|
|
|
| Research and application of the log-based comprehensive identification method for low-contrast oil layers:A case study of the Lufeng oilfield in the Pearl River Mouth Basin |
LIU Wei-Nan( ), GUAN Yao, LIU Dao-Li, SHI Lei, SONG Wei ), GUAN Yao, LIU Dao-Li, SHI Lei, SONG Wei |
| Shenzhen Branch,CNOOC Ltd.,Shenzhen 518054,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The accurate identification of fluid properties is critical for reservoir evaluation.However,for the Paleogene low-porosity and low-permeability reservoirs in the Lufeng area,Pearl River Mouth Basin,the low contrast between oil and water layers in conventional logs due to the presence of high-resistivity water layers complicates the identification of oil and water layers.This study first ascertained the reservoir characteristics and genetic analysis of low-contrast oil layers.Then,it developed the Flair gas logging response equation and the Flair logging response correction method,aiming to overcome the challenge that gas logging response values of low-porosity and low-permeability reservoirs are significantly influenced by factors such as drilling rate and porosity.Given the differences in the properties and components of various fluids,this study constructed new oil-bearing and water-content indices using Flair gas logging curves.Moreover,this study characterized the geochemical chromatogram using a gamma probability distribution function and extracted the shape and scale factors to describe the chromatogram characteristics.Based on sensitivity parameters,this study plotted the characteristic parameter-based fluid property identification chart.The practical application shows that the log-based comprehensive fluid property identification method can yield satisfactory effects,achieving a compliance rate of 91.3%.Therefore,this method can be popularized.
|
|
Received: 13 May 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
The regional geological map of Lufeng depression in the Pearl River Basin
|
|
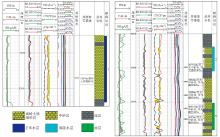
The logging well L1 response characteristics of low-contrast oil layer in Lufeng depression
|
|
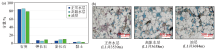
The comparison map of mineral content and pore characteristics of normal water,high resistivity water and oil in Paleogene of Lufeng
|

| 井名 | WC320 | WC330 | WC340 | WC430 | WC440 | WC510 | WC530 | WC540 | | L1 | 14000(1) | 14000(3) | 14000(1) | 14000(3) | 8500(2) | 8500(2) | 4400(2) | | | L2 | | | | | | | 5000(2) | 5000(2) | | L3 | | | | | 8000(2) | 8000(2) | | | | L4 | | | | | | | 6000(2) | |
|
The formation water salinity in different wells and layers in the study area mg·L-1
|
|
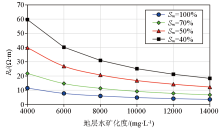
The simulation of resistivity with different salinity and saturation
|
|
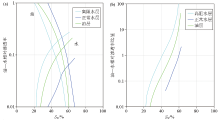
The relative permeability curve characteristics of normal water,high resistivity water and oil in Paleogene of Lufeng
|
|
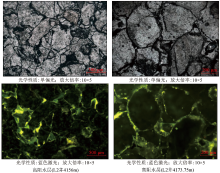
The fluorescence thin slice of high resistivity water layer in the study area
|
|
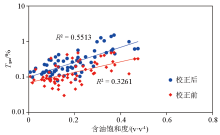
