|
|
|
| Petrogenesis and rubidium enrichment indication of the Fuling rock mass in southern Anhui Province |
ZHANG Jun1( ), TAO Nai1, QI Shang-Xing1, WANG Zhi-Qiang2, DA Hao-Xiang2 ), TAO Nai1, QI Shang-Xing1, WANG Zhi-Qiang2, DA Hao-Xiang2 |
1. Geological Exploration Technology Institute of Anhui Province, Hefei 230031, China
2. School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230002, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Fuling rock mass in southern Anhui Province, located in the eastern section of the Jiangnan uplift zone, is a complex granitic rock mass that has experienced multi-stage evolution. It primarily comprises two lithologies: Monzogranite and K-feldspar granite. By investigating the geological, petrographic, and petrogeochemical characteristics of the Fuling rock mass, this study delved into its evolutionary characteristics, genetic types, and tectonic environment, aiming to clarify its indication significance for rubidium enrichment. The results of this study are as follows: ① The geochemical characteristics of the Fuling rock mass demonstrate high SiO2, Na2O, K2O, and Al2O3 contents, high w(K2O)/w(Na2O) ratios, and aluminum saturation indices (A/CNK) ranging from 0.95~1.08 (average: 0.99), suggesting high-K calc-alkaline quasi-aluminous to peraluminous granites; ② In terms of trace elements, the Fuling rock mass possesses high Li, Rb, Nd, and Ta contents and significantly low Sr and Ba contents, which may be associated with the fractional crystallization of feldspar; ③ The w(Nb)/w(Ta) ratios ranging from 5.71~10.94 (average: 8.41) and Mg# values ranging from 0.02~0.31 (average: 0.13) indicate that the Fuling rock mass was primarily derived from the partial melting of lower crust rocks, suggesting A-type granites in a non-orogenic extensional environment; ④ The Rb content in the Fuling rock mass increases with the magmatic evolution degree. Compared to monzogranites, K-feldspar granites with a higher evolution degree display higher Rb content, implying that the Rb content in the Fuling rock mass is generally controlled by magmatic evolution. Overall, this study holds some reference significance for understanding the Yanshanian diagenesis and mineralization of southern Anhui Province.
|
|
Received: 19 June 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
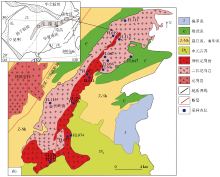
16] (a) and geological map[8](b) of Fuling pluton
">
|
Tectonic location[16] (a) and geological map[8](b) of Fuling pluton
|

|
Hand specimen and microscopic photo of Fuling pluton
a~d—monzonite granite; e~h—moyite. Qtz—quartz; Kfs—K-feldspar; Pl—plagioclase; Bt—biotite
|

| 样号 | FL67 | FL112 | FL66 | FL19 | FL47 | FL111 | FL61 | FL115 | FL70 | FL71 | FL72 | FL77 | FL12 | FL14 | FL54 | FL56 | FL74 | 花岗岩
