|
|
|
| Seismic wave impedance inversion based on the fully convolutional residual shrinkage network |
WANG Kang1( ), LIU Cai-Yun2( ), LIU Cai-Yun2( ), XIONG Jie1, WANG Yong-Chang1, HU Huan-Fa1, KANG Jia-Shuai1 ), XIONG Jie1, WANG Yong-Chang1, HU Huan-Fa1, KANG Jia-Shuai1 |
1. School of Electronics & Information Engineering,Yangtze University,Jingzhou 434023,China
2. School of Information and Mathematics,Yangtze University,Jingzhou 434023,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Convolutional neural networks(CNNs) have achieved good results in seismic wave impedance inversion,but the inversion accuracy and anti-noise performance need to be improved.Hence,this study proposed a seismic wave impedance inversion method based on the fully convolutional residual shrinkage network with channel-wise thresholds(FCRSN-CW).In this method,the attention mechanism and the soft thresholding were first added to the structure of the residual network to form a inversion network.Then,a synthetic seismic dataset was obtained through forward calculation using wave impedance data.Subsequently,the dataset was applied to train the FCRSN-CW.Finally,the seismic data were put into the trained FCRSN-CW to obtain the inversion results directly.The inversion results of the theoretical model show that the FCRSN-CW can accurately invert the wave impedance and possesses satisfactory learning capacity and anti-noise performance.The inversion results of field data demonstrates that the method based on FCRSN-CW can effectively achieve seismic wave impedance inversion.
|
|
Received: 25 November 2022
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
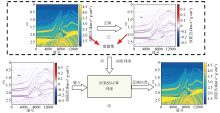
|
Flow chart of seismic impedance inversion using FCRSN-CW
|

| 残差块个数 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | | 均方根误差 | 0.00052 | 0.00021 | 0.00027 | 0.00031 |
|
Mean square error of predicted impedance and true impedance by different residual blocks
|
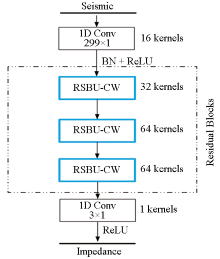
|
Architecture of the FCRSN-CW
|
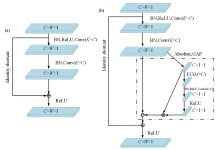
|
Residual building unit before(a) and after(b) improvement(different thresholds by channels)
|
|
Impedance(a) and synthetic seismic data(b) generated by 30 Hz 0° phase Ricker wavelet
|
19] and FCRSN-CW respectively
">
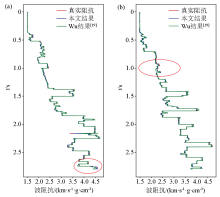
|
Inversion results of No.650(a) and No.1250(b) by FCRN[19] and FCRSN-CW respectively
|
19](a) and FCRSN-CW (b)
">
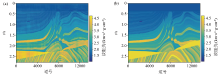
|
Predictions of FCRN[19](a) and FCRSN-CW (b)
|

| 子波相位 | 0° | 30° | 60° | 90° | 120° | 150° | | 均方误差 | 0.0002 | 0.2056 | 0.1259 | 0.0926 | 0.1054 | 0.1623 |
|
Mean square error of predicted impedance and true impedance by wavelet with different phases
|
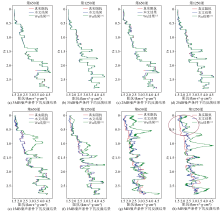
|
Predicted impedance from noisy data
|

| 噪声强度/dB | 35 | 25 | 15 | 5 | | FCRN反演结果均方误差 | 0.0583 | 0.0603 | 0.0797 | 0.2116 | | FCRSN-CW反演结果均方误差 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0045 | 0.1411 |
|
Mean square error of predicted impedance and true impedance with different noise
|

| 噪声强度/dB | 35 | 25 | 15 | 5 | | 浅层数据 | 0.9963 | 0.9881 | 0.8772 | 0.6335 | | 深层数据 | 0.9998 | 0.9997 | 0.9974 | 0.9009 |
|
The predicted impedance is compared with the true impedance at shallow and deep PCC
|
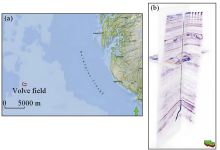
|
Location of the Volve oil field(a),seismic data and well log data from the Volve oil field(b)
|
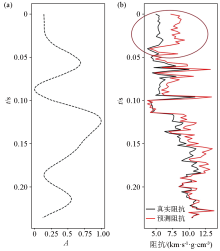
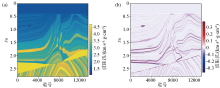
|
Input seismic data along well(a) and corresponding true and prediction impedance(b)
|

