|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil in Shizuishan area, Ningxia |
WANG Zhi-Qiang1( ), YANG Jian-Feng1( ), YANG Jian-Feng1( ), WEI Li-Xin2, SHI Tian-Chi1, CAO Yuan-Yuan1 ), WEI Li-Xin2, SHI Tian-Chi1, CAO Yuan-Yuan1 |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the comprehensive collection of samples from the alkaline soil in the Shizuishan area, Ningxia, this study analyzes the geochemical indicators of selenium and available selenium in soil in the area.The results are as follows. The seleniumin soil in the study area is mainly originated from the black rock series in the Helan Mountain area, followed by siltation brought in by the agricultural irrigation water diverted from the Yellow River. The bioavailability of selenium in the study area is at a relatively high level, and the effective selenium enrichment and above covers 79.2% of the whole study area, with an area of about 777.2 km2. The content of different forms of selenium is in the order ofresidualselenium>strongly organic matter-bound selenium>humic acid-bound selenium>ion exchangeableselenium≈water-soluble selenium > carbonate-bound selenium≈iron manganese oxide-boundselenium. The total selenium content is limited, while thewater-soluble selenium content is relatively high. The higher the total nitrogen and organic matter content in soil, the higher the total selenium and available selenium content. As the salt content in soil in the study area increases, the bioavailability of seleniumtends to gradually increase. The irrigation-silted soiland thefluvo-aquic soil with a pH value between 7.5 and 9 have moderate total selenium content and high available selenium content, and they are high-quality areas for planting selenium-rich agricultural products.
|
|
Received: 23 March 2021
Published: 25 February 2022
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YANG Jian-Feng
E-mail: nxw12@163.com;623552149@qq.com
|
|
|
|

| 硒含量分级 | 硒效应 | 谭见安等[11,12] | | 宁夏富硒土壤标准[13] | | 表层土壤总硒/10-6 | 占比/% | 表层土壤总硒/10-6 | 占比/% | | 缺乏 | 硒反应病 | <0.125 | 8.67 | | <0.116 | 7.58 | | 边缘 | 硒不足 | 0.125~0.175 | 10.22 | | 0.116~0.175 | 11.34 | | 中等 | 足硒 | 0.175~0.4 | 74.47 | | 0.175~0.222 | 16.30 | | 高 | 富硒 | 0.4~3.0 | 6.63 | | 0.222~3.0 | 64.80 | | 过剩 | 硒中毒 | ≥3.0 | | | ≥3.0 | |
|
Classification of soil selenium content in Shizuishan area
|
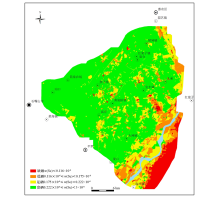
|
Distribution characteristics of soil selenium content in Shizuishan area
|

| 硒含量分级 | 表层土壤水溶态硒/10-9 | 硒效应 | 占比/% | | 缺乏 | <3 | 硒反应病 | 3.06 | | 边缘 | 3~6 | 硒不足 | 8.48 | | 中等 | 6~8 | 足硒 | 9.26 | | 高 | 8~20 | 富硒 | 71.31 | | 过剩 | ≥20 | 硒中毒 | 7.89 |
|
Classification of soil water-soluble selenium content and selenium effect in Shizuishan area
|
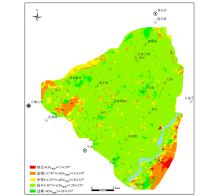
|
Distribution characteristics of soil available selenium content in Shizuishan area
|

