|
|
|
| Seismic response characteristics of the cavern group of the Beishan underground research laboratory for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste |
YUN Long1,2( ), CHEN Su3, FU Lei4, ZHUANG Hai-Yang5, WANG Ju1,2( ), CHEN Su3, FU Lei4, ZHUANG Hai-Yang5, WANG Ju1,2( ) ) |
1. Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing 100029, China
2. CAEA Innovation Center for Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste, Beijing 100029, China
3. College of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing 100024
4. Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing 100081, China
5. School of Civil Engineering and Architecture, East China Jiaotong University, Nanchang, 330013, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Hexi Corridor and northern Qilian region, adjacent to the Beishan underground research laboratory (URL) for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste, exhibit complex seismic environments characterized by frequent strong earthquakes. The Beishan URL, featuring a complex underground structure consisting of three vertical shafts and a spiral ramp, displays significant large-scale spatial distribution characteristics. Investigating the seismic response characteristics of the underground structure group holds great engineering significance for the subsequent assessment of crustal stability at the site. Based on the design of the URL, along with existing physical and mechanical parameters of surrounding rocks, this study established a fine-scale three-dimensional finite element model of the rock mass-underground structure system. Using this model, this study investigated the impacts of key faults on the near-field seismic safety of the URL. The results indicate that traditional seismic attenuation relationships are difficult to consider near-source effects, such as finite fault effects, fracturing directivity effects, and hanging wall effects. In contrast, the stochastic finite-fault method can effectively consider these near-field ground shaking characteristics. The target site exhibits hard granite bedrock, and the response spectra of the earthquakes induced by near-field seismogenic faults, received at the site, display pronounced high-frequency components. Furthermore, the ground shaking of the underground cavern group, caused by the irregular structure of the URL, presents significant spatial variability, with the rock mass softening zone exhibiting a notable accumulation of peak ground acceleration. This zone should be avoided in engineering applications. This study offers a basis for seismic safety analysis for the future site selection and evaluation of the disposal repositories of high-level radioactive waste.
|
|
Received: 21 December 2023
Published: 08 January 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 钻孔深度/m | 岩性 | 块体天然密度/
(g·cm-3) | 块体干密度/
(g·cm-3) | 块体饱和密度/
(g·cm-3) | 颗粒密度/
