|
|
|
| Application of the integrated geophysical exploration technology in the exploration of deep carbonate geothermal reservoirs: A case study of the Xiong'an New Area |
ZHANG Zhao1( ), YIN Quan-Zeng1, ZHANG Long-Fei1( ), YIN Quan-Zeng1, ZHANG Long-Fei1( ), ZHANG Da-Ming1, ZHANG Shi-Hui2, HUANG Guo-Shu2, ZHAO Shi-Feng1, YANG Biao3, TAI Li-Xun1, ZHANG Deng-Liang1, WANG Jin-Chao1, DUAN Gang1 ), ZHANG Da-Ming1, ZHANG Shi-Hui2, HUANG Guo-Shu2, ZHAO Shi-Feng1, YANG Biao3, TAI Li-Xun1, ZHANG Deng-Liang1, WANG Jin-Chao1, DUAN Gang1 |
1. Geophysical Exploration Team, Hebei Coal Field Geology Bureau, Xingtai 054000, China
2. School of Geophysics and Geomatics,China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),Wuhan 430074,China
3. Hebei Coal Field Geology Bureau,Shijiazhuang 050085, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Xiong'an New Area has great potential for geothermal resources. Carbonate rocks are favorable reservoirs for deep geothermal resources in this area. The integrated geophysical exploration technology is an effective way to ascertain the deep structures and the characteristic stratigraphic structure of carbonate geothermal reservoirs. Aiming at the exploration target of deep carbonate geothermal reservoirs, this study put forward a surface-line-point hierarchical and progressive geophysical exploration model. Using the high-precision gravity and aeromagnetic data, this model first investigated the distribution range of carbonate rocks, the thickness of carbonate strata, the distribution of deep-seated faults, and the fluctuation of bedrocks. Then, it analyzed the low-resistivity anomalies of geothermal reservoir strata using the magnetotelluric method. Finally, this model finely characterized the geothermal reservoir strata using two-dimensional seismic profiles and analyzed the velocity structure and regional structural characteristics of anomaly zones in the geothermal field. Based on the exploration precision and reliability of gravity, aeromagnetic, magnetotelluric, and seismic geophysical methods in the geothermal resource exploration of different stages, as well as other factors such as construction cost and efficiency, this study analyzed the economic applicability of geophysical methods in the exploration of deep karst geothermal reservoirs and suggested that the carbonate geothermal resources should be explored using the geophysical exploration technology combination of gravity, magnetic, and magnetotelluric methods.
|
|
Received: 13 July 2022
Published: 11 October 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
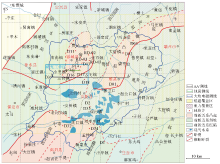
|
Geological structure distribution of Xiong'an New Area and geophysical work distribution of the study area
|

| 地层代号 | 岩性 | 平均密度/(g·c ) | 磁化率κ/10-5SI | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | | 新生界 | 第四系 | Q | 亚黏土、砂土、 | 2.05 | 55~610 | 5~12 | | 新近系 | Nm | 粉砂岩、细砂岩、含砾砂岩 | 2.21 | 0~200 | 4~15 | | Ng | 砂岩、含砾砂岩、泥岩 | 5~80 | 3~6 | | 古近系 | Ed+Es | 泥岩、粉砂岩、细砂岩、砂泥岩 | 2.4 | 0~500 | 1~10 | | 古生界 | 石炭—二叠系 | C-P | 泥岩、砂岩、含砾砂岩 | 2.50 | 0~50 | 10~35 | | 寒武—奥陶系 | ?-O | 灰岩、白云质灰岩 | 2.67 | 0 | 40~60 | | 元古宇 | | Pt | 泥岩、灰岩、白云岩 | 2.7 | 0~200 | >50 | | 太古宇 | | Ar | 片岩、片麻岩、变粒岩、斜
长角闪岩、混合岩、大理岩 | 2.73 | 1500~8500 | |
|
Physical parameters of strata in the working area
|
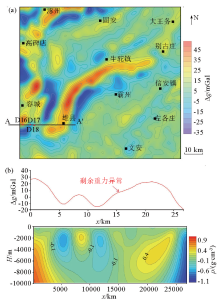
