|
|
|
| Hydrochemical characteristics and significance of the Hongshan Lake in the Tianshuihai area, Xinjiang, China |
XIAO Rui1( ), PANG Shou-Ji1( ), PANG Shou-Ji1( ), ZHU You-Hai1, ZHANG Shuai1, ZOU Yi1,2 ), ZHU You-Hai1, ZHANG Shuai1, ZOU Yi1,2 |
1. Oil & Gas Survey, China Geological Survey, Beijing 100083, China
2. School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Focusing on the spring and lake water in the Hongshan Lake in the Tianshuihai area, Xinjiang, China, this study explored the formation process of the hydrochemical components in the water and the geochemical characteristics and sources of the water bodies through hydrogeochemical testing and analyses. Accordingly, the hydrocarbon-related hydrogeochemical information was obtained. The results are as follows: The spring water in the Hongshan Lake is weakly alkaline in general and dominated by brackish water. The mass concentration of main ions in the water bodies increases with increasing salinity. The water has a hydrochemical type of Na-HCO3 and is mainly charged by atmospheric precipitation, which interacts with the surrounding rocks during the deep circulation along faults or fractures. The salinity, hydrochemical type, and characteristic coefficient of spring water indicate that the groundwater in this area features weak hydrodynamic force and deep metamorphic degree, which are similar to the characteristics of the formation water associated with hydrocarbon in oil fields. Therefore, it can be inferred that the geological environment in this area is conducive to the generation and preservation of hydrocarbon resources.
|
|
Received: 18 October 2021
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
PANG Shou-Ji
E-mail: didaxr@163.com;psj0409@163.com
|
|
|
|
20])
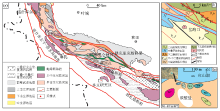
a—geological structure map of West Kunlun and adjacent areas;b—geological sketch of study area;c—the distribution of water samples
">
|
Simplified geological map of the research area (adapted from reference [20])
a—geological structure map of West Kunlun and adjacent areas;b—geological sketch of study area;c—the distribution of water samples
|

| 编号 | 采样点 | 矿化度/
(mg·L-1) | 水体化
学类型 | 电导率/
(μs·cm-1) | pH
值 | δD
V-SMOW | δO
V-SMOW | 阴、阳离子浓度/(mg·L-1) | | F- | Cl- | | | Na+ | | Mg2+ | Ca2+ | | | W1 | 间歇性冷泉水 | 2370 | 微咸水 | 3207 | 7.68 | -96.1 | -13.0 | 0.440 | 642 | <0.08 | 94.5 | 555 | 25.3 | 47.9 | 113.0 | 891 | | W2 | 泉华水,水中出现
钙华,池底发白 | 2102 | 微咸水 | 2897 | 7.98 | -83.7 | -11.3 | 0.540 | 616 | <0.08 | 95.5 | 553 | 25.8 | 49.8 | 55.1 | 707 | | W3 | 泉华水,间歇性冷
泉喷口处 | 1983 | 微咸水 | 2826 | 7.99 | -84.5 | -11.0 | 0.460 | 515 | <0.08 | 83.4 | 499 | 24.5 | 45.7 | 68.9 | 747 | | W4 | 钙华区水 | 2093 | 微咸水 | 3032 | 7.98 | -88.0 | -11.3 | 0.520 | 573 | <0.08 | 105.0 | 481 | 24.4 | 51.8 | 88.0 | 768 | | W5 | 最新形成的碳酸盐区 | 2091 | 微咸水 | 2963 | 7.4 | -94.0 | -12.6 | 0.560 | 506 | <0.08 | 104.0 | 447 | 21.5 | 46.5 | 125.0 | 841 | | W6 | 冷泉渗流口 | 3076 | 咸水 | 2896 | 7.28 | -93.9 | -11.9 | 0.560 | 815 | <0.08 | 112.0 | 693 | 28.9 | 55.9 | 186.0 | 1184 | | W7 | 底部呈红色的水体 | 2110 | 微咸水 | 4222 | 7.74 | -91.0 | -11.9 | 0.580 | 537 | <0.08 | 93.0 | 495 | 24.4 | 49.5 | 93.1 | 817 | | W8 | 湖水样 | 119177 | 盐水 | 137000 | 8.07 | -60.3 | -8.1 | <0.02 | 64082 | <0.08 | 8938.0 | 41149 | 1238.0 | 2407.0 | 538.0 | 825 |
|
Results of water chemical analysis in the study area
|
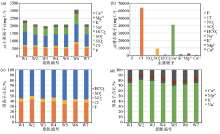
|
Ion concentration diagrams
a—total concentration of major ions in the springs; b—total concentration of major ions in the lake; c—percentage of major anion; d—percentage of major cation
|
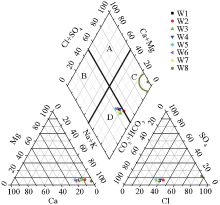
|
Piper diagram of ionic concentration in water samples from the study area
|
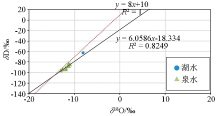
|
Relationship between hydrogen and oxygen isotope of the water samples in the study area
|
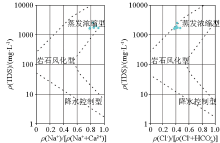
|
Gibbs diagram of the studied lakes in the study area
|
| [1] |
Ali S, Thakur S K, Sarkar A, et al. Worldwide contamination of water by fluoride[J]. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2016, 14(3):291 - 315.

