|
|
|
| Three-dimensional gravity and magnetic inversion of magmatic rocks in the Huayangchuan, North Qinling area |
GUO Pei-Hong1,2( ), FENG Zhi-Han1,2, WANG Wan-Yin3,4, TANG Xiao-Ping1,2, LIU Sheng-Rong1,2 ), FENG Zhi-Han1,2, WANG Wan-Yin3,4, TANG Xiao-Ping1,2, LIU Sheng-Rong1,2 |
1. Xi’an Center of Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Xi’an 710054, China
2. Orogen Research Center of China Geological Survey, Xi’ an 710054, China
3. Institute of Gravity and Magnetic Technology,Chang’an University, Xi’an 710054
4. College of Geology Engineering and Geomatics, Chang’an Uiversity, Xi’an 710054,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Huashan rock mass, Laoniushan complex and Huayangchuan ductile shear zone play an important role in the process of mineralization in Huayangchuan area of North Qinling Mountains. They are not only a record of tectonic evolution, but also an important indicator of tectono-magmatic mineralization.In this paper, based on the systematic study of the surface and airborne gravity, magnetic survey data, and surface electrical section and other geophysical data in Huayangchuan area, statistical analysis of physical properties;merge aviation data and ground data; and proceed 2.5 dimensional interactive inversion and three dimensional inversion with prior information constraints. The regional three-dimensional geology-geophysics model of Huayangchuan area is constructed, which provides the geophysical basis for the study of regional geological background and deep geological structure. Inference and interpretation of Huashan rock mass, Laoniushan complex and Huayangchuan ductile shear zone of the three dimensional shape and spatial distribution. This paper has analyzed and discussed the deep contact relationship among huayangchuan ductile shear zone, Laoniushan rock mass and Huashan rock mass, which has certain guiding significance for deep prospecting of uranium, molybdenum and other deposits in the peripheral contact zone of the large rock mass.
|
|
Received: 14 January 2021
Published: 15 December 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Geological background map and geophysical profile location diagram of Huayangchuan Area, Shaanxi Province
|
|
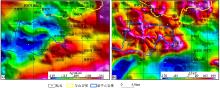
Gravity(a) and magnetic(b) anomaly map in the study area
|

地质
代号 | 岩性 | 块数/块 | 密度/
(g·cm-3) | 磁化率/
(10-5 SI) | 地质
代号 | 岩性 | 块数/块 | 密度/
(g·cm-3) | 磁化率/
(10-5 SI) | | ηγKD | 中粗粒含斑黑云
二长花岗岩 | 37 | 2.63 | 1430 | βμ | 含黄铁矿
辉绿岩脉 | 24 | 2.99 | 4558 | | ηγKH | 中粒含斑黑云
二长花岗岩 | 32 | 2.57 | 590 | Chd | 黄铁矿、辉钼
矿矿石 | 22 | 2.92 | 113 | | ηγKX | 中细粒含斑黑云
二长花岗岩 | 31 | 2.56 | 565 | Chd | 含辉钼矿的
石英岩 | 41 | 2.66 | 8 | | ηγKS | 细粒含斑黑云
二长花岗岩 | 18 | 2.65 | 1780 | Chl1 | 细碧岩、细
碧玢岩 | 70 | 2.85 | 4110 | | ηγKY | 中粒黑云二
长花岗岩 | 38 | 2.58 | 980 | Chb1 | 灰白—紫灰色
石英砂岩 | 31 | 2.63 | 8 | | ηγKC | 细粒黑云二
长花岗岩 | 31 | 2.62 | 795 | Chb2 | 灰色粘土板岩 | 25 | 2.66 | 10 | | Ar2Dgg | 花岗片麻岩 | 93 | 2.70 | 155 | Chb3 | 紫—紫灰色
石英砂岩 | 33 | 2.62 | 4 | | Ar2Mgn | 黑云角闪斜长
片麻岩 | 68 | 2.68 | 338 | Chb4 | 石英砂岩夹
粘土板岩 | 32 | 2.59 | 4 | | Ar2Hgn | 角闪花岗片麻岩 | 75 | 2.65 | 395 | Chb5 | 灰白色石英砂岩 | 32 | 2.62 | 7 | | Ar2Wgn | 黑云斜长片麻岩 | 106 | 2.62 | 1425 | Chb6 | 灰绿色—青灰色板岩 | 31 | 2.58 | 9 | | ηγPt2G | 细粒二长花岗岩 | 47 | 2.61 | 395 | Che1 | 肉红色石英砂岩 | 32 | 2.64 | 5 | | Jxl | 浅灰色白云岩 | 32 | 2.83 | 2 | Chch | 紫色泥质板岩 | 31 | 2.74 | 18 |
|
Statistical table of formation, rock mass density and susceptibility
|
|
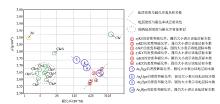
Dispersion distribution of rock mass, formation density and susceptibility in the study area
|
|
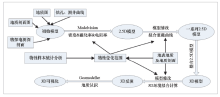
