|
|
|
| Delineation of areas with high geological background values of heavy metals in soils in Yunnan Province, China based on geological big data technology |
XIAO Gao-Qiang1,2,3( ), ZHAO Juan4( ), ZHAO Juan4( ), CHEN Zi-Wan2,3,5, SONG Xu-Feng2,3,5, ZHU Neng-Gang5 ), CHEN Zi-Wan2,3,5, SONG Xu-Feng2,3,5, ZHU Neng-Gang5 |
1. Yunnan Geological Survey, Kunming 650051, China
2. MNR Key Laboratory of Sanjiang Metallogeny and Resources Exploration & Utilization, Kunming 650051, China
3. Key Laboratory of Sanjiang Metallogeny and Resources Exploration and Utilization, Kunming 650051, China
4. Yunan Ecological and Environmental Monitoring Center, Yunnan 650034, China
5. Yunnan Institute of Geological Survey, Kunming 650216, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to systematically investigate the distribution and over-limit elements of areas with high geological background values of heavy metals in soils in Yunnan Province. GIS spatial analysis was conducted based on the heavy metal content data from a province-wide 1∶200,000 stream sediment survey and the regional geological map. The analysis results were validated using the data of heavy metals in soils in Kunming, Yuxi, Zhaotong, and other regions. A total of 61 geological units were identified, with heavy metal content in soils exceeding the screening values of agricultural land, accounting for 21.09% of the total land area of Yunnan. The cultivated land in high geological background areas covers an area of approximately 2.844 1 million hectares, accounting for 7.22% of the total land area of Yunnan. The lithologies that cause over-limit heavy metals in soils primarily comprise carbonate rocks, mafic-ultramafic volcanic rocks, intermediate mafic intrusive rocks, coal-bearing clastic rocks, and clastic rocks with mafic components. The over-limit heavy metal elements in high geological background areas are dominated by Cu, Cr, Ni, and Cd. In contrast, As manifests an over-limit risk mainly in carbonate rock formations, Pb and Zn only exhibit an over-limit risk in individual strata, and Hg almost shows no over-limit risk.
|
|
Received: 21 March 2023
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
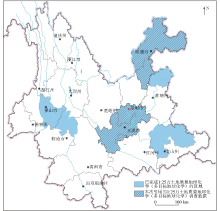
|
Map of 1∶250,000 geochemical survey of land quality in Yunnan Province
|
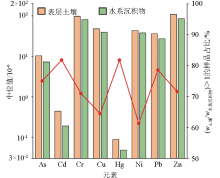
|
Comparison of heavy metals concentration in soil and stream sediments in Kunming-Yuxi and Zhaotong-Huize regions
|