| 形态 | 最大值/10-9 | 最小值/10-9 | 平均值/10-9 | 标准偏差 | 变异系数 | 去除极值
后平均值/10-9 | 占全硒百分比
均值(去除极值)/% | | 水溶态 | 12.90 | 10.09 | 11.21 | 0.69 | 0.061 | 11.13 | 4.88 | | 离子交换态 | 15.00 | 8.15 | 11.34 | 1.88 | 0.166 | 11.26 | 4.95 | | 碳酸盐结合态 | 8.36 | 3.48 | 5.61 | 1.44 | 0.257 | 5.52 | 2.35 | | 腐殖酸结合态 | 43.61 | 1.38 | 25.60 | 10.69 | 0.418 | 26.55 | 11.12 | | 铁锰氧化物结合态 | 6.39 | 3.51 | 5.10 | 0.81 | 0.159 | 5.15 | 2.24 | | 强有机结合态 | 84.12 | 10.62 | 52.36 | 20.12 | 0.384 | 53.90 | 22.39 | | 残渣态 | 206.54 | 45.88 | 114.76 | 37.56 | 0.327 | 111.24 | 47.45 | | 全量 | 318.00 | 86.00 | 230.53 | 59.77 | 0.259 | 239.31 | |
|
Statistical table of selenium element speciation analysis results
|

| 地区 | 全量/10-6 | 水溶态/10-9 | 水溶态占比/% | 参考文献 | | 宁夏石嘴山 | 0.23 | 11.21 | 4.88 | 本文 | | 黑龙江海伦市 | 0.29 | 8 | 4.68 | [17] | | 江西鄱阳湖 | 0.308 | 11 | 3.60 | [15] | | 天津市蓟州区 | 0.37 | 15 | 4.6 | [16] | | 南疆焉耆盆地 | 0.39 | 7 | 2.05 | [18] | | 青海东部 | 0.44 | 11.51 | 3.32 | [19] | | 安徽庐江 | 0.45 | 5 | 1.4 | [20] | | 湖北恩施沙地乡 | 1.88 | 13.3 | 0.71 | [21] |
|
Characteristics of soil water-soluble selenium content in some areas of China
|
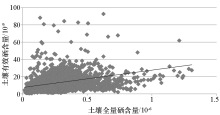
|
Scatter plot of soil available selenium and total selenium content
|

| 等级 | 全氮含量/10-6 | 样点数 | 全量硒/10-6 | 有效硒/10-69 | 硒活化度/% | | 低 | <0.9 | 5007 | 0.22 | 10.63 | 5.63 | | 一般 | 0.9~1.2 | 2995 | 0.30 | 14.27 | 5.04 | | 高 | >1.2 | 830 | 0.34 | 17.57 | 5.52 |
|
Characteristics of available selenium with different nitrogen content
|

| 等级 | 有机质含量/10-3 | 样点数 | 全量硒/10-6 | 有效硒/10-9 | 硒活化度/% | | 低 | <1 | 1959 | 0.155 | 8.266 | 6.437 | | 一般 | 1~1.8 | 4105 | 0.254 | 12.520 | 5.198 | | 高 | >1.8 | 2768 | 0.332 | 15.528 | 5.027 |
|
Characteristics of effective selenium with different organic matter content
|

| pH | 样品数 | 全量硒/10-6 | 有效硒/10-9 | 硒活化度/% | | 7.5~8 | 54 | 0.42 | 13.80 | 3.78 | | 8~8.5 | 3411 | 0.29 | 13.37 | 5.06 | | 8.5~9 | 4622 | 0.25 | 12.23 | 5.22 | | 9~9.5 | 584 | 0.14 | 8.45 | 6.30 | | 9.5~10 | 108 | 0.14 | 13.08 | 10.09 | | 10~10.5 | 53 | 0.08 | 25.46 | 28.38 |
|
Characteristics of effective selenium at different pH values
|

| 盐碱程度 | 土壤全盐量/10-3 | 全量硒/10-6 | 有效硒/10-9 | 硒活化度/% | | 无盐渍化 | <1.5 | 0.266 | 11.69 | 4.87 | | 轻度盐渍化 | 1.5~3 | 0.244 | 13.41 | 5.88 | | 中度盐渍化 | 3~6.0 | 0.240 | 12.91 | 6.06 | | 重度盐渍化 | 6~9.9 | 0.227 | 12.66 | 6.54 | | 盐土 | >9.9 | 0.245 | 16.42 | 7.20 |
|
Characteristics of effective selenium in different salinity levels
|

