|
|
|
| Geological and geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of rare element and rare earth element deposits in Saima alkaline complex |
NAN Zhe1( ), WANG Lin-Shi2( ), WANG Lin-Shi2( ), HOU Xu1, ZHAI Zheng-Bo3, WANG Yang1, LIU Yang1 ), HOU Xu1, ZHAI Zheng-Bo3, WANG Yang1, LIU Yang1 |
1. Liaoning Nuclear Industry Geology 241st Brigade Co., Ltd.,Fengcheng 118100,China
2. Liaoning Geology and Mining Group Energy Geology Co., Ltd.,Shenyang 110016,China
3. Natural Resources Bureau of Benxi Manchu Autonomous County, Liaoning Province,Benxi 117000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Saima alkaline complex is a unique and complex geologic body. It is well known for its diverse rock types and mineral types and high contents of uranium, thorium, and rare and rare earth elements. This study analyzed and summarized the geological exploration results of the Saima alkaline complex area in recent years, discovering that the rocks in the second intrusive stage of the Saima alkaline complex show the wide mineralization of rare and rare earth elements, with a moderate- to low- mineralization temperature. There are mainly two types of deposits in Saima alkaline complex area, namely the residual magmatic metasomatism type and the skarn type. Furthermore, the prospecting potential of the whole alkaline complex was analyzed by combining the 1∶200,000 stream sediment survey data and the 1∶10,000 primary halo survey data. Three predicted metallogenic zones of rare earth and radioactive elements were delineated in the Saima alkaline complex and its surrounding area, namely Saima-Gujia, Aiyang, and Shuangshanzi. This study is of great significance for the prospecting of rare and rare earth polymetals in the Saima alkaline complex area.
|
|
Received: 31 March 2021
Published: 05 July 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
12])
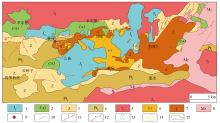
1—Jurassic basin; 2—Cambrian-Ordovician system; 3—Sinian system; 4—metamorphic rock series of Liaohe group; 5—Yanshanian intrusive rocks; 6—Indo-Chinese alkaline volcanic rocks; 7—Indosinian period alkaline intrusive rocks; 8—Proterozoic intrusive rock; 9—Saima large uranium, thorium, rare and rare earth deposits; 10—fault of unknown nature; 11—measured reverse fault; 12—presumed reverse fault; 13—survey area of uranium deposit in south contact zone of Saima 422 deposit, Fengcheng City, Liaoning Province; 14—survey area of uranium and rare and rare earth ore in Beitaiyanggou, Saima Town, Fengcheng City, Liaoning Province; 15—survey area of rare and rare earth ore in Caojiapuzi Village, Fengcheng City, Liaoning Province
">
|
Regional geological map of the Saima alkaline rocks(adapted form reference[12])
