|
|
|
| Research, development and utilization of selenium-rich soil of Shaanxi:A case study of Sanyuan-Yanliang area |
QIAO Xin-Xing1,2( ), CHAO Xu2, REN Rui1,2, ZHANG Ji-Jun1,2, HU Kui1,2, LI Ao-Rui1,2, ZHANG Zhi-Ming1,2 ), CHAO Xu2, REN Rui1,2, ZHANG Ji-Jun1,2, HU Kui1,2, LI Ao-Rui1,2, ZHANG Zhi-Ming1,2 |
1. Shaanxi Hydraulic Engineering and Environment Geological Survey Center, Xi'an 710068,China
2. Shaanxi Institute of Geological Survey, Xi'an 710054,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Through the sampling and analysis of soil and crops in Sanyuan-Yanliang area, it is found that the soil environment in the study area is generally clean.The medium-rich selenium soil accounts for 94.62% of the total survey area, selenium-rich soil is widely distributed and has the basic soil conditions for the development of selenium-rich crop. It has the basic soil conditions for developing selenium-enriched foods. For the analysis of crop products, it can be seen that the bulk crops are selenium-rich crops, and the selenium-enriched level is relatively stable. Some vegetables have also reached the standard of selenium-enriched vegetables. The selenium in crops has a good correlation with soil selenium. The correlation coefficient between the selenium content of corn and that of root soil is 0.788, and the correlation coefficient between the selenium content of wheat and that of root soil is 0.612. Hence the study area has a future for the development of selenium-enriched industries. Guanzhon is suitable for vigorously promoting the cultivation of selenium-enriched crops and vegetables as an important food and vegetable. The production area has great potential for the development of selenium-enriched crops. It is recommended to select demonstration sites to carry out selenium-enriched planting work, and to focus on building a group of selenium-rich grain and vegetable industry bases so as to provide a scientific basis for the development and utilization of selenium-rich resources in Guanzhong, Shaanxi Province, thus supporting the rural revitalization strategy and the precise poverty alleviation battle.
|
|
Received: 19 November 2019
Published: 01 March 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
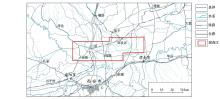
|
Location map of the study area
|

| 元素 | 一等(丰富) | | 二等(较丰富) | | 三等(中等) | | 四等(较缺乏) | | 五等(缺乏) | | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | | N | | | | | | | 825.62 | 65.79 | | 417.87 | 33.30 | | 11.40 | 0.91 | | P | | | | 31.39 | 2.50 | | 1033.27 | 82.34 | | 190.23 | 15.16 | | | | | K | | | | 1219.06 | 97.14 | | 35.83 | 2.86 | | | | | | | | 有机质 | 134.48 | 10.72 | | 786.61 | 62.68 | | 329.87 | 26.29 | | 3.92 | 0.31 | | | | | C | 1185.54 | 94.47 | | 68.78 | 5.48 | | 0.57 | 0.05 | | | | | | | | Ca | 661.29 | 52.70 | | 593.60 | 47.30 | | | | | | | | | | | Mg | 979.85 | 78.08 | | 275.05 | 21.92 | | | | | | | | | | | S | 1231.84 | 98.16 | | 23.05 | 1.84 | | | | | | | | | |
|
Statistics on soil fertility in Sanyuan-Yanliang area
|

| 元素 | 一等(无风险)
Ci≤Si | | 二等(风险可控)
Si<Ci≤Gi | | 三等(风险较高)
Ci>Gi | | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | | Cd | 1245.190 | 99.227 | | 9.582 | 0.764 | | 0.120 | 0.010 | | Hg | 1254.892 | 100 | | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | | As | 1254.892 | 100 | | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | | Pb | 1254.892 | 100 | | 0 | 0 | | 0 | 0 | | Cr | 1254.830 | 99.995 | | 0.062 | 0.005 | | 0 | 0 | | 综合等级 | 1245.128 | 99.222 | | 9.644 | 0.769 | | 0.120 | 0.010 |
|
Results of soil environmental quality assessment in Sanyuan-Yanliang area
|

|
Comprehensive evaluation map of soil environmental quality in Sanyuan-Yanliang area
|