| 序号 | 地层代码 | 地层名称 | 总点数/个 | 超标点
数比例/% | 地层面积/
km2 | 超标面
积比例/% | 主要岩性 | | 1 | SDq | 青山组 | 112 | 92.0 | 470 | 95.5 | 灰岩 | | 2 | Dd | 达莲塘组 | 283 | 85.2 | 1077 | 93.5 | 灰岩、硅质岩、页岩 | | 3 | Dlh | 莲花曲组 | 47 | 93.6 | 192 | 98.3 | 灰岩、页岩 | | 4 | Dg | 古木组 | 296 | 80.7 | 1189 | 89.5 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 5 | Dgg | 干沟组 | 26 | 96.2 | 97 | 98.6 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 6 | D2d | 东岗岭组 | 168 | 97.0 | 644 | 96.3 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 7 | D2q | 曲靖组 | 470 | 84.0 | 1863 | 86.9 | 灰岩、白云岩、页岩、硅质岩 | | 8 | Dl | 榴江组 | 69 | 92.8 | 343 | 99.5 | 灰岩、硅质岩 | | 9 | D2-3d-g | 东岗岭组、革当组并层 | 11 | 100.0 | 42 | 100.0 | 灰岩 | | 10 | D2-3q-zj | 曲靖组、一打得组、在结山组并层 | 14 | 85.7 | 60 | 100.0 | 白云岩、页岩、煤 | | 11 | D2-3y-zj | 一打得组、在结山组并层 | 46 | 97.8 | 191 | 100.0 | 灰岩 | | 12 | Dy | 一打得组 | 116 | 80.2 | 466 | 92.0 | 灰岩、页岩 | | 13 | D3g | 革当组 | 168 | 95.8 | 673 | 96.0 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 14 | D3zj | 在结山组 | 177 | 85.9 | 674 | 92.2 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 15 | D3-C1z-y | 海口组、宰格组、炎方组并层 | 13 | 92.3 | 46 | 98.8 | 白云岩、灰岩、页岩 | | 16 | DCy | 炎方组 | 53 | 94.3 | 207 | 96.3 | 白云岩、灰岩、页岩、煤 | | 17 | C1-2w-d | 万寿山组、大埔组并层 | 271 | 86.7 | 1029 | 94.8 | 灰岩、白云岩、页岩、煤 | | 18 | C1b | 坝达组 | 19 | 100.0 | 63 | 94.8 | 灰岩、硅质灰岩、硅质岩 | | 19 | C1pz | 平掌组 | 171 | 89.5 | 683 | 90.1 | 玄武岩、灰岩 | | 20 | C1-2h-m | 黄龙组、马平组并层 | 247 | 89.9 | 1035 | 97.8 | 灰岩 | | 21 | Ch | 黄龙组 | 798 | 96.1 | 3199 | 97.2 | 灰岩 | | 22 | Cw-m | 石炭系全系并层 | 134 | 82.8 | 575 | 90.0 | 灰岩 | | 23 | Cy | 鱼塘寨组 | 221 | 94.1 | 894 | 95.7 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 24 | C2m | 马平组 | 21 | 95.2 | 111 | 99.0 | 灰岩 | | 25 | Cj | 尖山营组 | 109 | 98.2 | 448 | 99.7 | 灰岩 | | 26 | C2s | 水长阱组 | 19 | 100.0 | 89 | 100.0 | 灰岩 | | 27 | C-Pt | 他披组 | 22 | 86.4 | 67 | 80.4 | 灰岩 | | 28 | C2d-w | 丁家寨组、卧牛寺组并层 | 266 | 82.3 | 1051 | 83.1 | 玄武岩、灰岩 | | 29 | Cx | 响姑组 | 62 | 85.5 | 245 | 94.0 | 灰岩、变基性火山岩 | | 30 | P1l-y | 梁山组、阳新组并层 | 2574 | 93.5 | 10251 | 95.8 | 灰岩、页岩、煤 | | 31 | P1y | 阳新组 | 809 | 95.2 | 3176 | 97.6 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 32 | P1d | 大名山组 | 199 | 93.5 | 786 | 97.3 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 33 | P1bm-s | 丙麻组、沙子坡组下部并层 | 60 | 88.3 | 228 | 83.3 | 灰岩、铁铝质页岩 | | 34 | Pe | 峨眉山玄武岩 | 4222 | 98.6 | 16983 | 99.1 | 玄武岩 | | 35 | P1-2e-l | 峨眉山玄武岩、龙潭组并层 | 23 | 95.7 | 100 | 87.4 | 玄武岩、页岩、煤 | | 36 | P2w | 吴家坪组 | 220 | 93.2 | 906 | 97.8 | 灰岩、铁铝质泥质岩 | | 37 | P2l | 龙潭组 | 160 | 98.8 | 647 | 99.5 | 页岩、硅质岩、煤 | | 38 | P2x | 宣威组 | 439 | 97.5 | 1694 | 99.2 | 页岩、砂岩、煤 | | 39 | P2h | 黑泥哨组 | 310 | 96.5 | 1195 | 98.6 | 灰岩、页岩、煤 | | 40 | Pg | 冈达概组 | 314 | 86.6 | 1276 | 90.7 | 玄武岩 | | 41 | T1l | 罗楼组 | 39 | 92.3 | 159 | 99.4 | 白云岩、灰岩 | | 42 | T1x | 洗马塘组 | 61 | 96.7 | 222 | 98.1 | 泥岩、页岩、粉砂岩 | | 43 | T1f | 飞仙关组 | 436 | 96.6 | 1831 | 97.4 | 泥岩、页岩、粉砂岩 | | 44 | Td | 东川组 | 151 | 94.7 | 574 | 99.7 | 泥岩、页岩、粉砂岩 | | 45 | T1q | 青天堡组 | 249 | 96.4 | 943 | 96.8 | 泥岩、页岩、粉砂岩 | | 46 | T1-2x-j | 洗马塘组、嘉陵江组并层 | 21 | 100.0 | 84 | 100.0 | 灰岩、白云岩、页岩、粉砂岩 | | 47 | T1-2f-j | 飞仙关组、嘉陵江组并层 | 636 | 89.2 | 2591 | 92.2 | 灰岩、白云岩、页岩、粉砂岩 | | 48 | T1-2d-j | 东川组、嘉陵江组并层 | 174 | 95.4 | 695 | 97.7 | 灰岩、白云岩、页岩、粉砂岩 | | 49 | Tj | 嘉陵江组 | 707 | 93.4 | 2808 | 97.9 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 50 | Tn | 尼汝组 | 300 | 81.7 | 1217 | 85.9 | 灰岩、砂岩、玄武岩 | | 51 | T2g | 个旧组 | 1503 | 92.5 | 5951 | 96.7 | 灰岩、白云岩 | | 52 | T2gl | 关岭组 | 1465 | 85.2 | 5843 | 93.1 | 灰岩、白云岩、页岩 | | 53 | T2b | 北衙组 | 832 | 87.5 | 3440 | 93.3 | 灰岩 | | 54 | T3nh | 牛喝塘组 | 120 | 85.0 | 448 | 96.8 | 玄武岩 | | 55 | νδ | | 13 | 92.3 | 64 | 95.3 | 辉长闪长岩 | | 56 | βμ | | 243 | 88.1 | 976 | 87.8 | 辉绿岩、辉长辉绿岩 | | 57 | N | | 8 | 87.5 | 30 | 96.4 | 基性岩 | | 58 | Σ-Ν | | 27 | 81.5 | 97 | 85.5 | 基性—超基性岩 | | 59 | σ | | 28 | 96.4 | 85 | 96.3 | 橄榄岩—橄辉岩 | | 60 | ψι | | 2 | 100.0 | 7 | 90.5 | 辉石岩 | | 61 | φω | | 14 | 100.0 | 47 | 82.5 | 蛇纹岩 |
|
Delineation results of high geological background areas of soil heavy metals in Yunnan Province
|
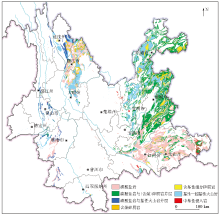
|
Distribution map of high geological background areas of soil heavy metals in Yunnan Province
|

