|
|
|
| Cumulative effects of atmospheric dust fall on major environmental elements in soils and their evaluation: A case study of Gaomi City, Shandong Province, China |
JIANG Bing1,2,3( ), ZHANG De-Ming1, LIU Yang1 ), ZHANG De-Ming1, LIU Yang1 |
1. Shandong Provincial No.4 Institute of Geological and Mineral Survey, Weifang 261021, China
2. Key Laboratory of Coastal Zone Geological Environment Protection of Shandong Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development Bureau, Weifang 261021, China
3. College of Earth Science and Engineering, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to investigate the pollution distribution of major environmental elements of atmospheric dust fall in Gaomi City, Shandong Province, as well as its effects on soils in a supergene environment. Hence, this study systematically collected and tested the atmospheric dust fall from Gaomi City, obtaining the testing data of nine environmental elements, including Cu, Pb, Zn, Ni, Cr, Cd, As, Hg, and Se. Furthermore, this study calculated the annual sediment fluxes and annual increments of these elements, simulated the minimum annual sediment fluxes for them to reach limit values, and evaluated their pollution levels. The results show that the average contents of various elements in atmospheric dust fall all exceeded their soil background values, exhibiting different degrees of enrichment. In terms of annual sediment fluxes, Cu was significantly positively correlated with Pb, while Zn, Ni, Cr, Cd, As, and Hg were mostly positively correlated in pairs, and Se showed a non-significant correlation with other elements. A higher correlation suggests a higher homology. Atmospheric dust fall, serving as an input end member of major environmental elements in soils, resulted in annual growth rates of various elements in topsoils ranging from 0.03%~0.52%. Cd would be the closest to its soil limit value over a few years. As revealed by geoaccumulation index-based evaluation, Ni, As, and Cr exhibited non-pollution to slight pollution, Se primarily manifested heavy pollution, Cd and Zn displayed moderate to heavy pollution, and Hg, Cu, and Pb mainly showed slight to moderate pollution, corresponding to a pollution order of Se>Cd>Zn>Hg>Cu>Pb>Ni>As>Cr.
|
|
Received: 24 March 2023
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sampling sites of the study area
|

| 元素 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异
系数 | 土壤背
景值[29] | | Cu | 296.2 | 30.7 | 67.4 | 59.4 | 0.88 | 17.7 | | Pb | 899.4 | 21.3 | 91.8 | 153.9 | 1.68 | 23.67 | | Zn | 746.5 | 157.2 | 374.5 | 188.3 | 0.50 | 45.29 | | Ni | 53.4 | 14.8 | 32.6 | 9.4 | 0.29 | 21.9 | | Cr | 153.5 | 19.3 | 64.7 | 38.5 | 0.60 | 59.62 | | Cd | 1.95 | 0.33 | 1.22 | 0.42 | 0.34 | 0.10 | | As | 20.30 | 2.58 | 10.33 | 3.44 | 0.33 | 8.75 | | Hg | 0.180 | 0.028 | 0.098 | 0.033 | 0.34 | 0.0266 | | Se | 5.41 | 0.08 | 3.22 | 1.22 | 0.38 | 0.17 |
|
Statistical parameters of main environmental elements in atmospheric dust fall 10-6
|

| 元素 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | | Cu | 26.66 | 2.04 | 5.67 | 4.77 | 0.84 | | Pb | 91.23 | 2.44 | 8.08 | 15.76 | 1.95 | | Zn | 100.05 | 10.49 | 33.85 | 21.11 | 0.62 | | Ni | 5.41 | 1.63 | 2.78 | 1.00 | 0.36 | | Cr | 14.98 | 1.86 | 5.67 | 3.55 | 0.63 | | Cd | 0.15 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.20 | | As | 3.20 | 0.30 | 0.91 | 0.54 | 0.59 | | Hg | 0.0174 | 0.0045 | 0.0084 | 0.0035 | 0.42 | | Se | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.08 | 0.30 |
|
Annual sedimentation flux of main environmental elements mg·(m2·a)-1
|

