|
|
|
| Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of groundwater in a typical chemical industry park in northwestern Shandong, China |
FAN Hai-Yin1,2( ), SONG Rui-Rui1,2, YU Lin-Song1,2, TENG Yong-Bo1,2( ), SONG Rui-Rui1,2, YU Lin-Song1,2, TENG Yong-Bo1,2( ), WAN Fang1,2, ZHANG Xiu-Wen1,2, LI Sheng-Yu1,2, ZHAO Chuang1,2 ), WAN Fang1,2, ZHANG Xiu-Wen1,2, LI Sheng-Yu1,2, ZHAO Chuang1,2 |
1. Shandong Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Jinan 250013, China
2. Shandong Engineering Research Center for High Precision Detection of Underground Resources and Environment, Jinan 250013, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to ascertain the heavy metal pollution of groundwater in a typical chemical industry park in northwestern Shandong. According to the investigation and evaluation requirements for groundwater environments in chemical industry parks, this study collected 10 groundwater samples to analyze the concentrations and spatial distributions of eight heavy metals, namely Fe, Cu, Zn, Al, Cd and Pb. Furthermore, it conducted the health risk assessment of groundwater for different populations. The results indicate that: (1) except Mn and Al, all heavy metals in the groundwater of the chemical industry park showed concentrations lower than the class III water quality standard stated in the Standard for Groundwater Quality (GB/T 14848—2017), with a comprehensive pollution index ranging from 0.37 to 0.78. The monitoring points for heavy metal elements are all pollution-free; (2) the overall spatial distributions of heavy metals are roughly consistent with the distribution areas of key enterprises in the chemical industry park. This consistency indicates that external factors such as the production activities of enterprises affect the spatial distributions of heavy metals in groundwater; (3) the health risks are lower for children than for adults and lower via skin contact than via drinking. The non-carcinogenic risks under different exposure routes are acceptable for different populations. Carcinogens As and Cd have slight carcinogenic risks for adults. Local authorities should strengthen the supervision of the production activities of enterprises and thoroughly inspect enterprises with suspected pollution. Only in this way can we effectively control and then gradually reduce the risks to human health caused by groundwater pollution.
|
|
Received: 18 July 2022
Published: 27 October 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
TENG Yong-Bo
E-mail: 741370828@qq.com;yongboteng@sina.com
|
|
|
|

|
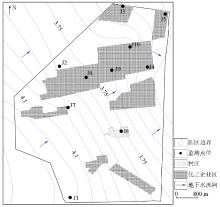
Regional hydrogeological map of the study area
|
|
Layout plan of the study area and distribution of sampling sites
|

| 参数定义范围 | 含义 | | Pi≤1.0 | P综≤0.7 | 无污染 | | 1.0<Pi≤2.0 | 0.7<P综≤1.0 | 轻微污染 | | 2.0<Pi≤3.0 | 1.0<P综≤2.0 | 轻度污染 | | 3.0<Pi≤5.0 | 2.0<P综≤3.0 | 中度污染 | | Pi>5.0 | P综>3.0 | 重度污染 |
|
Parameter value meaning
|
|
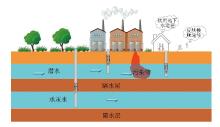
Conceptual model of pollutant risk exposure in the study area
|

| 参数符号及单位 | 参数含义 | 成人参考值 | 儿童参考值 | 参数来源 | | C/(mg·L-1) | 污染物浓度 | Ci | Ci | 本次研究 | | ED/a | 持续暴露时间 | 30 | 9 | [32-3] | | ET/(d·a-1) | 暴露时间 | 360 | 360 | [32-3] | | EF/(d·a-1) | 暴露频率 | 350 | 350 | [32-3] | | SA/cm2 | 接触的皮肤表面积 | 16000 | 9300 | [32-3] | | PC/(cm·h-1) | 皮肤渗透系数 | 0.0001(Fe)、0.0006(Cu)、0.0006(Zn)、
0.0018(As)、0.001(Cd)、0.000004(Pb) | [34] | | CF/(L·cm-1) | 体积转换因子 | 0.001 | 0.001 | [34] | | IR/(L·d-1) | 每日平均饮用量 | 1.70 | 1.14 | [32-3] | | BW/kg | 平均体重 | 57.00 | 23.80 | [32-3] | | AT/d | 平均暴露时间 | 25500 | 25500 | [32-3] |
|
Health risk assessment model parameter
|