|
| [2] |
Zhao G, Li W, Li F, et al. Hydrochemistry of waters in snowpacks,lakes and streams of Mt.Dagu,eastern of Tibet Plateau[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2018(610/611):641-650.
|
| [3] |
Wu C, Wu X, Qian C, et al. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality assessment of high fluoride levels in the Yanchi endorheic region,northwest China[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2018, 98:404-417.

|
| [4] |
Rashid A, Guan D X, Farooqi A, et al. Fluoride prevalence in groundwater around a fluorite mining area in the flood plain of the River Swat,Pakistan[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018, 635:203-215.

|
| [5] |
Li Z J, Yang Q C, Yang Y S, et al. Isotopic and geochemical interpretation of groundwater under the influences of anthropogenic activities[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019(576):685-697
|
| [6] |
Yan J, Chen J, Zhang W, et al. Determining fluoride distribution and influencing factors in groundwater in Songyuan,Northeast China,using hydrochemical and isotopic methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 217:106605.

|
| [7] |
刘崇禧, 张学全. 地下水中可溶气态烃的石油化探效果[J]. 物探与化探, 1985, 9(2):92-99.
|
| [7] |
Liu C X, Zhang X Q. The application of soluble gaseoushydrocarbon in underground water togeochemical petroleum exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1985, 9(2):92-99.
|
| [8] |
钱诗友, 曾溅辉. 东营凹陷沙河街组地层水化学特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2009, 20(4):603-609.
|
| [8] |
Qian S Y, Zeng J H. Chemical characteristics of Shahejie formation water and their petroleum geological significance,Dongying Sag[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2009, 20(4) :603-609.
|
| [9] |
张秋, 谭志伟, 张作祥, 等. 贝尔凹陷水文地球化学特征与油气藏的关系[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(1):37-41.
|
| [9] |
Zhang Q, Tan Z W, Zhang Z X, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of Beier depressionin relation to oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(1):37-41.
|
| [10] |
张志攀, 祝有海, 苏新. 羌塘盆地泉水化学特征及其意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(7):1233-1238.
|
| [10] |
Zhang Z P, Zhu Y H, Su X. Chemic charactoristics of fountains in Qiangtang Basin Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its implications[J]. Acta Geologica, 2011, 85(7):1233-1238.
|
| [11] |
梁晓伟, 牛小兵, 李卫成, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地油田水化学特征及地质意义[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 39(5):502-508.
|
| [11] |
Liang X W, Niu X B, Li W C, et al. Chemical character of oil-field water in Ordos Basin and geological significance[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition, 2012, 39(5):502-508.
|
| [12] |
李博秦, 姚建新, 高联达, 等. 西昆仑麻扎—康西瓦一带温泉沟群的形成时代及物源区分析[J]. 地质通报, 2007, 26(4):457-465.
|
| [12] |
Li B Q, Yao J X, Gao L D, et al. Age and source regions of the Wenquangou Group in the Mazar-Kangxiwar area,West Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2007, 26(4):457-465.
|
| [13] |
王炬川, 崔建堂, 罗乾周, 等. 喀喇昆仑南部侏罗系龙山组沉积环境分析及构造环境初探[J]. 陕西地质, 2004, 22(1):17-23.
|
| [13] |
Wang J C, Cui J T, Luo Q Z, et al. Analysis of the sedimentary environment and discussion of the structural setting of the Jurassic Longshan Formation in the southern Kunlun of Gela[J]. Geology of Shaanxi, 2004, 22(1):17-23.
