|
|
|
| Definition, classification, and functions of underground research laboratories for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and the scientific research plan of Beishan underground research laboratory |
WANG Ju1,2( ), LUN Long1,2 ), LUN Long1,2 |
1. CAEA Innovation Center for Geological Disposal of High-Level Radioactive Waste, Beijing 100029, China
2. Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing 100029, China |
|
|
|
|
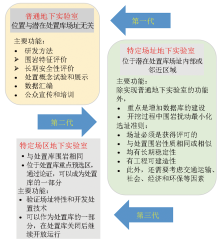
Abstract Underground research laboratories (URLs) for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste serve as critical facilities for verifying the safety and suitability of the sites of potential disposal repositories and for developing disposal technologies. URLs are irreplaceable in many aspects such as the siting and system design of potential disposal repositories, the development of the theories and technologies for disposal engineering, the safety and characteristic assessments, full-scale field tests, and on-site demonstration. This study highlights the definition, classification, and functions of URLs and categorizes existing primary URLs both in China and abroad. URLs are generally categorized into general URLs (first generation) and site-specific URLs (second generation). The construction of disposal repositories in China has progressed from national, regional, and site screening to site evaluation and to URL construction. The authors of this study proposed the concepts of "site-specific URLs" and "third-generation URLs" in 2010 and 2014, respectively. Furthermore, the Beishan URL-the world's first site-specific URL for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste-has been built. This study introduces the siting process, planning, positioning, and functions of the Beishan URL, as well as the functions of primary scientific experiments and main field experiments conducted during its construction. The results of this study serve as a guide for future siting and R&D of disposal repositories.
|
|
Received: 21 December 2023
Published: 08 January 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
13])
">
|
Overview of URL types and their characteristics
(modified from Blechschmidt,et al. [13])
|
|
General URLs (version 1.0) using existing mines or tunnels
|

| 序号 | 名称 | 国家与运行机构 | 运行时间 | 围岩与深度/m | 参考文献 | | 1 | Bukov Underground Research
Facility(URF) | 捷克,捷克放射性废物贮存管理
局(Radioactive Waste Repository
Authority,SúRAO) | 2013~至今 | 结晶岩/花岗岩,550~1200 | [14] | | 2 | Josef Regional Underground
Research Center (URC) | 捷克,捷克技术大学(Czech
Technical University) | 2007~至今 | 凝灰岩和花岗闪长岩, <200 | [16] | | 3 | Amelie | 法国,国家放射性废物管理机构
(French National Radioactive Waste
Management Agency,Andra) | 1979~1990 | 盐岩,>300 | [13] | | 4 | Fanay-Augeres underground
laboratory | 法国,辐射防护与核安全研究所
(Institute for Radiation Protection
and Nuclear Safety,IRSN) | 1980~1990 | 花岗岩 | [19] | | 5 | Tournemire Research Tunnel | 法国,辐射防护与核安全研究所
(Institute for Radiation Protection
and Nuclear Safety,IRSN) | 1989~至今 | 黏土岩,200~250 | [18] | | 6 | Asse II mine | 德国,联邦辐射防护局(Bunde-
samt für Strahlenschutz,BFS)/联
邦企业监事会(Bundes-Gesell-
schaft für Endlagerung mbH,
BGE) | 1965~1995 | 盐岩, 490~800 m水平巷道,
950 m的硐室 | [15,20] | | 7 | Tono | 日本,日本原子能机构(Japan
Atomic Energy Agency, JAEA) | 1986~2006 | 沉积岩,130 | [13] | | 8 | Kamaishi | 1988~1998 | 花岗岩 | [13] | | 9 | Stripa mine | 瑞典,瑞典核燃料和废料管理公
司(Swedish Nuclear Fuel and
Waste Management Company,
SKB) | 1976~1992 | 花岗岩,360~410 | [17] | | 10 | Climax Spent Fuel Test Facility,
Nevada | 美国,美国能源部(U.S.
Department of Energy, DOE) | 1978~1983 | 花岗岩,420 | [21] | | 11 | G-Tunnel, Nevada | 1979~1990 | 凝灰岩,300 | [22] | | 12 | Grimsel Test Site(GTS) | 瑞士,瑞士国家放射性废物处置
合作公司(National Cooperative
for the Disposal of Radioactive
Waste,Nagra) | 1984~至今 | 花岗岩,450 | [13] |
|
Overview of general URLs (version 1.0) introduction
|
|
New constructed general URLs (version 1.1)
|