| 元素 | 富硒 | | 低硒 | | >0.4×10-6 | | 0.3×10-6<Se≤0.4×10-6 | | 0.2×10-6<Se≤0.3×10-6 | ≤0.2×10-6 | | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | | Se | 76.55 | 6.10 | | 265.11 | 21.13 | | 850.98 | 67.81 | | 62.25 | 4.96 |
|
Statistics of Se element content in soil in Sanyuan-Yanliang region
|

| 作物种类 | 最大值/10-6 | 最小值/10-6 | 中位数/10-6 | 平均数/10-6 | 富硒样品数 | 富硒率/% | HB001/T—2013 | 大宗
作物 | 小麦 | 1.025 | 0.011 | 0.106 | 0.159 | 466 | 99.36 | (0.02~0.28)×10-6 | | 玉米 | 0.316 | 0.009 | 0.051 | 0.064 | 223 | 88.14 | | 油菜 | 0.359 | 0.060 | 0.171 | 0.153 | 12 | 100.00 | | 蔬菜 | 大蒜 | 0.083 | 0.024 | 0.056 | 0.059 | 11 | 100.00 | (0.01~0.9)×10-6 | | 大葱 | 0.044 | 0.008 | 0.030 | 0.028 | 3 | 75.00 | | 芹菜 | 0.146 | 0.007 | 0.014 | 0.029 | 30 | 73.17 | | 白萝卜 | 0.022 | 0.007 | 0.011 | 0.012 | 10 | 62.50 | | 豆角 | 0.038 | 0.004 | 0.016 | 0.018 | 4 | 57.14 | | 白菜 | 0.041 | 0.002 | 0.010 | 0.013 | 11 | 50.00 | | 花白 | 0.101 | 0.001 | 0.010 | 0.014 | 13 | 46.43 | | 辣椒 | 0.023 | 0.001 | 0.008 | 0.010 | 8 | 40.00 | | 菜花 | 0.101 | 0.001 | 0.006 | 0.014 | 10 | 32.26 | | 黄瓜 | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.006 | 2 | 28.57 | | 西红柿 | 0.021 | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.006 | 3 | 17.65 | | 茄子 | 0.019 | 0.001 | 0.004 | 0.005 | 1 | 7.14 |
|
Statistics of selenium-rich content and selenium-rich rate of crops
|

|
Average value of selenium content in various vegetables in Sanyuan-Yanliang area
|

土壤硒
含量 | 作物 | 样品数
/件 | 作物
w(Se)≥0.02×10-6 | 作物富硒率
/% | | <0.2×10-6 | 小麦 | 30 | 29 | 96.67 | | 玉米 | 2 | 0 | 0 | | ≥0.2×10-6 | 小麦 | 438 | 434 | 99.09 | | 玉米 | 251 | 223 | 88.84 |
|
Statistics of soil selenium and plant selenium content
|
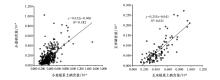
|
The relation of selenium contents in corn and wheat grains with its contents in soils
|

| 作物 | 样本数量 | r值 | | 玉米 | 253 | 0.788** | | 小麦 | 468 | 0.612** |
|
The correlation coefficient between corn and wheat grains with its contents in soils
|

| Se形态 | Se含量/10-6 | 占比/% | 与全量的
相关系数 | | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | | 全量 | 0.3637 | 0.0841 | 0.2304 | 0.0705 | | | | 水溶态 | 0.0201 | 0.0067 | 0.0131 | 0.0038 | 5.70 | 0.523* | | 离子交换态 | 0.0195 | 0.0076 | 0.0130 | 0.004 | 5.66 | 0.628** | | 碳酸盐结合态 | 0.0258 | 0.0012 | 0.0082 | 0.0067 | 3.55 | 0.631** | | 腐殖酸结合态 | 0.0534 | 0.0089 | 0.0319 | 0.013 | 13.83 | 0.861** | | 铁锰氧化结合态 | 0.0069 | 0.0012 | 0.0033 | 0.0015 | 1.45 | 0.800** | | 强有机结合态 | 0.1383 | 0.015 | 0.0722 | 0.0299 | 31.36 | 0.953** | | 残渣态 | 0.1233 | 0.038 | 0.0886 | 0.0226 | 38.46 | 0.924** |
|
Statistics of selenium speciation in surface soil
|