| 元素 | 主因子 | | F1 | F2 | F3 | | Ni | 0.919 | 0.072 | 0.168 | | As | 0.877 | 0.054 | -0.193 | | Zn | 0.760 | -0.019 | 0.139 | | Cd | 0.749 | -0.028 | 0.164 | | Cr | 0.705 | -0.012 | 0.285 | | Hg | 0.627 | 0.471 | 0.199 | | Pb | -0.097 | 0.956 | 0.157 | | Cu | 0.093 | 0.935 | -0.148 | | Se | 0.225 | 0.031 | 0.952 | | 特征根 | 3.709 | 2.021 | 1.187 | | 方差/% | 41.210 | 22.457 | 13.184 | | 贡献率/% | 41.210 | 63.667 | 76.851 |
|
Rotational load of main factor
|

| 元素 | Cu | Pb | Zn | Ni | Cr | Cd | As | Hg | Se | | Cu | 1 | | | | | | | | | | Pb | 0.840** | 1 | | | | | | | | | Zn | 0.087 | -0.063 | 1 | | | | | | | | Ni | 0.100 | 0.014 | 0.641** | 1 | | | | | | | Cr | 0.021 | -0.001 | 0.427* | 0.720** | 1 | | | | | | Cd | 0.108 | -0.103 | 0.629** | 0.652** | 0.387* | 1 | | | | | As | 0.114 | -0.053 | 0.528** | 0.724** | 0.548** | 0.531** | 1 | | | | Hg | 0.342 | 0.360 | 0.410* | 0.672** | 0.404* | 0.286 | 0.577** | 1 | | | Se | -0.079 | 0.160 | 0.300 | 0.328 | 0.356 | 0.333 | 0.078 | 0.340 | 1 |
|
Correlation analysis of annual sedimentation fluxes for main environmental elements
|
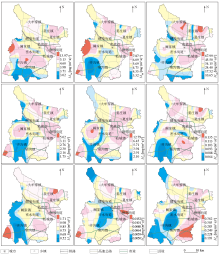
|
Spatial distribution of annual sedimentation fluxes for main environmental elements
|

| 元素 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异
系数 | 年均增长
速率/% | | Cu | 104.13 | 7.98 | 22.15 | 18.63 | 0.84 | 0.13 | | Pb | 356.39 | 9.52 | 31.55 | 61.56 | 1.95 | 0.13 | | Zn | 390.81 | 40.96 | 132.21 | 82.46 | 0.62 | 0.29 | | Ni | 21.15 | 6.38 | 10.87 | 3.90 | 0.36 | 0.05 | | Cr | 58.53 | 7.27 | 22.15 | 13.87 | 0.63 | 0.04 | | Cd | 0.57 | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.23 | 0.39 | | As | 12.52 | 1.15 | 3.57 | 2.09 | 0.59 | 0.04 | | Hg | 0.0678 | 0.0175 | 0.0329 | 0.0137 | 0.42 | 0.12 | | Se | 1.74 | 0.02 | 1.04 | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.61 |
|
Annual increment of main environmental elements in topsoil caused by atmospheric dust fall μg·(kg·a)-1
|

