|
|
|
| Rapid determination of soil cation exchange capacity using a cation exchange capacity pretreatment system and a Kjeldahl apparatus |
HU Meng-Ying1,2( ), ZHANG Peng-Peng1,2, XU Jin-Li1,2, LIU Bin1,2, ZHANG Ling-Huo1,2, DU Xue-Miao1,2( ), ZHANG Peng-Peng1,2, XU Jin-Li1,2, LIU Bin1,2, ZHANG Ling-Huo1,2, DU Xue-Miao1,2( ), BAI Jin-Feng1,2 ), BAI Jin-Feng1,2 |
1. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
2. Key Laboratory of Geochemical Exploration, Ministry of Natural Resources, Langfang 065000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The soil cation exchange capacity (CEC) refers to the total amount of various cations that can be absorbed by soil colloids. It is an important measure of the buffering capacity and fertilizer retention capacity of soil and is also an indicator that must be analyzed in soil environment assessment. The conventional ammonium acetate exchange method described in Chinese forestry standard LY/T 1243—1999 has been widely used in soil and agrochemical laboratories in China due to its high stability, buffering capacity, and repeatability. However, when applied to the batch analysis of soil, this conventional method is time-consuming and has other shortcomings such as cumbersome steps and low efficiency. Based on previous studies, this study optimized the conventional ammonium acetate exchange method in three steps, namely centrifugation, distillation, and titration. Specifically, samples were treated with displacement using mixed EDTA and ammonium acetate solution and cleaning with ethanol using the CEC pretreatment system. Then, the ammonium ions displaced were determined using an automatic Kjeldahl apparatus, followed by the calculation of the CEC. This study discussed the effects of the stirring time of ammonium acetate, ethanol dosage, and distillation time in the Kjeldahl apparatus on CEC determined. On this basis, this study comprehensively established and optimized the method for determining the CEC in soil using the CEC pretreatment system and the Kjeldahl apparatus. As shown by the experimental results, under the optimal conditions of displacement time, ethanol dosage, and distillation time, the optimized method determined the CEC of a batch of samples (100) in only 8 h, which was shortened by nearly 85% compared with the conventional method, thus greatly improving the efficiency. As verified using the certified reference material for the chemical composition of first-grade soil, the determined CEC values agreed with the certified values, with relative standard deviations (n = 6) of all less than 2%. The optimized method is characterized by high efficiency and simple operation and can greatly reduce possible errors caused by manual operation and improve the accuracy of results. Therefore, it is applicable to the bulk determination of soil CEC.
|
|
Received: 22 March 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 搅拌时间 | 测定值/(cmol·kg-1) | 测定平均值 | | min | 1 | 2 | 3 | (cmol·kg-1) | | 3 | 22.0 | 21.7 | 21.8 | 21.8 | | 5 | 21.8 | 22.0 | 21.9 | 21.9 | | 10 | 22.4 | 22.5 | 22.4 | 22.4 | | 15 | 21.5 | 22.0 | 22.5 | 22.0 | | 20 | 21.9 | 21.9 | 21.9 | 21.9 | | 25 | 21.2 | 21.8 | 22.3 | 21.8 |