| 地层代码 | 地层名称 | 总点数/个 | 超标点数
比例/% | | 地层代码 | 地层名称 | 总点数/个 | 超标点数
比例/% | | D2q | 曲靖组 | 142 | 88.0 | | Pe | 峨眉山玄武岩 | 1629 | 99.9 | | D2-3q-zj | 曲靖组、一打得组、在结山组并层 | 15 | 100.0 | | P1-2e-l | 峨眉山玄武岩、龙潭组并层 | 20 | 100.0 | | D2-3y-zj | 一打得组、在结山组并层 | 4 | 100.0 | | P2l | 龙潭组 | 91 | 100.0 | | Dy | 一打得组 | 54 | 98.1 | | P2x | 宣威组 | 209 | 100.0 | | D3zj | 在结山组 | 105 | 100.0 | | T1f | 飞仙关组 | 96 | 97.9 | | D3-C1z-y | 海口组、宰格组、炎方组并层 | 3 | 66.7 | | Td | 东川组 | 119 | 100.0 | | C1-2w-d | 万寿山组、大埔组并层 | 54 | 94.4 | | T1-2f-j | 飞仙关组、嘉陵江组并层 | 431 | 100.0 | | C1-2h-m | 黄龙组、马平组并层 | 38 | 100.0 | | T1-2d-j | 东川组、嘉陵江组并层 | 171 | 100.0 | | Ch | 黄龙组 | 34 | 82.4 | | Tj | 嘉陵江组 | 22 | 100.0 | | Cw-m | 石炭系全系并层 | 50 | 100.0 | | T2gl | 关岭组 | 264 | 96.2 | | C2m | 马平组 | 4 | 100.0 | | βμ | 辉绿岩、辉长辉绿岩 | 11 | 63.6 | | P1l-y | 梁山组、阳新组并层 | 1256 | 99.5 | | Σ-Ν、σ、φω | 基性—超基性岩 | 17 | 88.2 | | P1y | 阳新组 | 61 | 93.4 | | | 总计 | 4900 | 98.8 |
|
Risk assessment results of soil heavy metals in high geological background units in Kunming-Yuxi and Zhaotong-Huize regions
|