| 相位 | 0° | 10° | 20° | 30° | | 10 Hz | 0.8859 | 0.9068 | 0.8563 | 0.8902 | | 20 Hz | 0.9427 | 0.9158 | 0.9007 | 0.9153 | | 30 Hz | 0.8969 | 0.9104 | 0.8927 | 0.8932 | | 40 Hz | 0.8863 | 0.9095 | 0.8884 | 0.8562 |
|
PCC of predicted impedance and true impedance by wavelet with different phases and frequencies
|
| [1] |
李庆忠. 论地震约束反演的策略[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1998, 33(4):423-438,572.
|
| [1] |
Li Q Z. On strategy of seismic restricted inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1998, 33(4):423-438,572.
|
| [2] |
曾凡玲. 地震波阻抗反演及其在储层检测中的应用[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2012.
|
| [2] |
Zeng F L. Seismic impedance inversion and its application in reservoir prediction[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2012.
|
| [3] |
Huang W, Zhou H W. Least-squares seismic inversion with stochastic conjugate gradient method[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2015, 26(4):463-470.

|
| [4] |
Liu C, Song C, Lu Q, et al. Impedance inversion based on L1 norm regularization[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2015, 120:7-13.

|
| [5] |
张繁昌, 印兴耀, 吴国忱, 等. 用模拟退火神经网络技术进行波阻抗反演[J]. 石油大学学报:自然科学版, 1997, 21(6):16-18.
|
| [5] |
Zhang F C, Yin X Y, Wu G C, et al. Impedance inversion using simulated annealing neural network technique[J]. Journal of the University of Petroleum,China:Natural Science Edition, 1997, 21(6):16-18.
|
| [6] |
聂茹, 岳建华, 邓帅奇. 免疫遗传算法及其在波阻抗反演中的应用[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2010, 27(4):1273-1276.
|
| [6] |
Nie R, Yue J H, Deng S Q. Application of immune genetic algorithm in wave impedance inversion[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2010, 27(4):1273-1276.
|
| [7] |
Yang H J, Xu Y Z, Peng G X, et al. Particle swarm optimization and its application to seismic inversion of igneous rocks[J]. International Journal of Mining Science and Technology, 2017, 27(2):349-357.

|
| [8] |
Conti C R, Roisenberg M, Neto G S, et al. Fast seismic inversion methods using ant colony optimization algorithm[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2013, 10(5):1119-1123.

|
| [9] |
Wang B F, Zhang N, Lu W K, et al. Deep-learning-based seismic data interpolation:A preliminary result[J]. Geophysics, 2019, 84(1):V11-V20.
|
| [10] |
付超, 林年添, 张栋, 等. 多波地震深度学习的油气储层分布预测案例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(1):293-303.
|
| [10] |
Fu C, Lin N T, Zhang D, et al. Prediction of reservoirs using multi-component seismic data and the deep learning method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(1):293-303.
|
| [11] |
赵明, 陈石, Dave Yuen. 基于深度学习卷积神经网络的地震波形自动分类与识别[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(1):374-382.
|
| [11] |
Zhao M, Chen S, Yuen D. Waveform classification and seismic recognition by convolution neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(1):374-382.
|
| [12] |
Zhang H H, Zhang G Z, Gao J H, et al. Seismic impedance inversion based on geophysical-guided cycle-consistent generative adversarial networks[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2022, 218:111003.

|
| [13] |
梁立锋, 刘秀娟, 张宏兵, 等. 超参数GRU-CNN 混合深度学习弹性阻抗反演影响研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1):133-139.
|
| [13] |
Liang L F, Liu X J, Zhang H B, et al. A study of the effect of hyperparameters on GRU-CNN hybrid deep learning EI inversion[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1):133-139.
|
| [14] |
Das V, Pollack A, Wollner U, et al. Convolutional neural network for seismic impedance inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2019, 84(6):R869-R880.
|
| [15] |
Puzyrev V, Egorov A, Pirogova A, et al. Seismic inversion with deep neural networks:A feasibility analysis[C]// London:81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2019,European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 2019:1-5.
|
| [16] |
Xu P C, Lu W K, Tang J, et al. High-resolution reservoir prediction using convolutional neural networks[C]// London:81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2019,European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 2019:1-5.
|
| [17] |
Guo R, Zhang J J, Liu D, et al. Application of bi-directional long short-term memory recurrent neural network for seismic impedance inversion[C]// London:81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2019,European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers,2019, 2019(1):1-5.
|
| [18] |
Wu B Y, Xie Q, Wu B H. Seismic impedance inversion based on residual attention network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60:1-17.
|
| [19] |
Wu B Y, Meng D L, Wang L L, et al. Seismic impedance inversion using fully convolutional residual network and transfer learning[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 17(12):2140-2144.

|
| [20] |
Zhao M H, Zhong S S, Fu X Y, et al. Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7):4681-4690.

|
|
|
|