|
Influence of different stirring time of EDTA-ammonium acetate solution on the determination results
|
|
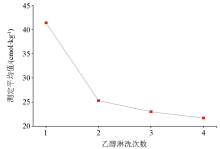
Influence of different ethanol dosage on the determination results
|
|
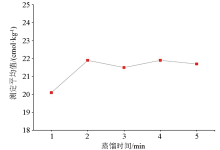
Influence of distillation time of automatic kieldahl apparatus on determination results
|

| 样品 | CEC/(cmol·kg-1) | RSD/% | | 6次测定结果 | 平均值 | 标准值 | | GBW07412a | 21.8
22.1
22.0
22.0
21.6
21.4 | 21.8 | 21.6±1.4 | 1.31 | | GBW07415a | 20.1
19.2
19.4
19.5
19.2
19.0 | 19.4 | 19±1 | 1.96 | | GBW07416a | 10.2
10.6
10.4
10.3
10.5
10.6 | 10.4 | 10.0±0.6 | 1.49 | | GBW07417a | 20.2
19.5
20.0
19.8
20.2
19.6 | 19.9 | 19.7±1.1 | 1.52 | | GBW07460 | 9.9
10.1
10.2
10.3
10.0
10.2 | 10.1 | 9.6±1.3 | 1.41 |
|
Precision and accuracy results of the method
|

| 对比 | 本方法 | 林业标准(LY/T1243-1999) | | 前处理步骤 | 全自动淋洗抽滤系统:加入样品后仪器全自动泵入EDTA-乙酸铵溶液进行搅拌置换和乙醇溶液的淋洗抽滤,普通样品耗时约25min,同时可处理4个样品 | 手动搅拌离心清洗:全程手动进行多次乙酸铵溶液的搅拌置换和乙醇溶液的清洗,且需要多次离心,单个样品耗时约1h | | 蒸馏与滴定步骤 | 全自动蒸馏滴定:加入固体氧化镁后仪器自动边蒸馏边滴定,自动判定终点准确,蒸馏效率100%,单个样品只需4min | 手动蒸馏滴定:手工蒸馏装置安装复杂,手工滴定终点易产生偏差,蒸馏效率和体积难以准确控制,单个样品耗时约30min | | 需配置试剂种类 | 7 | 12 | | 测定时长(1个样品) | 约0.5h | 约1.5h | | 测定时长(100个样) | 约8h | 约65h |
|
Comparison between this method and standard method
|
| [4] |
拉毛吉, 王玉功, 张榕. 乙酸铵离心交换法和乙酸钙离心交换法测定土壤阳离子交换量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2017, 7(3):38-41.
|
| [4] |
La M J, Wang Y G, Zhang R. Determination of cation exchange capacity of soil by centrifugal exchange of ammonium and calcium acetates[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 7(3):38-41.
|
| [5] |
LY/T 1243—1999森林土壤阳离子交换量的测定[S].
|
| [5] |
LY/T 1243—1999 Determination of cation exchange capacity in forest soil[S].
|
| [6] |
张彦雄, 李丹, 张佐玉, 等. 两种土壤阳离子交换量测定方法的比较[J]. 贵州林业科技, 2010, 38(2):45-49.
|
| [6] |
Zhang Y X, Li D, Zhang Z Y, et al. A comparison study of two methods for mensuration of soil cation exchange capacity[J]. Guizhou Forestry Science and Technology, 2010, 38(2):45-49.
|
| [7] |
褚龙, 贺斌. 土壤阳离子交换量的测定方法[J]. 黑龙江环境通报, 2009, 33(1):81-83.
|
| [7] |
Chu L, He B. Determining method of soil cation exchange capacity[J]. Heilongjiang Environmental Journal, 2009, 33(1):81-83.
|
| [8] |
迟伟伟, 徐苏红. 自动淋洗仪快速测定土壤阳离子交换量的研究[J]. 环境科技, 2019, 32(6):60-63.
|
| [8] |
Chi W W, Xu S H. Study on the method of rapid determination of soil cation exchange capacity with automatic elution apparatus[J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2019, 32(6):60-63.
|
| [9] |
史斌, 朱晓丹, 陆国兴, 等. 全自动淋洗仪在土壤阳离子交换量测定中的应用[J]. 环境与发展, 2017, 2(10):139-142.
|
| [9] |
Shi B, Zhu X D, Lu G X, et al. The application of automatic leaching instrument to detect the soil cation exchange capacity[J]. Environment and Development, 2017, 2(10):139-142.
|
| [10] |
周圆, 卞世闻, 张宇. 凯氏定氮仪测定土壤阳离子交换量的方法改进[J]. 环境科学导刊, 2015, 34(6):106-109.
|
| [10] |
Zhou Y, Bian S W, Zhang Y. Method improvement of detecting soil CEC by Kieldahl's azotometer[J]. Environmental Science Survey, 2015, 34(6):106-109.
