|
|
|
| An analysis of the fault framework in southern Ningxia based on geophysical data |
HU Xin-Jun1,2( ), CHEN Xiao-Jing1( ), CHEN Xiao-Jing1( ), WU Yang1, BAI Ya-Dong1, ZHAO Fu-Yuan1 ), WU Yang1, BAI Ya-Dong1, ZHAO Fu-Yuan1 |
1. Geophysical and Geochemical Survey Institute of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region,Yinchuan 750001,China
2. School of Earth Resources, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan),Wuhan 430074,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Southern Ningxia, located in a typical loess tableland area, hosts five semi-concealed - semi-exposed faults as boundaries of tectonic units. Based on the regional geotectonic conditions and outcrops, this study analyzed the distribution of the geophysical anomaly field in the study area, ascertained the distribution morphology of the concealed fault sections and the relationship between the faults, and established the fault framework in southern Ningxia. Based on the 1:200000 regional gravity and aeromagnetic data, this study extracted the weak signals of deep gravity and magnetic anomalies reflecting faults using both the multi-scale wavelet decomposition technique and the boundary recognition method and compared these signals with the deep faults depicted based on MT profiles. The results show that the five major faults in the study area are the boundaries of the significant gravity high anomaly zones in the detailed second-order wavelet field of gravity. The Niushoushan-Luoshan-Kongtongshan fault is the boundary between the north-south-trending long strip-shaped gravity anomalies and the north-west-trending flaky and banded gravity anomalies. This fault has typical dextral strike-slip characteristics and is the boundary fault between the Alxa microcontinent and the Ordos block. The Haiyuan fault is divided into Haiyuan faults Nos. 1 and 2 at depth. The No. 1 Haiyuan fault is concealed in the Haiyuan Basin and does not exhibit gravity anomalies. Moreover, the aeromagnetic anomaly field of this fault has significant zoning characteristics. The No. 2 Haiyuan fault is exposed at the northeastern feet of the northern and southern Mount Huashan and exhibits distinct characteristics of linear gravity anomalies but weak aeromagnetic anomalies. The two faults jointly constitute the composite boundary between the Early Paleozoic North Qilian Orogenic Belt and the Alxa microcontinent. Three faults in the Alxa microcontinent, namely the Tianjingshan fault, the Yantongshan-Yaoshan fault, and the fault at the eastern piedmont of Luoshan, are present as the northeastern boundary of the arcuate high-amplitude gravity anomaly zone.
|
|
Received: 02 August 2022
Published: 11 October 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
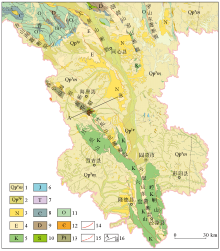
|
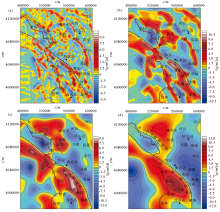
