|
|
|
| Prestack seismic inversion of fluid factors in fractured reservoirs based on the global adaptive MCMC algorithm |
ZHANG Jing1( ), WANG Yong1, ZHAO Hui-Yan1, HENG De1, HUANG Jun2, ZHANG Xiao-Dan2, WANG Wen-Wen2, HE Yan-Bing2 ), WANG Yong1, ZHAO Hui-Yan1, HENG De1, HUANG Jun2, ZHANG Xiao-Dan2, WANG Wen-Wen2, HE Yan-Bing2 |
1. Sichuan Changning Natural Gas Development Co.,Ltd.,Chengdu 610000,China
2. Chengdu Jiekesi Petroleum Natural Gas Technology Development Co.,Ltd.,Chengdu 610000,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Fractured reservoirs typically exhibit anisotropic characteristics,and their fractures show different seismic responses when filled with fluids.Accurate identification of fluids in fractured reservoirs plays a significant role in indicating the hydraulic fracturing process in the late hydrocarbon exploration and production stage.This study adopted the concepts of normal and tangential fracture quasi-weaknesses and constructed a new indicative factor for fluids in fractures.Combining the linear slip theory, this study derived the elastic stiffness matrix expression of the fracture-induced HTI medium.Based on the scattering theory and the Born approximation equation,this study derived the linearized P-wave incident anisotropic reflection coefficient equation for the weakly contrasted interface.Moreover,this study proposed an improved global adaptive MCMC algorithm by introducing the adaptation strategy into the MCMC algorithm.The results show that:(1)In the absence of noise,the model testing results were highly consistent with the log data,with a consistency degree of above 90%;(2)The inversion results of the actual data aligned closely with the log interpretation results,and hydrocarbons were discovered through drilling in the target interval.As indicated by the results of model testing and actual data application in a study area in Southwest China,the prestack seismic inversion of fluid factors in fractured reservoirs,yielding highly consistent results with log interpretation data,demonstrates certain reliability and applicability and thus can achieve accurate fluid identification and hydraulic fracturing indication.
|
|
Received: 06 December 2022
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|

| /GPa | /GPa | /(kg·m-3) | | | | 层1 | 58 | 18 | 2.6 | 0 | 0 | | 层2 | 78 | 23 | 2.5 | 1.15 | 1.07 |
|
Parameters of double-layer model
|
|
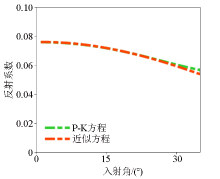
Reflection coefficient equation comparison
|
|
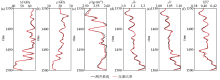
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d),tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e),and fluid indicator factor HFI(f) without noise
|
|
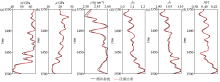
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d),tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e) and fluid indicator factor HFI(f) when the signal-to-noise ratio is 5∶1
|
|
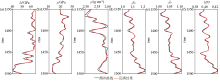
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d),tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e) and fluid indicator factor HFI(f) when the signal-to-noise ratio is 2∶1
|
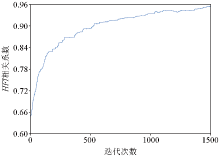
|
Convergence curve of fluid indicator factor HFI
|
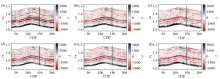
|
Azimuth seismic data
a—angle of incidence 6°,azimuth 45°;b—angle of incidence 18°,azimuth 45°;c—angle of incidence 30°,azimuth 45°;d—angle of incidence 6°,azimuth 135°;e—angle of incidence 18°,azimuth 135°;f—angle of incidence 30°,azimuth 135°
|
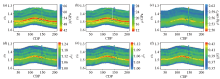
|
Inversion results of P-wave modulus(a),shear modulus(b),density(c),normal weakness of quasi-fracture(d), tangential weakness of quasi-fracture(e),and fluid indicator factor HFI(f)
|
| [1] |
Gassmann F. Elastic waves through a packing of spheres[J]. Geophysics, 2002, 16(4):673-685.

|
| [2] |
Russell B H, Hedlin K, Hilterman F J, et al. Fluid-property discrimination with AVO:A Biot-Gassmann perspective[J]. Geophysics, 2003, 68(1):29-39.

|
| [3] |
Russell B H, Gray D, Hampson D P. Linearized AVO and poroelasticity[J]. Geophysics, 2011, 76(3):C19-C29.

|
| [4] |
Yin X Y, Zhang S X. Bayesian inversion for effective pore-fluid bulk modulus based on fluid-matrix decoupled amplitude variation with offset approximation[J]. Geophysics, 2014, 79(5):R221-R232.

|
| [5] |
Schoenberg M, Douma J. Elastic wave propagation in media with parallel fractures and aligned cracks[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1988, 36(6):571-590.

|
| [6] |
Shaw R K, Sen M K. Born integral,stationary phase and linearized reflection coefficients in weak anisotropic media[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2004, 158(1):225-238.

