|
|
|
| Airborne gravity-magnetic anomalies in the Baiyunhu sag,Qiangtang Basin:Characteristics and implications for oil and gas exploration |
LIU Zhong-Rong1( ), HU Yue2( ), HU Yue2( ), FAN Zhi-Wei1, HE Hong-Bing1, ZHOU Dao-Qing2, GUO Zhi-Hong2, CAO Bao-Bao2, WEI Yan-Yan2 ), FAN Zhi-Wei1, HE Hong-Bing1, ZHOU Dao-Qing2, GUO Zhi-Hong2, CAO Bao-Bao2, WEI Yan-Yan2 |
1. SINOPEC Exploration Company,Chengdu 610041,China
2. China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Land and Resources,Beijing 100083,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Airborne gravity-magnetic data are effective in revealing the deep structures of a basin.Based on the latest airborne gravity-magnetic data,combined with field-measured physical property data,this study expounded the characteristics and geological origin of airborne gravity-magnetic anomalies present in the Baiyunhu sag.Using the airborne gravity-magnetic data,this study identified the distribution of faults and magmatic rocks in the Baiyunhu sag.Furthermore,it calculated the burial depth of the magnetic basement and the structural morphologies of the Mesozoic basement in the sag using the artificial tangent method, power spectrum analysis method,and Parker-Oldenburg iterative inversion algorithm.Additionally,this study verified the structural stratification results through the integrated interpretations of gravity and magnetism in target sections.The findings suggest that the undulations of the Mesozoic and Paleozoic sediments in the Baiyunhu sag are the primary cause of gravity anomalies,while the regional airborne magnetic anomaly primarily reflects the distribution features of the Precambrian basement.The deeply buried basement of the Baiyunhu sag,featuring continuously distributed,thick Mesozoic strata and the lack of regional faulting and magmatic activity,is scarcely affected by tectonic movements and possesses great potential for oil and gas exploration.
|
|
Received: 27 September 2023
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
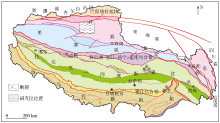
|
Location of the research area
|
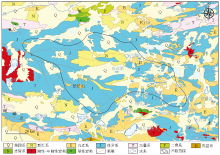
|
Regional geological map of research area
|

| 地层 |
岩性 | 密度/(g·cm-3) | 磁化率/(10-5SI) | | 界 | 系 | | 极大值 | 极小值 | 平均值 | 极大值 | 极小值 | 平均值 | 新
生
界 | 新近系 | 含砾砂岩 | 2.61 | 2.38 | 2.52 | 35 | 12 | 25 | | 古近系 | 砂岩 | 2.53 | 2.20 | 2.43 | 87 | 3 | 39 | | 油页岩 | 2.10 | 1.70 | 1.88 | 11 | 4 | 8 | 中
生
界 | 白垩系 | 砾岩 | 2.67 | 2.44 | 2.56 | 16 | 3 | 8 | | 砂岩 | 2.66 | 2.33 | 2.53 | 27 | 16 | 22 | | 灰岩 | 2.70 | 2.67 | 2.65 | 20 | 7 | 13 | | 侏罗系 | 砂岩 | 2.75 | 2.19 | 2.59 | 97 | 1 | 50 | | 膏盐 | 1.98 | 1.73 | 1.82 | 8 | 2 | 5 | | 灰岩 | 2.99 | 2.53 | 2.66 | 35 | 1 | 20 | | 三叠系 | 砂岩 | 2.82 | 2.40 | 2.55 | 47 | 4 | 18 | | 灰岩 | 2.69 | 2.63 | 2.66 | 11 | 4 | 8 | | 玄武岩 | 2.96 | 2.73 | 2.85 | 951 | 178 | 567 | 古
生
界 | 二叠系 | 灰岩 | 2.85 | 2.38 | 2.67 | 36 | 4 | 12 | | 砂岩 | 2.66 | 2.62 | 2.65 | 43 | 18 | 30 | | 玄武岩 | 2.94 | 2.83 | 2.89 | 1129 | 350 | 708 | | 石炭系 | 灰岩 | 2.69 | 2.63 | 2.67 | 17 | 8 | 12 | | 泥质粉砂岩 | 2.75 | 2.71 | 2.73 | 47 | 31 | 38 | | 泥盆系 | 灰岩 | 2.69 | 2.56 | 2.65 | 14 | 6 | 10 | | 白云岩 | 2.83 | 2.68 | 2.78 | 15 | 6 | 11 | 元
古
宇 | 前寒
武系 | 大理岩 | 2.84 | 2.71 | 2.75 | 84 | 5 | 27 | | 片麻岩 | 2.79 | 2.61 | 2.70 | 225 | 25 | 95 | | 斜长角闪片麻岩 | 2.90 | 2.72 | 2.76 | 6349 | 760 | 2479 | | 斜长角闪岩 | 2.97 | 2.75 | 2.91 | 3327 | 63 | 910 | | 角闪变粒岩 | 2.76 | 2.71 | 2.72 | 4121 | 1397 | 2349 |
