0 引言
锲墨格山地区位于青藏高原东北缘,属高原大陆性气候[1],为寒冷半干旱草原景观区。前人在该区主要开展过铜多金属矿勘查,对锂铍等稀有金属矿的勘查相对较少,地表也未开展与锂铍等稀有矿有关的大比例尺地球化学测量。相比于1∶5万水系沉积物测量[2-3],大比例尺微沟系测量不仅能够精确定位找矿靶区,还能准确反映表生地球化学特征[4]。近些年,青海省在重要成矿区带上开展的大比例尺(1∶2.5万)地球化学测量工作取得了明显的找矿效果,其关键技术问题是采样方法和样品截取粒级[5-6]将直接影响大比例尺地球化学找矿信息的提取。本文以青海省天峻县锲墨格山地区锂铍稀有矿为研究对象,对采样方法和样品截取粒级进行试验研究,了解成矿元素在微沟系中的分布规律和最佳富集粒度[7],确定适合寒冷半干旱草原景观区大比例尺微沟系测量的最佳方法技术,目的是获得真实、可靠的常规金属元素、稀有稀土元素地球化学信息和成矿元素在该区的分布情况、富集规律,为相同景观区寻找稀有金属矿提供地球化学依据[8]。
1 自然地理及景观特征
研究区位于柴达木盆地东北边缘锲墨格山,海拔3 800 m以上,高差在500~1 000 m,属高山类型,总体呈现中部高、东北及西南部低的格局。区内水系属内陆水系,水系不发育,大部分为间歇性河流,河水主要来源于高山融化冰雪及泉水;受气候影响,一级水系95%以上属于季节性冲沟,只在夏季多雨时节短暂蓄水,沉积物以冲洪积砂砾石为主;水系多呈网状、树杈状分布,局部为羽状、梳状,近沟脑处常形成“U”型谷或“V”型谷。区内气候属高原大陆性干旱型气候,以干燥寒冷、冬长夏短、少雨多风、冷热多变、温差悬殊、日照时间长等为特征。地理景观为青东北寒冷半干旱草原区[9]。
2 研究区地质特征
图1
图1
研究区大地构造位置
1—中祁连岩浆弧;2—南祁连岩浆弧;3—宗务隆山-夏河陆缘裂谷;4—全吉地块;5—滩间山岩浆弧;6—柴北缘蛇绿混杂岩带;7—柴达木盆地;8—祁漫塔格北坡-夏日哈岩浆弧;9—北昆仑岩浆弧;10—鄂拉山陆缘弧;11—泽库前陆盆地;12—边界断裂及研究区
Fig.1
Geotectonic location map of study area
1—central Qilian magmatic arc; 2—south Qilian magmatic arc; 3—Zongwulongshan-Xiahe terrestrial rift; 4—Quanji plot; 5—Tanjianshan magmatic arc; 6—ophiolite melange belt in northern Chaidamu basin; 7—Chaidamu basin; 8—the northern slope of Qimantage-Xiariha magmatic arc; 9—northern Kunlun magmatic arc; 10—continental margin arc of the Elashan; 11—Zeku foreland basin; 12—boundary faults and study area
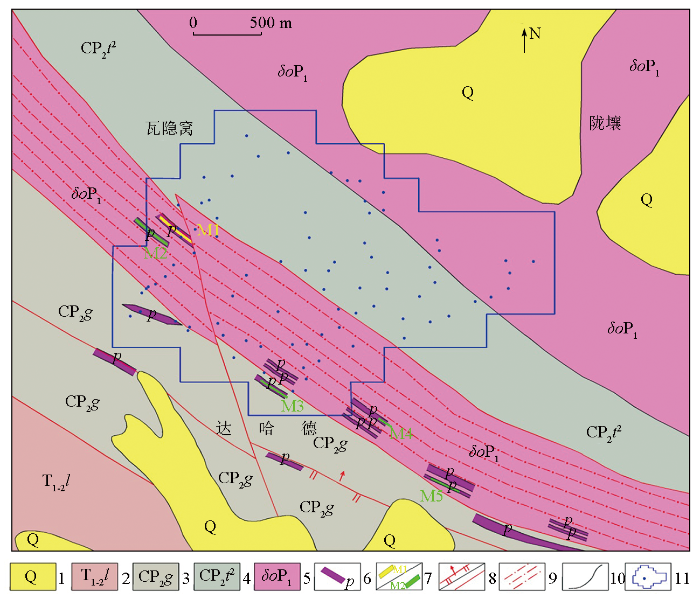