|
| [14] |
崔建堂, 王炬川, 边小卫, 等. 新疆喀喇昆仑地区甜水海岩群发现青白口纪叠层石[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2005, 25(1/2):194-197.
|
| [14] |
Cui J T, Wang J C, Bian X W, et al. The Qingbaikouan stromatolites from the Tianshuihai Group Complex in the Karakorum region,Xinjiang[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2005, 25(1/2):194-197.
|
| [15] |
李海兵, Franck Valli, 许志琴, 等. 喀喇昆仑断裂的变形特征及构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(2):239-255.
|
| [15] |
Li H B, Franck Valli, Xu Z Q, et al. Deformation and tectonic evolution of the Karakorum Fault,western Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(2):239-255.
|
| [16] |
林清茶, 夏斌, 张玉泉. 西昆仑—喀喇昆仑地区钾质碱性岩Ar-Ar年龄——以羊湖、昝坎和苦子干岩体为例[J]. 矿物岩石, 2006, 26(2):66-70.
|
| [16] |
Lin Q C, Xia B, Zhang Y Q. Ar-Ar dating of potassic alkali-rocks in the western Kunlun-Kalakorum Mountains—Example for the rocks of Yanghu,Zankan and Kuzigan[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2006, 26(2):66-70.
|
| [17] |
周军, 任燕. 新疆西昆仑岔路口—甜水海地区铅锌资源地球化学定量预测[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(2):220-226.
|
| [17] |
Zhou J, Ren Y. Geochemical quantitative prediction of lead-zinc resources in Chalukou-Tianshuihai area of west Kunlun Mountains,Xinjiang[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(2):220-226.
|
| [18] |
谢渝, 陶玲, 李惠, 等. 西昆仑甜水海地区地球化学普查及其找矿效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(3):410-420.
|
| [18] |
Xie Y, Tao L, Li H, et al. The application of geochemical exploration to geological prospecting in Tianshuihai area of Western Kunlun Mountains[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(3):410-420.
|
| [19] |
杨华, 梁月明. 全国航磁ΔT异常与中国地学断块构造[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(6):957-967.
|
| [19] |
Yang H, Liang Y M. Nationwide aeromagnetic ΔT anomalies and China’s geoscience block structures[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(6):957-967.
|
| [20] |
周能武, 陈邦学, 朱彦菲, 等. 西昆仑岔路口西花岗岩地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 新疆地质, 2016, 34(4):437-445.
|
| [20] |
Zhou N W, Chen B X, Zhu Y F, et al. Geochemistry and tectonic significance of granite from the west of Chalukou in western Kunlun,NW China[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2016, 34(4):437-445.
|
| [21] |
边小卫, 王炬川, 罗乾周, 等. 甜水海微陆块上二叠系地层的厘定及其特征[J]. 陕西地质, 2005, 23(2):44-49,75.
|
| [21] |
Bian X W, Wang J C, Luo Q Z, et al. Determination of the Permian system discovered on the micro-landmass in a freshwater sea and the characteristics[J]. Geology of Shaanxi, 2005, 23(2):44-49,75.
|
| [22] |
李世杰, 张宏亮, 施雅风, 等. 青藏高原甜水海盆地MIS 3阶段湖泊沉积与环境变化[J]. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28(1):122-131.
|
| [22] |
Li S J, Zhang H L, Shi Y F, Zhu Z Y, et al. A high resolution MIS 3 environmental change environmental record derived from lacustrine deposit of Tianshuihai Lake,Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28(1):122-131.
|
| [23] |
罗伟, 李佑国, 彭静, 等. 西昆仑地区水系沉积物地球化学异常识别[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(4):722-727.
|
| [23] |
Luo W, Li Y G, Peng J, et al. The identification of stream sediment geochemical anomalies in West Kunlun region[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(4):722-727.
|
| [24] |
王海雷, 郑绵平. 青藏高原湖泊水化学与盐度的相关性初步研究[J]. 地质学报, 2010, 84(10):1517-1522.
|
| [24] |
Wang H L, Zheng M P. Priliminary study on relationship between hydrochemistry and salinity of lakes in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2010, 84(10):1517-1522.
|
| [25] |
王鹏, 尚英男, 沈立成, 等. 青藏高原淡水湖泊水化学组成特征及其演化[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(3):874-881.
|
| [25] |
Wang P, Shang Y N, Shen L C, et al. Characteristics and evolution of hydrochemical compositions of freshwater lake in Tibetan Plateau[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(3):874-881.
|
| [26] |
李承鼎, 康世昌, 刘勇勤, 等. 西藏湖泊水体中主要离子分布特征及其对区域气候变化的响应[J]. 湖泊科学, 2016, 28(4):743-754.
|
| [26] |
Li C D, Kang S C, Liu Y Q, et al. Distribution of major ions in waters and their response to regional climatic change in Tibetan lakes[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2016, 28(4):743-754.