1—Jurassic basin; 2—Cambrian-Ordovician system; 3—Sinian system; 4—metamorphic rock series of Liaohe group; 5—Yanshanian intrusive rocks; 6—Indo-Chinese alkaline volcanic rocks; 7—Indosinian period alkaline intrusive rocks; 8—Proterozoic intrusive rock; 9—Saima large uranium, thorium, rare and rare earth deposits; 10—fault of unknown nature; 11—measured reverse fault; 12—presumed reverse fault; 13—survey area of uranium deposit in south contact zone of Saima 422 deposit, Fengcheng City, Liaoning Province; 14—survey area of uranium and rare and rare earth ore in Beitaiyanggou, Saima Town, Fengcheng City, Liaoning Province; 15—survey area of rare and rare earth ore in Caojiapuzi Village, Fengcheng City, Liaoning Province
|
14])
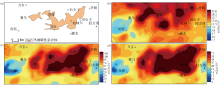
a—distribution of alkaline complex in Fengcheng;b—distribution of Nb geochemical anomalies;c—distribution of Ce geochemical anomalies;d—distribution of La geochemical anomalies
">
|
Geochemical map of Fengcheng alkaline complex(adapted form reference[14])
a—distribution of alkaline complex in Fengcheng;b—distribution of Nb geochemical anomalies;c—distribution of Ce geochemical anomalies;d—distribution of La geochemical anomalies
|

| 岩相 | 岩石名称 | | 喷出岩 | 喷溢相 | 白榴石斑岩、假白榴石响岩、响岩 | | 爆发相 | 白榴石响岩质凝灰岩、凝灰岩、凝灰角砾岩 | | 侵入岩 | 第一期 | 边缘相(同化系列) | 黑榴云霞正长岩、云霞正长岩 | | 内部相(分异系列) | 云霓霞正长岩、黑色霓石霓霞正长岩、暗绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | 第二期 | 残浆相(分异系列) | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩、异性石草绿色霓石霓霞正长岩、草绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | 脉岩 | 伟晶岩相 | 云(霓)霞正长伟晶岩、黑色霓石霓霞正长伟晶岩、
绿色霓石霓霞正长伟晶岩、草绿色霓石霓霞正长伟晶岩 | | 细晶岩相 | 正长细晶岩、霓石、霓霞正长细晶岩 | | 斑岩相 | 霓石正长斑岩、正长斑岩、白榴石斑岩 | | 交代岩 | 接触
交代岩 | 矽卡岩 | 钙镁质矽卡岩、镁质矽卡岩、碱性矽卡岩 | | 长霓岩 | 石英金云母微斜长石长霓岩、金云母霓辉石钠长石微斜长石长霓岩 | | 表生、热液蚀变岩 | 变生正长岩 |
|
The main rock types, stages and facies of the Saima alkaline rocks area classified
|
15])
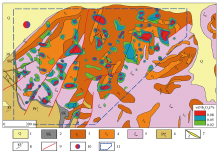
1—Quaternary; 2—skarn; 3—the first stage intrusive rock; 4—the second stage intrusive rock; 5—metamorphic syenite; 6—Dashiqiao formation of Liaohe group; 7—lamprophyre; 8—attitude of stratum; 9—fracture structure; 10—Saima large uranium, thorium, rare and rare earth deposits; 11—1∶ 10,000 rock survey range
">
|
Anomaly of niobium primary halo in Saima alkaline rock(adapted from reference [15])
1—Quaternary; 2—skarn; 3—the first stage intrusive rock; 4—the second stage intrusive rock; 5—metamorphic syenite; 6—Dashiqiao formation of Liaohe group; 7—lamprophyre; 8—attitude of stratum; 9—fracture structure; 10—Saima large uranium, thorium, rare and rare earth deposits; 11—1∶ 10,000 rock survey range
|
16])
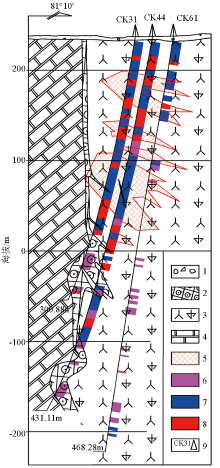
1—the surface regolith; 2—skarn; 3—grass-green aegirine nepheline syenite; 4—marble of Dashiqiao formation of Liaohe group; 5—the uranium ore body; 6—0.02%≤w(Nb2O5)≤0.05%;7—0.05%≤w(Nb2O5)≤0.08%;8—0.08%≤w(Nb2O5);9—drilling location and number
">
|
Geological profile of No.14 exploration line of Saima uranium deposit(adapted from reference[16])
1—the surface regolith; 2—skarn; 3—grass-green aegirine nepheline syenite; 4—marble of Dashiqiao formation of Liaohe group; 5—the uranium ore body; 6—0.02%≤w(Nb2O5)≤0.05%;7—0.05%≤w(Nb2O5)≤0.08%;8—0.08%≤w(Nb2O5);9—drilling location and number
|

矿体
编号 | 控制
工程 | 位置 | 厚度/m | 长度/m | Nb2O5平均
