|
|
|
| Suitability of geological conditions in Suanjingzi area for the disposal of high-level radioactive wastes |
JIANG Shi1( ), LUO Hui2( ), LUO Hui2( ), CHEN Wei-Ming2, LI Ya-Wei2, JIN Yuan-Xin2 ), CHEN Wei-Ming2, LI Ya-Wei2, JIN Yuan-Xin2 |
1. China Aero Geophysical Survey and Remote Sensing Center for Natural and Resources,Beijing 100083, China
2. CNNC Key Laboratory on Geological Disposal of High-level Radioactive Waste, Beijing Research Institute of Uranium Geology, Beijing 100029, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on investigations of geological characteristics of ground surface and deep parts and three-dimensional geological modeling, this study preliminarily ascertains the lithology of rock masses and the spatial distribution characteristics of faults in the Suanjingzi area, obtaining and the following understanding. In terms of lithology, the Suanjingzi area mainly consists of granodiorites with an exposed area of about 176 km2 and a depth of more than 2 km. The granites occur in the form of batholith and are generally distributed in the NE-SW trending, which is consistent with the direction of the main tectonic line in the study area. Meanwhile, they feature single lithology, high integrity of deep rock masses, and slight rock alteration. There are nine faults in the study area in total. They have roughly developed in rock masses and have steep dip angles. A rock mass with an area of greater than 31 km2 can be selected from the granites, which has single lithology, large enough volume, and high integrity and maybe used as a candidate site of the disposal repository of high-level radioactive wastes in the future. Overall, the Suanjingzi area has suitable geological conditions as a pre-selected site for the geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastes.
|
|
Received: 14 June 2021
Published: 15 December 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
LUO Hui
E-mail: 45493666@qq.com;luo1029hui@163.com
|
|
|
|
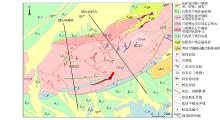
|
Geological map of Suanjingzi area
|

| 地层名称及代号 | 出露面积/km2 | 面积占比/% | | 第四系全新统(Qhapl) | 133.52 | 28.91 | | 白垩系下统赤金堡组(K1c) | 96.35 | 20.86 | | 石炭系下统白山组(C1b) | 29.37 | 6.36 | | 志留系中统公婆泉群(S2gp) | 13.52 | 2.93 | | 青白口系圆藻山群大豁落山组(Qbd) | 8.44 | 1.83 |
|
Statistics on the outcropping of each layer in the Shoujingzi area
|

| 编号 | 性质 | 长度/km | 产状 | | 倾向 | 倾角 | | F0 | 压扭性 | 8.5 | 311°~322° | 68°~86° | | F1 | 压扭性 | 5.0 | 26°~35° | 75°~85° | | F2 | 压扭性 | 5.5 | 227°~247° | 57°~72° | | F3 | 压扭性 | 5.3 | 151° | 65° | | F4 | 压扭性 | 7.0 | 322°~338° | 67°~72° | | F5 | 压扭性 | 19.0 | 293° | 53° | | F6 | 压扭性 | 20.0 | 325° | 83° | | F7 | 压扭性 | 4.5 | 220°~230° | 55°~65° | | F8 | 压扭性 | 3.8 | 32°~57° | 58°~82° |
|
Structural features of faults in the Suanjingzi area
|
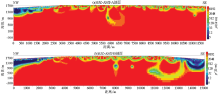
|
Two-dimensional inversion of resistivity of AMT probe profiles for geoelectrical area
|

|
Statistics of inclination angle of core fissures in BS22 and BS23
|
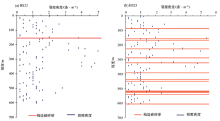
|
The degree of development of core fissures varies with depth in BS22 and BS23
|

| Jv/(条·m-3) | <3 | 3~10 | 10~20 | 20~35 | >35 | | Kv | >0.75 | 0.75~0.55 | 0.55~0.35 | 0.35~0.15 | <0.15 |
|
Comparison value of Jv and Kv
|

| 岩石完整程度 | Kv | BS22所占比例/% | BS23 所占比例/% | | 完整 | >0.75 | 77.9 | 61.3 | | 较完整 | 0.75~0.55 | 7.4 | 17.9 | | 较破碎 | 0.55~0.35 | 10.5 | 9.4 | | 破碎 | 0.35~0.15 | 4.2 | 11.3 | | 极破碎 | ≤0.15 | 0 | 0 |
|
Statistics of rock integrity in BS22 and BS23
|