岩性 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | | 主量元素/% | | SiO2 | 73.32 | 73.31 | 71.06 | 73.66 | 73.99 | 72.36 | 72.43 | 72.99 | 74.80 | 74.83 | 75.51 | 74.61 | 76.74 | 75.81 | 74.05 | 74.54 | 74.39 | | Al2O3 | 12.43 | 12.55 | 12.64 | 13.55 | 12.48 | 12.75 | 11.95 | 12.71 | 11.64 | 11.65 | 12.13 | 12.44 | 12.38 | 12.57 | 12.47 | 12.69 | 11.68 | | TFe2O3 | 1.79 | 1.55 | 2.05 | 2.04 | 1.36 | 1.72 | 1.64 | 1.76 | 1.11 | 1.10 | 1.05 | 0.97 | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 1.14 | | TFeO | 1.61 | 1.40 | 1.84 | 1.84 | 1.22 | 1.55 | 1.48 | 1.58 | 1.00 | 0.99 | 0.94 | 0.87 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.86 | 1.03 | | K2O | 5.10 | 5.27 | 5.06 | 5.48 | 5.19 | 5.19 | 5.00 | 5.62 | 4.59 | 4.60 | 4.29 | 4.89 | 4.45 | 4.39 | 4.62 | 4.61 | 4.64 | | Na2O | 3.40 | 3.32 | 3.10 | 3.18 | 3.69 | 3.36 | 3.22 | 3.29 | 3.59 | 3.61 | 3.99 | 3.85 | 3.99 | 4.12 | 4.09 | 3.93 | 3.63 | | CaO | 1.07 | 0.68 | 1.33 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.89 | 1.02 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.35 | 0.24 | 0.52 | 0.28 | 0.61 | | MgO | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.47 | 0.20 | 0.05 | 0.29 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.05 | | P2O5 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | | TiO2 | 0.18 | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.06 | | MnO | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 | | 烧失量 | 1.55 | 2.13 | 1.71 | 2.28 | 1.20 | 2.29 | 2.20 | 2.24 | 2.75 | 2.16 | 1.17 | 2.92 | 1.33 | 2.88 | 2.95 | 1.24 | 1.53 | | 总量 | 100.77 | 100.62 | 97.81 | 101.47 | 100.04 | 99.12 | 99.38 | 99.82 | 99.30 | 98.76 | 98.81 | 100.49 | 100.17 | 100.98 | 99.70 | 98.35 | 97.81 | | Mg# | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.08 | | A/NK | 1.12 | 1.12 | 1.20 | 1.21 | 1.07 | 1.14 | 1.12 | 1.11 | 1.07 | 1.07 | 1.08 | 1.07 | 1.09 | 1.09 | 1.06 | 1.11 | 1.06 | | A/CNK | 0.95 | 1.01 | 0.97 | 1.08 | 0.96 | 1.00 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.97 | 1.03 | 1.05 | 0.98 | 1.06 | 0.97 | | R1 | 2434 | 2429 | 2391 | 2439 | 2368 | 2365 | 2466 | 2330 | 2605 | 2597 | 2582 | 2434 | 2633 | 2538 | 2377 | 2467 | 2551 | | R2 | 370 | 330 | 414 | 359 | 325 | 360 | 353 | 336 | 299 | 299 | 298 | 317 | 282 | 273 | 301 | 279 | 297 | | 样号 | FL67 | FL112 | FL66 | FL19 | FL47 | FL111 | FL61 | FL115 | FL70 | FL71 | FL72 | FL77 | FL12 | FL14 | FL54 | FL56 | FL74 | 花岗岩
岩性 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 二长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | 钾长 | | 微量元素/10-6 | | Li | 57.70 | 27.00 | 47.20 | 33.10 | 33.00 | 50.90 | 46.30 | 49.70 | 109.00 | 19.90 | 31.80 | 79.40 | 93.20 | 91.00 | 202.00 | 149.00 | 20.50 | | Be | 2.80 | 4.22 | 2.87 | 1.73 | 1.63 | 3.14 | 3.54 | 3.27 | 4.80 | 5.01 | 6.54 | 3.06 | 2.68 | 1.59 | 1.56 | 0.94 | 11.40 | | Co | 1.93 | 1.89 | 3.18 | 5.54 | 7.21 | 1.84 | 1.98 | 1.81 | 0.63 | 0.46 | 0.59 | 0.55 | 6.00 | 6.16 | 1.90 | 2.35 | 0.76 | | Ni | 10.40 | 22.50 | 15.70 | 12.10 | 7.98 | 14.90 | 15.50 | 18.90 | 5.73 | 7.81 | 12.20 | 10.90 | 15.50 | 22.70 | 8.23 | 7.24 | 13.00 | | Rb | 220.00 | 255.00 | 243.00 | 209.00 | 268.00 | 230.00 | 208.00 | 228.00 | 386.00 | 348.00 | 421.00 | 340.00 | 416.00 | 571.00 | 708.00 | 605.00 | 427.00 | | Sr | 75.30 | 49.80 | 124.30 | 103.30 | 30.40 | 73.30 | 80.90 | 58.20 | 14.40 | 14.20 | 9.60 | 17.40 | 10.10 | 6.20 | 4.60 | 5.10 | 11.30 | | Zr | 158.90 | 138.10 | 192.30 | 228.90 | 153.20 | 143.40 | 151.20 | 147.70 | 101.10 | 101.40 | 119.30 | 90.10 | 80.10 | 113.20 | 50.70 | 113.30 | 95.30 | | Nb | 14.90 | 12.20 | 14.80 | 16.30 | 14.20 | 12.10 | 11.60 | 12.70 | 23.80 | 22.20 | 44.80 | 25.70 | 39.60 | 56.00 | 53.50 | 49.40 | 48.70 | | Sn | 4.68 | 5.15 | 6.49 | 3.17 | 3.56 | 4.95 | 3.93 | 3.32 | 8.78 | 5.95 | 12.00 | 5.37 | 3.98 | 3.17 | 2.36 | 1.63 | 4.67 | | Ba | 338.50 | 276.20 | 539.10 | 374.10 | 189.50 | 361.00 | 353.10 | 204.70 | 52.40 | 56.70 | 50.10 | 65.60 | 53.90 | 52.70 | 42.90 | 46.00 | 56.60 | | Ta | 2.30 | 1.94 | 1.55 | 1.49 | 1.46 | 1.37 | 1.32 | 1.17 | 3.12 | 2.59 | 4.86 | 2.84 | 6.93 | 8.28 | 5.21 | 7.46 | 6.30 | | W | 0.60 | 5.20 | 0.59 | 1.31 | 0.41 | 0.95 | 0.81 | 1.22 | 1.95 | 2.71 | 4.61 | 2.62 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 10.20 | 0.36 | 7.96 | | Th | 21.80 | 28.30 | 26.60 | 7.36 | 8.52 | 19.10 | 18.90 | 21.10 | 32.40 | 37.80 | 41.20 | 19.90 | 13.40 | 8.17 | 4.91 | 4.66 | 40.20 |
|
Analysis results of major elements, trace elements and characteristics of related parameters of Fuling pluton
|
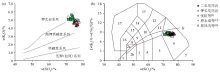
21]; Fig.b base image according to references [22].
">
|
w(SiO2)-w(K2O) diagram (a) and TAS classification diagram (b) of granite in Fuling pluton
Fig.b: 1—olivine-gabbro; 2a—alkaline gabbro; 2b—subalkaline gabbro; 3—gabbro-diorite; 4—diorite; 5—granodiorite; 6—granite; 7—quartzolite; 8—monzogabbro; 9—monzodiorite; 10—monzonite; 11—quartz-monzonite; 12—syenite; 13—subsyenite; 14—foid-monzosyenite; 15—foid-monzodiorite; 16—foid-gabbro; 17—foidolite; 18—aegironite/phosphonephelin/coarse leucoite. Fig.a base image according to references [21]; Fig.b base image according to references [22].
|
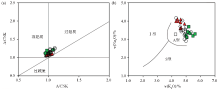
23]; Fig.b base image according to references [24]. The legend is the same as Fig.3
">
|
Diagram of A/CNK-A/NK (a) and w(K2O)-w(Na2O) (b) of Fuling pluton
Fig.a base image according to references [23]; Fig.b base image according to references [24]. The legend is the same as Fig.3
|
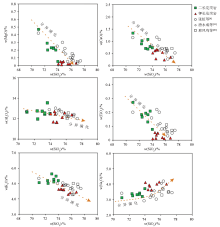
|
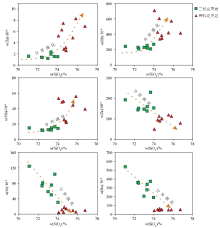
Harker diagram of major elements of Fuling pluton
|
|
Harker diagram of trace elements of Fuling pluton
|
39]; Fig.b and Fig.c base image according to references [23].
">
|
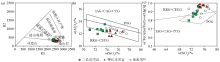
Tectonic environment discriminant diagram of Fuling pluton
RRG—granites associated with rift valley; CEUG—granitoids associated with continental uplift; POG—postorogenic granites; IAG—island arc granites; CAG—continental arc granites; CCG—continental collision granites. Fig.a base image according to references [39]; Fig.b and Fig.c base image according to references [23].
|
|
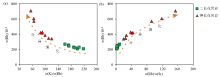
w(Rb)-w(K)/w(Rb) and w(Rb)-w(Rb)/w(Sr) covariation diagrams of different stages of Fuling pluton
|
50].