图2
图2
锲墨格山地区地质
1—第四系地层;2—下-中三叠统隆务河组;3—石炭系-中二叠统果可山组; 4—石炭系-中二叠统土尔根大坂组;5—早二叠世石英闪长岩;6—花岗伟晶岩脉;7—锂/铍矿体; 8—逆断层及性质不明断层; 9—韧性剪切带; 10—地质界线; 11—采样点位及范围
Fig.2
Geological map of Qiemogeshan area
1—Quaternary strata; 2—early-middle Triassic Longwuhe formation; 3—Carboniferous-middle Permian Guokeshan formation; 4—Carboniferous-middle Permian Tuergendaban formation; 5—early Permian quartz diorite; 6—granite pegmatite veins; 7—lithium/beryllium orebody; 8—reverse faults and faults of unknown nature; 9—ductile shear zones; 10—geological boundary; 11—sampling point and range
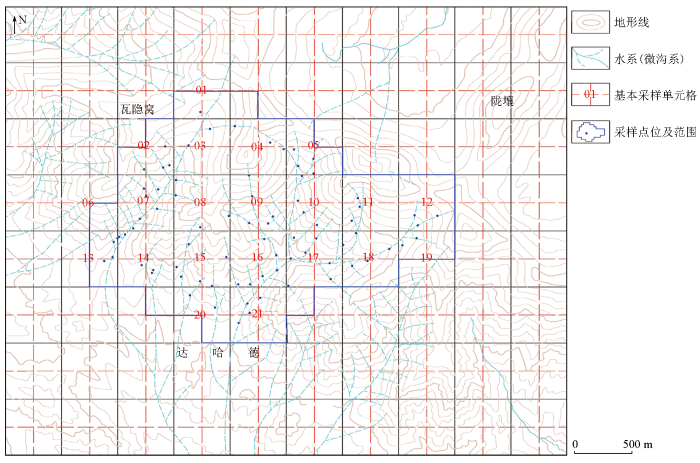
3 样品采集与粒级加工
3.1 样品采集
图3
3.2 粒级选择、加工与分析
本次研究共采集地球化学样品320件,同点位选择-4~+20目、-4~+40目、-10~+40目、-10~+60目加工截取粒级。样品加工后同批次送往青海省地质矿产测试应用中心,分析元素为Be、Cu、La、Li、Nb、Rb、Sn、W、Y、Zr,其中Li、Be、La、Y、W采用等离子质谱法(ICP-MS)测试,Cu、Nb、Rb、Zr采用射线荧光法(XRF)测试,Sn采用发射光谱法(ES)测试。测试数据质量经评审为优秀级,质量可靠。
3.3 数理统计及图件制作
为获取不同粒级富集离散特征最优解,分析表生地球化学特征,使用原始数据集的变异系数
4 试验效果
本文主要从水系沉积物及土壤粒级的元素含量分布、富集特征、变异系数及空间分布4个方面综合评价各粒级试验效果。
4.1 元素含量分布特征
表1 研究区各样品截取粒级元素参数特征
Table 1
| 样品粒级 | 参数 | Be | Cu | La | Li | Nb | Rb | Sn | W | Y | Zr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -4~+20目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.25 | 11.40 | 19.20 | 11.00 | 6.50 | 43.70 | 1.36 | 0.32 | 12.30 | 89.30 |
| 最大值/10-6 | 50.70 | 165.00 | 46.30 | 161.00 | 20.10 | 295.00 | 10.29 | 9.27 | 40.00 | 239.00 | |