| 序号 | 名称 | 国家与运行机构 | 运行时间 | 围岩与深度/m | 参考文献 | | 1 | Whiteshell Underground Research
Laboratory | 加拿大,加拿大原子能机构(Atomic
Energy of Canada,AECL) | 1963~1985 | 花岗岩, 240~420 | [23] | | 2 | High-Activity Disposal Experiment
Site URL, Mol (HADES) | 比利时,比利时国家放射性废物和浓缩
裂变材料机构(Belgian National Agency
for Radioactive Waste and Enriched
Fissile Material) | 1984~至今 | 黏土岩,225 | [24] | | 3 | Mizunami Underground Research
Laboratory (MIU) | 日本,日本原子能机构(Japan Atomic
Energy Agency, JAEA) | 2004~至今 | 花岗岩,500、1000 | [25] | | 4 | Horonobe Underground Research
Center | 2000~至今 | 沉积岩,1000 | [28] | | 5 | 北山坑探设施(Beishan
Exploration Tunnel, Bet) | 中国,核工业北京地质研究院(BRIUG,
CNNC) | 2015~至今 | 花岗岩,50 | [29] | | 6 | KAERI Underground Research
Tunnel (KURT) | 韩国,韩国原子能研究所(Korea Atomic
Energy Research Institute,KAERI) | 2006~至今 | 花岗岩,90 | [31] | | 7 | ?sp? Hard Rock Laboratory
(HRL) | 瑞典,瑞典放射性废物管理公司
(Svensk K?rnbr?nslehantering AB, SKB) | 1995~至今 | 花岗岩,200~460 | [26] | | 8 | Mont. Terri Rock Laboratory | 瑞士,瑞士国家放射性废物处置合作公
司(National Cooperative for the Disposal
of Radioactive Waste,Nagra) | 1995~至今 | 黏土岩,400 | [27] | | 9 | Busted Butte, Yucca Mountain,
Nevada | 美国,美国能源部( Department of
Energy,DOE) | 1987~2011 | 凝灰岩,420 | [30] |
|
Overview of new constructed generic URLs (version 1.1)
|
|
Schematic of major site-specific URLs abroad
|

| 序号 | 名称 | 国家与运行机构 | 运行时间 | 围岩与深度/m | 参考文献 | | 1 | ONKALO Underground Rock
Characterisation Facility | 芬兰,Posiva OY | 2003年至今 | 石英闪长岩,500 | [35] | | 2 | Meuse-Haute-Marne Research
Centre | 法国,法国国家放射性废物管理机构
(French national radioactive waste
management agency, ANDRA) | 2000年至今 | 页岩(黏土岩),450~
500 | [36] | | 3 | Gorleben Site | 德国,联邦辐射防护局(Bundesamt für
Strahlenschutz,BFS)/联邦企业监事会
(Bundes-Gesellschaft für Endlagerung
mbH, BGE) | 1985~1990年,
2010年 | 盐岩(盐丘),>900 | [33] | | 4 | Konrad | 1980年至今 | 灰岩,800~1300 | [34] | | 5 | Morsleben Repository (ERAM) | 1981~1998年 | 盐岩(盐丘),>525 | [37] | | 6 | Waste isolation pilot plant
(WIPP) | 美国,美国能源部( Department of
Energy,DOE) | 1982~1999年 | 盐岩(盐床),>655 | [32] | | 7 | Exploratory studies facility
(ESF),Yucca Mountain,Nevada | 1996~2010年 | 凝灰岩,300 | [38] |
|
Overview of Area-specific URLs
|

