|
|
|
| Construction of the petrogeochemical map of 76 elements in the exposed crust across the Chinese continent: Methods, challenges, and prospects |
LIU Dong-Sheng1,2( ), CHEN Yuan-Yuan3, CHI Qing-Hua1,2 ), CHEN Yuan-Yuan3, CHI Qing-Hua1,2 |
1. Key Laboratory of Geochemical Exploration, Ministry of Natural Resources, Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
2. UNESCO International Centre on Global-Scale Geochemistry, United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization, Langfang 065000, China
3. Hebei Regional Geological Survey Institute, Langfang 065000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The exposed crust is the critical interface where the lithosphere interacts with the pedosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere. The petrogeochemical map of the exposed crust can provide essential fundamental geochemical data for investigating the distributions and cycles of elements among different spheres. However, the plotting of the large-scale petrogeochemical map of the exposed crust has been constrained by the limited data volume and mapping technology. Consequently, no such a map covering the Chinese continent is available. This study proposed an innovative mapping technology roadmap based on over 16,000 petrogeochemical data and fundamental geological information. First, the databases for petrogeochemical information, stratigraphic structure information, and spatial information of geological units were constructed. Second, the geospatial information of strata and rock masses was extracted from the basic databases. Third, the petrogeochemical information was assigned to strata and rock masses to obtain their spatial distributions and element contents. Fourth, the spatial distribution patterns of 76 elements in the exposed crust were visualized using geographical information system (GIS) technology. Additionally, this study analyzed the challenges in the mapping process, including geological information accuracy, the lack of samples for special lithologies, reliability assessment, and scope of application, finally proposing corresponding solutions. The petrogeochemical map of the exposed crust demonstrates significant application potential, providing foundational data for investigating geochemical background and rock-sediment element cycling.
|
|
Received: 08 June 2024
Published: 23 October 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
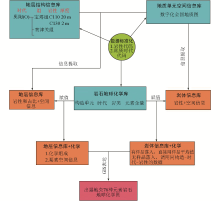
|
Technical route
|
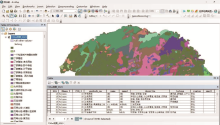
|
Spatial information dataset of geological units
|
|
Structure dataset of strata
|

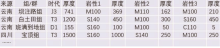