含量/% | 赋矿岩性 | | 起/m | 始/m | | Nb1矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 10.70 | 13.00 | 2.50 | 73.6 | 0.0506 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | TC18-4 | 11.00 | 19.50 | | Nb1-1矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 26.30 | 29.16 | 2.86 | 40.0 | 0.0261 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | Nb1-3矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 36.35 | 37.35 | 1.00 | 40.0 | 0.0448 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | Nb1-4矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 39.35 | 45.12 | 5.77 | 40.0 | 0.0312 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | Nb1-6矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 60.09 | 61.09 | 1.00 | 40.0 | 0.0460 | 绿色伟晶状霓霞正长岩 | | Nb1-7矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 64.84 | 70.59 | 5.75 | 40.0 | 0.0250 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | Nb1-9矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 108.17 | 121.17 | 13.00 | 40.0 | 0.0285 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩、霞石正长岩 | | Nb1-10矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 125.17 | 129.17 | 4.00 | 40.0 | 0.0298 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | Nb1-11矿体 | ZKⅠ-1 | 142.17 | 143.17 | 1.00 | 40.0 | 0.0370 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | | Nb2矿体 | ZKⅡ-1 | 3.00 | 5.80 | 2.05 | 46.9 | 0.0414 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩、黑云母霞石正长岩 | | TC18-5 | 14.30 | 16.50 |
|
Characteristics of some niobium orebodies in Beitaiyanggou area of Saima
|

| 岩性 | 样品数 | 化学成分含量/% | | SiO2 | TiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | FeO | MnO | MgO | CaO | Na2O | K2O | P2O5 | Los | 总量 | σ | A/CNK | | 赛马碱性岩 | 15 | 53.92 | 1.21 | 16.38 | 6.73 | 2.15 | 0.20 | 0.70 | 2.15 | 6.24 | 8.71 | 0.10 | 1.99 | 100.69 | 20.47 | 0.69 | | 诺科斯世界霞石正长岩[23] | 55.38 | 0.66 | 21.30 | 2.42 | 2.00 | 0.19 | 0.57 | 1.98 | 8.84 | 5.34 | 0.19 | 0.96 | 99.83 | 16.24 | 0.89 |
|
Chemical composition and content of alkaline rock of Saima
|

| 期次 | 岩性 | Nb | Ta | Zr | Hf | Ce | La | Be | Li | Rb | Sr | | 喷出岩 | 响岩、假白榴石响岩 | 123 | 3.0 | 993 | 54.9 | 355 | 140 | 7.2 | 38 | 168.5 | 3651 | 第一
侵入期 | 黑榴云霞正长岩 | 90 | 2.4 | 1602 | 81.2 | 294 | 103 | | | | 220 | | 云霓霞正长岩 | 59 | 2.7 | 802 | 45.9 | 354 | 237 | 11.2 | 40 | 299.3 | 2478 | | 黑色霓石霓霞正长岩 | 90 | 2.6 | 925 | 53.1 | 424 | 210 | 6.8 | 110 | 158.0 | 2168 | 第二
侵入期 | 绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | 367 | 9.5 | 7889 | 482.9 | 597 | 352 | | | | | | 异性石草绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | 370 | 7.7 | 8101 | 513.9 | 586 | 274 | 12.1 | 42 | 118.5 | 3278 | | 草绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | 374 | 6.3 | 7690 | 399.0 | 1005 | 469 | 10.5 | 30 | 119.0 | 5034 | | 交代岩 | 长霓岩 | 133 | | 327 | | 700 | 352 | | | | | | 钠铁闪石岩 | | | 766 | 12.0 | 95 | 65 | 2.5 | 20 | | | | 透闪石岩 | | | 112 | 7.2 | 106 | 873 | | | | | | 弱蚀变白色大理岩 | | | 96 | 0.5 | 12 | 9 | | | | | | 变生霓石正长岩 | | | 6490 | 393.3 | 392 | 220 | 5.0 | 20 | | | | 岩体平均含量 | 119 | 3.3 | 1605 | 92.7 | 413 | 211 | | | | | | 地壳平均丰度 | 10 | 2.0 | 200 | 3.2 | 45 | 45 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 310 | 400 | | 岩体平均含量/地壳平均丰度 | 12 | 1.7 | 8 | 29 | 9.2 | 11.7 | | | | |