">
|
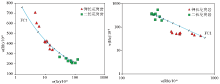
Simulation of trace elements in Fuling granite based on Rayleigh separation crystallization
Since Rb, Sr and Ba are mainly controlled by major minerals, the effect of accessory minerals is not considered in the separated phase here, and FC1 separates the mineral phase combination: 35% quartz + 40% plagioclase + 15% K-feldspar + 5% biotite; The trend line of separation crystallization evolution is spaced by 10%. The distribution coefficients of Rb, Sr and Ba for each mineral are quoted from references [50].
|
| [1] |
蔡连友, 翁望飞, 韩顺道. 皖南南山钨钼多金属矿地质特征及控矿因素[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2011, 34(4):290-298.
|
| [1] |
Cai L Y, Weng W F, Han S D. Geologic characteristic and ore-control factors of the Nanshan W-Mo polymetallic ore deposit in South Anhui Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2011, 34(4):290-298.
|
| [2] |
施珂, 张达玉, 丁宁, 等. 皖南逍遥岩体的年代学、地球化学特征及其成因分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2017, 47(6):1746-1762.
|
| [2] |
Shi K, Zhang D Y, Ding N, et al. Geochronology,geochemistry and formation of Xiaoyao rock in southern Anhui Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2017, 47(6):1746-1762.
|
| [3] |
Song G X, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Mesozoic magmatism and metallogeny in the Chizhou area,middle-lower Yangtze valley,SE China:Constrained by petrochemistry,geochemistry and geochronology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014,91:137-153.
|
| [4] |
陈雪锋, 范裕, 庾江华, 等. 江南隆起带(安徽段)首次发现铷矿床及其意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2018, 37(6):1349-1354.
|
| [4] |
Chen X F, Fan Y, Yu J H, et al. The first discovery of rubidium deposit in Jiangnan uplift belt (Anhui section) and its significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2018, 37(6):1349-1354.
|
| [5] |
赵玉琛. 皖南两花岗岩体的岩石学特征及成矿专属性判别[J]. 安徽地质, 1994, 4(4):31-43.
|
| [5] |
Zhao Y C. Petrological characteristics and metallogenic specificity discrimination of two granite bodies in southern Anhui[J]. Geology of Anhui, 1994, 4(4):31-43.
|
| [6] |
周涛发, 袁峰, 侯明金, 等. 江南隆起带东段皖赣相邻区燕山期花岗岩类的成因及形成的地球动力学背景[J]. 矿物岩石, 2004, 24(3):65-71.
|
| [6] |
Zhou T F, Yuan F, Hou M J, et al. Genesis and geodynamic background of yanshanian granitoids in the eastern Jiangnan uplift in the adjecent area of Anhui and Jiangxi Provinces,China[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2004, 24(3):65-71.
|
| [7] |
Castro A, Moreno-Ventas I, De La Rosa J D. H-type (hybrid) granitoids:A proposed revision of the granite-type classification and nomenclature[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1991, 31(3/4):237-253.
|
| [8] |
张虹, 戴圣潜, 管运财, 等. 皖南绩溪伏岭岩体岩石地球化学特征[J]. 中国地质, 2005, 32(3):411-416.
|
| [8] |
Zhang H, Dai S Q, Guan Y C, et al. Petrology and geochemistry of the Fuling mass in Jixi,southern Anhui[J]. Chinese Geology, 2005, 32(3):411-416.
|
| [9] |
翁望飞, 支利庚, 蔡连友, 等. 皖南及邻区燕山期两个类型花岗岩地球化学对比与岩石成因[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2011, 30(4):433-448.
|
| [9] |
Weng W F, Zhi L G, Cai L Y, et al. Petrogenesis and geochemical comparison of two types of yanshanian granite in South Anhui and its surrounding area[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2011, 30(4):433-448.
|
| [10] |
周洁, 姜耀辉, 葛伟亚. 江南造山带东部旌德高Sr/Y花岗闪长岩的形成机制及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(1):53-62.