(g·cm-3) | 天然含水率/% | | 112.77~113.59 | 中粒花岗闪长岩 | 2.652 | 2.650 | 2.653 | 2.658 | 0.068 | | 205.74~207.69 | 中细粒石英闪长岩 | 2.692 | 2.691 | 2.694 | 2.699 | 0.059 | | 302.65~309.27 | 中细粒石英闪长岩 | 2.682 | 2.680 | 2.682 | 2.687 | 0.063 | | 417.99~419.92 | 中粒花岗闪长岩 | 2.632 | 2.630 | 2.633 | 2.639 | 0.098 | | 500.40~501.25 | 中细粒花岗闪长岩 | 2.646 | 2.644 | 2.647 | 2.651 | 0.073 | | 548.42~549.22 | 中细粒花岗闪长岩 | 2.666 | 2.665 | 2.667 | 2.671 | 0.058 |
|
Basic physical property parameters of rock core
|

| 钻孔深度/m | 岩性 | 纵波波速/
(m·s-1) | 横波波速/
(m·s-1) | 动态泊松比 | 动弹性模量/
GPa | 动剪切模量/
GPa | 动体积模量/
GPa | 动拉梅系数/
GPa | | 112.77~113.59 | 中粒花岗闪长岩 | 4990.00 | 2839.67 | 0.26 | 53.88 | 21.42 | 37.47 | 23.19 | | 205.74~207.69 | 中细粒石英闪长岩 | 5254.00 | 2656.33 | 0.33 | 50.46 | 19.03 | 48.95 | 36.26 | | 302.65~309.27 | 中细粒石英闪长岩 | 5113.00 | 2802.33 | 0.28 | 53.89 | 21.13 | 41.94 | 27.85 | | 417.99~419.92 | 中粒花岗闪长岩 | 4895.67 | 2931.00 | 0.22 | 55.17 | 22.62 | 32.95 | 17.87 | | 500.40~501.25 | 中细粒花岗闪长岩 | 5103.67 | 2901.67 | 0.26 | 56.20 | 22.28 | 39.25 | 24.39 | | 548.42~549.22 | 中细粒花岗闪长岩 | 5251.67 | 2679.67 | 0.32 | 50.63 | 19.15 | 48.14 | 35.37 |
|
Elastic wave velocity parameters of borehole cores
|
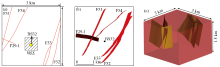
|
Spatial distribution of faults in the modeling area
a—modeling area; b—selected faults; c—rock mass calculation model
|
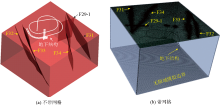
|
Regional rock-fault-underground laboratory structure model
|

| 震级 | 工况 | 穿越
F29-1 | 材料力
学参数 | 弱化带力学
参数/倍数 | 震级 | 工况 | 穿越
F29-1 | 材料力
学参数 | 弱化带力学
参数/倍数 | | 6.5 | C1 | 是 | 实际测试数据* | 0.3 | 7.0 | C10 | 是 | 实际测试数据 | 0.3 | | C2 | 是 | 0.9倍实际测试数据# | 0.3 | C11 | 是 | 0.9倍实际测试数据 | 0.3 | | C3 | 是 | 0.8倍实际测试数据 | 0.3 | C12 | 是 | 0.8倍实际测试数据 | 0.3 | | C4 | 是 | 1.1倍实际测试数据 | 0.3 | C13 | 是 | 1.1倍实际测试数据 | 0.3 | | C5 | 是 | 0.8倍实际测试数据 | 0.2 | C14 | 是 | 0.8倍实际测试数据 | 0.2 | | C6 | 是 | 实际测试数据 | 0.2 | C15 | 是 | 实际测试数据 | 0.2 | | C7 | 是 | 实际测试数据 | 0.5 | C16 | 是 | 实际测试数据 | 0.5 | | C8 | 否 | 实际测试数据 | 0.3 | C17 | 否 | 实际测试数据 | 0.3 | | C9 | 否 | 0.8倍实际测试数据 | 0.2 | C18 | 否 | 0.8倍实际测试数据 | 0.2 |
|
Model calculation conditions
|
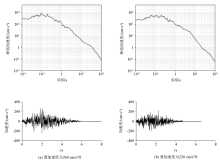
|
Time history and spectral characteristics of ground acceleration with 6.5 magnitude earthquake
|
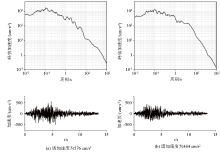
|
Time history and spectral characteristics of ground acceleration with 7.0 magnitude earthquake
|
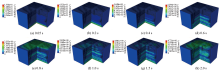
|
Acceleration distribution characteristics at different moments in the system
|
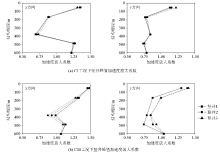
|
Acceleration amplification factor in rock mass under different working conditions
|
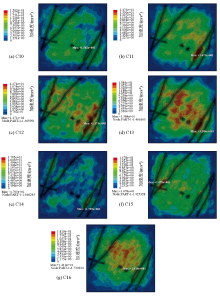
|
Acceleration distribution on the surface with 7.0 magnitude earthquake under different working conditions
|

| 震级 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | | 6.5 | 4.84 | 4.48 | 4.24 | 5.33 | 4.70 | 4.70 | 4.86 | 4.83 | 3.56 | | 震级 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 | C18 | | 7.0 | 11.40 | 11.39 | 9.58 | 10.90 | 8.89 | 10.30 | 12.42 | 11.38 | 8.93 |
|
Maximum acceleration response under different working conditions m·s-2
|
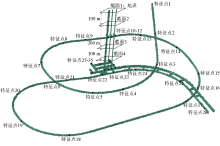
|
Feature points and corresponding node numbers selected in the analysis of the rock mass-underground structure system in the model area
|
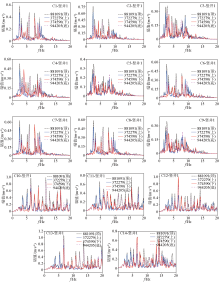
|