| 岩性组合 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 碳酸盐岩 | 33.0 | 0.48 | 156 | 62.1 | 0.126 | 77.1 | 39.6 | 134 | | 碳酸盐岩与(含煤)碎屑岩并层 | 16.9 | 0.37 | 159 | 72.7 | 0.078 | 66.1 | 31.2 | 121 | | 碳酸盐岩与基性火山岩并层 | 14.7 | 0.19 | 160 | 61.3 | 0.061 | 71.4 | 22.5 | 103 | | 含煤碎屑岩 | 6.10 | 0.20 | 210 | 128 | 0.038 | 75.5 | 20.7 | 122 | | 含基性组分碎屑岩 | 7.30 | 0.20 | 224 | 89.8 | 0.040 | 78.0 | 22.0 | 116 | | 基性—超基性火山岩 | 6.00 | 0.20 | 141 | 179 | 0.045 | 67.1 | 22.0 | 131 | | 中基性侵入岩 | 9.20 | 0.25 | 103 | 90.6 | 0.062 | 65.0 | 18.7 | 135 | | 超标风险评价值 | 40 | 0.30 | 150 | 50 | 1.80 | 70 | 90 | 200 |
|
Statistical results of median value of heavy metals in stream sediments in high geological background areas 10-6
|

| 岩性组合 | 样品数/个 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 碳酸盐岩 | 6664 | 40.19 | 64.33 | 53.24 | 68.01 | 0.48 | 59.11 | 8.55 | 24.94 | | 碳酸盐岩与(含煤)碎屑岩并层 | 6452 | 22.74 | 59.21 | 54.51 | 74.50 | 0.14 | 43.60 | 5.10 | 11.21 | | 碳酸盐岩与基性火山岩并层 | 799 | 12.64 | 24.16 | 54.69 | 66.08 | 0.50 | 51.81 | 3.25 | 3.00 | | 含煤碎屑岩 | 909 | 10.56 | 23.10 | 81.85 | 87.35 | 0.11 | 65.24 | 2.20 | 4.40 | | 含基性组分碎屑岩 | 897 | 5.57 | 24.41 | 76.81 | 96.43 | 0.00 | 66.33 | 1.23 | 2.23 | | 基性—超基性火山岩 | 4758 | 3.40 | 28.35 | 45.06 | 94.43 | 0.04 | 43.32 | 2.40 | 2.84 | | 中基性侵入岩 | 256 | 5.47 | 36.33 | 17.58 | 83.59 | 0.00 | 41.41 | 3.91 | 11.72 | | 总计 | 20735 | 22.03 | 49.05 | 53.65 | 78.29 | 0.23 | 50.74 | 5.21 | 12.70 |
|
Statistical results of the proportion of heavy metals exceeding the screening value in stream sediments in high geological background areas %
|

