|
|
|
| Reservoir lithology identification method based on multi-scale time-frequency-space feature combination |
WANG Zong-Ren1,2,3( ), WEN Chang4,5( ), WEN Chang4,5( ), XIE Kai1,2,3, SHENG Guan-Qun6, HE Jian-Biao7 ), XIE Kai1,2,3, SHENG Guan-Qun6, HE Jian-Biao7 |
1. School of Electronic Information,Yangtze University,Jingzhou 434023,China
2. Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Resources and Exploration Technology, Ministry of Education,Jingzhou 434023,China
3. National Experimental Teaching and Demonstration Center of Electrical Engineering and Electronics,Yangtze University,Jingzhou 434023,China
4. Western Research Institute of Yangtze University,Xinjiang 834000,China
5. School of Computer Science,Yangtze University,Jingzhou 434023,China
6. School of Computer and Information,China Three Gorges University,Yichang 443002,China
7. School of Computer Science,Central South University,Changsha 410083,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Conventional methods for reservoir lithology identification suffer low precision and efficiency since reservoir lithologies have various types and complex compositions and alternate frequently.This study proposed a reservoir lithology identification method based on multi-scale time-frequency-space feature combination.Based on the original logging characteristics,this method introduced the multi-scale frequency-domain components from the complementary ensemble empirical mode decomposition (CEEMD) to improve the longitudinal resolution of log curves.Moreover,a multi-scale convolutional neural network-bidirectional gated recurrent unit-attention mechanism (CNN-BiGRU-AT) model was constructed to extract the spatio-temporal features of log data containing multi-scale frequency-domain components.In this way,the joint learning of time-frequency-space features of log data was realized.Finally,the model output was optimized using the attention mechanism to reduce the propagation of error information.To verify the reliability of this method,an experimental analysis was conducted using the data from five wells that have relatively complete data.As revealed by the analysis results,the identification accuracy of training and verification sets containing multi-scale frequency-domain components was increased by 9.50% and 8.66%,respectively in the comparative experiments of different data combinations.The method proposed in this study yielded sample identification accuracy of 94.11%.Compared with support vector machine (SVM),backpropagation (BP) neural network,convolutional neural network (CNN),bidirectional gated recurrent unit (BiGRU),and CNN-BiGRU fusion models, the identification accuracy of this method increased by 16.21%,14.54%,11.69%,5.05%,and 3.38%,respectively.
|
|
Received: 25 January 2022
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
WEN Chang
E-mail: wangzongren1999@163.com;wenchang2016paper@163.com
|
|
|
|

| 步骤 | 描述 | | Step 1: | 将高斯白噪声 加入待分解 中得到新信号 , 为加入白噪声的次数, : | | Step 2: | 对加入噪声的新信号进行EMD分解,并得出一阶本征模态分量 : | | Step 3: | 对N个模态分量进行总体平均得到CEEMD分解的第一个本征模态分量: | | Step 4: | 去除第一个模态分量后的残差: | | Step 5: | 在 中加入正负的高斯白噪声,再次进行EMD分解,得到一阶模态分量 ,由此可得到第2个本征模态分量 : | | Step 6: | 去除第二个本征模态分量后的残差: | | Step 7: | 重复以上步骤,直到 不能再次分解,算法结束。此时本征模态分量数量为K,原始信号 被分解为: |
|
Algorithm process of CEEMD
|
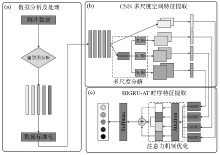
|
Flow chart of multi-scale CNN-BiGRU-AT lithology identification algoritm
|
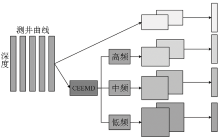
|
CNN multi-scale space feature extraction
|
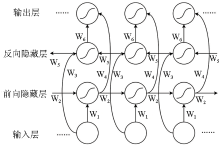
|
BiGRU network structure diagram
|
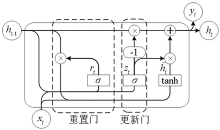
|
Cell structure of GRU
|
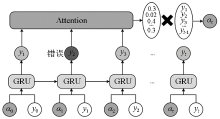
|
Attention mechanism optimization diagram
|

