|
|
|
| Geophysical characteristics and deep prospecting prediction of the Dachaigou gold deposit in the eastern Kunlun area |
YU Zhong-Hong1( ), YAN Ling-Qin2( ), YAN Ling-Qin2( ), ZHANG Zhan-Xiong1, LI Peng3, LI Feng-Ting1, FU Jia1 ), ZHANG Zhan-Xiong1, LI Peng3, LI Feng-Ting1, FU Jia1 |
1. No.3 Exploration Institute of Geology Resources of Qinghai Province, Xining 810000, China
2. Qinghai Geological Survey Institute, Xining 810000, China
3. Haidong Municipal Bureau of Nature Resources and Planning, Haidong 810600, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The eastern Kunlun metallogenic belt, as a significant metal metallogenic belt in China, hosts extensive orogenic gold deposits and large-scale Kunlunhe, Gouli, and Wulonggou gold concentration areas. The Dachaigou gold deposit is a large-scale gold deposit newly discovered in the Wulonggou gold field in recent years. Despite its high metallogenic potential, the western extension of its ore belt has not been defined. Hence, this study conducted induced polarization (IP) sounding and wide-field electromagnetic sounding in the deposit. The results show that the known ore belt is situated in the regional gravity anomaly gradient zone, the transition zone of positive and negative weak magnetic anomalies, the edge of IP anomalies, or the electrical gradient zone. The development zone of the regional tectonic belt resides in the large-scale IP anomaly section. The regional tectonic belt is characterized by a wide range of low-resistivity anomaly zones. The IV and III alteration zones of the known ore belt are located in the opening position of the low-resistivity anomaly zone and the shallow electrical anomaly gradient zone, respectively. Based on the above understanding and the electromagnetic anomaly change patterns of several parallel profiles in the western extension segment, it was inferred that the regional ore-controlling structure extends steadily in the W-NWW direction, forming a favorable prospecting space in the western extension segment of the deposit. The results of deep geophysical exploration in the Dachaigou deposit indicate that geophysical methods manifest significant advantages in deep geological prospecting research, providing successful experience for deep prospecting in the eastern Kunlun gold deposit area.
|
|
Received: 22 March 2023
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
16])
1—Quaternary alluvial proluvial; 2—Neoproterozoic Qiujidonggou formation; 3—Mesoproterozoic Changcheng Xiaomiao formation; 4—Paleoproterozoic Jinshuikou group; 5—late Triassic K-feldspar granite; 6—early Variscan biotite monzogranite; 7—early Variscan altered plagioclase granite; 8—early Caledonian biotite granodiorite; 9—Neoproterozoic biotite granodiorite; 10—Neoproterozoic dark enclave bearing granite; 11—Neoproterozoic quartz diorite; 12—basic dyke; 13—biotite granite veins; 14—geological boundary; 15—strike slip fault; 16— measured normal fault; 17—inferred reverse fault; 18—ductile shear zone; 19—gold deposit (occurrence); 20—polymetallic occurrences; 21—gold bearing alteration zone and its number; 22—mine location
">