重金属 | 致癌强度系数q/(mg·(kg·d)-1) | 日均参考剂量RfD/(mg·(kg·d)-1) |
参数来源 | | 饮用途径 | 皮肤接触途径 | 饮用途径 | 皮肤接触途径 | | | Cd | 6.1 | 0.38 | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | [35-36] | | As | 1.5 | 3.66 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 | [35-36] | | Fe | | | 0.3 | 0.0045 | [35-36] | | Cu | | | 0.04 | 0.012 | [35-36] | | Zn | | | 0.3 | 0.01 | [35-36] | | Pb | | | 0.0014 | 0.0014* | [35-36] |
|
Carcinogenic intensity coefficient (q) and daily average reference dose (RfD)
|

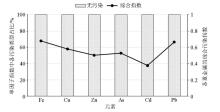
| 元素 | 最小值
/(mg·L-1) | 最大值
/(mg·L-1) | 平均值
/(mg·L-1) | 背景值
/(mg·L-1) | 标准差
/(mg·L-1) | 变异系
数/% | 偏度 | 峰度 | 超标率
/% | 国家Ⅲ类
标准 | | Fe | 0.003 | 0.294 | 0.133 | 0.049 | 0.107 | 70.9 | -0.499 | -1.362 | 0.00 | 0.3 | | Cu | 0.005 | 0.756 | 0.277 | 0.003 | 0.268 | 96.8 | 0.639 | -0.702 | 0.00 | 1.00 | | Zn | 0.003 | 0.762 | 0.196 | 0.019 | 0.255 | 130.1 | 1.74 | 1.946 | 0.00 | 1.00 | | As | 0.0005 | 0.0094 | 0.0038 | 0.00057 | 0.0028 | 73.7 | 1.36 | 0.961 | 0.00 | 0.01 | | Cd | 0.00005 | 0.00245 | 0.0010 | 0.00004 | 0.00082 | 82.0 | 0.409 | -1.105 | 0.00 | 0.005 | | Pb | 0.0005 | 0.0098 | 0.0054 | 0.0009 | 0.0033 | 61.1 | -0.399 | -1.275 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
|
Analysis of heavy metal concentration in groundwater
|
|
Evaluation of heavy metals in groundwater by single factor pollution index and comprehensive pollution index
|
|
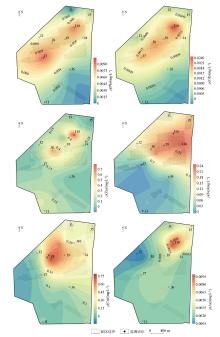
Spatial distribution characteristics of groundwater heavy metal concentration in the study area
|
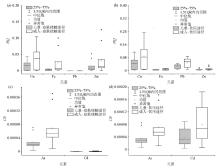
|
Box chart of health risk value of heavy metals in groundwater to children and adults under two ways
|
| [1] |
沈洪艳, 安冉, 师华定, 等. 湖南省某典型流域农用地土壤重金属污染及影响因素[J]. 环境科学究, 2021, 34(3):715-724.
|
| [1] |
Shen H Y, An R, Shi H D, et al. Heavy metal pollution and influencing factors of agricultural land in a typical watershed in Hunan Province[J]. Environmental Science Research, 2021, 34 (3):715-724.
|
| [2] |
师环环, 潘羽杰, 曾敏, 等. 雷州半岛地下水重金属来源解析及健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(9):4246-4256.
|
| [2] |
Shi H H, Pan Y J, Zeng M, et al. Source analysis and health risk assessment of heavy metals in groundwater of Leizhou Peninsula[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42 (9):4246-4256.
|
| [3] |
You D, Zhou J, Wang J, et al. Analysis of relations of heavy metal accumulation with land utilization using the positive and negative association rule method[J]. Mathematical & Computer Modelling, 2011, 54(3/4):1005-1009.
|
| [4] |
Rommel S H, Stinshoff P, Helmreich B. Sequential extraction of heavy metals from sorptive filter media and sediments trapped in stormwater quality improvement devices for road runoff[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 782:146875

|
| [5] |
秦承刚, 王旭东, 徐海峰, 等. 鲁南化工高科技园区地下水污染调查与分析[J]. 山东化工, 2016, 45(12):184-187.
|
| [5] |
Qin C G, Wang X D, Xu H F, et al. Groundwater pollution investigation and analysis of Lunan chemical high-tech industry zone[J] Shandong Chemical Industry, 2016, 45 (12):184-187
|
| [6] |
Wang T, Yuan Z, Yao J. A combined approach to evaluate activity and structure of soil microbial community in long-term heavy metals contaminated soils[J]. Environmental Engineering Research, 2017, 23(1):62-69.

