|
|
|
| Spatio-temporal distribution of groundwater in the local area of Pinggu,Beijing derived using the time-lapse resistivity method |
LI Kai-Fu1( ), MA Huan2,3( ), MA Huan2,3( ), ZHANG Yan3,4, LI Wei-Long2,3, JIANG Ji-Yi2,3, HUANG Bin1, ZHANG Long-Guan1, QIN Meng-Bo2,3 ), ZHANG Yan3,4, LI Wei-Long2,3, JIANG Ji-Yi2,3, HUANG Bin1, ZHANG Long-Guan1, QIN Meng-Bo2,3 |
1. China Railway Engineering Services Co.,Ltd.,Chengdu 610036,China
2. School of Earth Sciences,Institute Disaster of Prevention,Langfang 065201,China
3. Hebei Key Laboratory of Earthquake Dynamics,Langfang 065201,China
4. School of Ecology and Environment,Institute of Disaster Prevention, Langfang 065201,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The plain area in Pinggu is a major groundwater source for Beijing.To ascertain the spatio-temporal distribution of groundwater in the study area without damaging the strata,this study,using the non-intrusive time-lapse resistivity method,conducted the reciprocal measurements with Wenner and dipole-dipole arrays in Beiyangjiaqiao Village,Pinggu District.The least-squares inversion results of the profile observation data and normalized data show that:(1)the phreatic and confined aquifers in the study area are approximately horizontally stratified,with the phreatic aquifer being recharged from the north and flowing from north to south;(2)during the entire observation period,the phreatic aquifer showed a drop in water level and leakage into the confined aquifer below;(3)the water content in the aeration zone increased from April 24,2021 to September 12,2021.In contrast,the water content in the confined aquifer remained relatively stable in this period,without experiencing significant changes.The results of this study lay the foundation for the subsequent research on Quaternary strata and groundwater in the study area.Moreover,they can be used as an important reference for the development,management,and utilization of groundwater in the study area and provide a new philosophy for research on the dynamic process of groundwater.
|
|
Received: 14 October 2022
Published: 11 October 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
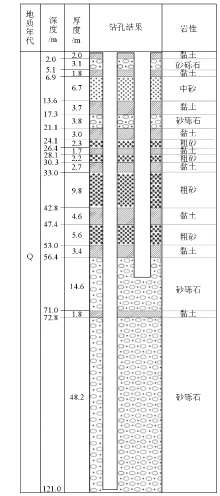
|
Stratigraphic columns of the monitoring boreholes
|
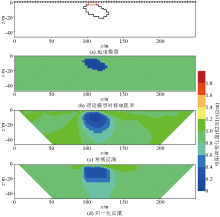
|
Comparison of different inversion methods for theoretical dynamics models and their synthetic time-lapse data
|
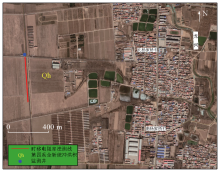
|
Geomorphology and survey line layout of study area
|