|
Three-dimensional fracture model of Shoujingzi section
|
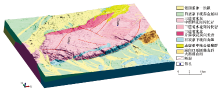
|
Three-dimensional geological model of Shoujingzi section
|
Fig.6)
">
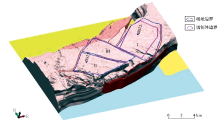
|
Three-dimensional relationship between granite bodies and faults in Shoujingzi area(the legend description is the same as Fig.6)
|
Fig.6)
">
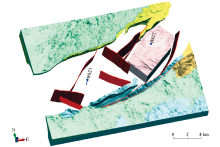
|
The spatial location of the potential site(the legend description is the same as Fig.6)
|
| [1] |
Savage D. The Scientific and regulatory basis for the geological disposal of radioactive waste[M]. Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, 1995.
|
| [2] |
潘自强, 沈文权. 2020年前我国核能发展的策略和目标研究[J]. 铀矿地质, 2004, 20(5):257-259.
|
| [2] |
Pan Z Q, Shen W Q. Tactics and targets for nuclear energy development in China by 2020[J]. Uranium Geology, 2004, 20(5):257-259.
|
| [3] |
潘自强, 钱七虎. 高放废物地质处置战略研究[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2009.
|
| [3] |
Pan Z Q, Qian Q H. Strategic research on geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste [M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2009.
|
| [4] |
王驹. 高放废物地质处置: 进展与挑战[J]. 中国工程科学, 2008, 10(3):58-65.
|
| [4] |
Wang J. Geological disposal of high level radio active waste: Progress and challenges[J]. Engineering Science, 2008, 10(3):58-65.
|
| [5] |
王驹, 陈伟明, 苏锐, 等. 高放废物地质处置及其若干关键科学问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(4):801-812.
|
| [5] |
Wang J, Chen W M, Su R, et al. Geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste and its key scientific issues[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(4):801-812.
|
| [6] |
王驹, 徐国庆, 郑华铃, 等. 中国高放废物地质处置研究进展1985~2004[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2005, 22(1):5-16.
|
| [6] |
Wang J, Xu G Q, Zheng H L, et al. Geological disposal of high level radioactive waste in China: Progress during 1985~2001[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2005, 22(1):5-16.
|
| [7] |
苏锐, 程琦福, 王驹, 等. 我国高放废物地质处置库场址筛选总体技术思路探讨[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2011, 28(1):45-51.
|
| [7] |
Su R, Cheng Q F, Wang J, et al. Discussion on technical ideas of site selection of geological disposal repository for high-level radioactive waste in China[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2011, 28(1):45-51.
|
| [8] |
王驹, 郭永海, 陈伟明, 等. 高放废物地质处置甘肃北山预选区选址和场址评价研究[R]. 北京:核工业北京地质研究院, 2007.
|
| [8] |
Wang J, Guo Y H, Chen W M, et al. Study on the site selection and site evaluation of the geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in Beishan pre-selection area, Gansu [R]. Beijing: Beijing Geological Research Institute of Nuclear Industry, 2007.
|
| [9] |
王驹. 中国高放废物地质处置21世纪进展[J]. 原子能科学技术, 2019, 53(10):2072-2082.
|
| [9] |
Wang J. Progress of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in China in the 21st century[J]. Atomic Energy Science and Technology, 2019, 53(10):2072-2082.
|
| [10] |
王驹, 金远新, 陈伟明, 等. 中国高放废物地质处置库场址区域筛选[R]. 北京:核工业北京地质研究院, 2009.
|
| [10] |
Wang J, Jin Y X, Chen W M, et al. Site selection of geological repository for high-level radioactive waste in China [R]. Beijing: Beijing Geological Research Institute of Nuclear Industry, 2009.
|
| [11] |
罗辉, 王驹, 蒋实, 等. 高放废物地质处置新场岩体三维地质模型构建与应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(3):568-575.
|
| [11] |
Luo H, Wang J, Jiang S, et al. Construction and application of three-dimensional geological model in Xinchang Block for high-level radioactive waste disposal[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(3):568-575.
|
| [12] |
罗辉, 王驹, 蒋实, 等. 高放废物地质处置地下实验室新场候选场址三维地质建模[J]. 铀矿地质, 2017, 33(3):178-183.
|
| [12] |
Luo H, Wang J, Jiang S, et al. Study on 3D geological modeling of Xinchang potential underground laboratory site for high-level radioactive waste disposal[J]. Uranium Geology, 2017, 33(3):178-183.
|
| [13] |
赵宏刚, 王驹, 杨春和, 等. 甘肃北山旧井地段高放废物处置库深度初步探讨[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007(S2):3966-3973.
|
| [13] |
Zhao H G, Wang J, Yang C H, et al. Preliminary discussion on depth for high-level radioactive waste repository in Jiujing block,Beishan area,Gansu Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007(S2):3966-3973.
|
| [14] |
王锡勇, 李冬伟, 成功, 等. 高放废物地质处置的岩体深部结构面特征研究——以甘肃北山高放废物地质处置地下实验室工程为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(3):481-490.
|
| [14] |
Wang X Y, Li D W, Cheng G, et al. Geological disposal of high-level radioactive wastebase to study the structural plane of deep rock mass:A case study of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste used in the underground research laboratory of Gansu Beishan area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(3):481-490.
|
| [15] |
陈伟明, 王驹, 赵宏刚, 等. 高放废物地质处置北山预选区新场地段地质特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007 (S2):4000-4006.
|
| [15] |
Chen W M, Wang J, Zhao H G, et al. Geological characters of Xinchang section in pre-selected beishan region for high-level radioactive waste disposal[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007(S2):4000-4006.
|
| [16] |
赵宏刚, 梁积伟, 王驹, 等. 甘肃北山南带沙枣园复式岩体年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(2):396-425.
|
| [16] |
Zhao H G, Liang J W, Wang J, et al. Geochronology, geochemical characteristics and tectonic significance of the Shazaoyuan Composite Pluton in the sounthern Beishan Mountains, Gansu Province, China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(2):396-425.
|
| [17] |
赵宏刚, 梁积伟, 王驹, 等. 甘肃北山算井子埃达克质花岗岩年代学、地球化学特征及其构造意义[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(2):329-352.
|
| [17] |
Zhao H G, Liang J W, Wang J, et al. Geochronology and geochemical characteristics of the Suanjingzi adakitic granites in the Beishan Mountains, Gansu Province, China, and their tectonic significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(2):329-352.

|
| [18] |
GB 50218—2014工程岩体分级标准[S]. 2014.
|
| [18] |
GB 50218—2014 Engineering rock mass classification standards[S]. 2014.
|
|
|
|