| 平均值/10-6 | 2.59 | 22.54 | 34.23 | 49.66 | 11.84 | 100.99 | 2.51 | 1.13 | 20.92 | 139.58 | |
| 中位数/10-6 | 2.38 | 22.00 | 34.00 | 36.20 | 10.85 | 101.00 | 2.38 | 0.91 | 20.95 | 131.00 | |
| 标准离差/10-6 | 0.67 | 6.66 | 5.52 | 37.89 | 3.41 | 31.46 | 0.58 | 0.66 | 4.56 | 30.47 | |
| 浓集系数 | 1.33 | 1.11 | 1.06 | 1.63 | 1.03 | 1.00 | 0.98 | 0.68 | 1.04 | 0.85 | |
| 变异系数CV1 | 1.565 | 0.723 | 0.161 | 0.763 | 0.288 | 0.414 | 0.523 | 0.969 | 0.247 | 0.229 | |
| 变异系数CV0 | 0.26 | 0.295 | 0.161 | 0.763 | 0.288 | 0.312 | 0.233 | 0.592 | 0.218 | 0.218 | |
| -4~+40目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.45 | 10.60 | 22.10 | 8.40 | 6.50 | 40.70 | 1.44 | 0.33 | 13.70 | 89.10 |
| 最大值/10-6 | 55.80 | 78.60 | 55.40 | 198.00 | 18.80 | 343.00 | 10.47 | 182.00 | 35.80 | 223.00 | |
| 平均值/10-6 | 2.69 | 23.76 | 32.45 | 45.47 | 12.13 | 106.30 | 2.61 | 1.12 | 20.65 | 143.75 | |
| 中位数/10-6 | 2.48 | 24.20 | 31.70 | 39.20 | 11.45 | 113.00 | 2.45 | 0.95 | 20.20 | 136.00 | |
| 标准离差/10-6 | 0.86 | 7.44 | 6.18 | 28.05 | 3.60 | 32.52 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 4.59 | 33.59 | |
| 浓集系数 | 1.38 | 1.17 | 1.00 | 1.49 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 1.02 | 0.67 | 1.03 | 0.87 | |
| 变异系数CV1 | 1.653 | 0.416 | 0.233 | 0.763 | 0.297 | 0.409 | 0.513 | 2.037 | 0.234 | 0.234 | |
