|
|
|
| Parameter inversion and application of the Cole-Cole model for time-domain induced polarization spectra based on the backpropagation neural network |
YANG Hai-Ming1( ), YAO Wei-Xing1( ), YAO Wei-Xing1( ), TANG Su1, PAN Zhan-Chao1,2, GUAN Li-Wei1,2 ), TANG Su1, PAN Zhan-Chao1,2, GUAN Li-Wei1,2 |
1. China Geological Survey Urumqi Comprehensive Survey Center on Natural Resources, Urumqi 830057, China
2. Innovation Base of Metallogenic Prediction and Prospecting in Central Asia Orogenic Belt, Urumqi 830057, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The spectral parameters of the Cole-Cole model can improve the resolution of comprehensive interpretation of time-domain induced polarization (IP) data, contributing somewhat to the exploration of metal deposits. Applying the backpropagation neural network (BPNN) model to the prediction and inversion of spectral parameters can avoid high computational complexity to improve the inversion speed. Moreover, the BPNN model can fully explore the utilization efficiency of time-domain IP data to enrich the characteristic information of subsurface ore bodies. Based on this, this study derived the mathematical expression of the time-domain apparent polarizability attenuation curve using the digital filtering algorithm. With the mathematical expression as the forward/inverse model, this study comparatively analyzed the impacts of four factors-the sample size of the training set, the number of neurons in the input layer, the node number of hidden layers, and the number of hidden layers-on the training and inversion effects of the BPNN model, determining the optimal model. Furthermore, this study trained the BPNN model using time-domain IP data from eight time windows. Finally, this study applied the trained BPNN model for prediction and inversion based on the measured time-domain IP data. The results indicate that the BPNN model is feasible in inverting spectral parameters based on both theoretical and measured datasets, manifesting high inversion accuracy and minor errors. Overall, the results of this study can assist in distinguishing paragenetic and associated minerals and reducing misinterpretation.
|
|
Received: 21 October 2024
Published: 22 April 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
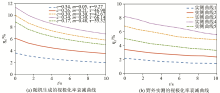
|
Comparison of two types of polarization attenuation curves
|
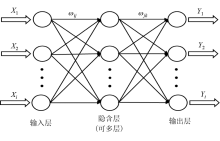
|
Back-Propagation neural network model
|
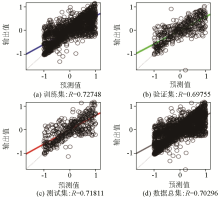
|
Regression curves for the training set(a)、validation set(b)、testing set (c) and total dataset(d) of Model 3-[5]-3 structure
|
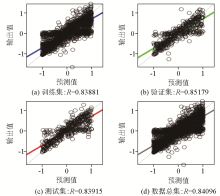
|
Regression curves for the training set(a)、validation set(b)、testing set(c) and total dataset(d) of Model 8-[3 3]-3 structure
|
|
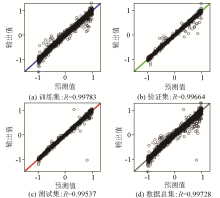
Regression curves for the training set(a)、validation set(b)、testing set(c) and total dataset(d) of Model 8-[10 10 10]-3 structure
|
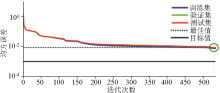
|
Transmission error variation curve with training times of Model 8-[10 10 10]-3
|
|