| 序号 | 名称 | 国家与运行机构 | 运行时间 | 围岩与深度/m | | 1 | 北山地下实验室(Beishan Underground
Research Laboratory, Beishan URL) | 中国,核工业北京地质研究院
(BRIUG, CNNC) | 在建 | 花岗岩,280和560m两个实验室水平 |
|
Overview of area-specific URLs
|
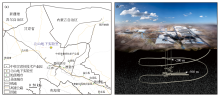
|
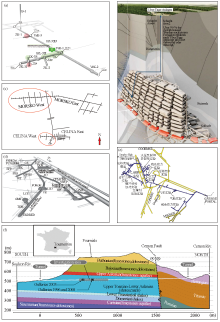
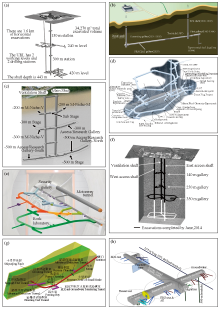
The Location(a) and design(b) of Beishan URL
|
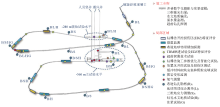
|
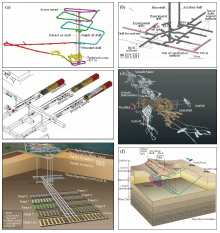
Schematic illustration of the planning of in-situ tests during URL construction
|

| 研究类别 | 研究项目 | 现场试验项目 | 地下实验室
场址特征评价 | 地下实验室场址深部地质环境研究 | 1.施工期全过程井巷地质编录
2.巷道钻探勘察与地球物理综合测井
3.巷道围岩地球物理精细探测
4.全场址三维微地震监测
5.跨断层与GNSS形变场监测 | | 地下实验室场址水文地质特性研究 | 6.巷道水文地质编录
7.巷道钻孔水文地质试验
8.钻孔与巷道水文地质监测
9.开挖过程结构面及其对渗透特性影响的精细识别
10.围岩非饱和过程及其水力学参数监测 | | 地下实验室深部围岩力学特性和长期稳定性研究 | 11.地应力测量
12.围岩变形监测 | | 地下实验室场址环境长期监测和影响研究 | 13.硐室施工过程中氡气防护及连续监测技术研究 | 深部岩体开挖
技术类 | 地下实验室深部岩体开挖关键技术研究 | 14.钻爆法施工参数优化及智能化施工现场试验
15.钻爆法EDZ评价
16.斜坡道TBM现场掘进及辅助智能化施工试验
17. -560 m开挖技术综合试验
18.超前探测技术试验
19.地下实验室注浆试验
20.斜坡道TBM施工微震监测
21.金属构件腐蚀监测
22.处置坑开挖试验及损伤区测试
23.围岩适宜性评价准则 | 现场试验关键
技术研发类 | 地下实验室深部岩体开挖关键技术研究 | 24.缓冲材料砌块安装和膨润土颗粒充填现场试验 |
|
Planning of in-situ tests during URL construction
|
| [1] |
Nuclear Energy Agency. The role of underground laboratories in nuclear waste disposal programmes[M]. New York: OECD Publications, 2001.
|
| [2] |
Nuclear Energy Agency. Underground research laboratories[M]. New York: OECD Publications, 2013.
|
| [3] |
International Atomic Energy Agency. The use of scientific and technical results from underground research laboratory investigations for the geological disposal of radioactive waste[R]. Vienna:IAEA, 2001.
|
| [4] |
Mayer S J, Van Marcke P, Jung H, et al. Important roles of underground research laboratories for the geological disposal of radioactive wastes:An international perspective[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 2023, 536(1):297-309.
|
| [5] |
Delay J, Bossart P, Ling L X, et al. Three decades of underground research laboratories:What have we learned?[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 2014, 400(1):7-32.