| 变异系数CV0 | 0.322 | 0.313 | 0.191 | 0.617 | 0.297 | 0.306 | 0.261 | 0.619 | 0.223 | 0.234 | |
| -10~+40目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.51 | 11.90 | 23.20 | 15.90 | 6.80 | 47.70 | 1.39 | 0.33 | 12.20 | 79.50 |
| 最大值/10-6 | 58.00 | 73.30 | 88.00 | 168.00 | 20.00 | 243.00 | 12.48 | 11.40 | 50.60 | 237.00 | |
| 平均值/10-6 | 2.60 | 22.42 | 34.85 | 39.04 | 12.39 | 104.63 | 2.49 | 1.50 | 23.18 | 141.90 | |
| 中位数/10-6 | 2.55 | 21.85 | 34.90 | 36.30 | 11.80 | 106.00 | 2.48 | 1.51 | 22.25 | 136.00 | |
| 标准离差/10-6 | 0.49 | 5.19 | 5.60 | 14.80 | 3.41 | 28.10 | 0.44 | 0.76 | 5.76 | 34.03 | |
| 浓集系数 | 1.33 | 1.11 | 1.08 | 1.28 | 1.08 | 1.04 | 0.97 | 0.9 | 1.15 | 0.86 | |
| 变异系数CV1 | 1.751 | 0.377 | 0.229 | 0.629 | 0.275 | 0.332 | 0.478 | 0.849 | 0.298 | 0.24 | |
| 变异系数CV0 | 0.188 | 0.232 | 0.161 | 0.379 | 0.275 | 0.269 | 0.175 | 0.508 | 0.248 | 0.24 | |
| -10~+60目 | 最小值/10-6 | 1.03 | 6.37 | 14.40 | 11.30 | 6.70 | 43.40 | 1.04 | 0.36 | 9.50 | 53.90 |
| 最大值/10-6 | 54.30 | 81.60 | 47.40 | 175.00 | 24.40 | 382.00 | 13.49 | 22.70 | 39.70 | 256.00 | |
| 平均值/10-6 | 2.30 | 23.57 | 32.60 | 38.11 | 12.30 | 97.60 | 2.45 | 1.20 | 20.63 | 129.29 | |
| 中位数/10-6 | 2.17 | 23.00 | 31.70 | 32.65 | 11.05 | 95.80 | 2.19 | 0.96 | 19.10 | 120.50 | |
| 标准离差/10-6 | 0.61 | 7.26 | 6.20 | 23.62 | 4.14 | 30.43 | 0.92 | 0.72 | 5.88 | 31.92 | |