| 深度 | AC | GR | MINV | MNOR | R4 | SP | Label | | 3200 | 192.5 | 3.735 | 5.183 | 4.34 | 20.923 | 17.097 | 3 | | 3200.125 | 190.439 | 3.939 | 5.217 | 5.908 | 22.488 | 17.065 | 3 | | 3200.25 | 189.385 | 4.278 | 4.716 | 6.812 | 24.14 | 16.997 | 3 | | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | | 3799.75 | 327.084 | 8.221 | 0.856 | 0.807 | 1.84 | 19.522 | 0 | | 3799.875 | 332.941 | 8.47 | 0.895 | 0.877 | 1.841 | 19.522 | 0 | | 3800 | 331.738 | 8.53 | 0.953 | 0.935 | 1.841 | 19.623 | 0 |
|
Partial logging lithology data
|
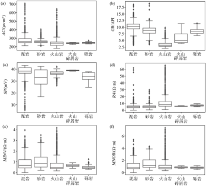
|
Logging lithology box diagram of Well Su 27
|

| 参数类型 | 参数值 | | 卷积层Ⅰ卷积核尺寸 | 3×6、5×6、7×6、9×6 | | 卷积层Ⅱ卷积核尺寸 | 3×1、5×1、7×1、9×1 | | 卷积层Ⅰ卷积核个数 | 32 | | 卷积层Ⅱ卷积核个数 | 64 | | 每层BiGRU的GRU单元个数 | 128×2 | | 丢弃概率 | 0.3 | | 学习率 | 0.0001 | | 迭代次数 | 300 | | 批次大小 | 64 | | 优化器 | Adam |
|
Experimental hyperparameter configuration
|
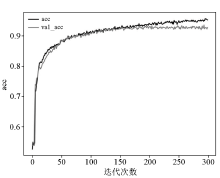
|
Relationship between accuracy rate and iteration times
|
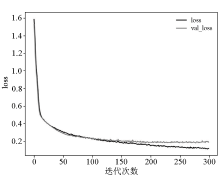
|
Relation diagram of loss value and iteration times
|
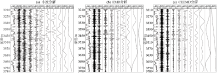
|
GR curve decomposition diagram of by different methods
|

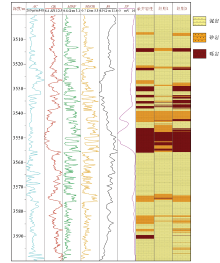
| 组别 | 数据类型 | | 原测井数据 | 多尺度频
率分量 | 训练识别
准确率/% | 验证识别
准确率/% | | 1 | √ | | 75.69 | 75.02 | | 2 | | √ | 71.86 | 71.27 | | 3 | √ | √ | 85.19 | 83.68 |
|
Experimental results of different combinations of data
|
|
Lithology identification bar charts for groups 1 and 3
|

| 岩性 | 精准率/% | | SVM | BP | CNN | BiGRU | CNN-
BiGRU | 本文
方法 | | 泥岩 | 80.76 | 81.78 | 84.01 | 88.53 | 89.55 | 93.05 | | 砂岩 | 55.68 | 60.34 | 64.26 | 82.81 | 84.79 | 90.41 | | 砾岩 | 39.13 | 16.13 | 68.00 | 70.73 | 81.55 | 95.10 | | 火山岩 | 92.34 | 93.08 | 93.72 | 96.61 | 99.18 | 99.64 | | 火山碎屑岩 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 55.56 | 82.61 | 88.00 | | 准确率/% | 77.90 | 79.57 | 82.42 | 89.06 | 90.73 | 94.11 |
|
Lithology identification results of different models in Well Su 27
|
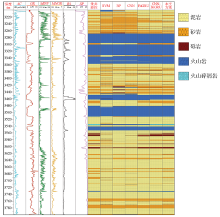
|
Histogram of lithology identification results of different models in Well Su 27
|

