|
|
|
| Stream sediment geochemistry and prospecting targets in Harper, Liberia |
BAI Yang1,2( ), CHEN Kai-Xu3( ), CHEN Kai-Xu3( ), CHEN Chong3, LI Fu-Lin3, ZHANG Ji-Chun3, WEI Ling-Xiao2, SI Ke-Fu2, ZHENG Xiong-Wei2, HU Yun-Fei2, WU Ying2, ZHANG Yuan-Pei2 ), CHEN Chong3, LI Fu-Lin3, ZHANG Ji-Chun3, WEI Ling-Xiao2, SI Ke-Fu2, ZHENG Xiong-Wei2, HU Yun-Fei2, WU Ying2, ZHANG Yuan-Pei2 |
1. Hubei Key Laboratory of Resources and Eeo-Environmental Geology,Wuhan 430056, China
2. Geophysical Exploration Brigade, Hubei Geological Bureau, Wuhan 430056, China
3. Wuhan Center, China Geological Survey (Central South China Innovation Center for Geosciences), Wuhan 430205, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Birimian rocks, the most significant Au ore-forming rocks in western Africa, are widespread in Harper, southeastern Liberia. As indicated by the geochemical parameters from the 1∶250 000 stream sediment survey of this region, elements Au and Hg exhibit high enrichment and high differentiation while element As manifests enrichment and high differentiation. These findings suggest considerable potential for Au prospecting. Based on the correlation analysis of elements, this study selected factors F1 (for the Au-Hg-Pb-Sn association) and F2 (for the As-Sb-W association) to effectively guide the exploration of gold deposits. Thirteen composite anomalies were delineated by extracting the anomaly information of Au, Hg, As, and Sb from the two principal factors, effectively reflecting the anomaly distributions of different gold deposits or ore occurrences. The geological and mineral surveys in anomaly areas reveal that areas HS1-HS3 and HS12-HS13 with composite anomalies characterized by directional distribution and high intensities show distinct Au mineralization information. Based on this, two major Au prospects, i.e., Seethum New and Behwan, have been identified for further detailed exploration.
|
|
Received: 20 March 2023
Published: 16 April 2024
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
CHEN Kai-Xu
E-mail: 493652968@qq.com;178372237@qq.com
|
|
|
|
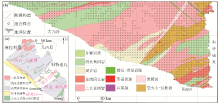
1](a) and distribution of sampling points (b) in the study area
">
|
Geotectonic location[1](a) and distribution of sampling points (b) in the study area
|

| 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | 元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限 | | Au | GFAAS | 3.00 | Cu | ICP-MS | 1.00 | Mo | ICP-MS | 0.15 | Co | ICP-MS | 0.40 | | Ag | ES | 0.01 | Pb | ICP-MS | 1.00 | Sn | ES | 0.70 | V | ICP-AES | 2.00 | | As | AFS | 0.30 | Zn | ICP-AES | 2.00 | Bi | ICP-MS | 0.02 | Ti | XRF | 10.00 | | Sb | AFS | 0.05 | F | ISE | 50.00 | Cr | ICP-AES | 3.00 | | | | | Hg | AFS | 5.00 | W | ICP-MS | 0.20 | Ni | ICP-MS | 1.00 | | | |
|
Elemental analysis methods and detection limit
|