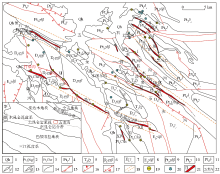
|
Geological sketch of Wulonggou gold field(modified by reference [16])
1—Quaternary alluvial proluvial; 2—Neoproterozoic Qiujidonggou formation; 3—Mesoproterozoic Changcheng Xiaomiao formation; 4—Paleoproterozoic Jinshuikou group; 5—late Triassic K-feldspar granite; 6—early Variscan biotite monzogranite; 7—early Variscan altered plagioclase granite; 8—early Caledonian biotite granodiorite; 9—Neoproterozoic biotite granodiorite; 10—Neoproterozoic dark enclave bearing granite; 11—Neoproterozoic quartz diorite; 12—basic dyke; 13—biotite granite veins; 14—geological boundary; 15—strike slip fault; 16— measured normal fault; 17—inferred reverse fault; 18—ductile shear zone; 19—gold deposit (occurrence); 20—polymetallic occurrences; 21—gold bearing alteration zone and its number; 22—mine location
|
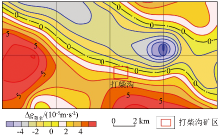
|
Regional residual gravity anomaly in Dachaigou mining area
|
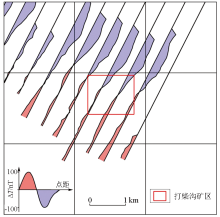
|
Section plan of 1∶50 000 ΔT geomagnetism anomaly in Dachaigou mining area
|
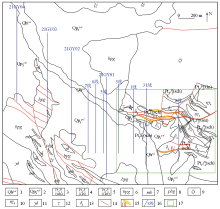
|
Geological and geophysical exploration layout of Dachaigou mining area
1—Holocene alluvial sediments; 2—Pleistocene alluvial sediments; 3—sericite quartz schist of Jinshuikou group; 4—limestone of Jinshuikou group; 5—schist interbedded with metamorphic sandstone interbedded with gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 6—gray black biotite plagioclase gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 7—marble of Jinshuikou group; 8—grayish black amphibolite gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 9—syenogranite; 10—monzogranite; 11—granodiorite; 12—granite; 13—diorite; 14—fracture; 15—ore belt and number; 16—geophysical profile; 17—Dachaigou mine
|

| 岩性 | 极化率/ % | 电阻率/ (Ω·m) | | 最大值 | 最小值 | 算术平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 几何平均值 | | 碎裂岩(含碳) | 7.45 | 1.95 | 5.45 | 503.76 | 130.65 | 264.48 | | 断层角砾岩 | 6.80 | 3.95 | 6.30 | 341.46 | 140.05 | 195.41 | | 白云石大理岩 | 3.90 | 2.15 | 2.90 | 1824.85 | 988.66 | 1574.87 | | 黑云角闪斜长片麻岩 | 4.70 | 1.85 | 2.75 | 3727.55 | 1126.85 | 1330.00 | | 脉石英 | 5.45 | 1.95 | 3.45 | 3695.20 | 2320.40 | 2933.71 | | 黑云母石英片岩 | 3.10 | 1.15 | 2.10 | 3576.50 | 2866.76 | 3216.85 | | 花岗岩 | 3.75 | 0.90 | 2.04 | 3377.40 | 2337.65 | 2865.56 |
|
Statistical table of electrical and physical parameters in Dachaigou mining area
|
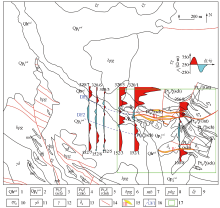
|
Comprehensive results of geological and apparent resistivity in Dachaigou mining area
1—Holocene alluvial sediments; 2—Pleistocene alluvial sediments; 3—sericite quartz schist of Jinshuikou group; 4—limestone of Jinshuikou group; 5—schist interbedded with metamorphic sandstone interbedded with gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 6—gray black biotite plagioclase gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 7—marble of Jinshuikou group; 8—grayish black amphibolite gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 9—syenogranite; 10—monzogranite; 11—granodiorite; 12—granite; 13—diorite; 14—fracture; 15—ore belts; 16—inferred structure; 17—Dachaigou mine.