| 时代 | 代号 | 时代 | 代号 | 时代 | 代号 | | 第四纪 | Q | 石炭纪 | C | 新元古代 | Pt3 | | 第三纪 | R | 泥盆纪 | D | 中元古代 | Pt2 | | 白垩纪 | K | 志留纪 | S | 古元古代 | Pt1 | | 侏罗纪 | J | 奥陶纪 | O | 新太古代 | Ar3 | | 三叠纪 | T | 寒武纪 |  | 中太古代 | Ar2 | | 二叠纪 | P | 震旦纪 | Z | 古太古代 | Ar1 |
|
Chronostratigraphic unit division
|
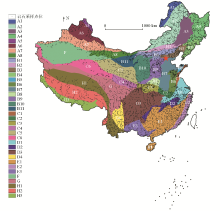
|
Distribution of rock samples and subdivision of second-order tectonic units in China
|

| 一级构造单元 | 二级构造单元 | 一级构造单元 | 二级构造单元 | | 序号 | 名称 | 序号 | 名称 | 序号 | 名称 | 序号 | 名称 | | A | 天山—兴蒙造山带 | | A1 | 额尔古纳造山带 | C | 秦—祁—昆造山带 | C1 | 苏鲁造山带 | | A2 | 兴蒙造山带 | C2 | 大别造山带 | | A3 | 松辽盆地 | C3 | 东秦岭造山带 | | A4 | 吉黑造山带 | C4 | 西秦岭造山带 | | A5 | 阿尔泰造山带 | C5 | 祁连造山带 | | A6 | 准噶尔造山带 | C6 | 昆仑造山带 | | A7 | 天山造山带 | D | 扬子克拉通 | D1 | 下扬子台褶带 | | A8 | 北山造山带 | D2 | 江南造山带 | | B | 华北克拉通 | | B1 | 内蒙地轴 | D3 | 上扬子台坳 | | B2 | 华北北缘造山带 | D4 | 康滇地轴 | | B3 | 燕山造山带 | E | 华南造山带 | E1 | 湘赣粤造山带 | | B4 | 辽东台隆 | E2 | 东南沿海火山带 | | B5 | 胶东台隆 | E3 | 右江造山带 | | B6 | 鲁西台隆 | F | 塔里木克拉通 | F | 塔里木克拉通 | | B7 | 华北盆地 | G | 松潘—甘孜造山带 | G | 松潘甘孜造山带 | | B8 | 豫西台隆 | H
西藏—三江造山带 | H1 | 羌塘—昌都地块 | | B9 | 山西台隆 | H2 | 改则那曲造山带 | | B10 | 鄂尔多斯盆地 | H3 | 喜马拉雅造山带 | | B11 | 阿拉善台隆 | | |
|
Tectonic zoning scheme
|

| 一级 | 二级 | 名称 | 一级 | 二级 | 名称 | 一级 | 二级 | 名称 | 一级 | 二级 | 名称 | 一级 | 二级 | 名称 | | G | | 酸性岩 | | K16 | 白榴岩 | | V30 | 安山质火山碎屑岩 | | le10 | 钾长变(浅)粒岩 | | D20 | 灰质白云岩 | | G01 | 低钙花岗岩 | | K17 | 霞石岩 | | V40 | 玄武安山质火山
碎屑岩 | | le20 | 二长变粒岩 | | D30 | 泥质白云岩 | | G02 | 高钙花岗岩 | B | | 基性岩 | | V50 | 粗面质火山碎屑岩 | | le30 | 斜长变粒岩 | | D40 | 砂质白云岩 | | G11 | 流纹岩 | | B01 | 辉长岩 | | V60 | 粗面安山质火山
碎屑岩 | | le40 | 矽线石榴变粒岩 | | D50 | 硅质白云岩 | | G12 | 碱性流纹岩 | | B02 | 二长辉长岩 | sl | | 板岩 | | le50 | 石墨变粒岩 | M | | 泥岩 | | G13 | 英安岩 | | B03 | 苏长岩 | | sl10 | 绢云板岩 | am | | 斜长角闪岩 | | M10 | 粉砂质泥岩 | | G14 | 石英角斑岩 | | B04 | 辉绿岩 | | sl20 | 钙质板岩 | | am00 | 玄武质斜长角闪岩 | | M20 | 砂质泥岩 | | G15 | 粗面英安岩 | | B05 | 斜长岩 | | sl30 | 硅质板岩 | | am10 | 紫苏斜长角闪岩 | | M30 | 钙质泥岩 | | I | | 中性岩 | | B06 | 变辉长岩 | | sl40 | 炭质板岩 | | am20 | 二辉斜长角闪岩 | | M40 | 铝土质页岩 | | I01 | 闪长岩 | | B11 | 钙碱性玄武岩 | | sl50 | 砂质板岩 | | am30 | VF透辉斜长角
闪岩 | | M50 | 硅质页岩 | | I02 | 二长闪长岩 | | B12 | 拉斑玄武岩 | | sl60 | 泥质板岩 | gr | | 麻粒岩 | | M60 | 炭质页岩 | | I03 | 二长岩 | | B13 | 碱性玄武岩 | | sl70 | 凝灰质板岩 | | gr10 | 花岗—花岗闪
长质麻粒岩 | | M70 | 铁铝质泥岩 | | I04 | 正长岩 | | B14 | 橄榄玄武岩 | ph | | 千枚岩 | | gr20 | 斜长麻粒岩 | | M80 | 灰泥岩 | | I05 | 碱长正长岩 | | B15 | 高铝玄武岩 | | ph10 | 绢云千枚岩 | | gr30 | 基性麻粒岩 | | M90 | 凝灰质页岩 | | I10 | 安山岩 | | B16 | 变玄武岩 | | ph20 | 绿泥千枚岩 | | gr40 | 超铁镁质麻粒岩 | S | | 砂岩 | | I12 | 玄武安山岩 | | B17 | 细碧岩 | | ph30 | 阳起千枚岩 | qu | | 石英岩类 | | S11 | 石英砂岩 | | I13 | 高镁(玻古)
