|
|
|
| The feasibility of applying hydrocarbon-mercury gas measurement method in the prospecting of sedimentary copper deposits in Central Africa |
HUANG Xue-Qiang1( ), CHEN Yuan-Rong2, WU Er3, LIU Feng1, LU An-Ning1 ), CHEN Yuan-Rong2, WU Er3, LIU Feng1, LU An-Ning1 |
1. Mineral Geology Institute Co., Ltd. of China Nonferrous Metal Mining (Group) Co., Ltd., Guilin 541006, China
2. College of Earth Sciences, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541006, China
3. Bowen College of Management, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541006, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Sedimentary copper deposits are the predominant type of copper (cobalt) mineralization in the Central African copper-cobalt metallogenic belt. To improve the prospecting efficiency of such deposits, the feasibility of applying the hydrocarbon-mercury gas measurement method in the prospecting of sedimentary copper deposits was studied in the Mabende-Likasi area of the Democratic Republic of Congo. As indicated by the test results, two known ore bodies show remarkable anomalies of multiple indicators of hydrocarbon and mercury, but the anomaly distribution is controlled by the occurrence of orebodies. Based on these findings, this study summarized the anomaly pattern of hydrocarbon-mercury gas and primarily explored the anomaly causes. Moreover, this study conducted the prospecting prediction of concealed copper (cobalt) deposits in the study area. An industrial copper orebody was discovered through drilling in the delineated favorable target area, thus achieving achieved prospecting results.
|
|
Received: 14 October 2021
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Traffic location of Lufrian Cu-Co metallogenic belt
|
|
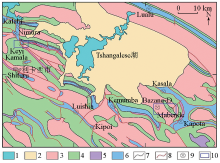
Regional geological map in research area
1—lake;2—Quaternary system;3—Kundelungu group;4—Nguba group;5—Mwashia group;6—the lower Roan subgroup;7—geological boundary;8—fault;9—Cu(Co) deposits above medium size and names;10—scope of research area(test area and inferred area)
|

| 矿区 | 烃汞组分 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 背景值 | 标准方差 | 异常下限 | 变异系数 | 异常衬度 | | BD矿区 | 甲烷 | 4.361 | 1.828 | 2.800 | 0.594 | 3.691 | 0.21 | 1.50 | | 乙烷 | 0.150 | 0.046 | 0.089 | 0.030 | 0.134 | 0.33 | 1.62 | | 丙烷 | 0.217 | 0.034 | 0.074 | 0.040 | 0.135 | 0.55 | 2.65 | | 异丁烷 | 0.032 | 0.006 | 0.013 | 0.006 | 0.022 | 0.45 | 2.12 | | 正丁烷 | 0.170 | 0.013 | 0.048 | 0.034 | 0.099 | 0.71 | 2.95 | | 乙烯 | 1.648 | 0.533 | 1.013 | 0.320 | 1.492 | 0.32 | 1.61 | | 丙烯 | 0.985 | 0.335 | 0.618 | 0.159 | 0.857 | 0.26 | 1.49 | | 汞 | 1.269 | 0.439 | 0.714 | 0.204 | 1.021 | 0.29 | 1.58 | | 马本德矿区 | 甲烷 | 4.948 | 1.821 | 3.169 | 0.993 | 4.658 | 0.31 | 3.03 | | 乙烷 | 1.666 | 0.101 | 0.529 | 0.486 | 1.258 | 0.92 | 2.85 | | 丙烷 | 1.724 | 0.052 | 0.513 | 0.479 | 1.231 | 0.93 | 2.91 | | 异丁烷 | 0.159 | 0.005 | 0.048 | 0.042 | 0.110 | 0.87 | 2.95 | | 正丁烷 | 1.385 | 0.038 | 0.363 | 0.377 | 0.929 | 1.04 | 3.77 | | 乙烯 | 2.176 | 0.270 | 0.994 | 0.611 | 1.911 | 0.61 | 2.18 | | 丙烯 | 2.919 | 0.435 | 1.128 | 0.669 | 2.131 | 0.59 | 2.27 | | 汞 | 2.390 | 0.236 | 0.771 | 0.378 | 1.338 | 0.49 | 3.10 |