| 元素 | 均值 | 中值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 标准差 | 全国水系沉积物均值 | 富集系数 | 变异系数 | | Au | 1.63 | 1.04 | 0.28 | 55.30 | 3.61 | 0.37 | 4.40 | 2.22 | | Ag | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.84 | 0.58 | | As | 0.83 | 0.50 | 0.28 | 27.00 | 1.40 | 0.54 | 1.54 | 1.68 | | Sb | 0.11 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 1.14 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 1.91 | 0.43 | | Hg | 36.00 | 24.10 | 2.40 | 1058.00 | 51.75 | 13.90 | 2.59 | 1.44 | | Cu | 4.80 | 3.57 | 0.85 | 51.80 | 4.17 | 2.54 | 1.89 | 0.87 | | Pb | 4.80 | 3.48 | 0.89 | 103.00 | 4.92 | 4.43 | 1.08 | 1.02 | | Zn | 14.30 | 12.35 | 3.51 | 88.30 | 8.78 | 10.90 | 1.31 | 0.61 | | W | 0.41 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 7.63 | 0.36 | 0.12 | 3.44 | 0.86 | | Sn | 1.20 | 1.10 | 0.65 | 27.50 | 0.82 | 1.10 | 1.10 | 0.67 | | Mo | 0.45 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 6.01 | 0.43 | 0.13 | 3.45 | 0.96 | | Bi | 0.06 | 0.04 | 0.01 | 1.18 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 6.24 | 1.25 | | F | 101.10 | 88.75 | 41.00 | 660.00 | 48.96 | 68.90 | 1.47 | 0.48 | | Cr | 32.80 | 23.45 | 1.98 | 393.00 | 32.77 | 9.70 | 3.38 | 1.00 | | Ni | 6.23 | 4.45 | 0.85 | 73.20 | 5.74 | 2.74 | 2.27 | 0.92 | | Co | 1.50 | 1.19 | 0.39 | 16.50 | 1.23 | 0.80 | 1.84 | 0.84 | | Ti | 1879.00 | 1447.00 | 95.80 | 13470.00 | 1622.23 | 687.00 | 2.73 | 0.86 | | V | 30.60 | 21.90 | 1.64 | 265.00 | 28.05 | 8.40 | 3.65 | 0.92 |
|
Statistical characteristics of elements geochemical values
|
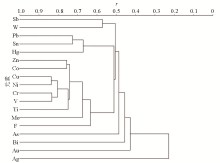
|
Pedigree diagram for R-type cluster analysis of all elements(range 0 to 1 standardize, centroid clustering cluster method, Pearson correlation interval)
|

| 因子 | 因子特征值及方差贡献率 | 元素 | 正交旋转载荷矩阵 | | 特征值 | 方差/% | 累积方差/% | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | | F1 | 7.69 | 42.72 | 42.72 | Au | -0.04 | 0.68 | 0.30 | -0.16 | | F2 | 1.94 | 10.78 | 53.50 | Ag | 0.04 | 0.10 | -0.03 | 0.72 | | F3 | 1.45 | 8.07 | 61.57 | As | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.81 | -0.15 | | F4 | 1.06 | 5.89 | 67.46 | Sb | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0.71 | -0.05 | | F5 | 0.95 | 5.26 | 72.72 | Hg | 0.28 | 0.78 | 0.07 | 0.08 | | F6 | 0.90 | 5.01 | 77.73 | Cu | 0.86 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.22 | | F7 | 0.68 | 3.78 | 81.50 | Pb | 0.38 | 0.77 | 0.04 | 0.26 | | F8 | 0.56 | 3.13 | 84.63 | Zn | 0.74 | 0.07 | 0.27 | 0.31 | | F9 | 0.45 | 2.52 | 87.15 | W | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.71 | 0.26 | | F10 | 0.41 | 2.29 | 89.43 | Sn | 0.15 | 0.85 | 0.02 | 0.10 | | F11 | 0.38 | 2.12 | 91.55 | Mo | 0.58 | 0.22 | 0.17 | -0.07 | | F12 | 0.34 | 1.87 | 93.42 | Bi | 0.24 | -0.004 | 0.43 | 0.49 | | F13 | 0.31 | 1.71 | 95.13 | F | 0.75 | 0.17 | -0.03 | -0.10 | | F14 | 0.22 | 1.24 | 96.37 | Cr | 0.79 | 0.10 | 0.27 | -0.07 | | F15 | 0.21 | 1.15 | 97.52 | Ni | 0.86 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.26 | | F16 | 0.16 | 0.91 | 98.43 | Co | 0.76 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.31 | | F17 | 0.15 | 0.86 | 99.29 | Ti | 0.69 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.29 | | F18 | 0.13 | 0.71 | 100.00 | V | 0.86 | 0.20 | 0.20 | -0.02 |
|
Characteristic parameters of factor analysis
|

| 分带 | w(Au)/
10-9 | w(As)/
10-6 | w(Sb)/
10-6 | w(Hg)/
10-9 | | 异常下限 | 2.70 | 1.50 | 0.17 | 70.00 | | 异常中带 | 5.40 | 3.00 | 0.34 | 140.00 | | 异常内带 | 10.80 | 6.00 | 0.68 | 280.00 |
|
Values for lower limit and concentration zoning of single element anomaly
|
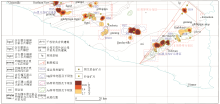
|
The distribution of Au-As-Sb-Hg composite anomaly and metallogenic prospecting area in the study area
|
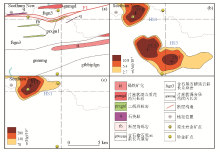
|
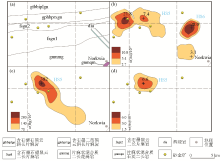
The profile maps of HS1-HS3 composite anomaly
a—geology map;b—Au anomaly;c—Hg anomaly
|