| 岩性组合 | 总面积/
万公顷 | 耕地面积/
万公顷 | 比例/
% | | 碳酸盐岩 | 267.18 | 87.44 | 32.73 | | 碳酸盐岩与(含煤)碎屑岩并层 | 259.43 | 102.55 | 39.53 | | 碳酸盐岩与基性火山岩并层 | 31.95 | 8.95 | 28.00 | | 含煤碎屑岩 | 35.37 | 12.48 | 35.30 | | 含基性组分碎屑岩 | 35.71 | 12.90 | 36.14 | | 基性—超基性火山岩 | 190.73 | 56.48 | 29.61 | | 中基性侵入岩 | 10.40 | 3.61 | 34.70 | | 合计 | 830.77 | 284.41 | 34.23 |
|
Statistical results of cultivated land areas in high geological background areas of soil heavy metals in Yunnan Province
|
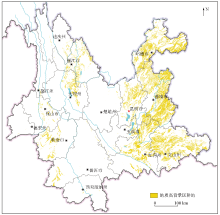
|
Distribution map of cultivated land in high geological background areas of soil heavy metals in Yunnan Province
|
| [1] |
Alloway B J. Heavy metals in soils:Trace metals and metalloids in soils and their bioavailability[M]. Netherlands:Springer, 2013.
|
| [2] |
Cai L M, Xu Z C, Bao P, et al. Multivariate and geostatistical analyses of the spatial distribution and source of arsenic and heavy metals in the agricultural soils in Shunde,Southeast China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 148:189-195.

|
| [3] |
Sardar A, Shahid M, Natasha, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s via Spinacia oleracea ingestion after sewage water irrigation practices in Vehari District[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2020, 27(32):39841-39851.
|
| [4] |
Chen H Y, Teng Y G, Lu S J, et al. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015,512-513:143-153.
|
| [5] |
Palma P, Lopez-Orozco R, Lourinha C, et al. Assessment of the environmental impact of an abandoned mine using an integrative approach:A case-study of the "Las Musas" mine (Extremadura,Spain)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 659:84-94.

|
| [6] |
Sun Z H, Xie X D, Wang P, et al. Heavy metal pollution caused by small-scale metal ore mining activities:A case study from a polymetallic mine in South China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 639:217-227.

|
| [7] |
Xie W S, Peng C, Wang H T, et al. Bioaccessibility and source identification of heavy metals in agricultural soils contaminated by mining activities[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(17):606.
|
| [8] |
Acosta J A, Martínez-Martínez S, Faz Á, et al. Accumulations of major and trace elements in particle size fractions of soils on eight different parent materials[J]. Geoderma, 2011, 161(1/2):30-42.

|
| [9] |
Hseu Z Y, Zehetner F, Fujii K, et al. Geochemical fractionation of chromium and nickel in serpentine soil profiles along a temperate to tropical climate gradient[J]. Geoderma, 2018, 327:97-106.

|
| [10] |
Wang H X, Li X M, Chen Y, et al. Geochemical behavior and potential health risk of heavy metals in basalt-derived agricultural soil and crops:A case study from Xuyi County,eastern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729:139058.

|
| [11] |
Wen Y B, Li W, Yang Z F, et al. Enrichment and source identification of Cd and other heavy metals in soils with high geochemical background in the karst region,Southwestern China[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 245:125620.

|
| [12] |
Wu W H, Qu S Y, Nel W, et al. The influence of natural weathering on the behavior of heavy metals in small basaltic watersheds:A comparative study from different regions in China[J]. Chemosphere, 2021, 262:127897.

|
| [13] |
Xia X Q, Ji J F, Yang Z F, et al. Cadmium risk in the soil-plant system caused by weathering of carbonate bedrock[J]. Chemosphere, 2020, 254:126799.