|
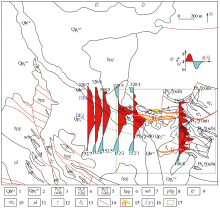
|
Comprehensive results of geological and apparent polarizability in Dachaigou mining area
1—Holocene alluvial sediments; 2—Pleistocene alluvial sediments; 3—sericite quartz schist of Jinshuikou group; 4—limestone of Jinshuikou group; 5—schist interbedded with metamorphic sandstone interbedded with gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 6—gray black biotite plagioclase gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 7—marble of Jinshuikou group; 8—grayish black amphibolite gneiss of Jinshuikou group; 9—syenogranite; 10—monzogranite; 11—granodiorite; 12—granite; 13—diorite; 14—fracture; 15—ore belt and number; 16—inferred structure; 17—Dachaigou mine
|
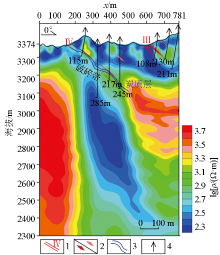
|
Geological and WFEM inversion results of Dachaigou line 8
|
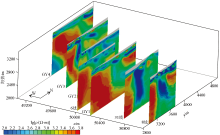
|
Three-dimensional display of WFEM inversion results in Dachaigou mining area
|
| [1] |
党兴彦, 范桂忠, 李智明, 等. 东昆仑成矿带典型矿床分析[J]. 西北地质, 2006, 39(2):143-155.
|
| [1] |
Dang X Y, Fan G Z, Li Z M, et al. Typic deposit analysis in the eastern Kunlun area,NW China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2006, 39(2):143-155.
|
| [2] |
刘建楠, 丰成友, 肖克炎, 等. 东昆仑成矿带成矿特征与资源潜力分析[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(7):1364-1376.
|
| [2] |
Liu J N, Feng C Y, Xiao K Y, et al. Mineralization characteristics and resource potential analysis of the East Kunlun metallogenic belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(7):1364-1376.
|
| [3] |
许长坤, 刘世宝, 赵子基, 等. 青海省东昆仑成矿带铁矿成矿规律与找矿方向研究[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(10):1621-1678.
|
| [3] |
Xu C K, Liu S B, Zhao Z J, et al. Metallogenic law and prospect direction of iron deposits in the East Kunlun metallogenic belt in Qinghai[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(10):1621-1678.
|
| [4] |
Feng L Q, Gu X X, Zhang Y M, et al. Genesis of the gold deposits in the Kunlun River area,East Kunlun,Qinghai Province:Constraints from geology,fluid inclusions and isotopes[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 139:104564.

|
| [5] |
焦和, 康继祖, 黄国彪, 等. 青海昆仑河北地区岩浆活动、金矿成矿特征及找矿前景分析[J]. 地质力学学报, 2022, 28(3):383-405.
|
| [5] |
Jiao H, Kang J Z, Huang G B, et al. Magmatism,metallogenic characteristics,and prospecting prediction for gold deposits in the north of Kunlun River area,Qinghai,China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2022, 28 (3):383-405.
|
| [6] |
黄国彪, 马文虎, 李长印, 等. 青海昆仑河地区黑海北金矿床地质特征及找矿前景[J]. 黄金, 2021, 42(6):26-30.
|
| [6] |
Huang G B, Ma W H, Li C Y, et al. Geological characteristics and prospecting prospects of Heihaibei gold deposit in Kunlunhe area,Qinghai Province[J]. Gold, 2021, 42(6):26-30.
|
| [7] |
杨宝荣, 张里斌, 马忠贤, 等. 青海沟里地区金矿床地质背景研究[J]. 矿产勘查, 2018, 9(10):1920-1925.
|
| [7] |
Yang B R, Zhang L B, Ma Z X, et al. Study on metallogenic geological background of gold deposits in Gouli area,Qinghai[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2018, 9(10):1920-1925.
|
| [8] |
岳维好. 东昆仑东段沟里金矿集区典型矿床地质地球化学及成矿机理研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2013.
|
| [8] |
Yue W H. Study on geology,geochemistry and metallogenic mechanism of typical deposits in Gouli gold concentration area in East Kunlun Mountains[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2013.
|
| [9] |
张纪田, 张志强, 孙国胜, 等. 青海沟里整装勘查区金矿成矿要素及预测意义[J]. 黄金, 2021, 42(7):11-16.