安山岩 | | B18 | 粗面玄武岩 | | ph40 | 石英千枚岩 | | qu10 | 石英岩 | | S12 | 长石石英砂岩 | | I14 | 变安山岩 | | B19 | 碱玄岩 | | ph50 | 方解千枚岩 | | qu20 | 长石石英岩 | | S13 | 长石砂岩 | | I20 | 粗面岩 | U | | 超基性岩 | ms | | 片岩 | | qu30 | 磁铁石英岩 | | S14 | 粉(细)砂岩 | | K | | 碱性岩 | | U01 | 橄榄岩 | | ms10 | 云母片岩 | ma | | 大理岩 | | S15 | 杂砂岩 | | K01 | 副长石正长岩 | | U04 | 辉石岩 | | ms20 | 石英片岩 | | ma10 | 方解石大理岩 | | S16 | 砂岩 | | K02 | 副长石二长岩 | | U06 | 角闪石岩 | | ms30 | 绿片岩 | | ma20 | 白云石大理岩 | | S17 | 泥质砂岩 | | K03 | 副长石闪长岩 | | U07 | 榴辉岩 | gn | | 片麻岩 | | ma30 | 富硅铝大理岩 | | S18 | 钙质砂岩 | | K04 | 副长石辉长岩 | | U11 | 麦美奇岩 | | gn10 | 花岗质—花岗闪
长质片麻岩 | L | | 灰岩 | | S19 | 灰砂岩 | | K05 | 霓霞岩 | | U12 | 科马提岩 | | gn20 | 贫碱长英质片麻岩 | | L10 | 石灰岩 | | S20 | 变余砂岩 | | K06 | 碳酸岩 | | U13 | 苦橄岩 | | gn30 | 斜长片麻岩类 | | L20 | 白云质灰岩 | | S30 | 凝灰质砂岩 | | K11 | 响岩 | | U14 | 玻基橄辉岩 | | gn40 | 富铝贫碱斜长
片麻岩 | | L30 | 泥质灰岩 | | S40 | 冰碛岩 | | K12 | 碱玄质响岩 | | U15 | 钾镁煌斑岩 | | gn50 | 黑云斜长片麻岩 | | L40 | 砂质灰岩 | | S50 | 含铜砂岩 | | K13 | 响岩质碱玄岩 | V | | 火山碎屑岩 | | gn60 | 角闪斜长片麻岩 | | L50 | 硅质灰岩 | Si | | 硅质岩 | | K14 | 碱玄岩 | | V10 | 流纹质火山
碎屑岩 | | gn70 | 辉石斜长片麻岩 | D | | 白云岩 | | Si10 | 炭质硅质岩 | | K15 | 碧玄岩 | | V20 | 英安质火山
碎屑岩 | le | | 变(浅)粒岩 | | D10 | 白云岩 | | Si20 | 燧石岩 |
|
Rock classification system
|
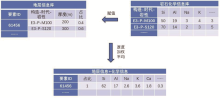
|
Schematic of assigning chemical composition values to strata
|

|
Schematic of assigning chemical composition values to exposed rocks
|
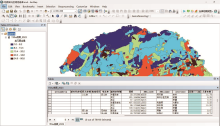
|
GIS representation of spatial distribution and chemical composition of geological units
|
| [1] |
National Academies of Sciences,Engineering,and Medicine. A vision for NSF earth sciences 2020—2030:Earth in time[M]. Washington,D. C.:The National Academies Press, 2020.
|
| [2] |
Gray J M, Bishop T F A, Wilford J R. Lithology and soil relationships for soil modelling and mapping[J]. Catena, 2016,147:429-440.
|
| [3] |
Dinelli E, Lima A, De Vivo B, et al. Hydrogeochemical analysis on Italian bottled mineral waters:Effects of geology[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 107(3):317-335.
|
| [4] |
Snæbjörnsdóttir S Ó, Sigfússon B, Marieni C, et al. Carbon dioxide storage through mineral carbonation[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(2):90-102.
|
| [5] |
Deng K, Yang S Y, Guo Y L. A global temperature control of silicate weathering intensity[J]. Nature Communications, 2022,13:1781.
|
| [6] |
Fang Q, Lu A H, Hong H L, et al. Mineral weathering is linked to microbial priming in the critical zone[J]. Nature Communications, 2023,14:345.
|
| [7] |
Wei X, Bai X Y, Wen X F, et al. A large and overlooked Cd source in karst areas:The migration and origin of Cd during soil formation and erosion[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2023,895:165126.
|
| [8] |
Huang J H, Huang F, Evans L, et al. Vanadium:Global (bio)geochemistry[J]. Chemical Geology, 2015,417:68-89.