|
| [1] |
鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科技出版社, 1999.
|
| [1] |
Lu R K. Methods for agrochemistry analysis of soil[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, 1999.
|
| [11] |
李龙飞, 李星, 李永立. 土壤阳离子交换量测定方法的优化与改进[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2019, 47(6):1-2.
|
| [11] |
Li L F, Li X, Li Y L. Optimization and improvement of cation exchange capacity method in agricultural soils[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(6):1-2.
|
| [2] |
王文艳, 张丽萍, 刘俏. 黄土高原小流域土壤阳离子交换量分布特征及影响因子[J]. 水土保持学报, 2012, 26(5):123-127.
|
| [2] |
Wang W Y, Zhang L P, Liu Q. Distribution and affecting factors of soil cation exchange capacity in watershed of the loess plateau[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2012, 26(5):123-127.
|
| [12] |
拉毛吉, 王玉功, 张榕, 等. 纳氏试剂分光光度法测定土壤阳离子交换量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2018, 8(4):16-20.
|
| [12] |
La M J, Wang Y G, Zhang R, et al. Determination of cation exchange capacity in soil by using Nessler's spectrophotometry[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2018, 8(4):16-20.
|
| [13] |
王炜, 朱晓丹, 史斌, 等. 全自动淋洗样品预处理—气相分子吸收光谱法测定土壤阳离子交换量[J]. 理化检验:化学分册, 2019, 55(3):314-318.
|
| [13] |
Wang W, Zhu X D, Shi B, et al. Determination of cation exchange capacity of soil by gas molecular absorption spectrometry with sample treatment by automatic rinsing device[J]. Physical Testing and Chemical Analysis part B:Chemical Analyiss, 2019, 55(3):314-318.
|
| [14] |
马怡飞, 张尼, 魏增, 等. 振荡交换—抽滤淋洗结合凯氏定氮法快速测定土壤中的阳离子交换量[J]. 岩矿测试, 2019, 38(1):129-135.
|
| [14] |
Ma Y F, Zhang N, Wei Z, et al. Rapid determination of soil cation exchange capacity by automatic Kjeldahl analyzer after oscillating exchange and suction filtration[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2019, 38(1):129-135.
|
| [15] |
李光一, 任晓荣, 周彧琛, 等. 振荡抽滤—pH计指示电位滴定法快速测定土壤样品中阳离子交换总量[J]. 中国无机分析化学, 2021, 11(2):31-35.
|
| [15] |
Li G Y, Ren X R, Zhou Y C, et al. Rapid determination of total cation exchange in soil samples by oscillating suction filtration-pH meter potentiometric titration[J]. Chinese Journal of Inorganic Analytical Chemistry, 2021, 11(2):31-35.
|
| [16] |
DB 33/T 966—2015土壤阳离子交换量的测定[S].
|
| [16] |
DB 33/T 966—2015 Determination of cation exchange capacity in soil[S].
|
| [17] |
肖艳霞, 赵颖, 王彦君, 等. 土壤中阳离子交换量分析方法的优化研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2019, 35(15):74-78.
|
| [17] |
Xiao Y X, Zhao Y, Wang Y J, et al. Analysis methods for cation exchange capacity in soil:Optimization[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2019, 35(15):74-78.
|
| [3] |
Dawid J, Dorota K. A comparison of methods for the determination of cation exchange capacity of soils[J]. Ecological Chemistry & Engineering S, 2014, 21(3):487-498.
|
| [1] |
XUE Dong-Xu, LIU Cheng, GUO Fa, WANG Jun, XU Duo-Xun, YANG Sheng-Fei, ZHANG Pei. Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1169-1178. |
| [2] |
QUE Ze-Sheng, LI Guan-Chao, HU Ying, JIAN Rui-Min, LIU Bing. GIS-based assessment of the radioactivity levels and risks of soil environment[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1336-1347. |
|
|
|
|