|
| [7] |
Diagomanolin V, Farhang M, Ghazi-khansari M, et al.Heavy metals(Ni,Cr,Cu) in the Karoon waterway river,Iran[J]. Toxicology Letters, 2004, 151(1):63-67.
|
| [8] |
Azevedo J S, Serafim A, Company R, et al. Biomarkers of exposure to metal contamination and lipid peroxidation in the benthic fish Cathorops spixii from two estuaries in South America,Brazil[J]. Ecotoxicology, 2009, 18(8):1001-1010.
|
| [9] |
谷阳光, 高富代. 我国省会城市土壤重金属含量分布与健康风险评价[J]. 环境化学, 2017, 36(1):62-71.
|
| [9] |
Gu Y G, Gao F D. Spatial distribution and health risk assessment of heavy metals in provincial capital cities,China[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2017, 36(1):62-71.
|
| [10] |
常亮. 重金属元素镉、铬、钴、铅、锰、铊在人体骨与血中含量与年龄变化的关系探究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2018:14-19.
|
| [10] |
Chang L. Study on the relationship between age and the content of heavy metal elements such as cadmium,chromium,cobalt,lead,manganese and thallium in human bone and blood[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2018:14-19.
|
| [11] |
赵玉. 渭河干流浅层地下水与地表水中重金属Cd污染特征及风险评价[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2020, 42(2):267-277.
|
| [11] |
Zhao Y. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy meatal Cd pollution of shallow groundwater and surface water in main stream of Weihe River,China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2020, 42(2):267-277.
|
| [12] |
杨婷婷, 王璐, 尚宏鑫, 等. 大连地区海洋生物中重金属Pb和Cd对人体健康的潜在风险评价[J]. 水产养殖, 2018, 39(7):15-19.
|
| [12] |
Yang T T, Wang L, Shang H X, et al. Potential risk assessment of heavy metals(Pb and Cd)to health form marine life in Dalian region[J]. Aquaculture, 2018, 39(7):15-19.
|
| [13] |
Pokkate W, Srilert C, Wattasit S, et al. Heavy metal contamination and human health risk assessment in drinking water from shallow groundwater wells in an agricultural area in Ubon Ratchathani Province,Thailand[J]. Environmental Geochemistry & Health, 2014, 36(1):169-182.
|
| [14] |
倪彬, 王洪波, 李旭东, 等, 湖泊饮用水源地水环境健康风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2010, 23(1):74-79.
|
| [14] |
Ni B, Wang H B, Li X D, et al., Water environment health risk assessment in lake sources of drinking water[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2010, 23(1):74-79.
|
| [15] |
Chotpantarat S, Wongsasuluk P, Siriwong W, et al. Non-Carcinogenic hazard maps of heavy metal contamination in shallow groundwater for adult and aging populations at an agricultural area in Northeastern Thailand[J]. Human & Ecological Risk Assessment An International Journal, 2014, 20(3/4):689-703.
|
| [16] |
Rattan R K, Datta S P, Chhonkar P K, et al. Long-termimpact of irrigation with sewage effluents on heavy metalcontent in soils,crops and groundwater:A case study[J]. Agriculture,Ecosystems and Environment, 2005, 109(3/4):310-322.