|
The geology and mineralization occurrence in anomaly area
|
|
The profile maps of HS5-HS6 composite anomaly
a—geology map, b—Au anomaly;c—Hg anomaly;d—As anomaly
|
|
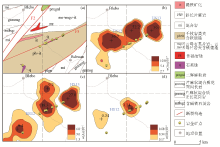
The profile maps of HS12-HS13 composite anomaly
a—geology map;b—Au anomaly;c—As anomaly;d—Sb anomaly
|
|
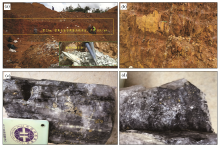
The geology and mineralization occurrence in HS12-HS13 anomaly area
|
| [1] |
陈冲, 陈开旭, 严永祥, 等. 利比里亚金矿成矿地质背景与资源潜力[J]. 地质通报, 2022, 41(1):72-84.
|
| [1] |
Chen C, Chen K X, Yan Y X, et al. Geological background and resource potential of gold mineralization in Liberia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(1):72-84.
|
| [2] |
张继纯, 严永祥, 王建雄, 等. 西非矿产资源的地质背景及重要成矿分区[J]. 华南地质与矿产, 2019, 35(1):76-89.
|
| [2] |
Zhang J C, Yan Y X, Wang J X, et al. Geological background and important metallogenic divisions of mineral resources in Western Africa[J]. Geology and Mineral Resources of South China, 2019, 35(1):76-89.
|
| [3] |
Xiao F, Chen J G, Agterberg F P, et al. Element behavior analysis and its implications for geochemical anomaly identification:A case study for porphyry Cu-Mo deposits in Eastern Tianshan,China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 145:1-11.

|
| [4] |
Grunsky E C. The interpretation of geochemical survey data[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration,Environment,Analysis, 2010, 10(1): 27-74.

|
| [5] |
赵娟, 王泰山, 李德彪, 等. 青海祁漫塔格地区1∶5万水系沉积物测量方法技术及应用成果[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(4):739-745.
|
| [5] |
Zhao J, Wang T S, Li D B, et al. The techniques and application achievements in 1∶50 000 stream sediment survey of the Qimantage area, Qinghai Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(4):739-745.
|
| [6] |
Thiéblemont D. Geological map of Africa-1∶10 million scale[R]. French Geological Survey, 2016.
|
| [7] |
徐云峰, 郝雪峰, 秦宇龙, 等. 四川岔河地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3):624- 638.
|
| [7] |
Xu Y F, Hao X F, Qin Y L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Chahe area of Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3):624-638.
|
| [8] |
袁和, 罗先熔, 李武毅, 等. 西藏邦卓玛地区土壤地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 2017, 53(3) :472-481.
|
| [8] |
Yuan H, Luo X R, Li W Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil and prospecting prediction of the Bangzhuoma Region, Tibet[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2017, 53(3) :472-481.
|
| [9] |
Xie X J, Liu D W. Geochemical blocks for predicting large ore deposit-concept and methodology[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 84(2):77-91.