3D geological modeling technology route
|
|
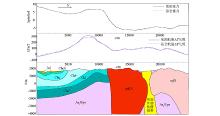
2.5D inversion interpretation result of the section L4083
|
Fig.1)
">
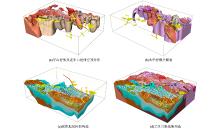
|
Diagram of three-dimensional geological model in the study area(the legend is the same as Fig.1)
|
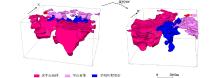
|
Spatial distribution of Huashan rock mass, Laoniushan rock mass and Huayangchuan ductile shear zone
|
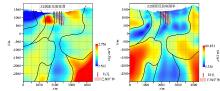
|
Deep contact relationship between Huashan rock mass, Laoniushan rock mass and Taihua rock group
|
| [1] |
高成, 康清清, 江宏君, 等. 秦岭造山带发现新型铀多金属矿:华阳川与伟晶岩脉和碳酸岩脉有关的超大型铀—铌—铅—稀土矿床[J]. 地球化学, 2017, 46(5):446-455.
|
| [1] |
Gao C, Kang Q Q, Jiang H J, et al. A unique uranium polymetallic deposit discovered in the Qinling orogenic belt: The Huayangchuan super-large U-Nb-Pb-REE deposit associated with pegmatites and carbonatites[J]. Geochimica, 2017, 46(5):446-455.
|
| [2] |
赵海杰, 毛景文, 叶会寿, 等. 陕西黄龙铺地区碱性花岗斑岩及辉绿岩的年代学与地球化学:岩石成因及其构造环境示踪[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(1):12-27.
|
| [2] |
Zhao H J, Mao J W, Ye H S, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the alkaline granite porphyry and diabase dikes in Huanglongpu area of Shaanxi Province: Petrogenesis and implications for tectonic environment[J]. Chinese Geology, 2010, 37(1):12-27.
|
| [3] |
毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 等. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2005, 21(1):169-188.
|
| [3] |
Mao J W, Xie G Q, Zhang Z H, et al. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 21(1):169-188.
|
| [4] |
焦建刚, 汤中立, 钱壮志, 等. 东秦岭金堆城花岗斑岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄、物质来源及成矿机制[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(6):1011-1022.
|
| [4] |
Jiao J G, Tang Z L, Qian Z Z, et al. Metallogenic mechanism,magma source and zircon U-Pb age of Jinduicheng granitic porphyry, East Qinling[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2010, 35(6):1011-1022.

|
| [5] |
孙晓明, 刘孝善. 金堆城钼矿区两类不同花岗岩的关系及其成因的研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 1987, 2(2):34-45.
|
| [5] |
Sun X M, Liu X S. Study on the relationship between two different types of granites and their genesis in Jinduicheng molybdenum mining area[J]. Contributions To Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 1987, 2(2):34-45.
|
| [6] |
Williams N C. Geologically-constrained UBC-GIF gravity and magnetic inversions with examples from the Agnew-Wiluna Greenstone Belt, Western Australia[D]. Canada: University of British Columbia, 2008.
|
| [7] |
Boszczuk P, Cheng L Z, Hammouche H, et al. A 3D Gravity data interpretation of the Matagami mining camp, Abitibi Subprovince, Superior Province, Quebec Canada[J]. Journal of applied Geophsics, 2011, 75(1):77-86.
|
| [8] |
兰学毅, 杜建国, 严加永, 等. 基于先验信息约束的重磁三维交互反演建模技术——以铜陵矿集区为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(12):4436-4449.
|
| [8] |
Lan X Y, Du J G, Yan J Y, et al. 3D gravity and magnetic interactive inversion modeling based on prior information: A case study of the Tongling ore concentration area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 2015, 58(12):4436-4449.
|
| [9] |
向杰, 陈建平, 胡彬, 等. 基于三维地质—地球物理模型的三维成矿预测——以安徽铜陵矿集区为例[J]. 地球科学进展, 2016, 31(6):603-614.
|
| [9] |
Xiang J, Chen J P, Hu B, et al. 3D Metallogenic prediction based on 3D geological-geophysical model: A case study in Tongling mineral district of Anhui[J]. Advance in Earth Sciences, 2016, 2016, 31(6):603-614.
|
| [10] |
祁光, 吕庆田, 严加永, 等. 先验地质信息约束下的三维重磁反演建模研究——以安徽泥河铁矿为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 88(4):466-477.