|
Geochemical parameters of hydrocarbon mercury components in test area
|
|
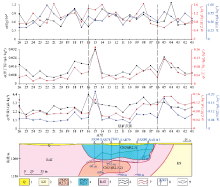
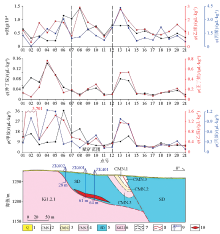
Geological hydrocarbon anomaly profile of 2680 in BD mining area
1—topsoil;2—Kundelungu group sandy shale with dolomite;3—silicified dolomite;4—argillaceous/dolomitic shale;5—the lower Roan subgroup (R1) heterogeneous (complex) breccia;6—measured/inferred geological boundary;7—measured/inferred fault;8—drill hole under construction and numbers;9—copper orebody
|
|
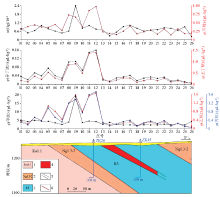
Geological hydrocarbon anomaly profile of P2 in Mabende-mining area
1—glacial migmatite (small conglomerate);2—dolomitized sandstone, siltstone or shale;3—Roan group (R3) dolomite, dolomitized siltstone;4—copper orebody;5—measured/inferred geological boundary;6—fault
|
|
Geological hydrocarbon anomaly profile of 04 in Keyi Mining area
1—Quaternary laterite layer;2—talc siltstone;3—silicified siltstone;4—siliceous shale intercalated argillaceous rock;5—dolomitic shale and argillaceous siltstone;6—Kundelungu group siltstone and shale;7—measured/inferred geological boundary;8—measured/inferred fault;9—verfication drill hole and numbers;10—industrial copper orebody
|
| [1] |
李志锋. 中非铜矿带地质勘查新进展[J]. 矿产与地质, 1992, 6(6):448-453.
|
| [1] |
Li Z F. Progress updated in geological exploration of copper ore belt in Central Africa[J]. Mineral Resource and Geology, 1992, 6(6):448-453.
|
| [2] |
任军平, 王杰, 刘晓阳, 等. 非洲中南部卢弗里安地区Cu-Co矿床研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(5),135-145.
|
| [2] |
Ren J P, Wang J, Liu X Y. Research progress of Cu-Co deposits in Lufilian area of South Central Africa[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(5):135-145.
|
| [3] |
陶则熙. 刚果(金)加丹加铜矿带地质特征及成矿前景[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(2):392-398.
|
| [3] |
Tao Z X. Geological characteristics and metallogenic prospect of Katanga Copper Belt in DRC[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2016, 52(2):392-398.
|
| [4] |
刘国平, 肖波, 孙希文, 等. 非洲卢富里安成矿带地质演化与找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2018.
|
| [4] |
Liu G P, Xiao B, Sun X W, et al. Geological evolution and exploration of the Lufilian metallogenic belt in Africa[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2018.
|
| [5] |
曾高福, 姚锦其, 黄学强, 等. 综合物探方法在刚果(金)马本德地区铜矿的应用研究[J]. 矿产与地质, 2016, 30(3):462-467.
|
| [5] |
Zeng G F, Yao J Q, Huang X Q, et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical prospecting to copper deposits in Mabende area,DRC[J]. Mineral Resource and Geology, 2016, 30(3):462-467.
|
| [6] |
黄学强, 姚锦其, 张学良, 等. 刚果(金)加丹加成矿带隐伏铜钴矿地质—地球化学找矿标志及应用效果[J]. 矿产与地质, 2019, 33(5):868-873,878.
|
| [6] |
Huang X Q, Yao J Q, Zhang X L, et al. Geological-geochemical prospecting mark of concealed Co-Cu deposits in Katanga metallogenic beltand the application effect,DRC[J]. Mineral Resource and Geology, 2019, 33 (5):868-873,878.