| 土壤类型 | 全量硒 | | 有效硒 | 硒活化度/% | | 均值/10-6 | 富硒比例/% | 均值/10-9 | 富硒比例/% | | 灰钙土 | 0.401 | 87.84 | | 7.60 | 29.80 | 2.11 | | 新积土 | 0.331 | 70.85 | | 9.99 | 61.97 | 3.44 | | 灌淤土 | 0.262 | 76.40 | | 13.63 | 90.69 | 5.33 | | 潮土 | 0.257 | 51.02 | | 12.99 | 84.17 | 5.75 | | 盐土 | 0.252 | 62.32 | | 13.00 | 82.13 | 5.52 | | 碱土 | 0.213 | 53.33 | | 13.92 | 83.33 | 6.60 | | 风沙土 | 0.119 | 20.67 | | 7.08 | 22.28 | 7.79 |
|
Characteristics of available selenium in different soil types
|
| [1] |
Rayman M P. The argument for increasing selenium intake[J]. Proc.Nutr.Soc., 2002,61:203-215.
|
| [2] |
Williams P N, Lombi E, Sun G X, et al. Selenium characterization in the global rice supply Chain[J]. Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009,43:6024-6030.
|
| [3] |
Winkel L H E, Johnson C A, Lenz M, et al. Environmental selenium research: From microscopic processes to global understanding[J]. Environ.Sci.Technol., 2012,46:571-579.
|
| [4] |
梁东丽, 彭琴, 崔泽玮, 等. 土壤中硒的形态转化及其对有效性的影响研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017,7(5):374-380.
|
| [4] |
Liang D L, Peng Q, Cui Z W, et al. Progress on selenium bioavailibility and influential factors in soil[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017,7(5):374-380.
|
| [5] |
Tan J, Zhu W, Wang W, et al. Selenium in soil and endemic diseases in China[J]. Sci.Total Environ., 2002,284:227-235.
|
| [6] |
Nedjimi B B B, Mansouri A, Tahtat D, et al. Selenium content in wheat and estimation of the selenium daily intake in different regions of Algeria[J]. Appl.Radiat. Isotopes, 2013,71:7-10.
|
| [7] |
Shardendu U, Salhani N, Boulyga S F, et al. Phytoremediation of selenium by two helophyte species in subsurface flow constructed wetland[J]. Chemosphere, 2003,50:967-973.
|
| [8] |
张艳玲, 潘根兴, 胡秋辉. 江苏省几种低硒土壤中硒的形态分布及生物有效性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2002,8(3):355-359.
|
| [8] |
Zhang Y L, Pan G X, Hu Q H. Selenium fraction and bio-availability in some low-Se soils of central Jiangsu Province[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2002,8(3):355-359.
|
| [9] |
梁若玉, 和娇, 史雅娟, 等. 典型富硒农业基地土壤硒的生物有效性与剖面分布分析[J]. 环境化学, 2017,36(7):1588-1595.
|
| [9] |
Liang R Y, He J, Shi Y J, et al. Bioavailability and profile distribution of selenium in soils of typical Se-enriched agricultural base[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017,36(7):1588-1595.
|
| [10] |
侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020.
|
| [10] |
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical dataset of china[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020.
|
| [11] |
谭见安. 环境生命元素与克山病[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 1996.
|
| [11] |
Tan J A. Environmental life elements and Keshan disease [M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 1966.
|
| [12] |
中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集编纂委员会. 中华人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1989.
|
| [12] |
Endemic disease and environment atlas compilation committee of People’s Republic of China. Endemic diseases and environment atlas of People’s Republic of China [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1989.
|
| [13] |
DB 64/T 1220—2016 宁夏富硒土壤标准[S]. 银川: 宁夏人民教育出版社, 2018.
|
| [13] |
DB 64/T 1220—2016 Standard for selenium-enriched soil in Ningxia[S]. Yinchuan: Ningxia People's Education Publishing House, 2018.
|
| [14] |
张元培, 胡晓明, 吴颖, 等. 湖北省天门市农作物种植区土壤中硒富集影响因素[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2015,29(6):822-824.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Y P, Hu X M, Wu Y, et al. Soil selenium enrichment factors of crop planting areas in Tianmen,Hubei province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2015,29(6):822-824.