| 浓集系数 | 1.18 | 1.16 | 1.01 | 1.25 | 1.07 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.72 | 1.02 | 0.79 | |
| 变异系数CV1 | 1.788 | 0.399 | 0.190 | 0.790 | 0.337 | 0.454 | 0.701 | 1.587 | 0.298 | 0.278 | |
| 变异系数CV0 | 0.265 | 0.308 | 0.19 | 0.62 | 0.337 | 0.312 | 0.378 | 0.598 | 0.285 | 0.247 | |
| 青海省丰度[17]/10-6 | 1.95 | 20.24 | 32.41 | 30.45 | 11.52 | 100.53 | 2.56 | 1.67 | 20.13 | 164.54 | |
1)Be、Li、Rb稀有轻金属元素组:含量特征规律较一致,-4~+20目粒级中最大值显现,-4~+40目粒级中最小值、平均值、标准离差和中位数相对偏高,在其他粒级中差异性不明显。
2)La、Y稀土元素组:含量特征规律相近,在-10~+40目粒级中平均值、最小值、最大值和中位数均表现为凸显,而在-10~+60目粒级中标准离差显示最高。
3)Nb、Zr稀有难熔金属元素组:含量特征差异性较大,-4~+20目粒级中最小值偏高,-4~+40目粒级中Zr平均值偏高,-10~+40目粒级时中位数显现,Nb平均值和标准离差较大,Zr最大值明显,而在-10~+60目粒级中Nb最大值显示较高。
4)W、Sn酸性岩元素组:含量特征规律基本相同,-4~+40目粒级中Sn平均值和最小值偏高,-10~+40目粒级时中位数显现,W平均值较大,而在-10~+60目粒级中最大值和标准离差均显示较高。
5)Cu含量特征在各粒级中表现不一。
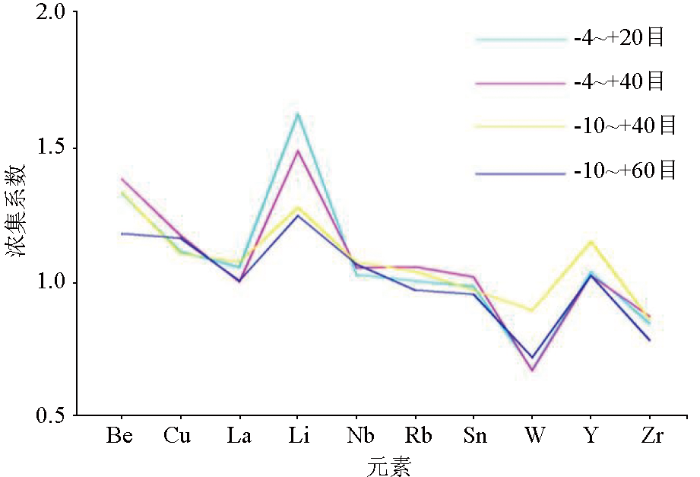
4.2 元素富集特征
以青海省元素丰度为依据,选用浓集系数作为参考指标进行富集特征讨论(图4)。从图中可以看出,Be、Li在各粒级中浓集系数偏高,Cu、La、Nb、Rb、Sn、Y等浓集系数均大于1,而W、Zr浓集系数小于1。Be在-4~+40目粒级、Li在-4~+20目及-4~+40目粒级中的浓集系数尤为明显,说明Be、Li富集程度较高,成矿可能性较大,显示强劲的成矿潜力。总之,在-4~+40目的粗粒级中,Be、Li高富集程度更突出。
图4
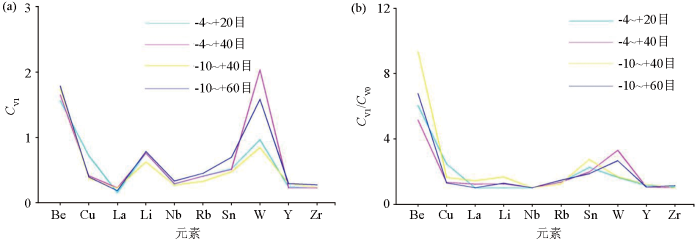
4.3 变异系数特征
利用原始数据集的变异系数(CV1)反映各元素的离散程度,CV1/CV0反映背景拟合处理时对离散值的削平程度(图5)。Be在各粒级中均表现含量变化幅度大、高强数据多、富集成矿可能性大的特点,其中在-4~+40目的粗粒级中Be离散程度表现更为突出,这与区内花岗伟晶岩极为发育相吻合,说明研究区Be成矿前景较大。Li、W、Sn在各粒级中表现为含量变化幅度较大、高强数据较多、成矿可能性较大的特点。Li与区内出露的大量锂辉石化伟晶岩密切相关,W在-4~+40目和-10~+60目粒级中离散程度显示较明显,W、Sn等高温元素反映了石英闪长岩岩体广泛分布的特征。而Cu、Y、Rb、Nb、Zr、La在各粒级中均表现为含量变化幅度小、高强数据少的特点,该类元素在区内不富集或局部富集,多反映区内地层、岩体和岩脉的地球化学背景特征,富集成矿的可能性相对较小。