| 元素 |
土壤背景值 |
限定值 | 当前年沉
降通量 | 所需最小年沉
降通量(10年) | | 10-6 | 10-6 | mg·(m2·a)-1 | mg·(m2·a)-1 | | Cu | 17.7 | 50.0 | 5.67 | 827.0 | | Pb | 23.67 | 70.00 | 8.08 | 1186.00 | | Zn | 45.29 | 200.00 | 33.85 | 3961.00 | | Ni | 21.9 | 60.0 | 2.78 | 975.0 | | Cr | 59.62 | 150.00 | 5.67 | 2314.00 | | Cd | 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 5.10 | | As | 8.75 | 30.00 | 0.91 | 544.00 | | Hg | 0.0266 | 1.3000 | 0.0084 | 32.6000 | | Se | 0.17 | 3.00 | 0.266 | 72.40 |
|
Minimum annual sedimentation fluxes required to reach the limit value and its comparison with the current annual sedimentation fluxes
|
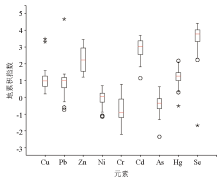
|
Box diagram of geoaccumulation index for main enviromental elements
|
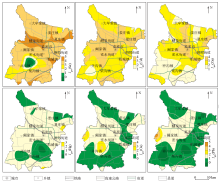
|
Spatial distribution of geoaccumulation index for main enviroment elements
|
| [1] |
庞绪贵, 王晓梅, 代杰瑞, 等. 济南市大气降尘地球化学特征及污染端元研究[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1):285-293.
|
| [1] |
Pang X G, Wang X M, Dai J R, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution sources identification of the atmospheric dust-fall in Jinan city[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(1):285-293.
|
| [2] |
Žibret G. Influences of coal mines,metallurgical plants,urbanization and lithology on the elemental composition of street dust[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2019, 41(3):1489-1505.
|
| [3] |
李晋昌, 董治宝. 大气降尘研究进展及展望[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2010, 24(2):102-109.
|
| [3] |
Li J C, Dong Z B. Research progress and prospect of dustfall research[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2010, 24(2):102-109.
|
| [4] |
姚瑶, 张丽, 施杨. 连云港市大气降尘时空分布特征[J]. 环境监控与预警, 2021, 13(1):56-60.
|
| [4] |
Yao Y, Zhang L, Shi Y. Temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of atmospheric dust fall in Lianyungang City[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Forewarning, 2021, 13(1):56-60.
|
| [5] |
陈莹, 赵剑强, 汤丹娜, 等. 西安市大气降尘重金属污染特征与生态风险[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(6):154-159.
|
| [5] |
Chen Y, Zhao J Q, Tang D N, et al. Heavy metal pollution characteristics and ecological risk of dust fall in Xi'an City[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(6):154-159.
|
| [6] |
Zhao H, Xia B, Fan C, et al. Human health risk from soil heavy metal contamination under different land uses near Dabaoshan Mine,Southern China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012,417-418:45-54.
|
| [7] |
任玉成, 阮丽, 李欣, 等. 基于粒度方法的大气降尘对浙江省新嵊盆地土壤的物源输入研究[J]. 土壤, 2021, 53(4):865-873.
|
| [7] |
Ren Y C, Ruan L, Li X, et al. Atmospheric dust input to soils in Xinsheng Basin,Zhejiang Province based on grain size analysis[J]. Soils, 2021, 53(4):865-873.
|
| [8] |
赵亚伟. 邯郸市大气干湿沉降特征及对水体影响研究[D]. 天津: 河北工程大学, 2019.
|
| [8] |
Zhao Y W. Study on characteristics of atmospheric dry and wet deposition and its influence on water body in Handan[D]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Engineering, 2019.
|
| [9] |
戴青云, 贺前锋, 刘代欢, 等. 大气沉降重金属污染特征及生态风险研究进展[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2018, 41(3):56-64.
|
| [9] |
Dai Q Y, He Q F, Liu D H, et al. Progress in research on heavy metals in atmospheric deposition:Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018, 41(3):56-64.
|
| [10] |
Chen B, Stein A F, Maldonado P G, et al. Size distribution and concentrations of heavy metals in atmospheric aerosols originating from industrial emissions as predicted by the HYSPLIT model[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013, 71(2):234-244.

|
| [11] |
王鸿钰, 俞炳琨, 李阳, 等. 降尘对乌鲁木齐市地产萝卜中Pb含量的影响[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2021, 35(10):128-134.
|
| [11] |
Wang H Y, Yu B K, Li Y, et al. Effect of dustfall on Pb content in radish produced in Urumqi[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2021, 35(10):128-134.
|
| [12] |
宋鹏程, 陆书玉, 魏永杰, 等. 上海市大气颗粒物生物毒性及二噁英呼吸暴露风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2018, 38(5):1961-1969.
|
| [12] |
Song P C, Lu S Y, Wei Y J, et al. Biotoxicity effects and respiratory risk assessment of PCDD/Fs exposured to atmospheric particulates in Shanghai[J]. China Environmental Science, 2018, 38(5):1961-1969.
|
| [13] |
Rachwał M, Wawer M, Jabłońska M, et al. Geochemical and mineralogical characteristics of airborne particulate matter in relation to human health risk[J]. Minerals, 2020, 10(10):866-866.