Geological structure map of Southern Ningxia
1—Quaternary eolian deposit;2—Quaternary diluviun;3—Neogene;4—Paleogene;5—Cretaceous;6—Jurassic;7—Triassic;8—Carboniferous;9—Devonian;10—Silurian;11—Ordovician;12—Caimbrian;13—Proterzoic;14—Exposed fault;15—Concealed fault;16—MT profile
|
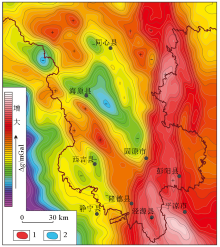
|
Bouguer gravity anomaly
1—high gravity anomaly;2—low gravity anomaly
|
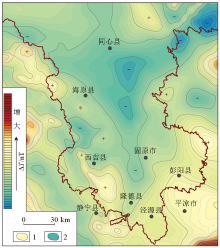
|
Polarization aeromagnetic anomaly
1—high aeromagnetic anomaly;2—low aeromagnetic anomaly
|
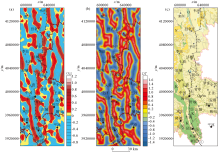
|
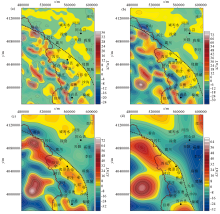
Comprehensive analysis of Niushoushan-Luoshan fault
a—vertical second derivative map;b—tilt angle map;c—fault distribution map
|

| 断裂亚段 | 走向 | 长度/km | 走滑距/km | 地质特征 | | 东侧 | 西侧 | | 第①亚段 | NNW335° | 17.4 | 2.3 | 大面积的古近系清水营组,穿插展布白垩系李洼峡组与三桥组 | 白垩系马东山组、古近系清水营组,局部见寺口子组 | | 第②亚段 | NNW329° | 27.8 | 大面积分布白垩系李洼峡组和马东山组,局部见有古近系寺口子组,在沙南东部见条带状出露的三叠系崆峒山组 | 大范围覆盖古近系寺口子组与清水营组,河流沟渠低洼处局部沉积第四系粉砂土层 | | 2.4 | | 第③亚段 | NNW352° | 46.3 | 全范围出露白垩系马东山组,在杨庄的东部,局部出露的奥陶系天景山组 | 分布古近系寺口子组与清水营组 | | 2.6 | | 第④亚段 | NNW349° | 10.3 | 被第四系黄土层覆盖,但在程几山附近有白垩系马东山组出露 | 分布第四系马兰组黄土层 | | 5.3 | | 第⑤亚段 | SN354° | 30.1 | 被第四系马兰组黄土层大面积覆盖,局部出露古近系寺口子组与清水营组,白垩系马东山组和三桥组,侏罗系延安组与中元古界王全口组 | 被第四系马兰组黄土层大面积覆盖,基本无前第四系地层出露 | | 12.0 | | 第⑥亚段 | NNW349° | 33.0 | 严湾东南地区出露地层主要为奥陶系天景山组、寒武系阿布切亥组和中元古界王全口组 | 双井地区出露白垩系马东山组、三桥组与侏罗系延安组 | | 9.4 | | 第⑦亚段 | SN354° | 36.5 | 被第四系马兰组黄土层覆盖,在汪家塬南部见有两处奥陶系天景山组出露 | 完全被第四系马兰组黄土层覆盖,未见前第四系地层出露 | | 9.5 | | 第⑧亚段 | SN360° | 38.3 | 甘沟地区见三叠系二马营组 | 大面积覆盖第四系马兰组黄土层与新近系彰恩堡组 |
|
Characteristics of Niushoushan-Luoshan fault
|
|
Gravity field characteristics of Haiyuan fault and Xiangshan South foot fault
a—first-level approximation of gravity wavelet transform;b—second-level approximation of gravity wavelet transform;c—third-level approximation of gravity wavelet transform;d—fourth-level approximation of gravity wavelet transform
|
|
Aeromagnetic field characteristics of Haiyuan fault
a—first-level approximation of aeromagnetic wavelet transform;b—second-level approximation of aeromagnetic wavelet transform;c—third-level approximation of aeromagnetic wavelet transform;d—fourth-level approximation of aeromagnetic wavelet transform
|
|
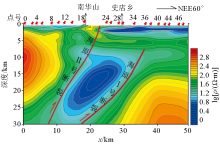
Electrical characteristics of Haiyuan fault
|
|
Spatial distribution of Haiyuan fault
|
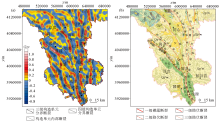
|
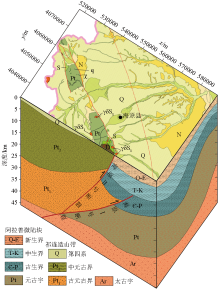
Fault framework in Southern Ningxia
a—fault interpretation map;b—fault distribution map
|
| [1] |
徐占海, 李捍国, 宋新华, 等. 中国区域地质志/宁夏志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017.
|
| [1] |
Xu Z H, Li H G, Song X H, et al. Regional geology of China,Ningxia[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017.
|
| [2] |
杜远生, 朱杰, 韩欣, 等. 从弧后盆地到前陆盆地—北祁连造山带奥陶纪—泥盆纪的沉积盆地与构造演化[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(9/10):911-917.