|
The average content of various rare elements in the alkaline rock mass of Saima[26]10-6
|

| 样品编号 | 83-64 | 83-51 | 83-52 | 83-1 | 83-3-2 | 83-3-5 | 83-97 | 83-8 | 93-34 | 83-105 | | 岩石名称 | 粗面岩 | 白榴石斑岩 | 假白榴石
响岩 | 黑榴云霞
正长岩 | 云霓霞
正长岩 | 黑色霓石霓
霞正长岩 | 绿色霓石霓
霞正长岩 | 草绿色霓石
霓霞正长岩 | 钙矽卡岩 | 镁矽卡岩 | | La | 144.0 | 104.8 | 140.0 | 100.0 | 162.5 | 150.0 | 240.0 | 377.0 | 82.0 | 96.0 | | Ce | 232.0 | 195.2 | 244.8 | 220.0 | 331.3 | 262.5 | 400.0 | 760.0 | 160.0 | 156.0 | | Pr | 28.8 | 19.2 | 28.8 | 40.0 | 48.8 | 39.4 | 34.4 | 125.0 | 29.0 | 18.4 | | Nd | 88.0 | 76.0 | 102.4 | 115.0 | 177.5 | 112.5 | 102.4 | 310.0 | 80.0 | 38.4 | | Sm | 18.4 | 15.2 | 20.8 | 24.0 | 32.5 | 40.0 | 25.6 | 77.0 | 18.0 | 16.8 | | Eu | 6.6 | 5.6 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 13.8 | 10.8 | 6.9 | 31.0 | 7.2 | 4.2 | | Gd | 9.2 | 6.4 | 10.4 | 21.0 | 21.3 | 17.5 | 12.8 | 53.0 | 16.0 | 5.6 | | Dy | 5.2 | 4.0 | 5.6 | 5.9 | 7.4 | 7.0 | 4.8 | 28.0 | 4.1 | 3.7 | | Er | | | | 7.0 | 8.0 | 7.3 | | 19.0 | 5.7 | | | Yb | 3.7 | 2.9 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 5.0 | 4.5 | 3.7 | 19.0 | 2.6 | 2.6 | | ∑w(REE) | 502.3 | 405.3 | 530.4 | 544.1 | 808.1 | 651.5 | 867.4 | 1799.0 | 404.6 | 325.7 | w(LREE)/
w(HREE) | 26.6 | 29.5 | 25.9 | 13.7 | 18.4 | 17.0 | 37.3 | 14.1 | | | | δEu | 1.39 | 1.49 | 1.40 | 1.08 | 1.52 | 1.08 | 1.05 | 1.42 | | | | w(La)/w(Yb) | 38.9 | 36.1 | 37.8 | 31.3 | 32.5 | 33.3 | 64.9 | 19.8 | | | | w(Eu)/w(Sm) | 0.36 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.33 | 0.42 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.40 | | |
|
Contents of REE in main rock types of Saima alkaline rocks10-6
|

| 矿化特征 | 矿化类型 | | 岩浆分异—绿层硅铈钛矿—残浆交代型 | 矽卡岩—烧绿石—接触交代型 | | 矿体部位 | 第二期侵入岩 | 接触带 | | 矿化岩石 | 绿色、草绿色霓石霓霞正长岩 | 矽卡岩 | | 矿化围岩 | 霞石正长岩 | 透闪大理岩、霓霞正长岩 | | 控矿构造 | 第一期侵入岩边缘节理 | 接触带构造 | | 围岩蚀变 | 霓石化、闪石化、针钠钙石化、萤石化 | 矽卡岩化、黑云母化、钠铁闪石化、透闪石化 | | 主要矿物 | 绿层硅铈钛矿、钛铌钙铈矿 | 烧绿石、铌钛铀矿、绿层硅铈钛矿 | | 矿化形态 | 似层状、透镜状 | 透镜状 | | 主要元素 | Nb、Ce、La、Zr、Ti、 | Nb、Ce、La、Zr、Ti | | 矿物组合 | 异性石、闪叶石、针钠钙石、钠锆石、钛铌钙铈矿、
钠铁闪石、榍石、萤石、金属硫化物 | 透闪石、闪叶石、针钠钙石、钛铌钙铈矿、磷灰石、
钛铁矿、锐钛矿、萤石、方解石、金属硫化物 |
|
Main mineralization types and characteristics of Saima alkaline rock area
|
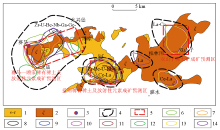
|
Metallogenic prediction map of the Saima alkaline rock area
1—indosinian period alkaline volcanic rocks; 2—indosinian alkaline intrusive rocks; 3—Saima large uranium, thorium, rare and rare earth deposits; 4—1∶ 200,000 abnormal range of stream sediment assemblage; 5—metallogenic prediction area; 6—Be abnormal outer zone; 7—Nb abnormal outer zone; 8—U abnormal outer zone; 9—Th abnormal outer zone; 10—Zr abnormal outer zone; 11—Ga abnormal outer zone; 12—Ge abnormal outer zone; 13—Ce abnormal outer zone; 14—La abnormal outer zone
|
| [1] |
王盘喜, 包民伟. 我国钽铌等稀有金属矿概况及找矿启示[J]. 金属矿山, 2015, 44(6):92-97.