|
| [10] |
Zhou J, Jiang Y H, Ge W Y. High Sr/Y Jingde pluton in the eastern Jiangnan Orogen,South China:Formation mechanism and tectonic implications[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(1):53-62.
|
| [11] |
李鹏举, 余心起, 邱骏挺, 等. 皖南侏罗—白垩纪两类花岗岩的岩石成因、氧逸度特征及成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(2):399-418.
|
| [11] |
Li P J, Yu X Q, Qiu J T, et al. Petrogenesis,oxygen fugacity characteristics and mineralization significance of two kinds of Jurassic-Cretaceous granites in southern Anhui,SE China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(2):399-418.
|
| [12] |
闫峻, 后田结, 王爱国, 等. 皖南中生代早期成矿和晚期非成矿花岗岩成因对比[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2017, 47(11):1269-1291.
|
| [12] |
Yan J, Hou T J, Wang A G, et al. Petrogenetic contrastive studies on the Mesozoic early stage ore-bearing and late stage ore-barren granites from the southern Anhui Province[J]. Scientia Sinica:Terrae, 2017, 47(11):1269-1291.
|
| [13] |
唐永成, 曹静平, 支利庚, 等. 皖东南区域地质矿产评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2010.
|
| [13] |
Tang Y C, Cao J P, Zhi L G, et al. Evaluation of regional geology and mineral resources in southeast Anhui Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2010.
|
| [14] |
于津海, 魏震洋, 王丽娟, 等. 华夏地块:一个由古老物质组成的年轻陆块[J]. 高校地质学报, 2006, 12(4):440-447.
|
| [14] |
Yu J H, Wei Z Y, Wang L J, et al. Cathaysia block:A young continent composed of ancient materials[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2006, 12(4):440-447.
|
| [15] |
侯明金. 江南隆起带(安徽部分)燕山晚期岩浆活动与深部过程[D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2005.
|
| [15] |
Hou M J. The magmatic activities and its deepth process of the later yanshannian granitoids in the Jiangnan uplift in the area of Anhui Province[D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2005.
|
| [16] |
郑勇, 余心起, 王德恩, 等. 安徽绩溪伏岭岩体隆升时代的磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J]. 地质论评, 2009, 55(3):385-394.
|
| [16] |
Zheng Y, Yu X Q, Wang D E, et al. Exhumation history of the Fuling granite,southern Anhui:New insights from apatite fission track analysis[J]. Geological Review, 2009, 55(3):385-394.
|
| [17] |
沈渭洲, 凌洪飞, 李武显, 等. 中国东南部花岗岩类Nd-Sr同位素研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 1999, 5(1):22-32.
|
| [17] |
Shen W Z, Ling H F, Li W X, et al. Nd-Sr isotopes of granites in southeast China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 1999, 5(1):22-32.
|
| [18] |
陈芳, 王登红, 杜建国, 等. 安徽绩溪伏岭花岗岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄的精确测定及其地质意义[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013, 32(6):970-977.
|
| [18] |
Chen F, Wang D H, Du J G, et al. New dating of the Fuling granite body with LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb in Jixi,Anhui Province and their geological significance[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2013, 32(6):970-977.
|
| [19] |
白玉岭, 王宗起, 王涛, 等. 赣东北地区瑶里花岗岩年代学、地球化学及其岩石成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2015, 34(1):35-50.
|
| [19] |
Bai Y L, Wang Z Q, Wang T, et al. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age,geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Yaoli pluton in northeastern Jiangxi Province[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2015, 34(1):35-50.
|
| [20] |
邢凤鸣, 徐祥. 皖南中生代花岗岩类Nd、Sr、Pb同位素特点[J]. 安徽地质, 1993, 3(1):35-41.
|
| [20] |
Xing F M, Xu X. Nd,Sr,Pb isotopic geochemistry of the Mesozoic granitoids in south Anhui[J]. Geology of Anhui, 1993, 3(1):35-41.
|
| [21] |
Peccerillo A, Taylor S R. Geochemistry of eocene calc-alkaline volcanic rocks from the Kastamonu area,Northern Turkey[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1976, 58(1):63-81.