|
| [14] |
Salim Akhter M, Madany I M. Heavy metals in street and house dust in Bahrain[J]. Water,Air,and Soil Pollution, 1993, 66(1/2):111-119.

|
| [15] |
赵西强, 庞绪贵, 王增辉, 等. 利用原子荧光光谱—电感耦合等离子体质谱法研究济南市大气干湿沉降重金属含量及年沉降通量特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2015, 34(2):245-251.
|
| [15] |
Zhao X Q, Pang X G, Wang Z H, et al. Study on the characteristics of heavy metal contents and annual fluxes of atmospheric dry and wet deposition in Jinan City using AFS and ICP-MS[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2015, 34(2):245-251.
|
| [16] |
栾慧君, 塞古, 徐蕾, 等. 徐州北郊大气降尘重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11):4679-4687.
|
| [16] |
Luan H J, Mohamed-Conde S, Xu L, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition in northern suburban of Xuzhou[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11):4679-4687.
|
| [17] |
张夏, 刘斌, 肖柏林, 等. 重庆主城大气降尘中重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12):5288-5294.
|
| [17] |
Zhang X, Liu B, Xiao B L, et al. Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in core urban areas,Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12):5288-5294.
|
| [18] |
杨新明, 钟雅琪, 李国锋, 等. 典型工业城市大气降尘中重金属分布特征及其来源解析——以济南市为例[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(1):94-103.
|
| [18] |
Yang X M, Zhong Y Q, Li G F, et al. Distribution characteristic and source apportionment of heavy metals in atmospheric dust in a typical industrial city—A case study of Jinan[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(1):94-103.
|
| [19] |
Ma W C, Tai L Y, Qiao Z, et al. Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator:A case study in North China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018,631-632:348-357.
|
| [20] |
赵成义. 土壤硒的生物有效性研究[J]. 中国环境科学, 2004, 24(2):57-60.
|
| [20] |
Zhao C Y. Studies on the bioavailability of soil selenium[J]. China Environmental Science, 2004, 24(2):57-60.
|
| [21] |
周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [21] |
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [22] |
柴华, 何念鹏. 中国土壤容重特征及其对区域碳贮量估算的意义[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(13):3903-3910.
|
| [22] |
Chai H, He N P. Evaluation of soil bulk density in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems for determination of soil carbon storage on a regional scale[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(13):3903-3910.
|
| [23] |
Pan H Y, Lu X W, Lei K. A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi'an,China:Contamination,source apportionment and spatial distribution[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 609:1361-1369.

|
| [24] |
李萍, 薛粟尹, 王胜利, 等. 兰州市大气降尘重金属污染评价及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(3):1021-1028.
|
| [24] |
Li P, Xue S Y, Wang S L, et al. Pollution evaluation and health risk assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition in Lanzhou[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(3):1021-1028.
|
| [25] |
韦炳干, 虞江萍, 曹志强, 等. 唐山市设施菜地土壤重金属累积与有效态含量的影响特征[J]. 环境化学, 2021, 40(9):2649-2657.
|
| [25] |
Wei B G, Yu J P, Cao Z Q, et al. Factors impact on accumulation and availability of heavy metals in greenhouse vegetable soil from Tangshan City[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2021, 40(9):2649-2657.
|
| [26] |
范拴喜, 甘卓亭, 李美娟, 等. 土壤重金属污染评价方法进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(17):310-315.
|
| [26] |
Fan S X, Gan Z T, Li M J, et al. Progress of assessment methods of heavy metal pollution in soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(17):310-315.
|
| [27] |
师荣光, 蔡彦明, 郑向群, 等. 天津郊区农田降雨径流重金属的污染特征及来源分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2011, 25(5):213-217.
|
| [27] |
Shi R G, Cai Y M, Zheng X Q, et al. Contamination characteristics and source analyses on heavy metals in farmland runoff of the Tianjin suburban areas[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2011, 25(5):213-217.
|
| [28] |
管孝艳, 王少丽, 高占义, 等. 盐渍化灌区土壤盐分的时空变异特征及其与地下水埋深的关系[J]. 生态学报, 2012, 32(4):198-206.
|
| [28] |
Guan X Y, Wang S L, Gao Z Y, et al. Spatio-temporal variability of soil salinity and its relationship with the depth to groundwater in salinization irrigation district[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(4):198-206.