The relationship between gas response value and oil saturation after correction
|
|
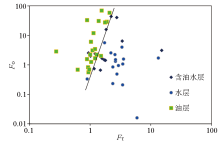
The crossplot of fluid index and oil-bearing index of different fluid types in Lufeng Paleogene
|
|
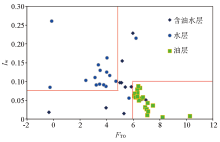
The identification chart of Paleogene reservoir fluid in Lufeng sag
|
|
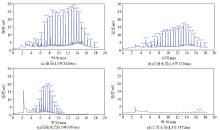
The geochemical chromatographic characteristics of different fluid types
|
|
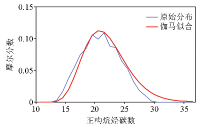
The fitting comparison between typical atlas morphology and gamma distribution
|
|
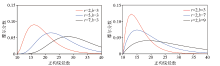
The gamma distribution simulation of different scale factors and shape factors
|
|
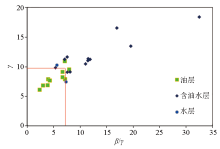
The fluid identification chart of geochemical chromatographic characteristic parameter in Lufeng depression
|

| 序号 | 井名 | 深度范围/m | 流体识别结果 | 取样结果 | 符合情况 | | Flair录井 | 地化色谱 | | 1 | L1 | 3278.8~3292.3 | 油层 | - | 地层水样 | 不符合 | | 2 | L1 | 3433~3443.7 | 含油水层 | - | 含油20%,其余为地层水 | 符合 | | 3 | L1 | 3657.3~3661.1 | 水层 | - | 取样微含油 | 符合 | | 4 | L1 | 3673.5~3680.7 | 水层 | - | 地层水样 | 符合 | | 5 | L1 | 3690.3~3698.1 | 油层 | - | 含油32%,其余为泥浆滤液 | 符合 | | 6 | L2 | 4095.6~4101.2 | 油层 | - | 油样 | 符合 | | 7 | L2 | 4145.2~4159.3 | 水层 | - | 地层水样 | 符合 | | 8 | L3 | 4165~4169 | 油层 | - | 油样 | 符合 | | 9 | L5 | 3298.7~3315.5 | 含油水层 | 含油水层 | 含油10%,其余为地层水 | 符合/符合 | | 10 | L5 | 3570.2~3598.5 | 水层 | 水层 | 地层水与泥浆滤液混合样 | 符合/符合 | | 11 | L6 | 3548.5~3552.1 | 水层 | 水层 | 地层水样 | 符合/符合 | | 12 | L7 | 4458.2~4559.2 | 油层 | 油层 | 生产油层 | 符合/符合 | | 13 | L7 | 4560.3~4565.4 | 含油水层 | 油层 | 生产油层 | 不符合/符合 | | 14 | L7 | 4166~4176.7 | 水层 | 水层 | 地层水样 | 符合/符合 | | 15 | L8 | 3946~3952.2 | 油层 | - | 测试油层 | 符合 | | 16 | L8 | 3954~3959 | 油层 | - | 测试油层 | 符合 | | 17 | L8 | 3960.5~3969.8 | 油层 | - | 测试油层 | 符合 | | 18 | L8 | 3970.5~3985.5 | 油层 | - | 测试油层 | 符合 | | 19 | L8 | 4004.2~4007 | 油层 | - | 测试油层 | 符合 | | 20 | L8 | 4008.5~4023.5 | 油层 | - | 测试油层 | 符合 | | 21 | L8 | 4041.4~4047 | 油层 | - | 测试油层 | 符合 | | 22 | L9 | 3551.6~3556.0 | 油层 | 油层 | 油样 | 符合/符合 | | 23 | L9 | 3562.1~3571.2 | 水层 | 水层 | 地层水样 | 符合/符合 |
|
The comparison of Paleogene fluid identification and sampling analysis in Lufeng sag
|
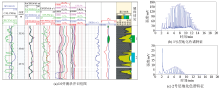
|
The fluid identification results comprehensive of logging well L9
|
| [1] |
代一丁, 牛子铖, 汪旭东, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰凹陷古近系与新近系油气富集规律的差异及其主控因素[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(S1):41-52.
|
| [1] |
Dai Y D, Niu Z C, Wang X D, et al. The difference of hydrocarbon enrichment law between Paleogene and Neogene in Lufeng Sag of Pearl River Mouth Basin and its main controlling factors[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(S1):41-52.
|
| [2] |
高楚桥, 杜坤, 王波, 等. 基于多图版识别可靠性分析的复杂流体性质识别方法[J]. 长江大学学报:自然科学版, 2023, 20(3):47-54.
|
| [2] |
Gao C Q, Du K, Wang B, et al. Recognition method of complex fluid properties based on multi-plate recognition reliability analysis[J]. Journal of Yangtze University:Natural Science Edition, 2023, 20(3):47-54.
|
| [3] |
吴应忠, 段毅, 赵阳, 等. 陇东地区长18低阻油层与高阻水层识别标准研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2017, 24(1):38-42.