|
| [9] |
Wang X, Liu X, Wang W. National-scale distribution and its influence factors of calcium concentrations in Chinese soils from the China Global Baselines Project[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2022,233:106907.
|
| [10] |
Wang W, Wang X, Zhang B, et al. Concentrations and spatial distribution of chlorine in the pedosphere in China:Based on the China Geochemical Baselines Project[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2022,242:107089.
|
| [11] |
Wen Y, Li W, Yang Z, et al. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region,Southwestern China[J]. Chemosphere, 2020,245:125620.
|
| [12] |
Miller H J. Tobler's first law and spatial analysis[J]. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 2004, 94(2):284-289.
|
| [13] |
迟清华, 鄢明才. 中国东部岩石地球化学图[J]. 地球化学, 2005, 34(2):97-108.
|
| [13] |
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Lithogeochemical map in the eastern part of China[J]. Geochimica, 2005, 34(2):97-108.
|
| [14] |
Liu D S, Chi Q H, Wang X Q, et al. National-scale cobalt geochemical mapping of exposed crust in China[J]. Minerals, 2022, 12(10):1220.
|
| [15] |
鄢明才, 迟清华. 中国东部地壳与岩石的化学组成[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1997.
|
| [15] |
Yan M C, Chi Q H. The chemical compositions of crust and rocks in the eastern part of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1997.
|
| [16] |
Wang X Q. Reprint of “China geochemical baselines:Sampling methodology”[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015,154:17-31.
|
| [17] |
刘东盛, 迟清华, 王学求, 等. 华南—西秦岭地球化学走廊带水系沉积物钴含量影响因素评价[J]. 地质学报, 2023, 97(5):1-15.
|
| [17] |
Liu D S, Chi Q H, Wang X Q, et al. Evaluation of factors influencing cobalt content in sediments of the hydrological system in the South China-West Qinling geological corridor[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(5):1-15.
|
| [18] |
Ye Z Q, Huang T Z, Deng C K. Spatial database of 1∶2,500,000 digital geologic map of people's republic of China[J]. Acta of Geoscientific Data & Discovery, 2017, 44(S1):24-31.
|
| [19] |
庞健峰, 丁孝忠, 韩坤英, 等. 1∶100 万中华人民共和国数字地质图空间数据库[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(S1):8-18.
|
| [19] |
Pang J F, Ding X Z, Han K Y, et al. 1∶100 million digital geological map spatial database of the People's Republic of China[J]. Geological China, 2017, 44(S1):8-18.
|
| [20] |
潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1):1-16,255,17-28.
|
| [20] |
Pan G T, Xiao Q H, Lu S N, et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(1):1-16,255,17-28.
|
| [21] |
任纪舜. 新一代中国大地构造图——中国及邻区大地构造图 (1∶5 000 000) 附简要说明:从全球看中国大地构造[J]. 地球学报, 2003, 24(1):1-2.
|
| [21] |
Ren J S. A new generation of geological map of China—Geological map of China and adjacent areas (1∶5,000,000) with brief explanation:China's tectonics in a global perspective[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2003, 24(1):1-2.
|
| [22] |
袁启玉, 李仰春, 吴亮, 等. 中华人民共和国地质图(1∶150万)空间数据库建设方法[J]. 地质学刊, 2024, 48(1):68-75.
|
| [22] |
Yuan Q Y, Li Y C, Wu L, et al. Construction method of geological map spatial database of People's Republic of China (1∶1.5 million)[J]. Geological Journal, 2024, 48(1):68-75.
|
| [23] |
Zheng X, Liu Y. Mechanisms of element precipitation in carbonatite-related rare-earth element deposits:Evidence from fluid inclusions in the Maoniuping deposit,Sichuan Province,southwestern China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2019,107:218-238.
|
| [24] |
Aranha M, Porwal A, Sundaralingam M, et al. Rare earth elements associated with carbonatite-alkaline complexes in western Rajasthan,India:Exploration targeting at regional scale[J]. Solid Earth, 2022, 13(3):497-518.
|
| [25] |
Orberger B, van der Ent A. Nickel laterites as sources of nickel,cobalt and scandium:Increasing resource efficiency through new geochemical and biological insights[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019,204:297-299.
|
| [26] |
谢学锦, 任天祥, 奚小环, 等. 中国区域化探全国扫面计划卅年[J]. 地球学报, 2009, 30(6):700-716.