|
| [6] |
潘自强, 钱七虎. 高放废物地质处置战略研究[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2009.
|
| [6] |
Pan Z Q, Qian Q H. Study on geological disposal strategy of high-level radioactive waste[M]. Beijing: Atomic Press, 2009.
|
| [7] |
王驹, 苏锐, 陈亮, 等. 中国高放废物地质处置地下实验室场址筛选[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2022, 39(1):1-13.
|
| [7] |
Wang J, Su R, Chen L, et al. Site selection of underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2022, 39(1):1-13.
|
| [8] |
Wang J. On area-specific underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2014, 6(2):99-104.
|
| [9] |
王驹, 苏锐, 陈亮, 等. 甘肃北山高放废物地质处置地下实验室若干战略问题的考虑,世界核地质科学[J]. 2014, 31(S1):125-130.
|
| [9] |
Wang J, Su R, Chen L, et al. Considerations on several strategic problems on underground laboratory for high-level radioactive waste disposal in Beishan, Gansu Province[J]. World Nuclear Geology, 2014, 31(S1):125-130.
|
| [10] |
王驹, 苏锐, 陈亮, 等. 论我国高放废物地质处置地下实验室发展战略[J]. 中国核电, 2018, 11(1):109-115.
|
| [10] |
Wang J, Su R, Chen L, et al. The development strategy of the underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste in China[J]. China Nuclear Power, 2018, 11(1):109-115.
|
| [11] |
Wang J, Chen W, Su R, et al. Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and its key scientific issues[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(4):801-812.
|
| [12] |
Wang J. High-level radioactive waste disposal in China:Update 2010[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2010, 2(1):1-11.
|
| [13] |
Blechschmidt I, Vomvoris S. Relevance of underground rock laboratories for deep geological repository programs[G]// Geological repository systems for safe disposal of spent nuclear fuels and radioactive waste.Amsterdam:Elsevier, 2017:113-142.
|
| [14] |
Radioactive Waste Repository Authority,SÚRAO. Experimental programme 2015-2020[R]. 2020.
|
| [15] |
Horst G. Retrieving waste from the Asse salt mine-Facts and challenges[R/OL]. Institut Für Nukleare Entsorgung. Https://www.nwtrb.gov/docs/default-source/meetings/2018/march/geckeis.pdf?sfvrsn=6.