|
| [10] |
Qi G, Lyu Q T, Yan J Y, et al. Geologic constrained 3D gravity and magnetic modeling of Nihe deposit—A case study of Nihe Iron Mine in Anhui Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 2012, 88(4):466-477.
|
| [11] |
罗凡, 严加永, 付光明. 基于已知信息约束的重磁三维反演在深部磁铁矿勘查中的应用——以安徽泥河铁矿为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(1):50-60.
|
| [11] |
Luo F, Yan J Y, Fu G M. The application of gravity and magnetic three-dimensional inversion based on known information constraint in deep magnetite exploration: A case study of the Nihe iron deposit in Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 2018, 42(1):50-60.
|
| [12] |
严加永, 吕庆田, 吴明安, 等. 安徽沙溪铜矿区域重磁三维反演与找矿启示[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(4):507-518.
|
| [12] |
Yan J Y, Lyu Q T, Wu M A, et al. Prospecting indicator of Anhui Shaxi Porphyry Copper Deposit based on regional gravity and magnetic 3D inversion[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 88(4):507-518.
|
| [13] |
严加永, 吕庆田, 陈向斌, 等. 基于重磁反演的三维岩性填图试验——以安徽庐枞矿集区为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 36(4):1041-1053.
|
| [13] |
Yan J Y, Lyu Q T, Chen X B, et al. 3D lithologic mapping test based on 3D inversion of gravity and magnetic data: A case study in Lu-Zong ore concentration district, Anhui Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 2014, 36(4):1041-1053.
|
| [14] |
胡斌, 贾正元, 张贵宾, 等. 青藏高原冈底斯带及邻区重磁三维反演及岩浆岩特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(4):1362-1376.
|
| [14] |
Hu B, Jia Z Y, Zhang G B, et al. Three-dimensional inversion of gravity and magnetic data and its application in the study on the characteristics of magmatic rocks in the Gangdise belt and adjacent areas, Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(4):1362-1376.
|
| [15] |
齐秋菊, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 华北地块南缘老牛山杂岩体时代、成因及地质意义——锆石年龄、Hf 同位素和地球化学新证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(1):279-301.
|
| [15] |
Qi Q J, Wang X X, Ke C H, et al. Geochronology and origin of the Laoniushan complex in the southern margin of North China Block and their implications: New evidences from zircon dating,Hf isotopes and geochemistry[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2005, 2012, 28(1):279-301.
|
| [16] |
王建其, 朱赖民, 郭波, 等. 华北陆块南缘华山、老牛山及合峪花岗岩体Sr-Nd, Pb同位素组成特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石, 2015, 35(1):63-72.
|
| [16] |
Wang J Q, Zhu L M, Guo B, et al. Characteristics of Sr-Nd and Pb isotopic composition and its geological significance of granitic plutons in the Huashan, Laoniushan and Heyu area at the southern margin of North China craton[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2015, 35(1):63-72.
|
| [17] |
郭波, 朱赖民, 李犇, 等. 华北陆块南缘华山和合峪花岗岩岩体锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf 同位素组成与成岩动力学背景[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(2):265-281.
|
| [17] |
Guo B, Zhu L M, Li B, et al. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope composition of the Huashan and Heyu granite plutons at the southern margin of North China Craton: Implications for geodynamic setting[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(2):265-281.
|
| [18] |
齐秋菊, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 等. 华北陆块南缘老牛山杂岩体岩石成因:来自黑云母的信息[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2018, 40(3):252-261.
|
| [18] |
Qi Q J, Wang X X, Ke C H, et al. Petrogenesis of Laoniushan granitoid complex in the southern margin of North China Block: Information from Biotite[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2018, 40(3):252-261.
|
| [19] |
张兴康, 叶会寿, 李正远, 等. 小秦岭华山复式岩基大夫峪岩体锆石U-Pb 年龄、Hf 同位素和地球化学特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(2):235-260.
|
| [19] |
Zhang X K, Ye H S, Li Z Y, et al. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf isotopic composition and geochemistry of Dafuyu granitoid poluton from Huashan complex batholith in Xiaoqinling[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2015, 34(2):235-260.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Bao-Feng, WANG Qi-Nian, GUO Xin, GUAN Da-Wei, CHEN Tong-Gang, FANG Wen. Gravity survey and audio magnetotellurics-based insights into the deep structures and geothermal resource potential of the Rucheng Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1147-1156. |
| [2] |
HE Sheng, WANG Wan-Ping, DONG Gao-Feng, NAN Xiu-Jia, WEI Feng-Feng, BAI Yong-Yong. Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in urban geological surveys[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1379-1386. |
|
|
|
|