|
| [7] |
van der Neut J, Shaw R K, Sen M K. Estimation of the fluid indicator from azimuthal AVO gradient variations at a fractured reservoir[C]// SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2007,Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2007.
|
| [8] |
陈怀震, 印兴耀, 张金强, 等. 基于方位各向异性弹性阻抗的裂缝岩石物理参数反演方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(10):3431-3441.
|
| [8] |
Chen H Z, Yin X Y, Zhang J Q, et al. Seismic inversion for fracture rock physics parameters using azimuthally anisotropic elastic impedance[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(10):3431-3441.
|
| [9] |
陈怀震, 印兴耀, 高成国, 等. 基于各向异性岩石物理的缝隙流体因子AVAZ反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(3):968-978.
|
| [9] |
Chen H Z, Yin X Y, Gao C G, et al. AVAZ inversion for fluid factor based on fracture anisotropic rock physics theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(3):968-978.
|
| [10] |
谢春辉, 雍学善, 杨午阳, 等. 裂缝型储层流体识别方法[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(5):1776-1784.
|
| [10] |
Xie C H, Yong X S, Yang W Y, et al. The method for identification of fluid in fractured reservoirs[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(5):1776-1784.
|
| [11] |
孙炜, 何治亮, 李玉凤, 等. 一种裂缝流体因子的提出及应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(7):2536-2545.
|
| [11] |
Sun W, He Z L, Li Y F, et al. A new factor of fluid-filled fractures and its application[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(7):2536-2545.
|
| [12] |
Pan X P, Zhang G Z, Chen H Z, et al. Elastic impedance parameterization and inversion for fluid modulus and dry fracture quasi-weaknesses in a gas-saturated reservoir[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 49:194-212.

|
| [13] |
印兴耀, 张洪学, 宗兆云. 五维地震油气识别方法[J]. 应用声学, 2020, 39(1):63-70.
|
| [13] |
Yin X Y, Zhang H X, Zong Z Y. Seismic fluid identification based on 5D seismic data[J]. Journal of Applied Acoustics, 2020, 39(1):63-70.
|
| [14] |
张丰麒, 刘俊州, 刘兰锋, 等. 确定性反演协同约束的叠后随机地震反演方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2021, 56(5):1137-1149,930-931.
|
| [14] |
Zhang F Q, Liu J Z, Liu L F, et al. The methodology of a post-stack stochastic seismic inversion with the co-constraint of deterministic inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2021, 56(5):1137-1149,930-931.
|
| [15] |
张广智, 赵晨, 涂奇催, 等. 基于量子退火Metropolis-Hastings算法的叠前随机反演[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(1):153-160,9.
|
| [15] |
Zhang G Z, Zhao C, Tu Q C, et al. Prestack stochastic inversion based on the quantum annealing Metropolis-Hastings algorithm[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53(1):153-160,9.
|
| [16] |
Buland A, Omre H. Bayesian linearized AVO inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2003, 68(1):185-198.

|
| [17] |
孙瑞莹, 印兴耀, 王保丽, 等. 基于Metropolis抽样的弹性阻抗随机反演[J]. 物探与化探, 2015, 39(1):203-210.
|
| [17] |
Sun R Y, Yin X Y, Wang B L, et al. Stochastic inversion of elastic impedance based on Metropolis sampling algorithm[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(1):203-210.
|
| [18] |
张繁昌, 肖张波, 印兴耀. 地震数据约束下的贝叶斯随机反演[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2014, 49(1):176-182,306.
|
| [18] |
Zhang F C, Xiao Z B, Yin X Y. Bayesian stochastic inversion constrained by seismic data[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2014, 49(1):176-182,306.
|
| [19] |
向坤, 陈科, 段心标, 等. 基于APSO-MCMC的叠前三参数同步随机反演方法研究[J]. 石油物探, 2022, 61(4):673-682.
|
| [19] |
Xiang K, Chen K, Duan X B, et al. Stochastically simultaneous inversion of prestack data using APSO-MCMC method[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2022, 61(4):673-682.
|
| [20] |
纪永祯, 张渝悦, 朱立华, 等. 多道随机稀疏反射系数反演[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(6):912-917.
|
| [20] |
Ji Y Z, Zhang Y Y, Zhu L H, et al. Multi-trace stochastic sparse-spike inversion for reflectivity[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(6):912-917.
|
| [21] |
Schoenberg M, Sayers C M. Seismic anisotropy of fractured rock[J]. Geophysics, 1995, 60(1):204-211.

|
| [22] |
Shaw R K, Sen M K. Use of AVOA data to estimate fluid indicator in a vertically fractured medium[J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(3):C15-C24.

|
| [23] |
Pšenčík I, Martins J L. Properties of weak contrast PP reflection/transmission coefficients for weakly anisotropic elastic media[J]. Studia Geophysica et Geodaetica, 2001, 45(2):176-199.

|
| [24] |
Ulrych T J, Sacchi M D, Woodbury A. A Bayes tour of inversion:A tutorial[J]. Geophysics, 2001, 66(1):55-69.

|
| [25] |
Alemie W, Sacchi M D. High-resolution three-term AVO inversion by means of a Trivariate Cauchy probability distribution[J]. Geophysics, 2011, 76(3):R43-R55.

|
| [26] |
Zong Z Y, Yin X Y, Wu G C. Elastic impedance parameterization and inversion with Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio[J]. Geophysics, 2013, 78(6):N35-N42.

|
| [1] |
LIU Hao-Jie, CHEN Yu-Mao, WANG Yan-Guang, ZONG Zhao-Yun, WU Guo-Chen, HOU Qing-Jie. Prestack four-parameter synchronous inversion method based on viscoelastic medium theory and its applications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 140-148. |
| [2] |
CHEN Zhi-Gang, MA Wen-Jie, ZHAO Hong-Zhong, XU Feng, CUI Quan-Zhang, MA Hui, SUN Xing. A technical workflow of fracture prediction with curvature-related attributes and its applications[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5): 1201-1207. |
|
|
|
|