|
Magnetic determination results of rocks and density distribution of the strata in the research area
|
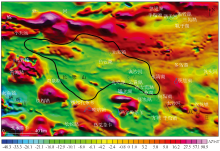
|
Reduced-to-pole regional aeromagnetic (ΔT) anomalies in the Baiyunhu sag
|
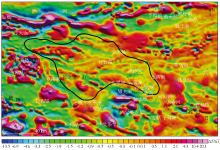
|
Diagram of the vertical first derivative for reduced to pole regional aeromagnetic (ΔT) in the Baiyunhu sag
|

|
Color grid of the airborne Bouguer gravity in the Baiyunhu sag
|
|
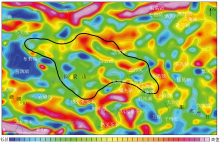
Diagram of the vertical first derivative for airborne Bouguer gravity in the Baiyunhu sag
|

|
Tectonic map of igneous rocks in the Baiyunhu sag
|
|
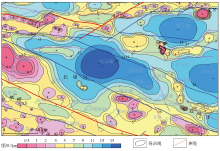
Color shaded grid of the depth of the top of the magnetic basement in the Baiyunhu sag
|
|
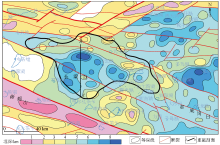
Burial depth of the Mesozoic bottom in the Baiyunhu sag
|
|
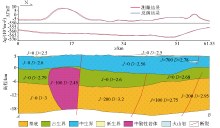
Interpretation of gravity and magnetic anomaly profiles
|
| [1] |
王剑, 付修根, 沈利军, 等. 论羌塘盆地油气勘探前景[J]. 地质论评, 2020, 66(5):1091-1110.
|
| [1] |
Wang J, Fu X G, Shen L J, et al. Prospect of the potential of oil and gas resources in Qiangtang Basin,Xizang(Tibet)[J]. Geological Review, 2020, 66(5):1091-1110.
|
| [2] |
王成善, 伊海生. 羌塘盆地地质演化与油气远景评价[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2001.
|
| [2] |
Wang C S, Yi H S. Geological evolution and gas potential evolution[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2001.
|
| [3] |
李志, 赵炳坤, 杨亚斌, 等. 青藏高原及邻区重力系列图及说明书(1∶3000000)[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013.
|
| [3] |
Li Z, Zhao B K, Yang Y B, et al. The gravity map of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau and adjacent areas(1∶3000000)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2013.
|
| [4] |
熊盛青, 丁燕云, 李占奎. 西藏羌塘盆地的重磁场特征及地质意义[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2013, 48(6):999-1007.
|
| [4] |
Xiong S Q, Ding Y Y, Li Z K. The characteristics of gravity and magnetic fields and their geological significance in Qiangtang Basin,Tibet[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2013, 48(6):999-1007.
|
| [5] |
熊盛青, 周道卿, 曹宝宝, 等. 羌塘盆地中央隆起带的重磁场证据及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 69(9):3491-3502.
|
| [5] |
Xiong S Q, Zhou D Q, Cao B B, et al. Characteristics of the central uplift zone in Qiangtang basin and its tectonic implications:Evidences from airborne gravity and magnetic data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 69(9):3491-3502.
|
| [6] |
陈文彬, 付修根, 谭富文, 等. 羌塘盆地二叠系白云岩油苗地球化学特征及意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(3):611-618.
|
| [6] |
Chen W B, Fu X G, Tan F W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and significance of Permain dolomite oil seep-ages in Qiangtang Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2017, 35(3):611-618.
|
| [7] |
付修根, 王剑, 宋春彦, 等. 羌塘盆地第一口油气科学钻探井油气地质成果及勘探意义[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(1):15-24.
|
| [7] |
Fu X G, Wang J, Song C Y, et al. Petroleumgeological achievements and exploration significance of the first oil and gas scientific drilling well in the Qiangtang Basin[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2020, 40(1):15-24.
|
| [8] |
周道卿, 曹宝宝, 赵睿, 等. 羌塘盆地高精度航空重磁调查对盆地基底性质与构造格局的启示[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(11):3178-3191.