|
| [26] |
Xie X J, Ren T X, Xi X H, et al. The implementation of the regional geochemistry-national reconnaissance program(RGNR) in China in the past thirty years[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009, 30(6):700-716.
|
| [27] |
de Caritat P, Cooper M. A continental-scale geochemical atlas for resource exploration and environmental management:The national geochemical survey of Australia[J]. Geochemistry:Exploration, Environment,Analysis, 2016, 16(1):3-13.
|
| [28] |
Ottesen R T, Bogen J, Bølviken B, et al. Overbank sediment:A representative sample medium for regional geochemical mapping[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1989, 32(1-3):257-277.
|
| [29] |
成杭新, 谢学锦. 泛滥平原沉积物的超低密度采样代表性研究 (一)[J]. 长春地质学院学报, 1997, 27(3):289-95.
|
| [29] |
Cheng H X, Xie X J. Research on the representativeness of ultra-low-density sampling of floodplain sediments (1)[J]. Journal of Changchun Institute of Geology, 1997, 27(3):289-95.
|
| [30] |
Bølviken B, Bogen J, Jartun M, et al. Overbank sediments:A natural bed blending sampling medium for large-scale geochemical mapping[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2004, 74(1):183-199.
|
| [31] |
Gong Q J, Deng J, Jia Y J, et al. Empirical equations to describe trace element behaviors due to rock weathering in China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015,152:110-117.
|
| [32] |
Stolar D, Roe G, Willett S. Controls on the patterns of topography and erosion rate in a critical orogen[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface, 2007, 112(F4):2006JF000713.
|
| [33] |
Lipp A G, Roberts G G, Whittaker A C, et al. River sediment geochemistry as a conservative mixture of source regions:Observations and predictions from the cairngorms,UK[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface, 2020, 125(12):e2020JF005700.
|
| [34] |
李仰春, 王永志, 陈圆圆, 等. 智绘地质——新一代智能化地质编图模式及应用[J]. 地质通报, 2020, 39(6):861-870.
|
| [34] |
Li Y C, Wang Y Z, Chen Y Y, et al. Intelligent geological mapping:A novel pattern for smart geological compilation[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(6):861-870.
|
| [35] |
王涛, 童英, 丁毅, 等. DDE-岩浆岩数据库初步构建与应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2024, 40(3):873-888.
|
| [35] |
Wang T, Tong Y, Ding Y, et al. Preliminary construction and application of DDE-database of igneous rocks[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2024, 40(3):873-888.
|
| [36] |
Reimann C, Garrett R G. Geochemical background—Concept and reality[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2005, 350(1-3):12-27.
|
| [37] |
Gong Q J, Zhang G X, Zhang J, et al. Behavior of REE fractionation during weathering of dolomite regolith profile in southwest China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica-English Edition, 2010, 84(6):1439-1447.
|
| [38] |
Garzanti E, Resentini A. Provenance control on chemical indices of weathering[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2016,336:81-95.
|
| [39] |
Guo Y L, Yang S Y, Deng K. Disentangle the hydrodynamic sorting and lithology effects on sediment weathering signals[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021,586:120607.
|
| [40] |
Carranza E J M. Analysis and mapping of geochemical anomalies using logratio-transformed stream sediment data with censored values[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 110(2):167-185.
|
| [41] |
Collins A L, Blackwell M, Boeckx P, et al. Sediment source fingerprinting:Benchmarking recent outputs,remaining challenges and emerging themes[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(12):4160-4193.
|
| [42] |
Harris J R, Grunsky E C. Predictive lithological mapping of Canada's North using Random Forest classification applied to geophysical and geochemical data[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2015,80:9-25.
|
| [43] |
郭志娟, 孔牧, 张华, 等. 适合地球化学勘查的景观划分研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(1):12-15.
|
| [43] |
Guo Z J, Kong M, Zhang H, et al. Landscape division suitable for geochemical exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(1):12-15.
|
| [44] |
Hilton R G, West A J. Mountains, erosion and the carbon cycle[J]. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 2020, 1(6):284-299.
|
| [45] |
王学求. 透视全球资源与环境,实施“化学地球” 国际大科学计划[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(1):201-202.
|
| [45] |
Wang X Q. The initiative for international cooperation project of "Mapping Chemical Earth" for sustaining global resources and environments[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(1):201-202.
|
|
|
|