|
| [14] |
马宏宏, 彭敏, 刘飞, 等. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤—作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(1):449-459.
|
| [14] |
Ma H H, Peng M, Liu F, et al. Bioavailability,translocation,and accumulation characteristic of heavy metals in a soil-crop system from a typical carbonate rock area in Guangxi,China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(1):449-459.
|
| [15] |
唐豆豆, 袁旭音, 汪宜敏, 等. 地质高背景农田土壤中水稻对重金属的富集特征及风险预测[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(1):18-26.
|
| [15] |
Tang D D, Yuan X Y, Wang Y M, et al. Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological background[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(1):18-26.
|
| [16] |
夏学齐, 季峻峰, 杨忠芳, 等. 母岩类型对土壤和沉积物镉背景的控制:以贵州为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2022, 29(4):438-447.
|
| [16] |
Xia X Q, Ji J F, Yang Z F, et al. Parent rock type control on cadmium background in soil and sediment:An example from Guizhou Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2022, 29(4):438-447.
|
| [17] |
赵万伏, 宋垠先, 管冬兴, 等. 典型黑色岩系分布区土壤重金属污染与生物有效性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(7):1332-1341.
|
| [17] |
Zhao W F, Song Y X, Guan D X, et al. Pollution status and bioavailability of heavy metals in soils of a typical black shale area[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(7):1332-1341.
|
| [18] |
彭敏. 西南典型地质高背景区土壤—作物系统重金属迁移富集特征与控制因素[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
| [18] |
Peng M. Heavy metals in soil-crop system from typical high geological background areas,southwest China:Transfer characteristics and controlling factors[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2020.
|
| [19] |
谢学锦, 任天祥, 孙焕振. 中国地球化学图集[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2012.
|
| [19] |
Xie X J, Ren T X, Sun H Z. Geochemical atlas of China[M]. Beijing: The Geological Publishing House, 2012.
|
| [20] |
Tian H Y, Zhang C, Qi S H, et al. Concentration and spatial distribution of potentially toxic elements in surface soil of a peak-cluster depression,Babao Town,Yunnan Province,China[J]. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 2021, 18(6):3122.

|
| [21] |
Zhang L, Mckinley J M, Cooper M, et al. Transfer processes of potential toxic elements (PTE) between rock-soil systems and soil risk evaluation in the Baoshan area,Yunnan Province,Southwest China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2020, 121:104712.

|
| [22] |
Zhang L, Mckinley J M, Cooper M, et al. A regional soil and river sediment geochemical study in Baoshan area,Yunnan province,southwest China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 217:106557.