|
| [29] |
刘阳. 高密市土壤地球化学背景值研究[J]. 上海国土资源, 2019, 40(4):89-92.
|
| [29] |
Liu Y. Study on geochemical background value of soil in Gaomi city[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2019, 40(4):89-92.
|
| [30] |
姜冰, 王松涛, 孙增兵, 等. 基于不同参比值的土壤重金属潜在生态风险评价[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(7):2964-2971.
|
| [30] |
Jiang B, Wang S T, Sun Z B, et al. Potential ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals based on different reference ratios[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(7):2964-2971.
|
| [31] |
赵西强, 王增辉, 王存龙, 等. 济南市近地表大气降尘元素地球化学特征及污染评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(1):154-159.
|
| [31] |
Zhao X Q, Wang Z H, Wang C L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and pollution assessment of near-surface atmospheric dust in Jinan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(1):154-159.
|
| [32] |
孙厚云, 吴丁丁, 毛启贵, 等. 新疆东天山某铜矿区土壤重金属污染与生态风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2019, 38(12):2690-2699.
|
| [32] |
Sun H Y, Wu D D, Mao Q G, et al. Soil heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment in a copper mining area in East Tianshan,Xinjiang[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2019, 38(12):2690-2699.
|
| [33] |
闫晓露, 郑欢, 赵烜杭, 等. 辽东湾北部河口区土壤重金属污染源识别及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(8):3028-3039.
|
| [33] |
Yan X L, Zheng H, Zhao X H, et al. Source identification and health risk assessment of soil heavy metal in the estuary of Northern Liaodong Bay,China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(8):3028-3039.
|
| [34] |
刘杰, 高敏, 梁俊宁, 等. 陕西省某工业园区春季大气降尘重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2019, 32(7):1195-1203.
|
| [34] |
Liu J, Gao M, Liang J N, et al. Characteristics and assessment of heavy metal pollution in spring atmospheric dust of an industrial park in Shanxi Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2019, 32(7):1195-1203.
|
| [35] |
卢红玲, 肖光辉, 刘青山, 等. 土壤镉污染现状及其治理措施研究进展[J]. 南方农业学报, 2014, 45(11):1986-1993.
|
| [35] |
Lu H L, Xiao G H, Liu Q S, et al. Advances in soil Cd pollution and solution measures[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2014, 45(11):1986-1993.
|
| [36] |
陆平, 赵雪艳, 殷宝辉, 等. 临沂市PM2.5和PM10中元素分布特征及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(5):2036-2043.
|
| [36] |
Lu P, Zhao X Y, Yin B H, et al. Distribution characteristics and source apportionment of elements bonded with PM2.5 and PM10 in Linyi[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(5):2036-2043.

|
| [37] |
黄子茵, 管东生, 王刚. 海南岛社会经济发展对红树林表层土壤重金属污染的影响[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2020, 39(6):831-837.
|
| [37] |
Huang Z Y, Guan D S, Wang G. Heavy metal contents of mangrove surface soils affected by the social and economic development in Hainan Island[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2020, 39(6):831-837.
|
| [38] |
吕建树. 烟台海岸带土壤重金属定量源解析及空间预测[J]. 地理学报, 2021, 76(3):713-725.
|
| [38] |
Lyu J S. Source apportionment and spatial prediction of heavy metals in soils of Yantai coastal zone[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021, 76(3):713-725.
|
|
|
|