| 样品类别 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 小麦 | 0.721 | 0.14 | 0.806 | 9.41 | 0.009 | 6.577 | 0.307 | 46.514 | | 玉米 | 0.07 | 0.012 | 0.405 | 2.45 | 0.005 | 0.181 | 0.173 | 24.81 | | 油菜 | 0.032 | 0.025 | 0.142 | 3.673 | 0.007 | 0.053 | 0.384 | 42.492 | | 大蒜 | 0.035 | 0.013 | 0.019 | 1.867 | 0.001 | 0.097 | 0.027 | 7.983 | | 芹菜 | 0.047 | 0.025 | 0.446 | 1.701 | 0.002 | 0.272 | 0.079 | 3.763 | | 萝卜 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.039 | 0.264 | 0 | 0.045 | 0.028 | 2.126 | | 花白 | 0.004 | 0 | 0.037 | 0.169 | 0 | 0.055 | 0.015 | 0.979 | | 菜花 | 0.006 | 0 | 0.055 | 0.28 | 0 | 0.045 | 0.031 | 1.631 | | 白菜 | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.052 | 0.209 | 0 | 0.046 | 0.023 | 1.694 | | 食品中污染物限量/10-6 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.1 | ≤1 | | ≤0.02 | | ≤0.2 | |
|
Statistics of heavy metal elements contents in crops
|

|
Spatial planning for the development and utilization of selenium-rich land in Sanyuan-Yanliang area
|
| [1] |
郦逸根, 董岩翔, 郑洁, 等. 地质因素影响下的硒在土壤—系统中的迁移转化[J]. 物探与化探, 2007,31(1):77-79.

|
| [1] |
Li Y G, Dong Y X, Zheng J, et al. Migration and transformation of selenium in soil-system under the influence of geological factors[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2007,31(1):77-79.

|
| [2] |
孙朝, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 典型土壤环境中硒的迁移转化影响因素研究——以四川省成都经济区为例[J]. 中国地质, 2010,31(1):1760-1761.
|
| [2] |
Sun C, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. Study on the factors affecting the migration and transformation of selenium in typical soil environment—A case study of Chengdu Economic Zone in Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Geology, 2010,31(1):1760-1761.
|
| [3] |
Altekin E, Coker C, Sisman A R, et al. The relationship between trace elements and cardiac markers in acute coronary syndromes[J]. Trace Elem Med Biol, 2005,18(3):235-242.

|
| [4] |
汪庆华, 唐根年, 李睿, 等. 浙江省特色农产品立地地质背景研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [4] |
Wang Q H, Tang G N, Li R, et al. Study on the geological background of the characteristic agricultural products in Zhejiang Province [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
|
| [5] |
魏然, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 江西省鄱阳湖流域根系土硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J]. 物探与化探, 2012,36(1):109-113.

|
| [5] |
Wei R, Hou Q Y, Yang Z Y, et al. Selenium speciation analysis and migration and enrichment of roots in Poyang Lake watershed, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012,36(1):109-113.

|
| [6] |
许学宏, 余云飞, 高芹, 等. 富硒农产品开发现状与发展对策[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2010(1):311-313.

|
| [6] |
Xu X H, Yu Y F, Gao Q, et al. Development status and development strategies of selenium-enriched agricultural products[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2010(1):311-313.

|
| [7] |
夏学齐, 杨忠芳, 薛圆, 等. 黑龙江省松嫩平原南部土壤硒元素循环特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(5):850-858.

|
| [7] |
Xia X Q, Yang Z F, Xue Y, et al. Selenium cycling characteristics of soil in the Southern Songnen Plain of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Modern Geology, 2012,26(5):850-858.

|
| [8] |
任蕊, 尹宗义, 王明霞, 等. 三原—阎良地区土壤及农作物Se含量特征[J]. 西北地质, 2012,49(4):194-196.
|
| [8] |
Ren R, Yin Z Y, Wang M X, et al. Characteristics of Se content in soil and crops in Sanyuan-Yanliang area[J]. Northwest Geology, 2012,49(4):194-196.
|
| [9] |
迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素丰度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [9] |
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Application of geochemical elemental abundance data handbook[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
|
| [10] |
中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990:87-91,370-373.
|
| [10] |
China National Environmental Monitoring Center. Chinese soil element background value [M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990:87-91,370-373.
|
| [11] |
尹宗义, 王会锋, 任蕊, 等. 陕西省石头河一带土壤及植物富硒特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2014,38(2):349-351.