|
| [8] |
Zhou D Q, Cao B B, Zhao R, et al. High-precision airborne gravity and magnetic survey analysis of the Qiangtang basin implications for basin basement properties and tectonic framework[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(11):3178-3191.
|
| [9] |
潘桂棠, 王立全, 尹福光, 等. 青藏高原形成演化研究回顾、进展与展望[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2022, 42(2):151-172.
|
| [9] |
Pan G T, Wang L Q, Yin F G, et al. Researches on geological-tectonic evolution of Tibetan plateau:A review,recent advances,and directions in the future[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2022, 42(2):151-172.
|
| [10] |
解超明, 李才, 李庆林, 等. 藏北羌塘中部首次发现泥火山[J]. 地质通报, 2009, 28(9):1319-1324.
|
| [10] |
Xie C M, Li C, Li Q L, et al. First discovery of mud volcanoes in central Qiangtang,northern Tibet,China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2009, 28(9):1319-1324.
|
| [11] |
付修根, 王剑, 谭富文, 等. 藏北羌塘盆地油气地质勘探新进展[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2015, 35(1):16-24.
|
| [11] |
Fu X G, Wang J, Tan F W, et al. Recent progress in oil and gas geological exploration in the Qiangtang Basin,northern Xizang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2015, 35(1):16-24.
|
| [12] |
吴珍汉, 赵珍, 吴忠海, 等. 西藏双湖古近纪唢呐湖组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄与古海拔高度[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(7):1352-1368.
|
| [12] |
Wu Z H, Zhao Z, Wu Z H, et al. U-Pb ages of detrital zircons from the Suonahu formation and Paleo-elevation determination in late Paleogene in the Suonahu area,northern Tibet[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(7):1352-1368.
|
| [13] |
刘中戎, 张佳伟. 西藏羌塘盆地中生代晚期构造事件与油气的关系[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2017, 37(2):23-29.
|
| [13] |
Liu Z R, Zhang J W. Late mesozoic tectonic events and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Qiangtang Basin,northern Xizang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2017, 37(2):23-29.
|
| [14] |
张明华, 乔计花, 黄金明, 等. 重磁电数据处理解释软件RGIS[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.
|
| [14] |
Zhang M H, Qiao J H, Huang J M, et al. Gravity magnetic and electric data processing and interpretation software RGIS[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011.
|
| [15] |
郭祖军, 李永铁, 南征兵, 等. 羌塘盆地变形构造与油气聚集保存关系[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2008, 35(5):563-568.
|
| [15] |
Guo Z J, Li Y T, Nan Z B, et al. Relationship between deformation structure and petroleum accumulation and preservation,Qiangtang Basin,Tibet[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2008, 35(5):563-568.

|
| [16] |
李才, 解超明, 王明, 等. 羌塘地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.
|
| [16] |
Li C, Xie C M, Wang M, et al. Qiangtang geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016.
|
| [17] |
潘桂棠, 陆松年, 肖庆辉, 等. 中国大地构造阶段划分和演化[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(6):1-23.
|
| [17] |
Pan G T, Lu S N, Xiao Q H, et al. Division of tectonic stages and tectonic evolution in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(6):1-23.
|
| [18] |
王剑, 付修根. 论羌塘盆地沉积演化[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(2):237-259.
|
| [18] |
Wang J, Fu X G. Sedimentary evolution of the Qiangtang basin[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(2):237-259.
|
| [19] |
赵珍, 陆露, 吴珍汉. 羌塘盆地中央隆起带的抬升演化:构造—热年代学约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2019, 26(2):249-260.
|
| [19] |
Zhao Z, Lu L, Wu Z H. Uplifting evolution of the central uplift belt,Qiangtang:Constraints from tectono-thermochronology[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(2):249-260.
|
| [20] |
南征兵, 张艳玲, 李永铁, 等. 羌塘中生代盆地演化特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(3):534-539.
|
| [20] |
Nan Z B, Zhang Y L, Li Y T, et al. Evolution characteristics of the Qiangtang Basin in the Mesozoic Era[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(3):534-539.
|
| [1] |
WANG Fei, PEI Jin-Mei, LIU Feng-Zhi, LIU Zhi-Huan, LI Guo-Shun. Box wave analysis of Nima area in Qiangtang basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2): 352-357. |
| [2] |
YANG Zhi-Bin, ZHOU Ya-Long, SUN Zhong-Jun, ZHANG Fu-Gui, ZHANG Shun-Yao, LI Guang-Zhi. Geochemical exploration of natural gas hydrate in mud volcano area of the Qiangtang Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(3): 452-458. |
|
|
|
|