Spectral parameter regression curve of Model 8-[3 3]-3 structure:(a) Frequency correlation coefficient、(b) charge rate、(c) time constant
|
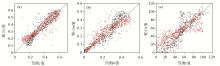
|
Spectral parameter regression curve of Model 8-[10 10 10]-3 structure:(a) Frequency correlation coefficient、(b) charge rate、(c) time constant
|

| 参数 | c | m | τ | | 模型结构 | R | Mse | R | Mse | R | Mse | | 3-[3]-3 | 0.686 672 | 0.164 371 | 0.659 548 | 0.178 509 | 0.616 054 | 0.226 556 | | 3-[5]-3 | 0.703 721 | 0.158 974 | 0.699 014 | 0.177 708 | 0.680 032 | 0.190 873 | | 5-[5]-3 | 0.825 955 | 0.105 401 | 0.833 382 | 0.090 517 | 0.726 354 | 0.209 827 | | 8-[10]-3 | 0.883 236 | 0.124 673 | 0.869 024 | 0.120 921 | 0.853 044 | 0.152 909 | | 8-[15]-3 | 0.833 561 | 0.165 781 | 0.812 135 | 0.143 291 | 0.752 719 | 0.190 345 | | 8-[3 3]-3 | 0.826 257 | 0.095 627 | 0.840 143 | 0.100 481 | 0.804 028 | 0.187 341 | | 8-[5 5]-3 | 0.945 304 | 0.038 803 | 0.953 647 | 0.046 215 | 0.873 556 | 0.180 023 | | 8-[10 10]-3 | 0.956 072 | 0.035 238 | 0.965 203 | 0.026 610 | 0.924 37 | 0.119 473 | | 8-[15 15]-3 | 0.943 289 | 0.424 467 | 0.949 861 | 0.058 321 | 0.879 808 | 0.130 944 | | 8-[3 3 3]-3 | 0.955 658 | 0.043 565 | 0.980 468 | 0.028 764 | 0.915 581 | 0.125 348 | | 8-[5 5 5]-3 | 0.975 376 | 0.032 639 | 0.982 149 | 0.027 649 | 0.973 748 | 0.071 334 | | 8-[10 10 10]-3 | 0.992 135 | 0.018 607 | 0.997 192 | 0.011 095 | 0.996 653 | 0.025 730 | | 8-[15 15 15]-3 | 0.979 347 | 0.033 456 | 0.969 457 | 0.037 855 | 0.968 965 | 0.085 321 |
|
Correlation coefficient and mean square error of spectral parameters in BP neural network training (8,000 sample set)
|
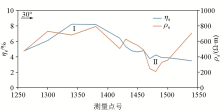
|
Abnormal curves of apparent polarization and apparent resistivity
|
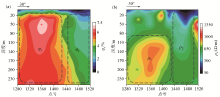
|
Cross section of apparent polarization rate (a) and apparent resistivity (b) contour lines in induced polarization depth measurement
|
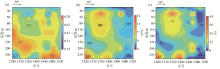
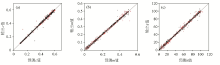
|
Contour map of inverted spectral parameters for training and prediction using measured data input into BP neural network:(a) Frequency correlation coefficient、(b) charge rate、(c) time constant
|
| [1] |
Grissemann C, Rammlmair D, Siegwart C, et al. Spectral induced polarisation linked to image analyses:A new approach[C]// Applied mineralogy:In research,economy,technology,ecology and culture,vol.2:Sixth international congress on applied mineralogy, 2000.
|
| [2] |
Pelton W H, Ward S H, Hallof P G, et al. Mineral discrimination and removal of inductive coupling with multifrequency IP[J]. Geophysics, 1978, 43(3):588.
|
| [3] |
Major J, Silic J. Restrictions on the use of Cole-Cole dispersion models in complex resistivity interpretation[J]. Geophysics, 1981, 46(6):916-931.
|
| [4] |
Carlson N, Hughes L, Zonge K. Hydrocarbon exploration using induced polarization apparent resistivity,and electromagnetic scattering[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petrole, 1983, 47(4):451-451.
|
| [5] |
罗延钟, 方胜. 视复电阻率频谱的一种近似反演方法[J]. 地球科学, 1986, 11(1):93-102.
|
| [5] |
Luo Y Z, Fang S. An approximate inversion of the apparent complex resistivity spectrum[J]. Earth Science Journal, 1986, 11,(1):93-102.