|
| [11] |
Yin Z Y, Wang H F, Ren R, et al. Selenium-rich characteristics of soil and plants in the Shihe River area of Shaanxi Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014,38(2):349-351.

|
| [12] |
李家熙, 张光弟, 葛晓立, 等. 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.
|
| [12] |
Li J X, Zhang G D, Ge X L, et al. Characteristics and prediction of human selenium deficiency and excess geochemical environment [M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000.
|
| [13] |
谭见安, 王五一, 朱紫瑜, 等. 环境硒及其复合因子与大骨节病[J]. 环境科学学报, 1987,7(1):8-13.

|
| [13] |
Tan J A, Wang W Y, Zhu Z Y, et al. Environmental selenium and its complex factors and Kashin-Beck disease[J]. Journal of Environmental Science, 1987,7(1):8-13.

|
| [14] |
任蕊, 王明霞, 陈继平, 等. 陕西关中地区土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 矿产勘查, 2018,9(9):1827-1828.
|
| [14] |
Ren R, Wang M X, Chen J P, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in Guanzhong Area and its influencing factors[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2018,9(9):1827-1828.
|
| [15] |
晁旭, 王会锋, 任蕊, 等. 关中-天水经济区(关中盆地)富硒区地球化学调查与评价成果报告[R]. 西安:陕西省地质调查中心, 2017.
|
| [15] |
Chao X, Wang H F, Ren R, et al. Geochemical investigation and evaluation report of selenium-rich area in Guanzhong-Tianshui Economic Zone (Guanzhong Basin) [R]. Xi’an: Shaanxi Geological Survey Center, 2017.
|
| [16] |
陈怀满. 环境土壤学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006.
|
| [16] |
Chen H M. Environmental soil science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2006.
|
| [17] |
董广辉, 武志杰, 陈利军, 等. 土壤—植物生态系统中硒的循环和调节[J]. 农业系统科学与综合研究, 2002,18(1):65-68.
|
| [17] |
Dong G H, Wu Z J, Chen L J, et al. Circulation and regulation of selenium in soil-plant ecosystem[J]. Journal of Agricultural Systems Science and Comprehensive Research, 2002,18(1):65-68.
|
| [18] |
商靖敏, 罗维, 吴光红, 等. 洋河流域不同土地利用类型土壤硒(Se)分布及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2015,36(1):301-308.
|
| [18] |
Shang J M, Luo W, Wu G H, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of soil selenium (Se) in different land use types in the Yanghe River Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2015,36(1):301-308.
|
| [19] |
梁若玉, 和娇, 史雅娟, 等. 典型富硒农业基地土壤硒的生物有效性与剖面分布分析[J]. 环境化学, 2017,36(7):1588-1595.
|
| [19] |
Liang R Y, He J, Shi Y J, et al. Bioavailability and profile distribution of selenium in soils of typical Se-enriched agricultural base[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017,36(7):1588-1595.
|
| [20] |
赵少华, 宇万太, 张璐, 等. 环境中硒的生物地球化学循环和营养调控及分异成因[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005,24(10):1197-1203.
|
| [20] |
Zhao S H, Yu W T, Zhang L, et al. The biogeochemical cycle of selenium in the environment and the regulation of nutrition and the causes of differentiation[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2005,24(10):1197-1203.
|
| [21] |
徐绍清, 柴春燕, 陈晓强, 等. 土壤硒含量与杨梅果实硒含量相关性研究[J]. 浙江林业科技, 2012,32(5):13-15.
|
| [21] |
Xu S H, Chai C Y, Chen X Q, et al. Correlation between selenium content in soil and selenium content in bayberry fruit[J]. Zhejiang Forestry Science and Technology, 2012,32(5):13-15.
|
| [22] |
张雪莲, 周俊, 张先凤, 等. 皖南地区茶园土壤硒与茶叶硒的相关性及其影响因素研究[J]. 皖西学院学报, 2013,29(5):105-109.
|
| [22] |
Zhang X L, Zhou J, Zhang X F, et al. Study on the correlation between soil selenium and selenium in tea garden in southern Fujian and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of West Anhui University, 2013,29(5):105-109.
|
| [23] |
张栋, 张妮, 侯振安, 等. 石灰性土壤硒含量与小麦籽粒硒相关性研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2016,34(5):152-157.
|
| [23] |
Zhang D, Zhang N, Hou Z A, et al. Study on correlation between selenium content in calcareous soil and selenium in wheat[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2016,34(5):152-157.
|
| [24] |
李碧波, 余彦铭, 张轶. 栗林嘴村富硒水稻硒含量与土壤的相关性研究[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2018,57(16):16-20.
|
| [24] |
Li B B, Yu Y M, Zhang Y. Relationship between selenium content and soil in selenium-enriched rice in Lilinzui Village[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, 2018,57(16):16-20.
|
| [25] |
方金梅. 福州市土壤硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J]. 岩矿测试, 2008,27(2):103-107.
|
| [25] |
Fang J M. Soil selenium speciation analysis and its migration and accumulation in Fuzhou City[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2008,27(2):103-107.
|
| [26] |
王金达, 于君宝, 张学林. 黄土高原土壤中硒等元素的地球化学特征[J]. 地理科学, 2000,20(5):469-473.