|
| [1] |
Wang P X, Bao M W. General situation and prospecting revelation of tantalum-niobiumrare metal deposits in China[J]. Metals Mines, 2015, 44(6):92-97.
|
| [2] |
程兴国, 陈新, 闫红圃, 等. 河南省方城县双山碱性正长岩型铌矿综合找矿方法及找矿模型[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(2):247-252.
|
| [2] |
Cheng X G, Chen X, Yan H P, et al. An integrated ore-prospectingmethod and model in search for Shuangshan alkali syenite Nb depositin Fangcheng County,Henan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2):247-252.
|
| [3] |
黄景孟, 熊意林, 张笑, 等. 南秦岭竹山县土地岭火山岩型钽铌矿综合找矿方法及找矿模型[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(5):1135-1143.
|
| [3] |
Huang J M, Xiong Y L, Zhang X, et al. An integrated ore-prospecting method and model for volcanic Ta-Nbdeposits in Tudiling,Zhushan County,south Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5):1135-1143.
|
| [4] |
陈肇博, 范军, 郭智添, 等. 赛马碱性岩与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社,1996.
|
| [4] |
Chen Z B, Fan J, Guo Z T, et al. Saima alkaline rocks and relevant metallogenesis[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press,1996.
|
| [5] |
彭瑞琪. 与碱性岩有关的稀有元素矿床[J]. 地质科学, 1959, 2(9):260-267.
|
| [5] |
Peng R Q. Rare element deposits related to alkaline rocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1959, 2(9):260-267.
|
| [6] |
鞠楠, 张森, 毕中伟, 等. 辽宁凤城赛马铌矿床成矿岩体地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 世界地质, 2019, 38(1):130-139,153.
|
| [6] |
Ju N, Zhang S, Bi Z W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological significance of metallogenic rock bodiesof Saima niobium deposit in Fengcheng, Liaoning[J]. World Geology, 2019, 38 (1): 130-139,153.
|
| [7] |
北京铀矿地质研究所赛马矿床研究组. 我国东北赛马碱性岩体中的铀矿床[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 1977, 8(5):466-483,503-506.
|
| [7] |
Saima Mineral Deposit Research Group of Beijing Institute of Uranium Geology. Uranium deposits in Saima alkaline rock mass, northeast China[J]. Science in China:Series D, 1977, 8(5):466-483,503-506.
|
| [8] |
袁忠信, 白鸽. 中国内生稀有稀土矿床的时空分布[J]. 矿床地质, 2001, 20(4):347-354.
|
| [8] |
Yuan Z X, Bai G. Temporal and spatial distribution of endophytic rare and rare earth mineral deposits of China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2001, 20(4):347-354.
|
| [9] |
辽宁省地质矿产局. 辽宁省区域地质志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1989.
|
| [9] |
Liaoning Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources Exploration. Regional geology of Liaoning Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House,1989.
|
| [10] |
鞠楠, 张森, 毕中伟, 等. 辽宁凤城赛马铌矿床成矿条件研究[C]// 第八届全国成矿理论与找矿方法学术讨论会, 2017:192.
|
| [10] |
Ju N, Zhang S, Bi Z W, et al. Study on ore-forming conditions of Fengcheng Saima niobium deposit in Liaoning Province[C]// The Eighth National Symposium on Metallogenic Theory and Prospecting Method, 2017:192.
|
| [11] |
蔡肖, 宋扬. 东北地区铌钽矿产分布与成矿条件初析[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(S):1155-1156.
|
| [11] |
Cai X, Song Y. Distribution of niobium and tantalum minerals and metallogenic conditions in Northeast China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2014, 33(S):1155-1156.