Spectrum characteristics of ground motion propagation under different working conditions from C1 to C14
|

| 方向 | 测点编号 | | 特征点1 | 特征点2 | 特征点3 | 特征点4 | 特征点5 | 特征点6 | 特征点7 | 特征点8 | 特征点13 | 特征点14 | | x | 1.58 | 1.25 | 0.64 | 0.51 | 0.96 | 0.93 | 1.16 | 0.95 | 0.74 | 0.85 | | y | 1.33 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.82 | 0.92 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 1.07 | 0.91 | | z | 2.23 | 1.62 | 1.29 | 1.02 | 1.04 | 0.95 | 1.05 | 1.39 | 1.27 | 1.19 | | 方向 | 测点编号 | | 特征点16 | 特征点17 | 特征点18 | 特征点19 | 特征点20 | 特征点22 | 特征点24 | 特征点25 | 特征点26 | | x | 0.45 | 0.48 | 0.86 | 0.63 | 0.87 | 1.18 | 1.19 | 1.05 | 0.50 | | y | 0.51 | 0.57 | 0.70 | 0.48 | 0.89 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 1.08 | 0.54 | | z | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.97 | 0.80 | 1.39 | 1.54 | 1.67 | 1.88 | 0.86 |
|
Working condition C8 down ramp amplification factor with 6.5 magnitude earthquake
|

| 方向 | 特征点 | | 特征点1 | 特征点2 | 特征点3 | 特征点4 | 特征点5 | 特征点6 | 特征点7 | 特征点8 | 特征点13 | 特征点14 | | x | 1.52 | 1.17 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 0.73 | 0.74 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.93 | | y | 1.94 | 1.07 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 1.22 | 1.48 | 1.46 | 1.37 | 1.20 | 1.21 | | z | 2.10 | 1.56 | 1.08 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 1.48 | 1.45 | 1.40 | 1.00 | | 方向 | 特征点 | | 特征点16 | 特征点17 | 特征点18 | 特征点19 | 特征点20 | 特征点22 | 特征点24 | 特征点25 | 特征点26 | | x | 0.51 | 0.58 | 0.93 | 0.68 | 1.18 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.98 | 0.61 | | y | 0.58 | 0.53 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 1.17 | 1.36 | 1.49 | 1.07 | 0.68 | | z | 0.74 | 0.77 | 1.07 | 0.69 | 1.14 | 1.40 | 1.37 | 1.48 | 0.63 |
|
Working condition C17 down ramp amplification factor with 7.0 magnitude earthquake
|
| [1] |
Kickmaier W, Mckinley I. A review of research carried out in European rock laboratories[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Design, 1997, 176(1/2):75-81.
|
| [2] |
Zhang C L, Wang J, Su R. Concepts and tests for disposal of radioactive waste in deep geological formations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(4):750e68.
|
| [3] |
王驹, 陈伟明, 苏锐, 等. 高放废物地质处置及其若干关键科学问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(4):801-802.
|
| [3] |
Wang J, Chen W M, Su R, et al. Geology disposal of high-level radioactive waste and its key scientific issues[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(4):801-812.
|
| [4] |
Wang J. High-level radioactive waste disposal in China:Update 2010[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2010, 2(1):1-11.
|
| [5] |
Uenishi K, Sakurai S. Characteristic of the vertical seismic waves associated with the 1995 Hyogo-ken Nanbu (Kobe),Japan earthquake estimated from the failure of the Daikai Underground Station[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Structural Dynamics, 2000, 29(6):813-822.
|
| [6] |
Tsinidis G, Silva F D, Snastasopoulo I, et al. Seismic behaviour of tunnels:From experiments to analysis[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 5:99.