|
| [26] |
Wang J D, Yu J B, Zhang X L. Geochemical characteristics of selenium and other elements in soils of the Loess Plateau[J]. Geographical Science, 2000,20(5):469-473.

|
| [27] |
李辉勇. 土壤溶液中硒的价态变换及其影响因素[J]. 湖南农业大学学报:自然科学版, 2001,27(2):139-142.
|
| [27] |
Li H Y. Valence transformation of selenium in soil solution and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University:Natural Science, 2001,27(2):139-142.
|
| [28] |
王兴明, 刘登义, 涂俊芳, 等. 芜湖钢铁厂周边土壤及油菜籽中镉、铜、锌、铅含量和形态分布研究[J]. 应运生态学报, 2015,16(10):1927-1930.

|
| [28] |
Wang X M, Liu D Y, Tu J F, et al. Research on the content and morphological distribution of cadmium, copper, zinc and lead in the soil and rapeseed around Wuhu iron and steel plant[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015,16(10):1927-1930.
|
| [29] |
代天飞, 王昌全, 李冰. 油菜各部位对土壤中活性态重金属的累积特征分析[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2006,25:471-475.
|
| [29] |
Dai T F, Wang C Q, Li B. Accumulation characters of heavy metals at different parts of rape growing at various soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2006,25:471-475.
|
| [30] |
方慧, 柳小兰, 颜秋晓, 等. 贵州油菜各器官在不同生育时期对土壤重金属的富集[J]. 北方园艺, 2018,42(5):111-117.
|
| [30] |
Fang H, Liu X L, Yan Q X, et al. Enrichment of heavy metals in soil of rape organs in different growth stage in Guizhou Province[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2018,42(5):111-117.
|
| [31] |
杜少喜, 钞中东, 游军, 等. 民生地质如何精准支撑服务“乡村振兴战略”[J]. 矿产勘查, 2018,9(9):1834-1840.
|
| [31] |
Du S X, Chao Z D, You J, et al. How does minsheng geology accurately support the service “rural revitalization strategy”[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2018,9(9):1834-1840.
|
| [1] |
REN Rui, ZHANG Zhi-Min, WANG Hui, CHEN Ji-Ping, QIAO Xin-Xing, LIANG Dong-Li. Exploring selenium enrichment criteria for soils in the Guanzhong area, Shaanxi Province: A case study of wheat[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1354-1360. |
| [2] |
LI Shi-Bao, YANG Li-Guo, XIONG Wan-Li, MA Zhi-Chao, YUAN Hong-Wei, DUAN Ji-Xue. Speciation of selenium in the selenium-rich cultivated land in Linhe District, Bayannur City, Inner Mongolia and its influencing factors[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 477-486. |
|
|
|
|