|
| [12] |
南哲, 刘伟, 辛良. 辽宁省凤城市赛马北太阳沟铀及稀有稀土矿普查[R]. 辽宁核地地质调查院(二四一), 2019.
|
| [12] |
Nan Z, Liu W, Xin L. A survey of uranium and rare earth deposits in northern Taiyanggou,Saima,Fengcheng, Liaoning Province[R]. Liaoning Institute of Nuclear Geological Survey(241),2019.
|
| [13] |
孙立军, 张永红, 于金辉, 等. 辽宁东部凤城碱性岩体的地质特征及形成时代探讨[J]. 辽宁省交通高等专科学校学报, 2008, 10(4):41-44.
|
| [13] |
Sun L J, Zhang Y H, Yu J H, et al. Discussion geological features and age on the alkaline-complex of Fengcheng of the eastern Liaoning[J]. Journal of Liaoning Provincial College of Communications, 2008, 10(4):41-44.
|
| [14] |
董庆光, 付海涛, 杨占兴, 等. 辽宁省1∶20万水系沉积物地球化学测量报告[R]. 辽宁省物测勘查院, 2015.
|
| [14] |
Dong Q G, Fu H T, Yang Z X, et al. A geochemistry survey report of the 1∶200,000 stream sediments in Liaoning Province[R]. Liaoning Provincial Institute of Physical Survey and investigation, 2015.
|
| [15] |
佟国元, 冷教千, 辛良, 等. 辽宁省凤城市赛马地区稀有稀土矿产找矿报告[R]. 辽宁省核工业地质局二四一大队, 2009.
|
| [15] |
Tong G Y, Leng J Q, Xin L, et al. Rare and rare earth mineral prospecting report in Saima,Fengcheng, Liaoning Province[R]. 241 Brigade of Liaoning Nuclear Industry Geological Bureau,2009.
|
| [16] |
张集庆, 王宗英, 桑吉盛, 等. 四二二矿床储量报告[R]. 辽宁省核工业地质局二四一大队,1974.
|
| [16] |
Zhang Q J, Wang Z Y, Sang J S, et al. Reserve report of No.422 deposit[R]. 241 Brigade of Liaoning Nuclear Industry Geological Bureau,1974.
|
| [17] |
邬斌, 王汝成, 郭国林, 等. 辽宁赛马碱性岩体层硅铈钛矿化学成分变化及其对碱性岩浆演化的指示意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(2):467-478.
|
| [17] |
Wu B, Wang R C, Guo G L, et al. Compositional variations of rinkite in the Saima alkaline complex, Liaoning Province,and its implications for alkaline magma evolution[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 45(2):467-478.
|
| [18] |
楼凤升, 张荣英, 刘汉儒. 层硅铈钛矿的矿物学研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 1988, 7(1):58-65,96.
|
| [18] |
Lou F S, Zhang R Y, Liu H R. Mineralogy of mosandrite[J]. Journal of Petrology and Mineralogy, 1988, 7(1):58-65,96.
|
| [19] |
成曦晖, 徐九华, 张辉. 辽东赛马—柏林川碱性岩区石英脉中的包裹体[J]. 矿床地质, 2014, 33(S):503-504.
|
| [19] |
Cheng X H, Xu J H, Zhang H, et al. Inclusion study of the quartz dikes in the Saima-Bailinchuan alkaline complex in Liaoning Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2014. 33(S):503-504.
|
| [20] |
邬斌, 王汝成, 刘晓东, 等. 辽宁赛马碱性岩异性石化学成分特征及其蚀变组合对碱性岩浆—热液演化的指示意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(6):1741-1757.
|
| [20] |
Wu B, Wang R C, Liu X D, et al. Chemical composition and alteration assemblages of eudialyte in the Saima alkaline complex,Liaoning Province, and its implication for alkaline magmatic-hydrothermal evoolution[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(6):1741-1757.
|
| [21] |
沈敢富, 徐金沙, 姚鹏, 等. 凤城石:异性石族矿物N(5)位贫钠的空位类似物新种[J]. 矿物学报, 2017, 37(Z1):140-151.
|
| [21] |
Shen G F, Xu J S, Yao P, et al. Fengchengite: A new species with the Na-poor but vacancy-dominant N(5) site in the eudialyte group[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2017, 37(Z1):140-151.