|
| [3] |
Wu Y Z, Duan Y, Zhao Y, et al. Standards for discernment of low-resistivity oil zones and high-resistivity water zones in L18 Formation of the Longdong Area[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2017, 24(1):38-42.
|
| [4] |
赵阳, 段毅. 华庆地区长8段油层组高阻水层成因分析[J]. 油气藏评价与开发, 2020, 10(1):118-122,128.
|
| [4] |
Zhao Y, Duan Y. Analysis on water layers with high resistivity of Chang-8 oil formation in Huaqing Area[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development, 2020, 10(1):118-122,128.
|
| [5] |
张志升, 王小军, 冯立勇, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地华庆地区延长组长8高阻水层成因分析与识别[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(2):244-252.
|
| [5] |
Zhang Z S, Wang X J, Feng L Y, et al. Genetic analysis and identification of Yanchang 8 high-resistivity water layer in Huaqing area,Ordos Basin[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(2):244-252.
|
| [6] |
黄志龙, 蒲秀刚, 梁春秀, 等. 松辽盆地南部低阻储层特征及其形成机理[J]. 天然气工业, 2006, 26(8):27-29,159.
|
| [6] |
Huang Z L, Pu X G, Liang C X, et al. Characteristics and formation mechanism of low-resistivity reservoirs in the southern Songliao Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2006, 26(8):27-29,159.
|
| [7] |
叶新民, 付强, 顾俊. 松辽盆地南部腰英台油田低阻油层的成因及识别[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2006, 25(3):245-249.
|
| [7] |
Ye X M, Fu Q, Gu J. Origin and recognition of the low electric-resistance oil layer in the yaoyingtai oil field,southern Songliao Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2006, 25(3):245-249.
|
| [8] |
肖圣东. 松辽盆地葡萄花油层低阻特征及成因机理研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2020, 27(6):108-113.
|
| [8] |
Xiao S D. Study on low-resistivity characteristics and genetic mechanism of putaohua oil layers in Songliao Basin[J]. Special Oil & Gas Reservoirs, 2020, 27(6):108-113.
|
| [9] |
王淼, 李瑞娟, 熊镭, 等. 渤海C油田东营组高阻水层成因分析及识别方法研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(5):547-553.
|
| [9] |
Wang M, Li R J, Xiong L, et al. Genetic analysis and identification method for high resistivity water layer in the Dongying formation of Bohai C oilfield[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(5):547-553.
|
| [10] |
刘娟霞, 刘朋波, 袁胜斌, 等. 渤海油田轻质油气藏气测流体评价方法[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2017, 33(11):54-59.
|
| [10] |
Liu J X, Liu P B, Yuan S B, et al. Fluid evaluation of light oil-gas accumulations with gas logging in Bohai oilfield[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2017, 33(11):54-59.
|
| [11] |
袁胜斌. FLAIR “重组分” 解释评价原则及其应用[J]. 录井工程, 2008, 19(4):46-49.
|
| [11] |
Yuan S B. Principle and its application for FLAIR “Heavy Component” interpretation and evaluation[J]. Mud Logging Engineering, 2008, 19(4):46-49.
|
| [12] |
胡云, 刘宝生, 汪芯, 等. 基于气测烃组分的储层流体相快速识别评价方法——以渤中19-6构造为例[J]. 石油钻采工艺, 2018, 40(S1):44-47.
|
| [12] |
Hu Y, Liu B S, Wang X, et al. Rapid identification and evaluation method of reservoir fluid phase based on gas detection of hydrocarbon components—Taking Bozhong 19-6 structure as an example[J]. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2018, 40(S1):44-47.
|
| [13] |
吴昊晟, 郭明宇, 刘坤, 等. 基于FLAIR技术识别储层流体[J]. 长江大学学报:自科版, 2018, 15(15):30-34,4-5.
|
| [13] |
Wu H S, Guo M Y, Liu K, et al. Fluid identification method based on the technology of FLAIR well logging[J]. Journal of Yangtze University:Natural Science Edition, 2018, 15(15):30-34,4-5.
|
| [14] |
毛平, 姚红舵, 余逸凡, 等. 地化录井解释评价技术研究[J]. 断块油气田, 2009, 16(2):55-57.
|
| [14] |
Mao P, Yao H D, Yu Y F, et al. Interpretation and evaluation techniques for geochemical logging[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2009, 16(2):55-57.