|
| [7] |
童海奎, 杨自安, 张普斌, 等. 刚果(金)东南部加丹加成矿带遥感找矿前景分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2008, 22(6):547-550.
|
| [7] |
Tong H K, Yang Z A, Zhang P B, et al. Prospect analysis of remote sensing exploration of Katanga Metallogenic Belt in Southeast Congo[J]. Mineral Resource and Geology, 2008, 22(6):547-550.
|
| [8] |
陈远荣, 贾国相, 徐庆鸿. 气体集成快速定位预测隐伏矿的新技术研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2003:58-63.
|
| [8] |
Chen Y R, Jia G X, Xu Q H. Research on new technology aboutgas integration rapid orientation and prognois of concealed ore[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003:58-63.
|
| [9] |
徐庆鸿, 陈远荣, 贾国相, 等. 烃类组分在金属矿床的成矿理论和矿产勘查研究中的应用[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(10):2623-2638.
|
| [9] |
Xu Q H, Chen Y R, Jia G X, et al. Application of hydrocarbon components in metallogenic theory and mineral exploration of metal deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(10):2623-2638.
|
| [10] |
李向前. 中非铜带刚果(金)段成矿系列和成矿规律[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2011.
|
| [10] |
Li X Q. Metallogenic series and regularity of the Congo(DRC) section of the Central African copper belt[D]. Bejing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2011.
|
| [11] |
Boyle R W, Brown A C, Jafferson, et al. Sediment-hosted stratiform copper deposits[J]. Geological Association of Canada:Special Paper, 1989, 36:710.
|
| [12] |
Kirkiiam R V. Distribution,settings,and genesis of sediment-hosted stratiform copper deposits[J]. Geological Association of Canada:Special Paper, 1989, 36:3-38.
|
| [13] |
Hitzman M, Kirkham R, Broughton D, et al. The sediment-hosted stratiform copper ore system[J]. Economic Geology 100th Anniversary Volume, 2005, 160:609-642.
|
| [14] |
张东红, 肖波. 中部非洲沉积型铜—钴矿地质及找矿潜力[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2013:76,113.
|
| [14] |
Zhang D H, Xiao B. Geology and prospecting potential of sedimentary Co-Cu deposits in Central Africa[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2013:76,113.
|
| [15] |
任超, 孙希文, 王洪勇. 赞比亚卢安夏盆地控矿特征及矿床成因探讨[J]. 有色矿冶, 2017, 33(3):1-6.
|
| [15] |
Ren C, Sun X W, Wang H Y. Ore-control characteristics and genesis of the luanshya Basin in Zambia[J]. Non-Ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2017, 33(3):1-6.
|
| [16] |
陈远荣, 戴培根. 金属矿床有机烃气常见异常模式和成因机理研究[J]. 中国地质, 2001, 28(6):32-37.
|
| [16] |
Chen Y R, Dai P G. Study on common anomaly model and genetic mechanism of organic hydrocarbon gas in metal deposits[J]. Geology in China, 2001, 28(6):32-37.
|
| [17] |
陈远荣, 贾国相, 徐庆鸿, 等. 金属矿床成矿和勘查中有机物的作用研究[J]. 南方国土资源, 2004(11):89-90.
|
| [17] |
Chen Y R, Jia G X, Xu Q H, et al. Study on the role of organic matter in mineralization and exploration of metal deposits[J]. Land and Resources of Southern China, 2004(11):89-90.
|
| [1] |
XU Xue-Yi, XIONG Sheng-Qing, YANG Xue, GAO Wei-Hong, FAN Zheng-Guo, JIA Zhi-Ye. Aerogeophysical anomalies and prospecting direction in the Fengtai ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1157-1168. |
| [2] |
TAI Wen-Xing, YANG Cheng-Fu, JIN Xiao-Ye, SHAO Yun-Bin, LIU Guang-Fu, ZHAO Ping, WANG Ze-Peng, TAN Li-Jin. Application of the multi-dimensional study of geochemical anomalies in deep metallogenic prediction of the Zhexiang gold deposit in southwestern Guizhou, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 856-867. |
|
|
|
|