|
| [22] |
丁奎首, 周剑雄, 庄世杰. 赛马矿(钛硅锶矿)的新研究[J]. 科学通报, 1984, 29(11):678-681.
|
| [22] |
Ding K S, Zhou J X, Zhuang S J. A new study of the Saima deposit (titanium silicon strontium ore)[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1984, 29(11):678-681.
|
| [23] |
祝铭. 中生代侵入岩体三维几何形态及其成因意义[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2019.
|
| [23] |
Zhu M. Three-dimensional geometry of Mesozoic intrusive rock mass and its genetic significance[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2019.
|
| [24] |
周玲棣, 王杨传. 赛马和紫金山碱性杂岩体稀土元素地球化学及成因模式[J]. 地球化学, 1991, 20(3):229-235.
|
| [24] |
Zhou L D, Wang Y C. REE geochemistry and genetic model of Saima and Zijinshan alkaline rock bodies[J]. Geochemistry, 1991, 20(3):229-235.
|
| [25] |
张培善, 杨主明, 陶克捷, 等. 我国铌钽稀土矿物学及工业利用[J]. 稀有金属, 2005, 29(2):206-210.
|
| [25] |
Zhang P S, Yang Z M, Tao K J, et al. Niobium-tantalum and rare earth mineralogy in China and their industrial utilization[J]. Rare Metals, 2005, 29(2):206-210.
|
| [26] |
陈肇博, 范军, 郭智添, 等. 赛马碱性岩与成矿作用[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社,1996.
|
| [26] |
Chen Z B, Fan J, Guo Z T, et al. Saima alkaline rocks and mineralization[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press,1996.
|
| [27] |
李建康, 李鹏, 王登红, 等. 中国铌钽矿成矿规律[J]. 科学通报, 2019, 64(15):1545-1566.
|
| [27] |
Li J K, Li P, Wang D H, et al. A review of niobium and tantalum metallogenic regularityin China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2019, 64(15):1545-1566.
|
| [28] |
任康绪. 碱性岩研究进展评述[J]. 化工矿产地质, 2003, 25(3):151-163.
|
| [28] |
Ren K X. Review on research progress of alkaline rocks[J]. Geology of Chemical Minerals, 2003, 25(3):151-163.
|
| [29] |
麻菁, 曾普胜, 苟瑞涛, 等. 中国碱性杂岩的成因及其成矿作用[J]. 金属矿山, 2015, 51(3):466-477.
|
| [29] |
Ma J, Zeng P S, Gou R T, et al. Genesis and mineralization of alkaline complexs in China mainland[J]. Metals Mines, 2015, 51(3):466-477.
|
| [30] |
谭东波, 李东永, 肖益林. “孪生元素”铌—钽的地球化学特征和研究进展[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(1):317-332.
|
| [30] |
Tan D B, Li D Y, Xiao Y L. Geochemical characteristics of niobium and tantalum: A review of Tw in elements[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(1): 317-332.
|
| [31] |
景立珍, 郭裕嘉, 丁彩霞. 辽宁赛马碱性岩的年代学及碱性岩浆的形成[J]. 辽宁地质, 1995, 12(4):257-271.
|
| [31] |
Jing L Z, Guo Y J, Ding C X. Geochronology andorigin of Saima alkaline rocks in Liaoning Province[J]. Liaoning Geology, 1995, 12(4):257-271.
|
| [32] |
钟军, 范洪海, 陈金勇, 等. 辽宁赛马霓霞正长岩黑云母地球化学特征、40Ar-39Ar 年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(1):131-144.
|
| [32] |
Zhong J, Fan H H, Chen J Y, et al. Geochemistry characteristics and 40Ar-39Ar age of biotite from the Saima aegirine-nepheline syenite and its geological significance[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 45(1):131-144.
|
| [1] |
JIANG Bing, LIU Yang, WU Zhen, ZHANG De-Ming, SUN Zeng-Bing, MA Jian. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in irrigation water and soils in the Gaomi area, Shandong Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1348-1353. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Jia-Sheng, ZHOU Wei, LI Wei-Liang, QI Xiao-Peng, YANG Jie, WANG Lu. Geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of Jianchi Town, Shaanxi Province, China based on 1∶25,000 stream sediment survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 659-669. |
|
|
|
|