|
| [27] |
卢双舫, 张敏. 油气地球化学[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008.
|
| [27] |
Lu S F, Zhang M. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008.
|
| [28] |
王启军, 陈建渝. 油气地球化学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社,1988.
|
| [28] |
Wang Q J, Chen J Y. Petroleum geochemistry[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press,1988.
|
| [29] |
陈义才, 沈忠民, 罗小平. 石油和天然气有机地球化学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2007.
|
| [29] |
Chen Y C, Shen Z M, Luo X P. Oil & gas organic geochemistry[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2007
|
| [30] |
胡绪龙, 李瑾, 张敏, 等. 地层水化学特征参数判断气藏保存条件——以呼图壁、霍尔果斯油气田为例[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2008, 31(4):23-26,82-83.
|
| [30] |
Hu X L, Li J, Zhang M, et al. Judge gas reservoir preservation by chemical characteristic parameters of formation water:Examples from Hutubi and Horgos oil-gas fields[J]. Natural Gas Exploration & Development, 2008, 31(4):23-26,82-83.
|
| [31] |
林晓英, 曾溅辉, 杨海军, 等. 塔里木盆地哈得逊油田石炭系地层水化学特征及成因[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(2):377-383.
|
| [31] |
Lin X Y, Zeng J H, Yang H J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and origin of formation water from the Carboniferous in Hadson oil field,Tarim Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(2):377-383.
|
| [32] |
李建森, 董华庆, 姜有旭, 等. 大柴旦温泉沟泉的地球化学成因[J]. 盐湖研究, 2017, 25(2):55-59.
|
| [32] |
Li J S, Dong H Q, Jiang Y X, et al. Geochemical genesis of the springs in Wenquan Ditch of Da Qaidam area[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2017, 25(2):55-59.
|
| [33] |
杨丽杰, 侯读杰, 陈晓东, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷中部古近系地层水化学特征及地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(4):559-571,596.
|
| [33] |
Yang L J, Hou D J, Chen X D, et al. Chemical characteristics and geological significance of Palaeogene formation water in central Xihu Depression,East China Sea Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(4):559-571,596.
|
| [34] |
韩佳君, 周训, 姜长龙, 等. 柴达木盆地西部地下卤水水化学特征及其起源演化[J]. 现代地质, 2013, 27(6):1454-1464.
|
| [34] |
Han J J, Zhou X, Jiang C L, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics,origin and evolution of the subsurface brines in western Qaidam Basin[J]. Geoscience, 2013, 27(6):1454-1464.
|
| [35] |
牛新生, 黄华, 郑绵平. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷地下卤水地球化学特征和分布规律[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(6):56-65.
|
| [35] |
Niu X S, Huang H, Zheng M P. Geochemical characteristics and distribution patterns of subsurface brines in the Qiangjiang Depression,Jianghan Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(6):56-65.
|
| [36] |
邢晓红, 刘桂民, 李红琴, 等. 哈思山地区泉水成因及其氢氧稳定同位素特征探讨[J]. 水文, 2016, 36(2):46-50.
|
| [36] |
Xing X H, Liu G M, Li H Q, et al. Sources of spring water and its characteristics of hydrogen and oxygen stable isotopes in Hasi Mountain[J]. Journal of China Hydrology, 2016, 36(2):46-50.
|
| [37] |
张景涛, 史浙明, 王广才, 等. 柴达木盆地大柴旦地区地下水水化学特征及演化规律[J]. 地学前缘, 2021, 28(4):194-205.
|
| [37] |
Zhang J T, Shi Z M, Wang G C, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the Dachaidan area,Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(4):194-205.
|
| [1] |
JIANG Bing, LIU Yang, WU Zhen, ZHANG De-Ming, SUN Zeng-Bing, MA Jian. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in irrigation water and soils in the Gaomi area, Shandong Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1348-1353. |
| [2] |
LIU Yun-Xiang, SI Hua-Lu, QIAO Hai-Yan, LIU Bai-Chuan. Progress and prospect of gravity and magnetic techniques for hydrocarbon exploration in China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 563-574. |
|
|
|
|