|
| [23] |
成杭新, 彭敏, 赵传冬, 等. 表生地球化学动力学与中国西南土壤中化学元素分布模式的驱动机制[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(6):159-191.
|
| [23] |
Cheng H X, Peng M, Zhao C D, et al. Epigenetic geochemical dynamics and driving mechanisms of distribution patterns of chemical elements in soil,southwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6):159-191.
|
| [24] |
周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 等. 云南省镇雄县土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [24] |
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang C W, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong County,Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [25] |
洪涛, 孔祥胜, 岳祥飞. 滇东南峰丛洼地土壤重金属含量、来源及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(10):4620-4627.
|
| [25] |
Hong T, Kong X S, Yue X F. Concentration characteristics,source analysis,and potential ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in a peak-cluster depression area,southeast of Yunnan Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(10):4620-4627.
|
| [26] |
李丽辉, 王宝禄. 云南省土壤As、Cd元素地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2008, 32(5):497-501.
|
| [26] |
Li L H, Wang B L. Geochemical characteristics of As and Cd in soils of Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 32(5):497-501.
|
| [27] |
范晨子, 袁继海, 刘成海, 等. 云南省安宁地区土壤重金属等元素生态地球化学调查与评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):761-771.
|
| [27] |
Fan C Z, Yuan J H, Liu C H, et al. Eco-geochemical survey and evaluation of heavy metals and other elements in soil in Anning City,Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):761-771.
|
| [28] |
唐瑞玲, 王惠艳, 吕许朋, 等. 西南重金属高背景区农田系统土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(5):917-927.
|
| [28] |
Tang R L, Wang H Y, Lyu X P, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland system from an area with high background of heavy metals,southwestern China[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(5):917-927.
|
| [29] |
王乔林, 宋云涛, 王成文, 等. 滇西地区土壤重金属来源解析及空间分布[J]. 中国环境科学, 2021, 41(8):3693-3703.
|
| [29] |
Wang Q L, Song Y T, Wang C W, et al. Source identification and spatial distribution of soil heavy metals in western Yunnan[J]. China Environmental Science, 2021, 41(8):3693-3703.
|
| [30] |
王宇, 彭淑惠, 杨双兰. 云南岩溶区As、Cd元素异常特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2012, 31(4):377-381.
|
| [30] |
Wang Y, Peng S H, Yang S L. The anomaly features of As and Cd in the Karst area in Yunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2012, 31(4):377-381.
|
| [31] |
肖高强, 陈杰, 白兵, 等. 云南典型地质高背景区土壤重金属含量特征及污染风险评价[J]. 地质与勘探, 2021, 57(5):1077-1086.
|
| [31] |
Xiao G Q, Chen J, Bai B, et al. Content characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in soil of typical high geological background areas,Yunnan Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2021, 57(5):1077-1086.
|
| [32] |
张富贵, 彭敏, 王惠艳, 等. 基于乡镇尺度的西南重金属高背景区土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(9):4197-4209.
|
| [32] |
Zhang F G, Peng M, Wang H Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals at township scale in the high background of heavy metals,Southwestern,China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(9):4197-4209.
|
| [33] |
谢学锦, 任天祥, 奚小环, 等. 中国区域化探全国扫面计划卅年[J]. 地球学报, 2009, 30(6):700-716.
|
| [33] |
Xie X J, Ren T X, Xi X H, et al. The implementation of the regional geochemistry-national reconnaissance program (RGNR) in China in the past thirty years[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2009, 30(6):700-716.
|
| [34] |
张春霖, 黄立勇冯沾明, 等. 用水系沉积物分析数据评价浙江土壤环境质量[J]. 物探与化探, 2005, 29(4):329-333.
|
| [34] |
Zhang C L, Huang L Y, Feng Z M, et al. The application of the stream sediments analytical date to the evaluation of soil environmental quality of Zhejiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2005, 29(4):329-333.
|
| [35] |
周余国, 高启芝, 刘继顺, 等. 个旧地区区域地球化学环境的系统评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(6):620-625.
|
| [35] |
Zhou Y G, Gao Q Z, Liu J S, et al. A systematical evaluation of the regional geochemical environment of Gejiu area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(6):620-625.
|
| [36] |
朱辉, 黄强, 马瑛, 等. 基于水系沉积物的土壤环境预测模型——以青海省东部地区为例[J]. 矿产勘查, 2021, 12(12):2440-2446.
|
| [36] |
Zhu H, Huang Q, Ma Y, et al. Soil environment prediction model based on stream sediment—A case study of eastern Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2021, 12(12):2440-2446.
|
| [37] |
中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社,1990.
|
| [37] |
China Environmental Testing Center. Chinese soil element background value[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press,1990.
|
| [38] |
刘东盛, 王学求, 聂兰仕, 等. 中国钴地球化学异常特征、成因及找矿远景区预测[J]. 地球科学, 2022, 47(8):2781-2794.
|
| [38] |
Liu D S, Wang X Q, Nie L S, et al. Cobalt geochemical anomalies characteristics and genesis in China and metallogenic prospecting areas prediction[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(8):2781-2794.
|
| [39] |
刘东盛, 王学求, 周建, 等. 中国钴地球化学基准值特征及影响因素[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(6):807-817.
|
| [39] |
Liu D S, Wang X Q, Zhou J, et al. Characteristics of China's cobalt geochemical baselines and their influence factors[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(6):807-817.
|
| [40] |
张衡, 李仁涛, 巴金, 等. 川西南美姑地区下三叠统飞仙关组地球化学特征及其对物源和构造环境的指示意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2019, 39(3):52-59.
|
| [40] |
Zhang H, Li R T, Ba J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the lower Triassic Feixianguan formation in Meigu area,southwestern Sichuan and its significance for the provenance and tectonic setting[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2019, 39(3):52-59.
|
| [41] |
张英利, 王宗起, 王刚, 等. 上扬子会泽地区早三叠世飞仙关组砂岩物源特征:来自重矿物铬尖晶石和碎屑锆石的限定[J]. 地质论评, 2016, 62(1):54-72.
|
| [41] |
Zhang Y L, Wang Z Q, Wang G, et al. Chromian spinel,zircon age constraints on the provenance of early Triassic Feixianguan formation sandstones from Huize Area,Upper Yangtze Region[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(1):54-72.
|
| [42] |
Yang Q, Yang Z F, Filippelli G M, et al. Distribution and secondary enrichment of heavy metal elements in karstic soils with high geochemical background in Guangxi,China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021,567.
|
| [43] |
刘炫志. 碳酸盐岩风化成土过程中重金属元素的富集行为及其环境风险评价——以贵州岩溶区为例[D]. 衡阳: 南华大学, 2019.
|
| [43] |
Liu X Z. Enrichment behavior of heavy metal elements and environmental risk assessment during weathering and soil formation of carbonate rocks—A case study of karst region in Guizhou Province[D]. Hengyang: University of South China, 2019.
|
| [44] |
王济, 王世杰. 土壤中重金属环境污染元素的来源及作物效应[J]. 贵州师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2005, 23(2):113-120.
|
| [44] |
Wang J, Wang S J. The sources and crops effect of heavy metal elements of contamination in soil[J]. Journal of Guizhou Normal University:Natural Science, 2005, 23(2):113-120.
|
| [45] |
邹若松. 浙西典型黑色岩系区重金属地表迁移规律及农田土壤风险评价[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.
|
| [45] |
Zou R S. Surface migration of heavy metals and risk assessment of farmland soil in typical black shale area of western Zhejiang Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2021.
|
| [46] |
Peng B, Rate A, Song Z L, et al. Geochemistry of major and trace elements and Pb-Sr isotopes of a weathering profile developed on the Lower Cambrian black shales in central Hunan,China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2014, 51:191-203.