|
| [15] |
邵东波. 西峰油田地球化学录井应用研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2007.
|
| [15] |
Shao D B. Study on application of geochemical logging in Xifeng Oilfield[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum (Huadong), 2007.
|
| [16] |
熊亭, 毛敏, 关利军. 惠州凹陷古近系文昌组、恩平组录井解释方法研究[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(1):67-73.
|
| [16] |
Xiong T, Mao M, Guan L J. A discussion on well logging interpretation method:A case from Paleogene Wengchang and Enping formations in the Huizhou depression[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(1):67-73.
|
| [17] |
彭光荣, 庞雄奇, 徐帜, 等. 珠江口盆地陆丰南地区古近系全油气系统特征与油气藏有序分布[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(7):2494-2508.
|
| [17] |
Peng G R, Pang X Q, Xu Z, et al. Characteristics of Paleogene whole petroleum system and orderly distribution of oil and gas reservoirs in South Lufeng depression,Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(7):2494-2508.
|
| [18] |
秦刚, 张丽娟. 基于水系多样性影响下的砂岩储层流体识别技术探讨[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(14):21-26.
|
| [18] |
Qin G, Zhang L J. The discussion on fluid identification technologies in the sandstone reservoirs based on diversity of formation water salinity[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(14):21-26.
|
| [19] |
黄导武, 刘建新. 海上油气田油气水层自然电位特征及机理浅析[J]. 测井技术, 2006, 30(2):164-167,194.
|
| [19] |
Huang D W, Liu J X. Analysis of the offshore oil or gas reservoirs spontaneous potential characteristic and its orgins[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2006, 30(2):164-167,194.
|
| [20] |
雍世和, 张超谟. 测井数据处理与综合解释[M]. 东营: 石油大学出版社,1996.
|
| [20] |
Yong S H, Zhang C M. Logging data processing and comprehensive interpretation[M]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum Press,1996.
|
| [21] |
Wang Y J, Sun Y H, Yang S Y, et al. Saturation evaluation of microporous low resistivity carbonate oil pays in Rub Al Khali Basin in the Middle East[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2022, 49(1):94-106.
|
| [22] |
杨胜来, 魏俊之. 油层物理学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2004.
|
| [22] |
Yang S L, Wei J Z. Reservoir physics[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2004.
|
| [23] |
李琴. 相对渗透率法评定储集层岩石表面润湿性[J]. 石油实验地质, 1996, 18(4):454-458.
|
| [23] |
Li Q. A relative permeability method for assessing the moisteninc capacity of reservoir rock surface[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geological, 1996, 18(4):454-458.
|
| [24] |
邴磊. 流体录井气体解释在白云凹陷的研究和运用[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2015.
|
| [24] |
Bing L. Research and apply of FLAIR logging gas interpretation in Baiyun Depression[D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2015.
|
| [25] |
张国栋. 气测录井全量正演计算方法判别低孔低渗储层含气性[J]. 中国海上油气, 2017, 29(1):46-51.
|
| [25] |
Zhang G D. Gas bearing interpretation method for low porosity and low permeability reservoir with total gas forward calculation method of gas logging data[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2017, 29(1):46-51.
|
| [26] |
Zhu L Q, Zhang C, Zhang C M, et al. A new and reliable dual model- and data-driven TOC prediction concept:A TOC logging evaluation method using multiple overlapping methods integrated with semi-supervised deep learning[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020,188:106944.
|
| [27] |
Hirose H. Parameter estimation for the 3-parameter Gamma distribution using the continuation method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 1998, 47(2):188-196.
|
| [1] |
SU Ke-Jia, QIN Zhen, FENG Min, AI Han-Bing, WANG Gang, GUAN Hua-Ling, FU Yu. Application of PNN logging in residual oil evaluation: A case study of the Gaotaizi oil layer in mature oilfields[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(2): 393-402. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Jing, WANG Yong, ZHAO Hui-Yan, HENG De, HUANG Jun, ZHANG Xiao-Dan, WANG Wen-Wen, HE Yan-Bing. Prestack seismic inversion of fluid factors in fractured reservoirs based on the global adaptive MCMC algorithm[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 105-112. |
|
|
|
|