| 序号 | 观测时间 | 观测装置 | 观测方法 | 时移观
测时间
间隔/d | | T1 | 2020-11-22 | 温纳 | 单次观测 | - | | T2 | 2021-04-24 | 温纳、偶极—偶极 | 互换原理2次观测 | 153 | | T3 | 2021-09-12 | 温纳、偶极—偶极 | 互换原理2次观测 | 141 |
|
Observation scheme time-lapse resistivity method
|
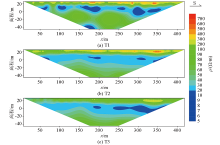
|
Inversion results of time-lapse data of Wenner array
|
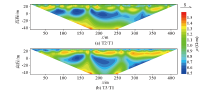
|
Inversion results of time-lapse normalized data of Wenner array
|
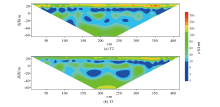
|
Inversion results of time-lapse data of Dipole-Dipole array
|
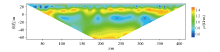
|
Inversion results of time-lapse normalized(T3/T2) data of Dipole-Dipole array
|
| [1] |
徐海珍, 李国敏, 张寿全, 等. 北京市平谷盆地地下水三维数值模拟及管理应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2011, 38(2):27-34.
|
| [1] |
Xu H Z, Li G M, Zhang S Q, et al. Development of a 3-D numerical groundwater flow model of the Pinggu Basin and groundwater resources management[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2011, 38(2):27-34.
|
| [2] |
姜体胜, 曲辞晓, 王明玉, 等. 北京平谷平原区浅层地下水化学特征及成因分析[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2017, 31(11):122-127.
|
| [2] |
Jiang T S, Qu C X, Wang M Y, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics of shallow groundwater and the origin in the Pinggu Plain,Beijing[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2017, 31(11):122-127.
|
| [3] |
李文鹏, 郑跃军, 郝爱兵. 北京平原区地下水位预警初步研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(6):166-173.
|
| [3] |
Li W P, Zheng Y J, Hao A B. A preliminary study of groundwater level pre-warning in Beijing Plain[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(6):166-173.
|
| [4] |
王丽亚, 刘久荣, 周涛, 等. 北京平原地下水可持续开采方案分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2010, 37(1):9-17.
|
| [4] |
Wang L Y, Liu J R, Zhou T, et al. Analysis of sustainable groundwater resources development scenarios in the Beijing Plain[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2010, 37(1):9-17.
|
| [5] |
Travelletti J, Sailhac P, Malet J P, et al. Hydrological response of weathered clay-shale slopes:water infiltration monitoring with time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2012, 26(14):2106-2119.

|
| [6] |
Xu D, Hu X Y, Shan C L, et al. Landslide monitoring in southwestern China via time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2016, 13(1):1-12.

|
| [7] |
Chambers J E, Gunn D A, Wilkinson P B, et al. 4D electrical resistivity tomography monitoring of soil moisture dynamics in an operational railway embankment[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 2014, 12(1):61-72.

|
| [8] |
Xu S, Sirieix C, Riss J, et al. A clustering approach applied to time-lapse ERT interpretation—Case study of Lascaux cave[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2017, 144:115-124.

|
| [9] |
Legaz A, Vandemeulebrouck J, Revil A, et al. A case study of resistivity and self-potential signatures of hydrothermal instabilities,Inferno Crater Lake,Waimangu,New Zealand[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2009, 36(12):L12306.

|
| [10] |
Power C, Gerhard J I, Karaoulis M, et al. Evaluating four-dimensional time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography for monitoring DNAPL source zone remediation[J]. Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2014, 162:27-46.
|
| [11] |
Power C, Gerhard J I, Tsourlos P, et al. Improved time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography monitoring of dense non-aqueous phase liquids with surface-to-horizontal borehole arrays[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2015, 112:1-13.

|
| [12] |
Tesfaldet Y T, Puttiwongrak A. Seasonal groundwater recharge characterization using time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography in the Thepkasattri watershed on Phuket Island,Thailand[J]. Hydro-logy, 2019, 6(2):36.
|
| [13] |
Chang P Y, Puntu J M, Lin D J, et al. Using time-lapse resistivity imaging methods to quantitatively evaluate the potential of groundwater reservoirs[J]. Water, 2022, 14(3):420.

|
| [14] |
Bai L G, Huo Z J, Zeng Z F, et al. Groundwater flow monitoring using time-lapse electrical resistivity and self potential data[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2021, 193,104411.

|
| [15] |
Meyerhoff S B, Maxwell R M, Revil A, et al. Characterization of groundwater and surface water mixing in a semiconfined karst aquifer using time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Water Resources Research, 2014, 50(3):2566-2585.