|
| [47] |
周东晓, 彭渤, 王勤, 等. 扬子地台西缘下寒武统黑色页岩土壤元素地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(1):59-71.
|
| [47] |
Zhou D X, Peng B, Wang Q, et al. Elemental geochemical characteristics of soils derived from the lower Cambrian black shales in the western Yangtze Platform,China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39(1):59-71.
|
| [48] |
刘意章, 肖唐付, 熊燕, 等. 西南高镉地质背景区农田土壤与农作物的重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(6):2877-2884.
|
| [48] |
Liu Y Z, Xiao T F, Xiong Y, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from an area with a high geochemical background of cadmium,southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(6):2877-2884.

|
| [49] |
杨连升, 周明忠, 熊康宁, 等. 贵州黑色页岩土壤地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(5):1023-1037.
|
| [49] |
Yang L S, Zhou M Z, Xiong K N, et al. Geochemical characteristics of black-shale soils in Guizhou Province,China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39(5):1023-1037.
|
| [50] |
张迪, 周明忠, 熊康宁, 等. 贵州遵义下寒武统黑色页岩区土壤重金属污染和人体健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2021, 34(5):1247-1257.
|
| [50] |
Zhang D, Zhou M Z, Xiong K N, et al. Assessment of pollution and human health risk from heavy metals in soils and crops in the lower Cambrian black shale area,Zunyi,Guizhou Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 34(5):1247-1257.
|
|
|
|