图5
图5
研究区各粒级变异系数CV1曲线(a)和CV1/CV0曲线(b)
Fig.5
The CV1 curve (a) and CV1/CV0 curve (b) of each particle size were studied
4.4 地球化学特征对比分析
综合地质特征,选取与锂、铍矿化相关或含量范围较宽的元素进行地球化学特征对比,能更直观地反映各粒级试验的有效性。
图6
图6
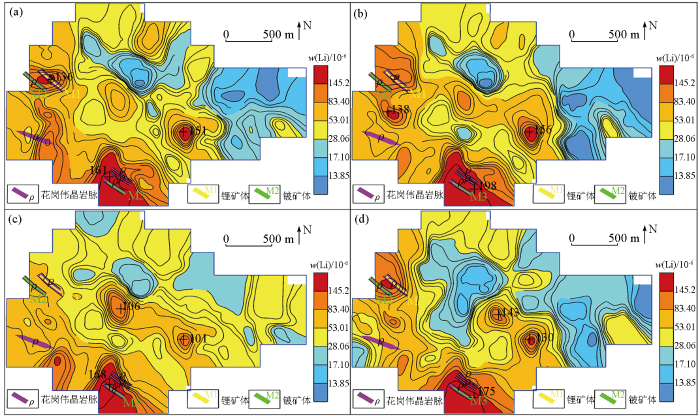
-4~+20目(a)、-4~+40目(b)、-10~+40目(c)、-10~+60目(d)样品中Be地球化学分布
Fig.6
Geochemical maps of element Be in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
图7
图7
-4~+20目(a)、-4~+40目(b)、-10~+40目(c)、-10~+60目(d)样品中Li地球化学分布
Fig.7
Geochemical maps of element Li in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
图8
图8
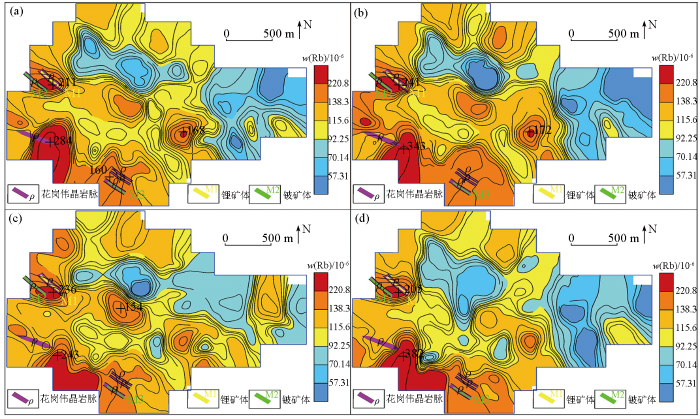
-4~+20目(a)、-4~+40目(b)、-10~+40目(c)、-10~+60目(d)样品中Rb地球化学分布
Fig.8
Geochemical maps of element Rb in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
图9
图9
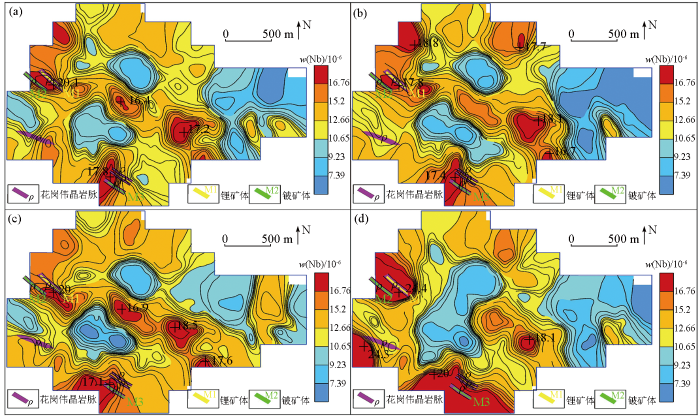
-4~+20目(a)、-4~+40目(b)、-10~+40目(c)、-10~+60目(d)样品中Nb地球化学分布
Fig.9
Geochemical maps of element Nb in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
图10
图10
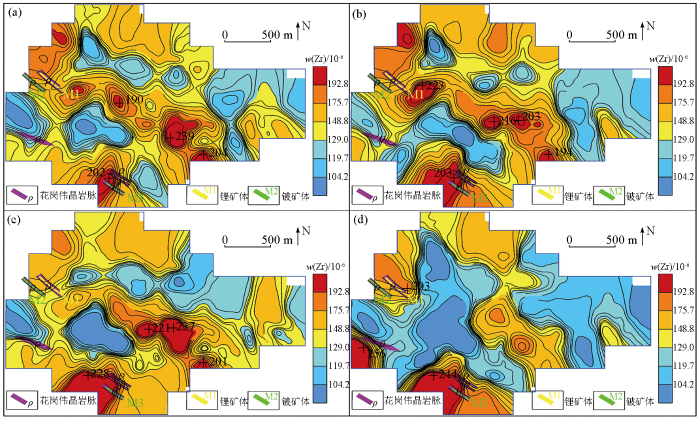
-4~+20目(a)、-4~+40目(b)、-10~+40目(c)、-10~+60目(d)样品中Zr地球化学分布
Fig.10
Geochemical maps of element Zr in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
图11
图11
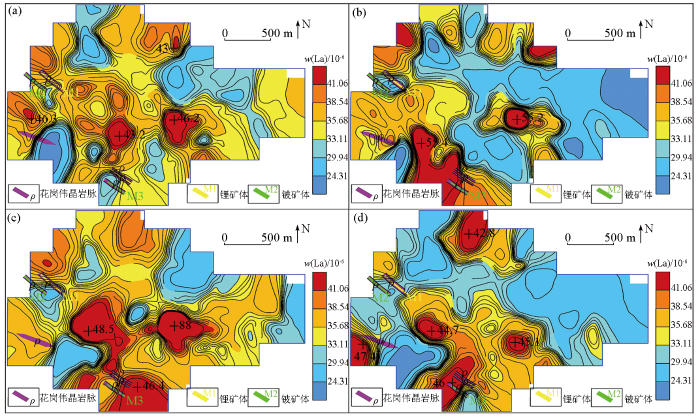
-4~+20目(a)、-4~+40目(b)、-10~+40目(c)、-10~+60目(d)样品中La地球化学分布