|
| [2] |
Du Y S, Zhu J, Han X, et al. From the Back-arc basin to foreland basin-Ordovician-Devonian sedimentary basin and tectonic evolution in the North Qilian Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(9/10):911-917.
|
| [3] |
刘亢, 曹代勇, 徐浩, 等. 鄂尔多斯煤盆地西缘古构造应力场演化分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2014, 26(8):87-90.
|
| [3] |
Liu K, Cao D Y, Xu H, et al. Paleotectonic stress field evolutional analysis in west margin of Ordos Coal Basin[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2014, 26(8):87-90.
|
| [4] |
汤桦, 白云来, 房乃珍, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部“古陆梁”的形成和演化[J]. 甘肃地质, 2006, 15(1):3-9.
|
| [4] |
Tang H, Bai Y L, Fang N Z, et al. Forming and evolution of ancient land rise in the Western Ordos Basin[J]. Gansu Geology, 2006, 15(1):3-9.
|
| [5] |
汤锡元, 郭忠铭, 王定一. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部逆冲推覆构造带特征及其演化与油气勘探[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1988, 9(1):1-10.
|
| [5] |
Tang X Y, Guo Z M, Wang D Y. The characteristics and evolution of the thrust nappe tectonic belt and its petroleum potential in the West Ordos Basin[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 1988, 9(1):1-10.
|
| [6] |
翟明国. 华北克拉通构造演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(5):722-745.
|
| [6] |
Zhai M G. Tectonic evolution of the North China Craton[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(5):722-745.
|
| [7] |
吴文忠, 马瑞赟, 潘进礼, 等. 宁夏西吉盆地花岗岩地球化学特征、锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地质通报, 2018, 37(7):1271-1278.
|
| [7] |
Wu W Z, Ma R Y, Pan J L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and Zircon U-Pb ages of the granite in Xiji Basin of Ningxia[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2018, 37(7):1271-1278.
|
| [8] |
杨勇, 闫国祥. 宁夏西吉盆地磁异常带综合地球物理特征及其地质认识[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2017(4):129-132.
|
| [8] |
Yang Y, Yan G X. Comprehensive geophysical characteristics and geological understanding of magnetic anomaly zone in Xiji Basin[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2017(4):129-132.
|
| [9] |
宋新华, 张鹏川, 程建华, 等. 六盘山盆地时空演化与岩盐成矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015.
|
| [9] |
Song X H, Zhang P C, Cheng J H, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution and salt mineralization in Liupanshan Basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015.
|
| [10] |
张磊. 六盘山盆地白垩系沉积构造演化及原型盆地研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学(华东), 2009.
|
| [10] |
Zhang L. The depositional evolution and tertiary tectonic and reconstruction of the cretaceous proto-type basin in Liupanshan Basin[D]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2009.
|
| [11] |
汤济广, 梅廉夫, 李祺, 等. 六盘山盆地构造演化及对成藏的控制[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2009, 31(5):1-6.
|
| [11] |
Tang J G, Mei L F, Li Q, et al. Tectonic evolution and its control on reservoir formation in Liupanshan Basin[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2009, 31(5):1-6.
|
| [12] |
舒志国. 六盘山盆地西缘逆掩推覆构造的发现与油气地质意义[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2007, 29(3):176-177.
|
| [12] |
Shu Z G. Discovery of overridden structure in the western margin of Liupanshan Basin and it’s geologic significance of oil and gas[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2007, 29(3):176-177.
|
| [13] |
施玮, 张岳桥, 马寅生, 等. 六盘山盆地形成和改造历史及构造应力场演化[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(5):1066-1074.
|
| [13] |
Shi W, Zhang Y Q, Ma Y S, et al. Formation and modification history of the Liupanshan Basin on the southwestern margin of the Ordos Block and tectonic stress field evolution[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(5):1066-1074.
|
| [14] |
赵国泽, 詹艳, 王立凤, 等. 鄂尔多斯断块地壳典型结构[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(3):345-359.