|
| [16] |
Chambers J E, Meldrum P I, Wilkinson P B, et al. Spatial monitoring of groundwater drawdown and rebound associated with quarry dewatering using automated time-lapse electrical resistivity tomography and distribution guided clustering[J]. Engineering Geo-logy, 2015, 193:412-420.
|
| [17] |
邓泽政. 平谷盆地典型污染区地下水污染监测网优化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.
|
| [17] |
Deng Z Z. Optimization of groundwater pollution monitoring network in typical polluted areas in Pinggu basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2021.
|
| [18] |
王新娟, 韩旭, 许苗娟, 等. 环境同位素在北京平谷盆地山前侧向补给研究中的应用[J]. 地质评论, 2023, 69(1):266-274.
|
| [18] |
Wang X J, Han X, Xu M J, et al. Application of environmental isotopes in the study of lateral recharge in front of Pinggu basin Beijing[J]. Geological Review, 2023, 69(1):266-274.
|
| [19] |
周怀斌. 三维密度反演算法在川西和三河—平谷地区的应用研究[D]. 廊坊: 防灾科技学院, 2022.
|
| [19] |
Zhou H B. Application of 3D density inversion algorithm in western Sichuan and Sanhe-Pinggu region[D]. Langfang: Insitute of Disaster Prevention, 2022.
|
| [20] |
邓前辉, 王继军, 汤吉, 等. 三河—平谷8级大震区地壳上地幔电性结构特征研究[J]. 地震地质, 2001, 23(2):178-185.
|
| [20] |
Deng Q H, Wang J J, Tang J, et al. Electrical structures of the crust and upper mantle in Sanhe-Pinggu M8 earthquake area,China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2001, 23(2):178-185.
|
| [21] |
傅甜甜. EnKF方法在北京市平谷区地下水数值模拟中的应用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2021.
|
| [21] |
Fu T T. Study on application of EnKF method in groundwater numerical simulation in Pinggu district,Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2021.
|
| [22] |
Daily W, Ramirez A, LaBrecque D, et al. Electrical resistivity tomography of vadose water movement[J]. Water Resources Research, 1992, 28(5):1429-1442.

|
| [23] |
Miller C R, Routh P S, Brosten T R, et al. Application of time-lapse ERT imaging to watershed characterization[J]. Geophysics, 2008, 73(3):G7-G17.

|
| [24] |
Daily W, Ramirez A, Binley A, et al. Electrical resistance tomography[J]. The Leading Edge, 2004, 23(5):438-442.

|
| [25] |
LaBrecque D J, Yang X J. Difference inversion of ERT data:a fast inversion method for 3-D in situ monitoring[J]. Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 2001, 6(2):83-89.

|
| [26] |
Cassiani G, Bruno V, Villa A, et al. A saline trace test monitored via time-lapse surface electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2006, 59(3):244-259.

|
| [27] |
马欢, 张洪洋, 郭越, 等. 时移电阻率法归一化数据反演分辨电阻率结构微小变化[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1320-1325.
|
| [27] |
Ma H, Zhang H Y, Guo Y, et al. The normalized data inversion of time-lapse resistivity method for resolving small resistivity changes[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1320-1325.
|
| [28] |
Kim J H, Yi M J, Park S G, et al. 4-D inversion of DC resistivity monitoring data acquired over a dynamically changing earth model[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2009, 68(4):522-532.

|
| [29] |
Hayley K, Pidlisecky A, Bentley L R. Simultaneous time-lapse electrical resistivity inversion[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2011, 75(2):401-411.

|
| [30] |
Loke M H, Dahlin T. A comparison of the gauss-newton and quasi-newton methods in resistivity imaging inversion[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2002, 49(3):149-162.

|
| [31] |
LaBrecque D J, Miletto M, Daily W, et al. The effects of noise on Occam’s inversion of resistivity tomography data[J]. Geophysics, 1996, 61(2):538-548.

|
| [32] |
阮百尧. 视电阻率对模型电阻率的偏导数矩阵计算方法[J]. 地质与勘探, 2001, 37(6):39-41.
|
| [32] |
Ruan B Y. A generation method of the partial derivatives of the apparent resistivity with respect to the model resistivity parameter[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2001, 37(6):39-41.
|
| [1] |
FAN Hai-Yin, SONG Rui-Rui, YU Lin-Song, TENG Yong-Bo, WAN Fang, ZHANG Xiu-Wen, LI Sheng-Yu, ZHAO Chuang. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of groundwater in a typical chemical industry park in northwestern Shandong, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1326-1335. |
| [2] |
YANG Tian-Chun, HU Feng-Ming, YU Xi, FU Guo-Hong, LI Jun, YANG Zhui. Analysis and application of the responses of the frequency selection method of telluric electricity field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1010-1017. |
|
|
|
|