Fig.11
Geochemical maps of element La in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
图12
图12
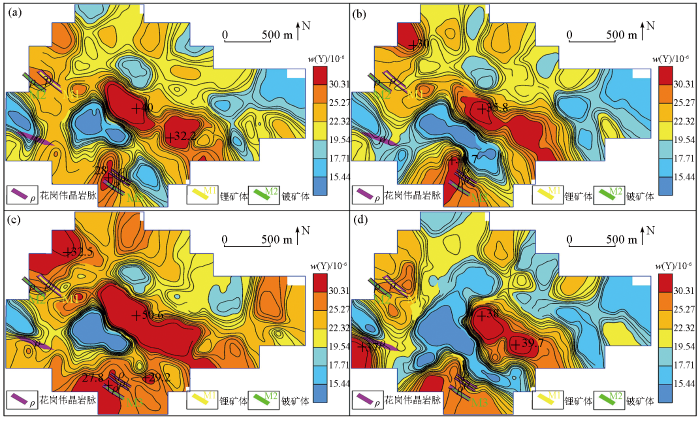
-4~+20目(a)、-4~+40目(b)、-10~+40目(c)、-10~+60目(d)样品中Y地球化学分布
Fig.12
Geochemical maps of element Y in samples of mesh -4~+20(a), -4~+40(b), -10~+40(c), -10~+60(d)
4.5 有效性分析
从元素含量分布特征分析,Be、Li、Rb、Nb、Zr稀有金属元素在-4~+40目粒级中最小值、平均值、标准离差和中位数相对偏高,在其他粒级中差异性不明显;La、Y稀土元素在-10~+40目粒级中元素含量分布特征表现更为凸显;Cu、W、Sn在各粒级中显示差异较大。
从元素的富集特征看,Be、Li在各粒级中的浓集系数偏高,在-4~+40目粒级中显示更高,富集程度尤为明显,说明Be、Li成矿可能性较大,这与区内发现的锂铍矿体化相印证。其他元素在各粒级中富集程度显示不明显,成矿可能性较小。
从元素离散程度分析,Be在各粒级中均表现优异,在-4~+40目的粗粒级中离散程度表现更突出,与花岗伟晶岩脉相吻合,已发现的铍成矿事实即为最好的佐证。Li、W、Sn在各粒级中表现为离散程度较大等特征,而Cu、Y、Rb、Nb、Zr、La在各粒级中均表现不富集或局部富集,富集成矿的可能相对较小。
Be、Li、Rb、Nb、Zr地球化学特征对比表明,-4~+40目的粗粒级显示的地球化学特征分布与区内地质矿产吻合度更高,地球化学高背景—正异常区与花岗伟晶岩脉及锂铍矿体对应性好,与NW向韧性剪切带套合较好,异常规模及强度整体上较其他粒级特征更明显。较其他粒级,La、Y在-10~+40目的粗粒级中表现凸显,地球化学高背景—正异常区与花岗伟晶岩脉对应性好,也与NW向韧性剪切带较套合。
Cu、W、Sn在各粒级中含量分布未见明显的相关趋势,可能归因于试验区为Cu、W、Sn的背景区或低背景区,绝大多数样品含量值较低,且含量范围很窄,故结合相同景观条件下其他区域勘查效果[20],粒级选择较倾向于-10~+60目。
5 结论
1)本文采用大比例尺微沟系测量,其4种采样截取粒级的分析结果显示,在花岗伟晶岩脉和锂铍矿体上方均获得了明显的地球化学异常,说明大比例尺微沟系测量方法具有显著的地球化学找矿效果。
2)通过试验研究,Cu、W、Sn等有色金属元素选择-10~+60目中粗粒级,Be、Li、Nb、Rb、Zr稀有元素和La、Y稀土元素选择-4~+40目粗粒级找矿更有效,其地球化学分布与地质矿产吻合度更高。
3)Li、Be、Rb元素浓集中心明显、峰值高、与花岗伟晶岩脉相吻合的异常部位是寻找锂铍稀有矿最直接的找矿标志。
4)在寒冷半干旱草原景观条件下,寻找稀有稀土金属矿的最佳采样粒级为-4~+40目。
参考文献
青藏高原条件下现场分析方法的适应性
[J].