|
| [10] |
陈开旭, 孟庆敏, 王超, 等. 援利比里亚矿产资源调查技术合作项目2019年度报告[R]. 中国地质调查局武汉地质调查中心, 2019.
|
| [10] |
Chen K X, Meng Q M, Wang C, et al. Report of PRC-Aided survey project of Liberia's Mineral Resources for the year of 2019[R]. Wuhan Center of China Geological Survey, 2019.
|
| [11] |
于俊博, 宋云涛, 郭志娟, 等. R型聚类分析在区域化探元素分组中的作用探讨[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2014, 36(6):771-776.
|
| [11] |
Yu J B, Song Y T, Guo Z J, et al. Discussion on the affection of the R-cluster analysis applied in grouping elements in regional geochemical exploration[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 36(6):771-776.
|
| [12] |
杨龙坤, 罗先熔, 文美兰, 等. 地电提取测量法在黑龙江金厂外围区寻找隐伏金矿的应用[J]. 桂林理工大学学报, 2015, 35(4):809-816.
|
| [12] |
Yang L K, Luo X R, Wen M L, et al. Application of geoelectric extraction method on prospecting for hidden gold deposit in peripheral area of Jinchang, Heilongjiang[J]. Journal of Guilin University of Technology, 2015, 35(4) :809-816.
|
| [13] |
刘亚剑, 范继璋, 李钟山, 等. 吉林省小石人金矿区微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2008, 38(2):202-210.
|
| [13] |
Liu Y J, Fan J Z, Li Z S, et al. Geochemical characteristics of trace elements in the Xiaoshiren gold deposit in Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2008, 38(2):202-210.
|
| [14] |
杨笑笑, 罗先熔, 郑超杰, 等. 衡阳盆地北缘国庆矿区土壤地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 地质与勘探, 2018, 54(4):762-771.
|
| [14] |
Yang X X, Luo X R, Zheng C J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil and prospecting direction in the Guoqing area, northern margin of the Hengyang Basin[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2018, 54(4):762-771.
|
| [15] |
姚旺, 卞姗姗, 余先川. 基于IFA的组合分析算法及其在矿产预测中的应用[J]. 地质学刊, 2018, 42(4) :623-631.
|
| [15] |
Yao W, Bian S S, Yu X C. IFA-based combination analysis algorithm and its application in mineral prediction[J]. Journal of Geology, 2018, 42(4):623-631.
|
| [16] |
陈建平. 深地矿产资源定量预测理论与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2019.
|
| [16] |
Chen J P. Theory and method of quantitative prediction of deep mineral resources[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2019.
|
| [17] |
苏为华. 多指标综合评价理论与方法问题研究[D]. 厦门: 厦门大学, 2000.
|
| [17] |
Su W H. Research on the theory and method of multi-index comprehensive evaluation[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2000.
|
| [18] |
张宝一, 陈伊如, 黄岸烁, 等. 地球化学场及其在隐伏矿体三维预测中的作用[J]. 岩石学报, 2018, 34(2):352-362.
|
| [18] |
Zhang B Y, Chen Y R, Huang A S, et al. Geochemical field and its roles on the 3D prediction of concealed orebodies[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2018, 34(2):352-362.
|
| [19] |
张小静. 西昆仑地区地球化学异常识别及最小预测区划分[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009.
|
| [19] |
Zhang X J. The identification of geochemical anomalies and delineation of prospective mineralization areas in the region of West Kun-lun[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009.
|
| [20] |
Cheng Q M. Mapping singularities with stream sediment geochemical data for prediction of undiscovered mineral deposits in Gejiu, Yunnan Province,China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32(1/2):314-324.

|
| [21] |
Zhao J, Wang W L, Dong L H, et al. Application of geochemical anomaly identification methods in mapping of intermediate and felsic igneous rocks in eastern Tianshan,China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 122:81-89.

|
| [22] |
翟培英, 刘念池. 蚀变岩型金矿物化探找矿模式初探[J]. 物探与化探, 1987, 11(1): 57-63.
|
| [22] |
Zhai P Y, Liu N C. A Preliminary discussion on the geophysical and geochemical ore prospecting model for gold deposits of altered rock type[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1987, 11(1): 57-63.
|
| [23] |
胡鹏, 姜军胜, 张海坤, 等. 西非克拉通优势金属矿产地质特征、成矿作用及开发现状[J]. 华南地质, 2022, 38(4):614-625.
|
| [23] |
Hu P, Jiang J S, Zhang H K, et al. Geological characteristics, mineralization,and development situation of principal metal mineral resources in the west African Craton[J]. South China Geology, 2022, 38(4): 614-625.
|
| [1] |
YU Zhong-Hong, YAN Ling-Qin, ZHANG Zhan-Xiong, LI Peng, LI Feng-Ting, FU Jia. Geophysical characteristics and deep prospecting prediction of the Dachaigou gold deposit in the eastern Kunlun area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 40-47. |
| [2] |
WAN Tai-Ping, ZHANG Li, LIU Han-Liang. Regional geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prospect area prediction of strategic mineral antimony in the Eerguna block, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1179-1188. |
|
|
|
|