|
| [22] |
Middlemost E A K. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 1994, 37(3/4):215-224.
|
| [23] |
Maniar P D, Piccoli P M. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1989, 101(5):635-643.
|
| [24] |
Collins W J, Beams S D, White A J R, et al. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 1982, 80(2):189-200.
|
| [25] |
Rapp R P, Watson E B. Dehydration melting of metabasalt at 8-32 kbar:Implications for continental growth and crust-mantle recycling[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1995, 36(4):891-931.
|
| [26] |
Frey F A, Green D H, Roy S D. Integrated models of basalt petrogenesis:A study of quartz tholeiites to olivine melilitites from south eastern Australia utilizing geochemical and experimental petrological data[J]. Journal of Petrology, 1978, 19(3):463-513.
|
| [27] |
Green T H. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system[J]. Chemical Geology, 1995, 120(3-4):347-359.
|
| [28] |
Rudnick R L, Fountain D M. Nature and composition of the continental crust:A lower crustal perspective[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1995, 33(3):267-309.
|
| [29] |
Sun S S, McDonough W F. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts:Implications for mantle composition and processes[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publications, 1989, 42(1):313-345.
|
| [30] |
Yuan F, Zhou T F, Yue S C, et al. Rare earths of magmatic rocks in yanshanian stage in adjacent region of Anhui and Jiangxi Provinces,Jiangnan uplift[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2003, 21(5):591-594,500.
|
| [31] |
陈江峰, 周泰禧, 李学明, 等. 安徽南部燕山期中酸性侵入岩的源区锶、钕同位素制约[J]. 地球化学, 1993, 22(3):261-268.
|
| [31] |
Chen J F, Zhou T X, Li X M, et al. Sr and nd isotopic constraints on source regions of the intermediate and acid intrusions from southern Anhui Province[J]. Geochimica, 1993, 22(3):261-268.
|
| [32] |
邢凤鸣, 陈江峰, 徐祥, 等. 皖南浅变质岩和沉积岩的钕同位素特点及其大地构造意义[J]. 现代地质, 1991, 5(3):290-299.
|
| [32] |
Xing F M, Chen J F, Xu X, et al. Nd isotopic characteristics of low grade metamorphicand sedimentary rocks from southern Anhui provinceand their significance in tectonics[J]. Geoscience, 1991, 5(3):290-299.
|
| [33] |
黄定堂. 灵山岩体演化特征及其与稀有金属的成矿关系[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003, 39(4):35-40.
|
| [33] |
Huang D T. Evolving characteristics and related rare-metal metallogenesis of Lingshan rock body[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2003, 39(4):35-40.
|
| [34] |
Dostal J, Chatterjee A K. Contrasting behaviour of Nb/Ta and Zr/Hf ratios in a peraluminous granitic pluton (Nova Scotia,Canada)[J]. Chemical Geology, 2000, 163(1-4):207-218.
|
| [35] |
Weyer S, Münker C, Mezger K. Nb/Ta,Zr/Hf and REE in the depleted mantle:Implications for the differentiation history of the crust-mantle system[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2003, 205(3-4):309-324.
|
| [36] |
张舒, 张招崇, 艾羽, 等. 安徽黄山花岗岩岩石学、矿物学及地球化学研究[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(1):25-38.
|
| [36] |
Zhang S, Zhang Z C, Ai Y, et al. The petrology,mineralogy and geochemistry study of the Huangshan granite intrusion in Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(1):25-38.
|
| [37] |
朱光, 刘国生. 皖南江南陆内造山带的基本特征与中生代造山过程[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2000, 24(2):103-111.
|
| [37] |
Zhu G, Liu G S. Basic characteristics and Mesozoic orogenicprocess of the Jiangnan intracontinentalorogenic belt in southern Anhui[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2000, 24(2):103-111.
|
| [38] |
Zhou J, Jiang Y H, Xing G F, et al. Geochronology and petrogenesis of Cretaceous A-type granites from the NE Jiangnan Orogen,SE China[J]. International Geology Review, 2013, 55(11):1359-1383.