|
| [6] |
Ghorbani A, Camerlynck C, Florsch N, et al. Bayesian inference of the Cole-Cole parameters from time- and frequency- domain induced polarization[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 55:589-605.
|
| [7] |
梁盛军. 复电阻率法三维正反演问题研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.
|
| [7] |
Liang S J. Research on complex resistivity 3D modeling and inversing problem[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2011.
|
| [8] |
Mark H, Bülent T. 1D and 2D Cole-Cole inversion of time-domain induced polarization data[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 55:117-133.
|
| [9] |
罗润林, 李亚南. 基于时域激电数据的Cole-Cole模型频谱参数反演[C]//. 第九届中国国际地球电磁学术讨论会,桂林, 2009,285-288.
|
| [9] |
Luo R L, Li Y N. Spectrum parameters of Cole-Cole model inversion based on time-domain IP data[C]// The 9th China International Symposium on Electromagnetics of the Earth,Guilin, 2009:285-288.
|
| [10] |
彭伟, 梁义强, 张淳, 等. Cole-Cole模型参数在时间域激电找矿中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(3):513-517.
|
| [10] |
Peng W, Liang Y Q, Zhang C et al. The application of Cole-Cole model parameters to the time domain induced polarization prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(3):513-517.
|
| [11] |
李密. 基于时间域激电数据的频谱参数反演研究与应用[D]. 广西: 桂林理工大学, 2011.
|
| [11] |
Li M. Time domain induced polarization data based on the spectral parameters and application of inversion[D]. Guangxi: Guilin University of Technology, 2011.
|
| [12] |
岑海波. 基于人工智能的时域激电解释研究[D]. 广西: 桂林理工大学, 2023.
|
| [12] |
Cen H B. Research on time domain IP interpretation based on artificial intelligence[D]. Guangxi: Guilin University of Technology, 2023.
|
| [13] |
李健, 王晓明, 张英海, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的地震震相拾取方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(4):1591-1606.
|
| [13] |
Li J, Wang X M, Zhang Y H, et al. Research on the seismic phase picking method based on the deep convolution neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(4):1591-1606.
|
| [14] |
杨凯, 刘诚, 贺景龙, 等. 基于人工神经网络的大地电磁时序分类研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(2):498-507.
|
| [14] |
Yang K, Liu C, He J L, et al. Research on magnetotelluric time series classification based on artificial neural network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(2):498-507.
|
| [15] |
赵军, 冉琦, 朱博华, 等. 基于前馈神经网络井控多属性融合的断裂识别方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(4):1045-1053.
|
| [15] |
Zhao J, Ran Q, Zhu B H, et al. A method for identifying faults based on well-controlled multi-attribute fusion using a feedforward neural network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4):1045-1053.
|
| [16] |
Guptasarma D. Computation of the time-domain response of a polarizable ground[J]. Geophysics, 1982, 47(11):534-541.
|
| [17] |
刘瑞泽. 时间域谱激电法正演与谱特征参数最优化计算研究[D]. 河北: 河北地质大学, 2022.
|
| [17] |
Liu R Z. Research on time-domain spectral induced polarization methodforward modeling and optimal calculation of spectralcharacteristic parameters[D]. Hebei: Hebei GEO University, 2022.
|
| [18] |
傅良魁. 电法勘探教程[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1983.
|
| [18] |
Fu L K. Electrical Exploration Tutorial[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1983.
|
| [19] |
李金铭. 激发极化法方法技术指南[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004.
|
| [19] |
Li J M. Technical Specifications for Induced Polarization Method[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004.
|
| [20] |
罗延钟, 吴之训. 谱激电法中频率相关系数的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 1992, 35(4):490-500.
|
| [20] |
Luo Y Z, Wu Z X. The application of frequency dependent factor in spectral induced polarization method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1992, 35(4):490-500.
|
|
|
|