|
| [7] |
张雨霆, 肖明, 李玉婕. 汶川地震对映秀湾水电站地下厂房的震害影响及动力响应分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(2):3663-3671.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Y T, Xiao M, Li Y J. Effect of earthquake on earthquake damage and dynamic response analysis of underground powerhouse of Yingxiuwan Hydropower Station[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(2):3663-3671.
|
| [8] |
杜修力, 蒋家卫, 许紫刚, 等. 浅埋矩形框架地铁车站结构抗震性能指标标定研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2019, 52(10):111-119,128.
|
| [8] |
Du X L, Jiang J W, Xu Z G, et al. Study on quantification of seismic performance index for rectangular frame subway station structure[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2019, 52 (10):111-119,128.
|
| [9] |
刘晶波, 王文晖, 赵冬冬, 等. 复杂断面地下结构地震反应分析的整体式反应位移法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2014, 47(1):134-142.
|
| [9] |
Liu J B, Wang W G, Zhao D D, et al. Integral response deformation method in seismic analysis of complex section underground structures[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2014, 47(1):134-142.
|
| [10] |
Yuan Y, Yu H T, Chen Z Y. Evaluation of seismic calculation methods for shallow-buried frame structures in soft soil[J]. Journal of Vibration & Shock, 2009, 28(8):50-56.
|
| [11] |
Zhang H Y, Zhao C, Chen S, et al. Seismic performance of underground subway station with sliding between column and longitudinal beam-Science Direct[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology, 2020, 102:103439.
|
| [12] |
何川, 耿萍. 强震活动断裂带铁路隧道建设面临的挑战与对策[J]. 中国铁路, 2020, 702(12):65-72.
|
| [12] |
He C, Geng P. Challenges and countermeasures of railway tunnel construction in macroseismic active fault zone[J]. China Railway, 2020, 702(12):65-72
|
| [13] |
崔臻, 盛谦, 冷先伦, 等. 地下洞室地震动力响应的岩体结构控制效应[J]. 岩土力学, 2018, 39(5):274-287.
|
| [13] |
Cui Z, Sheng Q, Leng X L, et al. Control effect of large geological discontinuity on seismic response and stability of underground rock caverns[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(5):274-287.
|
| [14] |
Hashash Y M A., Park D, Yao J I C. Ovaling deformations of circular tunnels under seismic loading,an update on seismic design and analysis of underground structures[J]. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol, 2005, 20 (5),435-441.
|
| [15] |
Coigliano M, Scandella L, Lai C G, et al. Seismic analysis of deep tunnels in near fault conditions:A case study in Southern Italy[J]. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering, 2011, 9(4):975-995.
|
| [16] |
Wang J, Chen L, Su R, et al. The Beishan underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China:Planning,site selection,site characterization and in situ tests[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 10(3):411-435.
|
| [17] |
Ungless R F. An infinite finite element[D]. Vancouver: University of British Columbia, 1973.
|
| [18] |
Bettess P. More on infinite element[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 2010, 15(11):1613-1626.
|
| [19] |
Beer G, Meek J L. Infinite domain element[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1981, 17(1):43-52.
|
| [20] |
陈继峰, 赵翠萍, 杨立明. 甘肃地区S波非弹性衰减Q值研究[J]. 地震, 2010, 30(1):125-130.
|
| [20] |
Chen J F, Zhao C P, Yan G L M. Q values of S wave inelastic attenuation in Gansu Region[J]. Earthquake, 2010, 30(1):125-130
|
| [21] |
陈继峰, 杨立明. 甘肃地区震源参数的相关性研究[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 2011, 32(1):10-14.
|
| [21] |
Chen J F, Yang L M. Study on source parameters and its similar relationship of earthquakes occurred in Gansu region[J]. Seismological and geomagnetic observation and research, 2011, 32(1):10-14
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Jia-Chang, LI Tao, LIANG Hong-Gang, FEI E, SUN Zhi-Yuan, YUE Tong. Strike-slip fault system in the Erbatai area, Tarim Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(6): 1588-1598. |
| [2] |
YAO Ming. A fault extraction technique based on structure-oriented filtering and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1313-1321. |
|
|
|
|