|
| [39] |
Batchelor R A, Bowden P. Petrogenetic interpretation of granitoid rock series using multicationic parameters[J]. Chemical Geology, 1985, 48(1-4):43-55.
|
| [40] |
Irber W. The lanthanide tetrad effect and its correlation with K/Rb,Eu/Eu,Sr/Eu,Y/Ho,and Zr/Hf of evolving peraluminous granite suites[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1999, 63(3/4):489-508.
|
| [41] |
穆尚涛, 邵拥军, 宋泽友, 等. 湖南仁里—传梓源伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床云母地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2021, 52(9):2973-2989.
|
| [41] |
Mu S T, Shao Y J, Song Z Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and indication of mica in Renli-Chuanziyuan pegmatite type rare metal deposit in Hunan Province[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2021, 52(9):2973-2989.
|
| [42] |
Taylor S R. The application of trace element data to problems in petrology[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, 1965,6:133-213.
|
| [43] |
Shaw D M. A review of K-Rb fractionation trends by covariance analysis[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1968, 32(6):573-601.
|
| [44] |
林德松. 钾、铷比值在研究某些岩石和矿床成因中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1978, 14(6):45-48.
|
| [44] |
Lin D S. Application of the ratio of potassium to rubidium in studying the genesis of some rocks and deposits[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1978, 14(6):45-48.
|
| [45] |
刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1984.
|
| [45] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M, Li Z L, et al. Elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1984.
|
| [46] |
Shearer C K, Papike J J, Laul J C. Chemistry of potassium feldspars from three zoned pegmatites,Black Hills,South Dakota:Implications concerning pegmatite evolution[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica, 1985, 49(3):663-673.
|
| [47] |
陆杰. 个旧花岗岩的微量元素和稀土元素地球化学演化特征[J]. 地球化学, 1987, 16(3):249-259.
|
| [47] |
Lu J. Geochemical evolution characteristics of trace elements and ree in Gejiu granites[J]. Geochimica, 1987, 16(3):249-259.
|
| [48] |
Ballouard C, Poujol M, Boulvais P, et al. Nb-Ta fractionation in peraluminous granites:A marker of the magmatic-hydrothermal transition[J]. Geology, 2016, 44(3):231-234.
|
| [49] |
王志强, 胡滑志帆, 陈斌, 等. 辽东半岛早白垩世三股流岩体岩石成因:微量元素模拟和Sr-Nd同位素的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(12):3683-3704.
|
| [49] |
Wang Z Q, Hu H, Chen B, et al. The petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous Sanguliu pluton in the Liaodong Peninsula,NE China:Constrained from the trace-element modelling and Sr-Nd isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(12):3683-3704.
|
| [50] |
Rollinson H R. Using geochemical data:Evaluation,presentation,interpretation[M]. England: Longman Scientific,1993.
|
| [51] |
张旗. 花岗质岩浆能够结晶分离和演化吗?[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2012, 31(2):252-260.
|
| [51] |
Zhang Q. Could granitic magmas experience fractionation and evolution?[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2012, 31(2):252-260.
|
| [52] |
Fiedrich A M, Bachmann O, Ulmer P, et al. Mineralogical,geochemical,and textural indicators of crystal accumulation in the Adamello Batholith (Northern Italy)[J]. American Mineralogist, 2017, 102(12):2467-2483.
|
| [53] |
Putirka K D, Canchola J, Rash J, et al. Pluton assembly and the genesis of granitic magmas:Insights from the GIC pluton in cross section,Sierra Nevada Batholith,California[J]. American Mineralogist, 2014, 99(7):1284-1303.
|
| [1] |
DU Wei-Yi, ZHANG Chong, HAN Hua-Yang, ZHAO Teng-Teng, ZHANG Wen-Yi. A numerical simulation study on array acoustic logging of fractured granite reservoirs in buried hills[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(2): 514-520. |
| [2] |
ZHOU Si-Chun, WANG Deng-Hong, LIU Xiao-Hui, WANG Ya-Dong, WEN Chun-Hua, HU Bo, WANG Guang-Xi. Technical methods for integrated geogas survey and their applications in the exploration of pegmatite-type rare metal deposits[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1627-1634. |
|
|
|
|