|
Analysis of residual gravity anomaly in Xiong'an New Area
a—qravity anomaly in the study area;b—gravity inversion of A-A' line
|
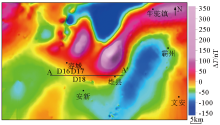
|
Study area 1:50,000 to geomagnetic pole after aeromagnetism ΔT anomaly
|
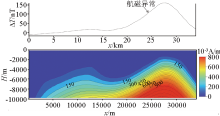
|
Magnetization inversion section across A-A' line
|
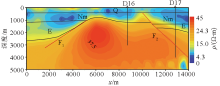
|
Inversion resistivity profile and geological interpretation profile of line D3
|
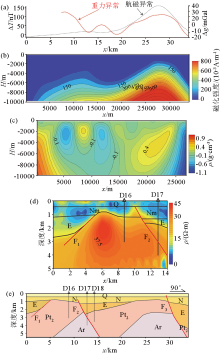
|
Geological geophysical comprehensive interpretation section of A-A' line
a—gravity and magnetic anomaly profile;b— magnetization inversion profile;c—gravity inversion profile;d—magnetotelluric inversion profile; e—comprehensive interpretation of geological profile
|
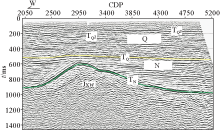
|
2D seismic survey line in the south of Rongcheng uplift
|
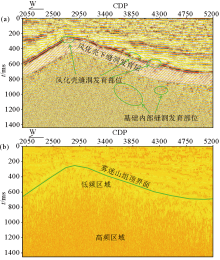
|
Seismic wave anomaly analysis
a—amplitude attribute; b—instantaneous frequency
|

工作
手段 | 优势 | 劣势 | 调查阶段 | 预可行性勘查阶段 | 可行性勘
查阶段 | 开采阶段 | 权重
比 | | 重力 | 控制地热的区域构造;探测热田位置和与热源有关的火成岩;了解热田的基底面起伏及计算基岩的埋藏深度 | 对具体控热构造探测效果差 | 圈定勘查区基底面起伏及断裂构造的空间展布 | 圈定勘查区基底面起伏及断裂构造的空间展布 | 圈定勘查区基底面起伏及断裂构造的空间展布 | 8 | | 磁法 | 勾画出地热区的坳陷和基底构造,寻找控制地下热水资源的构造,如断层和火成岩体等 | 无法精细划分热储构造,热储层埋藏深度等 | 确定岩浆岩岩体的分布及蚀变带位置 | 确定岩浆岩岩体的分布及蚀变带位置 | 查明热储地层结构、岩浆岩分布范围 | 8 | 大地
电磁 | 控制热储盖层的结构、形态、范围、厚度等;对大型导热断裂带有良好反映;其中电阻率与地热温度预测关系密切,可进行热储温度预测 | 对热储层精细分层,小构造控制略差 | 一般不采用 | 确定热储深度与范围,断裂构造和热异常 | 基本确定热储深度与范围,断裂构造和热异常,结合公式预测热储温度 | 12 | | 地震 | 精确推测断层位置、产状、地层埋深;通过地震波速分布,可以圈定地热田的范围 | 地震属性参数与地热探测温度预测难于发生联系 | 一般不采用 | 一般不采用 | 准确圈定热储埋深、储层结构及断裂位置和产状 | 详细查明热储地质构造、岩性、厚度、分布范围和埋藏条件 | 10 |
|
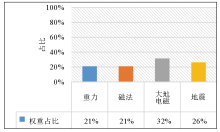
List of accuracy and reliability of geophysical methods in detecting deep thermal storage
|

| 名称 | 调查
阶段 | 预可行勘
查阶段 | 勘查
阶段 | 开采
阶段 | 小计 | 归一化
百分比/% | | 重力 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 21 | | 磁法 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 21 | | 大地电磁 | 1.5 | 4 | 3.5 | 3 | 12 | 32 | | 地震 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 10 | 26 |
|
Proportion statistics of geothermal exploration in different stages
|
|
Histogram of exploration accuracy and reliability weight of geophysical method in detecting deep thermal reservoir
|

工作
方式 | 工作
方法 | 结构探测
精度及
可靠性 | 施工
成本 | 人员
投入 | 设备
投入 | 施工
工期 | 剖面
测量 | 重力 | 21% | 4.78% | 18% | 11% | 21% | | 磁法 | 21% | 1.85% | 18% | 11% | 17% | | 大地电磁 | 32% | 12.29% | 18% | 11% | 27% | | 地震 | 26% | 81.08% | 48% | 67% | 35% | 面积
测量 | 重力 | 21% | 1.33% | 15% | 13% | 16% | | 磁法 | 21% | 0.34% | 19% | 13% | 16% | | 大地电磁 | 32% | 4.75% | 19% | 13% | 27% | | 地震 | 26% | 93.59% | 46% | 63% | 40% |
|
Proportion of geothermal in geophysical exploration
|

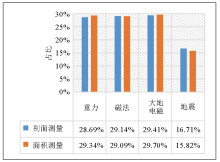
| 项目 | 结构探测
精度及
可靠性 | 施工
成本 | 人员
投入 | 设备
投入 | 施工
工期 | 小计 | 结构探测
精度及
可靠性 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | | 施工成本 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 | | 人员投入 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 | | 设备投入 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 | | 施工工期 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2 |
|
Statistics of weight proportion of economic applicability evaluation items based on priority chart method
|

| 工作方式 | 工作方法 | 结构探测精度