|
| [14] |
Zhao G Z, Zhan Y, Wang L F, et al. Electric structure of the crust beneath the Ordos Fault Block[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2010, 32(3):345-359.
|
| [15] |
李斌. 鄂尔多斯盆地西部冲断带构造与控油气因素研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.
|
| [15] |
Li B. Thrust structure and its effect on hydrocarbon in the western margin of Ordos Basin[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2019.
|
| [16] |
李天斌. 宁夏南部弧形推覆构造带特征及演化[J]. 地质力学学报, 1999, 5(3):22-27.
|
| [16] |
Li T B. The feature and formation mechanism of arciform thrust-nappe structure zone of the southern Ningxia[J]. Journal of Geomechannics, 1999, 5(3):22-27.
|
| [17] |
白亚东, 安百州, 张海波, 等. 宁夏区内北祁连构造带与鄂尔多斯地块边界探讨[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2017, 39(5):587-597.
|
| [17] |
Bai Y D, An B Z, Zhang H B, et al. A discussion of the north Qilian structural in Ningxia and Ordos Block Boundary[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 39(5):587-597.
|
| [18] |
俞岗, 尹功明, 王旭龙. 香山—天景山断裂活动时代的光释光测年[J]. 华南地震, 2013, 33(4):87-92.
|
| [18] |
Yu G, Yin G M, Wang X L. Optical dating of the Xiangshan-Tianjingshan Fault[J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 2013, 33(4):87-92.
|
| [19] |
王伟涛, 张培震, 雷启云. 牛首山—罗山断裂带的变形特征及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(2):195-207.
|
| [19] |
Wang W T, Zhang P Z, Lei Q Y. Deformational characteristics of the Niushoushan-Luoshan fault zone and its tectonic implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2013, 35(2):195-207.
|
| [20] |
郑文俊, 张博繯, 袁道阳, 等. 阿拉善地块南缘构造活动特征与青藏高原东北缘向外扩展的最新边界[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2021, 43(2):224-236.
|
| [20] |
Zheng W J, Zhang B X, Yuan D Y, et al. Tectonic activity in the southern Alashan Block and the latest boundary of outward expansion on the Northeastern Tibetan Plateau,China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2021, 43(2):224-236.
|
| [21] |
王勇, 施玮. 六盘山盆地白垩纪构造变形分析及其盆地形成演化[J]. 煤炭技术, 2007, 26(11):101-104.
|
| [21] |
Wang Y, Shi W. Analysis of structural deformation of Liupanshan Basin and basin formation and Changing[J]. Coal Technology, 2007, 26(11):101-104.
|
| [22] |
李宁生, 冯志民, 朱秦, 等. 宁夏区域重磁资料开发利用研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.
|
| [22] |
Li N S, Feng Z M, Zhu Q, et al. Development and utilization of gravity and magnetic data in Ningxia area[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016.
|
| [23] |
尹秉喜, 闵刚. 宁夏中上地壳结构特征研究[M]. 宁夏: 宁夏人民出版社, 2014.
|
| [23] |
Yin B X, Min G. Study on the structural characterristics of the middle and upper crust in NingXia[M]. NingXia: Ningxia People’s Publishing House, 2014.
|
| [24] |
金胜, 张乐天, 金永吉, 等. 青藏高原东北缘合作—大井剖面地壳电性结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(12):3979-3990.
|
| [24] |
Jin S, Zhang L T, Jin Y J, et al. Crustal electrical structure along the Hezuo-Dajing profile across the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(12):3979-3990.
|
| [1] |
MENG Qing-Kui, ZHANG Wen-Zhi, GAO Wei, SHU Qing, LI Rui, XU Guang-Jing, ZHANG Kai-Song. Property analysis and application of multi-scale wavelet decomposition of gravity potential field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4): 946-954. |
| [2] |
XIA Hong-Min, ZHENG Xiao-Wen, HUANG Han-Dong, XIAO Yan-Hui, DONG Jin-Chao, LIAO Jun. The application of low-amplitude structure based on low-frequency reduction[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4): 998-1003. |
|
|
|
|