|
| [9] |
Zhang J T, Zhang Z Q, Sun G S, et al. Metallogenic elements of gold deposits in the Gouli integrated exploration area in Qinghai Province and their predictive significance[J]. Gold, 2021, 42(7):11-16.
|
| [10] |
贾福聚, 高建国, 周家喜, 等. 青海果洛龙洼金矿床矿化元素组合特征及找矿意义[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2017, 32(3):360-366.
|
| [10] |
Jia F J, Gao J G, Zhou J X, et al. Characterisitics of ore elements association and the prospecting significance in Guoluolongwa gold deposit,Qinghai Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2017, 32(3):360-366.
|
| [11] |
付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 谭俊, 等. 东昆仑沟里整装勘查区脉状金矿床多级构造控矿规律[J]. 矿物学报, 2015, 35(S1):388-389.
|
| [11] |
Fu L B, Wei J H, Tan J, et al. Ore-controlling regularity of multi-level structure of vein gold deposits in Gouli exploration area,East Kunlun[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2015, 35(S1):388-389.
|
| [12] |
陈柏林, 王永, 韩玉, 等. 东昆仑五龙沟矿田岩金沟金矿床成矿时代新认识[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(3):541-556.
|
| [12] |
Chen B L, Wang Y, Han Y, et al. Metallogenic age of Yanjingou gold deposit in Wulonggou gold orefield,eastern Kunlun Mountains[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(3):541-556.
|
| [13] |
陈柏林. 东昆仑五龙沟金矿田地质特征与成矿地质体厘定[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(1):179-196.
|
| [13] |
Chen B L. Geological characteristics of the Wulonggou gold ore field and determination of metallogenic geological bodies in East Kunlun Mountains[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(1):179-196.

|
| [14] |
马国栋, 贾建团, 韩玉, 等. 青海五龙沟金矿矿床成因及成矿模式探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2016, 49(4):172-178.
|
| [14] |
Ma G D, Jia J T, Han Y, et al. Genesis and metallogenic model of the wulonggou gold deposit in Qinghai Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2016, 49(4):172-178.
|
| [15] |
周永生, 张冬瑞, 潘增龙, 等. 青海省都兰县打柴沟金矿外围金矿详查报告[R]. 都兰西金矿业有限公司, 2019.
|
| [15] |
Zhou Y S, Zhang D R, Pan Z L, et al. Detailed investigation report on gold deposits around Dachaigou gold mine,Dulan county,Qinghai province[R]. Dulan Xijin Mining Co.,Ltd, 2019
|
| [16] |
张延林, 陈建林, 马永久, 等. 青海省都兰县五龙沟地区红旗沟—深水潭金矿勘查报告[R]. 青海省第一地质矿产勘查院, 2016.
|
| [16] |
Zhang Y L, Chen J L, Ma Y J, et al. Exploration report of Hongqigou-Shenshuitan gold deposit in Wulonggou area,Dulan County,Qinghai Province[R]. The First Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province, 2016
|
| [17] |
张胜业, 潘玉玲. 应用地球物理学原理[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2004.
|
| [17] |
Zhang S Y, Pan Y L. Applied geophysical principles[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2004.
|
| [18] |
何继善. 广域电磁测深法研究[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2010, 41(3):1065-1072.
|
| [18] |
He J S. Wide field electromagnetic sounding methods[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology Edition, 2010, 41(3):1065-1072.
|
| [1] |
XU Xue-Yi, XIONG Sheng-Qing, YANG Xue, GAO Wei-Hong, FAN Zheng-Guo, JIA Zhi-Ye. Aerogeophysical anomalies and prospecting direction in the Fengtai ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1157-1168. |
| [2] |
YUAN Yu-Ting, LIU Xue-Min, WANG Xue-Qiu, TAN Qin-Ping. Sulfur-lead isotopes based tracing of the metal element anomalies identified in the total metal measurement of surface fine-grained soils: A case study of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type concealed gold deposit[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1083-1097. |
|
|
|
|