|
| [17] |
Zhang Y, Li F, Li J, et al. Spatial distribution,potential sources,and risk assessment of trace metals of Groundwater in the North China Plain[J]. Human & Ecological Risk Assessment An International Journal, 2015, 21(3/4):726-743.
|
| [18] |
Cheng X, Qi W, Danek T, et al. Heavy metal contamination of surface water and groundwater in and Around Gejiu Tin Mine,Southwest China[J]. Inzynieria Mineralna, 2016, 17(1):93-98.
|
| [19] |
生态环境部. 化工园区地下水环境状况调查评估技术方案[S].
|
| [19] |
Ministry of Ecology and Enviroment. Technical scheme for investigation and evaluation of groundwater environmental status in Chemical Park[S].
|
| [20] |
HJ 168—2020环境监测分析方法标准制定技术导则[S].
|
| [20] |
HJ 168—2020 Technical guidelines for the development of environmental monitoring analysis method standards[S].
|
| [21] |
于林松, 万方, 范海印, 等. 姜湖贡米产地土壤重金属空间分布、源解析及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 43(8):4199-4211.
|
| [21] |
Yu L S, Wan F, Fan H Y, et al. Spatial distribution,source apportionment,and ecological risk assessment of soil heavymetals in Jianghugongmi producing area,Shandong Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 43(8):4199-4211.
|
| [22] |
Brady J P, Ayoko G A, Martens W N, et al. Development of a hybrid pollution index for heavy metals in marine and estuarine sediments[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2015, 187 (5):306.
|
| [23] |
Teng Q, Zhang D M, Deng F C, et al. Divergent patterns of heavy metal accumulation in paddy fields affect the dietary safety of rice:A case study in Maoming City,China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research International, 2021, 28(38):53533-53543.
|
| [24] |
罗杰, 张嵚, 罗密密, 等. 某离子型稀土矿不同功能区土壤退化特征[J]. 中国稀土学报, 2022, 40(2):329-338.
|
| [24] |
Luo J, Zhang Q, Luo M M, et al. Degradation characteristics of soil in different functional areas of an ion-type rare earth mine[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2022, 40(2):329-338.
|
| [25] |
GB/T 14848—2017地下水质量标准[S].
|
| [25] |
GB/T 14848—2017 Standard for groundwater quality[S].
|
| [26] |
李政红, 毕二平, 张胜, 等. 地下水污染健康风险评价方法[J]. 南水北调与水利科技, 2008, 6(6):47-51.
|
| [26] |
Li Z H, Bi E P, Zhang S, et al. Method for health risk assessment of groundwater pollution[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2008, 6(6):47-51.
|
| [27] |
艾提业古丽·热西提, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 王维维, 等. 博斯腾湖流域地下水重金属污染的人体健康风险评估[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2019, 14(2):251-259.
|
| [27] |
Atiyagul R, Mamattursun E, Wang W W, et al. The human health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution from groundwater in Bosten Lake Basin[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2019, 14(2):251-259.
|
| [28] |
Bian B, Zhou L J, Li L, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals in air,water,vegetables,grains,and related soils irrigated with biogas slurry in Taihu Basin,China[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research, 2015, 22:7794-7807.
|
| [29] |
US EPA. Regionnal screening levels[EB/OL]. 2010 [2022-03-13].Http://www.epa.gov.

|
| [30] |
刘蕊, 张辉, 勾昕, 等. 健康风险评估方法在中国重金属污染中的应用及暴露评估模型的研究进展[J]. 生态环境学报, 2014, 23(7):1239-1244.
|
| [30] |
Liu R, Zhang H, Gou X, et al. Preliminary risk assessment oftrace metal pollution in surface water from Yangtze River in Nanjing section,China[J]. Journal of Ecology and Environment, 2014, 23(7):1239-1244.
|
| [31] |
US EPA. Risk assessment guidance for superfund:Human health evaluation manual Part A, vol.1(EPA/540/1-89/002)[R]. Washington DC: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, 1989.
|
| [32] |
段小丽, 赵秀阁. 中国人群暴露参数手册(成人卷)概要[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2014.
|
| [32] |
Duan X L, Zhao X G. Highlights of the Chinese exposure factors handbook (adult)[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2014.
|
| [33] |
段小丽, 赵秀阁. 中国人群暴露参数手册(儿童卷)概要[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2016.
|
| [33] |
Duan X L, Zhao X G. Highlights of the Chinese exposure factors handbook (children )[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2016.
|
| [34] |
US EPA. Exposure factors handbook(EPA/600/P-95/002)[R]. Washington DC: Office of Emergency and Remedial Response, 1997:104-126.
|
| [35] |
US EPA. Integrated risk information system[EB/OL].[2022-03-14].Http:www.epa.gov/iris.

|
| [36] |
U.S.Department of energy the risk assessment information system[EB/OL].[2022-03-14].Http://rais.ornl.gov.

|
| [37] |
庞绪贵, 李秀章, 滕兆令, 等. 山东省黄河下游地区浅层地下水地球化学特征[J]. 岩矿测试, 2007, 26(4):298-304.
|
| [37] |
Pang X G, Li X Z, Teng Z L, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the shallow groundwater in downstream area of the Yellow River in Shandong Province[J]. Rock or Mine Testing, 2007, 26(4):298-304.
|
| [38] |
Stoeva N, Berova M, Zlatev Z. Effect of arsenic on some physiological parameters in bean plants[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2005, 49(2):293-296.

|
| [1] |
YANG Chan, WU Juan-Juan, CHE Xu-Xi, YUE Si-Yu, LIU Zhi-Feng, SONG Feng-Min. Pollution analysis and assessment of sediments in the upper reaches of the Hanjiang River[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1361-1370. |
| [2] |
LI Kai-Fu, MA Huan, ZHANG Yan, LI Wei-Long, JIANG Ji-Yi, HUANG Bin, ZHANG Long-Guan, QIN Meng-Bo. Spatio-temporal distribution of groundwater in the local area of Pinggu,Beijing derived using the time-lapse resistivity method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1002-1009. |
|
|
|
|