The suitability of field analytical methods under the special conditions of Tibetan plateau
[J].
青海省都兰县金水口地区水系沉积物地球化学异常特征及找矿前景
[J].
Geochemical anomalies characteristics of stream sediments and ore-search prospect in Jinshuikou area of Dulan County,Qinghai Province
[J].
1∶5万水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿意义
[J].
Geochemical characteristics of 1∶50,000 stream sediments and in Xainza,Tibet,and their prospecting significance
[J].
东昆仑东段都兰地区地球化学特征及其成矿意义——基于大比例尺微沟系(土壤)测量工作
[J].
Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic significance of the Dulan area in the eastern section of the East Kunlun Mountains derived from large-scale micro channel system (soil) measurement
[J].
热带雨林景观土壤测量采样深度与样品粒级试验研究——以加纳国雅卡锰金矿为例
[J].
Experimental study on sampling depth and sample granularity of soil survey in tropical rainforest landscape:Taken the Yakau Mn-Au deposit in Ghana as an example
[J].
岩屑测量方法在干旱荒漠区的找矿效果——以贺兰山北段嘎拉斯台白钨矿的发现为例
[J].
The prospecting effect of rock debris measurement method in arid desert area:Exemplified by the discovery of the Galasitaischeelite deposit in northern Helan Mountain
[J].
广东北市地区1∶5万水系沉积物测量粒级试验
[J].
A study on 1∶50,000 stream sediments survey in Beishiarea,Guangdong Province
[J].
青海省冷湖行委俄博梁地区稀有稀土元素地球化学特征及找矿潜力分析
[J].
Geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of rare rare-earth element in Eboliang area,Lenghu,Qinghai Province
[J].
青藏高原东北缘茶卡北山印支期(含绿柱石)锂辉石伟晶岩脉群的发现及Li-Be成矿意义
[J].
The Discovery of the indosinian(beryl-bearing) spodumene pegmatitic dike swarm in the Chakaibeishan area on the northeastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau:Implications for Li-Be mineralziation
[J].
我国三稀(稀有稀土稀散)矿产资源调查研究成果综述
[J].
A review of achievements in the three-type rare mineral resources(rare resources,rare earth and rarely scattered resources)survey in China
[J].
锂同位素在伟晶岩矿床成因研究中的应用
[J].
Application of lithium isotopes in genetic study of pegmatite deposits
[J].
1∶25,000沟系沉积物地球化学测量方法有效性探讨——以东昆仑巴隆地区为例
[J].
A discussion of effectiveness to the 1∶25,000 sulcus sediments geochemical survey:The Balong area of east Kunlun as an example
[J].
1∶20万区域化探方法核心技术“取样粒级”的讨论
[J].
A Discussion on the "Samplinggrade",a key technology in 1∶200,000 regional geochemical exploratioa
[J].
安徽北淮阳典型矿区水系沉积物采样方法
[J].
Research on sampling methods for stream sediments survey in the typical ore district of northern Huaiyang area in Anhui Province
[J].
用地球化学异常图和方差分析比较两种采样粒级的化探效果
[J].
The application of geochemical anomaly map and varaiance analysis to comparing gochemical exploration effects of two sizes of fractions
[J].
青海省矿产资源调查评价成果报告
[R].
Investigation and evaluation of mineral resources in Qinghai Province
[R].
稀土配分模式在确定西天山风积物干扰粒级中的应用研究
[J].
Application of REE assemblage in determining the interference granularity of aeolian sediments in West Tianshan
[J].
土壤地球化学测量在甘肃北山白头山铷矿找矿中的应用
[J].
Application of soil geochemical survey in the Baitoushan rubidium deposit,Beishan area,Gansu Province
[J].