及可靠性 | 施工成本 | 人员投入 | 设备投入 | 施工工期 | 小计 | 归一化百分占比 | | 剖面测量 | 重力 | 0.95 | 1.90 | 1.65 | 1.78 | 1.59 | 7.87 | 28.69% | | 磁法 | 0.95 | 1.96 | 1.65 | 1.78 | 1.65 | 7.99 | 29.14% | | 大地电磁 | 1.42 | 1.75 | 1.65 | 1.78 | 1.46 | 8.06 | 29.41% | | 地震 | 1.18 | 0.38 | 1.05 | 0.67 | 1.30 | 4.58 | 16.71% | | 面积测量 | 重力 | 0.95 | 1.97 | 1.70 | 1.75 | 1.67 | 8.05 | 29.34% | | 磁法 | 0.95 | 1.99 | 1.61 | 1.75 | 1.67 | 7.98 | 29.09% | | 大地电磁 | 1.42 | 1.91 | 1.61 | 1.75 | 1.45 | 8.14 | 29.70% | | 地震 | 1.18 | 0.13 | 1.07 | 0.75 | 1.20 | 4.34 | 15.82% |
|
Proportion of economic applicability evaluation of geothermal resources detected by geophysical methods
|
|
Histogram of economic applicability of geophysical method to detect deep thermal reservoir
|
| [1] |
刘桂宏. 城市深层热储热水力多场耦合模拟方法与应用[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学(徐州), 2019.
|
| [1] |
Liu G H. Multi-field coupling simulation method and application of urban deep thermal storage water power[D]. Xuzhou: China Mining University(Xuzhou), 2019.
|
| [2] |
江勇. 基于系统动力学的地热产业发展财税政策模拟与选择[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.
|
| [2] |
Jiang Y. Simulation and selection of fiscal and tax policies for geothermal industry development based on system dynamics[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2020
|
| [3] |
杨学新, 刘洪升. 雄安新区建置的历史沿革及其特征[J]. 河北大学学报:哲学社会科学版, 2019, 44(4):131-135.
|
| [3] |
Yang X X, Liu H S. Historical evolution and characteristics of the administrative organization system of the Xiong'an New Area[J]. Journal of Hebei University:Philosophy and Social Science, 2019, 44(4):131-135.
|
| [4] |
武斌. 松潘甘孜地区地热资源的地球物理勘探研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013.
|
| [4] |
Wu B. Geophysical exploration of geothermal resources in Songpan Ganzi area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013.
|
| [5] |
赵佳怡, 张薇, 马峰, 等. 雄安新区容城地热田地热流体化学特征[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1991-2001.
|
| [5] |
Zhao J Y, Zhang W, Ma F, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the geothermal fluid in the Rongcheng geothermal field,Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):1991-2001.
|
| [6] |
马峰, 王贵玲, 张薇, 等. 雄安新区容城地热田热储空间结构及资源潜力[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1981-1990.
|
| [6] |
Ma F, Wang G L, Zhang W, et al. Structure of geothermal reservoirs and resource potential in the Rongcheng geothermal field in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):1981-1990.
|
| [7] |
尹军. 流域干旱还原理论与方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国水利水电科学研究院, 2017.
|
| [7] |
Yin J. Study on theory and method of drought reduction in river basin[D]. Beijing: China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, 2017.
|
| [8] |
魏广仁. 雄安新区蓟县系岩溶热储缝洞储层发育规律研究[J]. 石化技术, 2020, 27(8):248-249.
|
| [8] |
Wei G R. Study on the development law of Jixian karst thermal reservoir fracture cave reservoir in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology, 2020, 27(8):248-249.
|
| [9] |
姜鲁光, 吕佩忆, 封志明, 等. 雄安新区土地利用空间特征及起步区方案比选研究[J]. 资源科学, 2017, 39(6):991-998.
|
| [9] |
Jiang L G, Lyu P Y, Feng Z M, et al. Study on spatial characteristics of land use and scheme comparison of starting area in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Resource Science, 2017, 39 (6):991-998.
|
| [10] |
胡秋韵, 高俊, 马峰, 等. 雄安新区容城凸起区地热可采资源量动态预测[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):2013-2025.
