng, LI Guan-Chao, HU Ying, JIAN Rui-Min, LIU Bing. GIS-based assessment of the radioactivity levels and risks of soil environment[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1336-1347. |
|
|
|
|