|
| [16] |
Pacovská D, Hausmannová L, Levorová M. The josef regional underground research centre (JOSEF URC)[J]. Rudarsko-Geolosko-Naftni Zbornik, 2012, 24(1).
|
| [17] |
Hans Carlsson. Update : The international stripa project A progress report from the test station in an old Swedish iron mine[J]. IAEA Bulletin, 2007, 3:25-28.
|
| [18] |
Matray J M, Savoye S, Cabrera J. Desaturation and structure relationships around drifts excavated in the well-compacted Tournemire's argillite(Aveyron,France)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2007, 90(1/2):1-16.
|
| [19] |
Barbreau A. Le laboratoire souterrain de fanay-augères[C]// Design and instrumentation of in situ experiments in underground laboratories for radioactive waste disposal.London:Routledge, 2022:128-141.
|
| [20] |
Bundesgesellschaftfúr Endlagerung. Schachtanlage Asse II[R/OL]. Bundesgesellschaftfúr Endlagerung. https://www.bge.de/de/asse.

|
| [21] |
Nevada test site. NTS PHOTO LAB Publication Date[R/OL]. Nevada test site. https://www.alamy.com/stock-photo/nevada-test-site-map.html?sortBy=relevant.

|
| [22] |
Connolly J R, Mansker W L, Hicks R, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of the grouse canyon member of the belted range tuff,rock-mechanics drift,U12g tunnel,Nevada test site[J]. Nuclear Fuels, 1983, 4:1-68.
|
| [23] |
Chandler N A. Twenty years of underground research at Canada's URL[R]. Atomic Energy of Canada Limited,Whiteshell Laboratories,Pinawa,Manitoba (CA), 2003.
|
| [24] |
Li X L, Neerdael B, Raymaekers D, et al. The construction of the HADES underground research laboratory and its role in the development of the Belgian concept of a deep geological repository[J]. Geological Society,London,Special Publications, 2023, 536(1):159-184.
|
| [25] |
Nakano K, Takeuchi S, Hama K. Mizunami underground research laboratory project results from 1996-1999 period[R]. Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Inst., 2001.
|
| [26] |
Svensk Kärnbränslehantering AB. Äspö hard rock laboratory annual report 2020[R]. 2021.
|
| [27] |
Bossart P, Bernier F, Birkholzer J, et al. Mont Terri rock laboratory,20 years of research:Introduction,site characteristics and overview of experiments[G]// Bossart P,Milnes A G.Swiss journal of geosciences supplement. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017:3-22.
|
| [28] |
The Horonobe Underground Research Center. Previous R&D tasks & main achievements[R/OL]. The Horonobe Underground Research Center. https://www.jaea.go.jp/english/04/horonobe/index.html.

|
| [29] |
Wang J, Chen L, Su R, et al. The Beishan underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China:Planning,site selection,site characterization and in situ tests[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 10(3):411-435.
|
| [30] |
Adams M. Yucca mountain-nevada's perspective[J]. Idaho L.Rev., 2009, 46:423.
|
| [31] |
Kim G Y, Lee J Y, Kim K. KAERI underground research tunnel (KURT)-Phase II activities for HLW disposal technology development in Korea—15253[C]// WM Symposia,Inc.,PO Box 27646,85285-7646 Tempe,AZ (United States), 2015.
|
| [32] |
Krieg R D. Reference stratigraphy and rock properties for the waste isolation pilot plant (WIPP) project[R]. Sandia National Labs.,Albuquerque,NM (USA), 1984.
|
| [33] |
Bracke G, Fischer-Appelt K, Baltes B. Preliminary safety analysis of the gorleben site:Overview-13298[C]// WM2013 Conference, 2013.
|
| [34] |
Kunze V. The Construction of the konrad repository-status and perspective-13034[C]// WM Symposia,1628 E.Southern Avenue,Suite 9-332,Tempe,AZ 85282 (United States), 2013.
|
| [35] |
Young R P, Nasseri M H B, Sehizadeh M. Mechanical and seismic anisotropy of rocks from the ONKALO underground rock characterization facility[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2020, 126:104190.
|
| [36] |
Delay J, Forbes P L, Roman J. The meuse/haute-marne underground research laboratory:Seven years of scientific investigations[J]. Clay minerals, 2007, 25(55):41.
|
| [37] |
Wolf K. The closure of the morsleben repository (ERAM)[R/OL]. Bundesgesellschaft für Endlagerung mbH (BGE). https://www.bge.de/en.

|
| [38] |
Birkholzer J T, Webb S W, Halecky N, et al. Evaluating the moisture conditions in the fractured rock at Yucca Mountain:The impact of natural convection processes in heated emplacement drifts[J]. Vadose Zone Journal, 2006, 5(4):1172-1193.
|
| [39] |
王驹, 苏锐, 陈伟明, 等. 论特定场区地下实验室[C]// 第三届废物地下处置学术研讨会, 2010.
|
| [39] |
Wang J, Su R, Chen W M, et al. Describe the area-site URLs[C]// The Third Symposium on Disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste Disposal, 2010.
|
| [40] |
王驹, 陈亮, 苏锐, 等. 中国高放废物地质处置北山地下实验室重大进展[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2023, 40(S1):473-490.
|
| [40] |
Wang J, Chen L, Su R, et al. Beishan underground research laboratory for geological disposal of high level radioactive waste in China-update 2023[J]. World Nuclear Geology, 2023, 40(S1):473-490.
|
| [1] |
YUN Long, CHEN Su, FU Lei, ZHUANG Hai-Yang, WANG Ju. Seismic response characteristics of the cavern group of the Beishan underground research laboratory for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(6): 1519-1529. |
| [2] |
JI Zi-Jian, Zhou Zhi-Chao, Zhao Jing-Bo, JI Rui-Li, ZHANG Ming. A method for identifying anomalous values of groundwater levels at candidate sites for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(6): 1530-1538. |
|
|
|
|