|
| [10] |
Hu Q Y, Gao J, Ma F, et al. Dynamic prediction of geothermal recoverable resources in the Rongcheng uplift area of the Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):2013-2025.
|
| [11] |
陈墨香, 汪集旸, 汪缉安, 等. 华北断陷盆地热场特征及其形成机制[J]. 地质学报, 1990, 64(1):80-91.
|
| [11] |
Chen M X, Wang J Y, Wang J A, et al. The characteristics of the geothermal field and its formation mechnism in the north China down-faulted basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1990, 64(1):80-91.
|
| [12] |
汪集旸, 邱楠生. 含油气沉积盆地古地温研究方法[J]. 地球物理学进展, 1992, 7(4):46-62.
|
| [12] |
Wang J Y, Qiu N S. Research method of paleogeothermal in petroliferous sedimentary basin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 1992, 7 (4):46-62.
|
| [13] |
王贵玲, 李郡, 吴爱民, 等. 河北容城凸起区热储层新层系——高于庄组热储特征研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(5):533-541.
|
| [13] |
Wang G L, Li J, Wu A M, et al. A study of the thermal storage characteristics of Gaoyuzhuang formation:A new layer system of thermal reservoir in Rongcheng uplift area, Hebei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2018, 39(5):533-541.
|
| [14] |
郭世炎, 李小军. 河北保定容城凸起地热田储层属性与资源潜力[J]. 地质科学, 2013, 48(3):922-931.
|
| [14] |
Guo S Y, Li X J. Reservoir stratum characterstics and geothermal resources potential of Rongcheng uplift geothermal field in Baoding, Hebei[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2013, 48(3):922-931.
|
| [15] |
陈墨香, 汪集旸, 邓孝. 中国地热系统类型图及其简要说明[J]. 地质科学, 1996, 31(2):114-121.
|
| [15] |
Chen M X, Wang J Y, Deng X. The map of geothermal system types in China and its brief explantion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1996, 31(2):114-121.
|
| [16] |
庞忠和, 胡圣标, 汪集旸. 中国地热能发展路线图[J]. 科技导报, 2012, 30(32):18-24.
|
| [16] |
Pang Z H, Hu S B, Wang J Y. A Roadmap to geothermal energy development in China[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2012, 30(32):18-24.
|
| [17] |
王贵玲, 高俊, 张保建, 等. 雄安新区高阳低凸起区雾迷山组热储特征与高产能地热井参数研究[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(7):1970-1980.
|
| [17] |
Wang G L, Gao J, Zhang B J, et al. Study on the thermal storage characteristics of the Wumishan Formation and huge capacity geothermal well parameters in the Gaoyang low uplift area of Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(7):1970-1980.
|
| [18] |
鲁锴, 鲍志东, 季汉成, 等. 雄安新区蓟县系雾迷山组岩溶热储特征、主控因素及有利区预测[J]. 古地理学报, 2019, 21(6):885-900.
|
| [18] |
Lu K, Bao Z D, Ji H C, et al. Characteristics, main controlling factors and favorable area prediction of karstic geothermal reservoirs of the Jixianian Wumishan Formation in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2019, 21(6):885-900.
|
| [19] |
赵丰年, 刘金侠, 马春红. 积极实施标准化开发引领地热行业科学发展[J]. 中国石化, 2015(7):64-65.
|
| [19] |
Zhao F N, Liu J X, Ma C H. Actively implement standardized development and lead the scientific development of geothermal industry[J]. China Petroleum and Chemical Industry, 2015(7):64-65.
|
| [20] |
陈雄. 地球物理方法在干热岩勘查中的应用研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016.
|
| [20] |
Chen X. Study on the application of geophysical methods in dry-hot rock exploration[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016.
|
| [21] |
曾昭发, 陈雄, 李静, 等. 地热地球物理勘探新进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(1):168-178.
|
| [21] |
Zeng Z F, Chen X, Li J, et al. Advancement of geothermal geophysics exploration[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(1):168-178.
|
| [1] |
ZHENG Xu-Ying, XU Ke-Wei, GU Lei, WANG Guo-Jian, LI Guang-Zhi, GUO Jia-Qi, ZOU Yu, BORJIGIN Tenger. Distribution of microorganisms in the typical geothermal field environment and its significance for geothermal exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1127-1136. |
| [2] |
ZHAO Bao-Feng, WANG Qi-Nian, GUO Xin, GUAN Da-Wei, CHEN Tong-Gang, FANG Wen. Gravity survey and audio magnetotellurics-based insights into the deep structures and geothermal resource potential of the Rucheng Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1147-1156. |
|
|
|
|