|
| [15] |
魏然, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 江西省鄱阳湖流域根系土硒形态分析及其迁移富集规律[J]. 物探与化探, 2012,36(1):109-113.
|
| [15] |
Wei R, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. An analysis of speciation of selenium asits transformation and enrichment in root soil of Poyang lake basin, Jiangxi Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012,36(1):109-113.
|
| [16] |
谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等. 天津市蓟州区土壤硒的有效性及影响因素[J]. 环境化学, 2019,38(10):2306-2316.
|
| [16] |
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y, et al. Bioavailability of selenium and its influencing factors in soil of Jizhou district,Tianjin[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019,38(10):2306-2316.
|
| [17] |
张立, 刘国栋, 吕石佳, 等. 黑龙江省海伦市农耕区土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 现代地质, 2019,33(5):1046-1054.
|
| [17] |
Zhang L, Liu G D, Lyu S J, et al. Distribution characteristics of selenium cultivated soil and its influencing factors in Hailun County of Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geoscience, 2019,33(5):1046-1054.
|
| [18] |
赵禹, 白金, 刘拓, 等. 南疆焉耆盆地土壤—小麦系统硒耦合关系及生物有效性[J]. 地质通报, 2020,39(12):1960-1970.
|
| [18] |
Zhao Y, Bai J, Liu T, et al. Se coupling relation and biological effectiveness study of the soilwheat system in Yanqi Basin, southern Xinjiang[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020,39(12):1960-1970.
|
| [19] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海东部碱性土壤中硒的形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019,43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [19] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of Se speciation of alkaline soil in eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019,43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [20] |
杨奎, 李湘凌, 张敬雅, 等. 安徽庐江潜在富硒土壤硒生物有效性及其影响因素[J]. 环境科学研究, 2018,31(4):715-724.
|
| [20] |
Yang K, Li X L, Zhang J Y, et al. Selenium bioavailability and the Influential Factors in potentially selenium enriched soils in Lujiang County, Anhui Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2018,31(4):715-724.
|
| [21] |
王锐, 余涛, 杨忠芳, 等. 富硒土壤硒生物有效性及影响因素研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境, 2018,27(7):1647-1654.
|
| [21] |
Wang R, Yu T, Yang Z F, et al. Bioavailability of soil selenium and its influencing factors in selenium-enriched soil[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2018,27(7):1647-1654.
|
| [22] |
Winkel L H E, Johnson C A, Lenz M, et al. Environmental selenium research: From microscopic processes to global understanding[J]. Environ.Sci.Technol., 2012,46:571-579.
|
| [23] |
杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012,26(5):837-849.
|
| [23] |
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Q Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012,26(5):837-849.
|
| [24] |
马玉兰. 宁夏测土配方施肥技术[M]. 银川: 宁夏人民出版社, 2008.
|
| [24] |
Ma Y L. Soil testing and formulated fertilization technology in Ningxia [M]. Yinchuan: Ningxia People’s Publishing House, 2008.
|
| [1] |
JIANG Bing, LIU Yang, WU Zhen, ZHANG De-Ming, SUN Zeng-Bing, MA Jian. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in irrigation water and soils in the Gaomi area, Shandong Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1348-1353. |
| [2] |
NAN Zhe, WANG Lin-Shi, HOU Xu, ZHAI Zheng-Bo, WANG Yang, LIU Yang. Geological and geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of rare element and rare earth element deposits in Saima alkaline complex[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 670-680. |
|
|
|
|