| 真实岩性 | 预测岩性(本文方法/CNN-BiGRU) | 精准率/% | 召回率/% | F1得分/% | | 泥岩 | 砂岩 | 砾岩 | 火山岩 | 火山碎屑岩 | | 泥岩 | 2503/2468 | 80/107 | 3/9 | 2/4 | 0/0 | 93.05/89.55 | 96.72/95.36 | 94.85/92.37 | | 砂岩 | 174/260 | 792/697 | 2/10 | 1/2 | 0/0 | 90.04/84.79 | 81.73/71.93 | 85.85/77.83 | | 砾岩 | 7/18 | 0/2 | 97/84 | 0/0 | 0/0 | 95.10/81.55 | 93.27/80.77 | 94.17/81.16 | | 火山岩 | 3/6 | 2/14 | 0/0 | 1104/1088 | 3/4 | 99.64/99.18 | 99.28/97.84 | 99.46/98.51 | | 火山碎屑岩 | 3/4 | 2/2 | 0/0 | 1/3 | 22/19 | 88.00/82.61 | 78.57/67.86 | 83.02/74.51 |
|
Confusion matrix of this method and CNN-BiGRU model for Well Su 27
|
| [1] |
付光明, 严加永, 张昆, 等. 岩性识别技术现状与进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(1):26-40.
|
| [1] |
Fu G M, Yan J Y, Zhang K, et al. Current status and progress of lithology identification technology[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(1):26-40.
|
| [2] |
Adeniran A A, Adebayo A R, Salami H O, et al. A competitive ensemble model for permeability prediction in heterogeneous oil and gas reservoirs[J]. Applied Computing and Geosciences, 2019, 1:100004.

|
| [3] |
袁照威, 段正军, 张春雨, 等. 基于马尔科夫概率模型的碳酸盐岩储集层测井岩性解释[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2017, 38(1):96-102.
|
| [3] |
Yuan Z W, Duan Z J, Zhang G Y, et al. Interpretation of logging lithology in Carbonate reservoirs based on Markov Chain probability model[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2017, 38(1):96-102.
|
| [4] |
成大伟, 袁选俊, 周川闽, 等. 测井岩性识别方法及应用——以鄂尔多斯盆地中西部长7油层组为例[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(5):117-126.
|
| [4] |
Cheng D W, Yuan X J, Zhou C M, et al. Logging-lithology identifi cation methods and their application:A case study on Chang 7 Member in central-western Ordos Basin,NW China[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2016, 21(5):117-126.
|
| [5] |
王泽华, 朱筱敏, 孙中春, 等. 测井资料用于盆地中火成岩岩性识别及岩相划分:以准噶尔盆地为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(3):254-268.
|
| [5] |
Wang Z H, Zhu X M, Sun Z C, et al. Igneous lithology identification and lithofacies classification in the basin using logging data:Taking Junggar Basin as an example[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(3):254-268.
|
| [6] |
Bai X L, Zhang S N, Huang Q Y, et al. Origin of dolomite in the Middle Ordovician peritidal platform carbonates in the northern Ordos Basin,western China[J]. Petroleum Science, 2016, 13(3):434-449.

|
| [7] |
Bressan T S, Souza M, Girelli T J, et al. Evaluation of machine learning methods for lithology classification using geophysical data[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2020, 139:104475.

|
| [8] |
Corina A N, Hovda S. Automatic lithology prediction from well logging using kernel density estimation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 170:664-674.

|
| [9] |
安鹏, 曹丹平. 基于深度学习的测井岩性识别方法研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(3):1029-1034.
|
| [9] |
An P, Cao D P. Research and application of logging lithology identification based on deep learning[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(3):1029-1034.
|
| [10] |
蔡泽园, 鲁宝亮, 熊盛青, 等. 基于自适应核密度的贝叶斯概率模型岩性识别方法研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):919-927.
|
| [10] |
Cai Z Y, Lu B L, Xiong S Q, et al. Lithology identification based on Bayesian probability using adaptive kernel density[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):919-927.
|
| [11] |
谷宇峰, 张道勇, 鲍志东, 等. GBDT识别致密砂岩储层岩性[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(5):1956-1965.
|
| [11] |
Gu Y F, Zhang D Y, Bao Z D, et al. Lithology prediction of tight sandstone reservoirs using GBDT[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 169(5):1956-1965.
|
| [12] |
苏赋, 马磊, 罗仁泽, 等. 基于改进多分类孪生支持向量机的测井岩性识别方法研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(1):174-180.
|
| [12] |
Su F, Ma L, Luo R Z, et al. Research and application of logging lithology identification based on improve multi-class twin support vector machine[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(1):174-180.
|
| [13] |
杨柳青, 陈伟, 查蓓. 利用卷积神经网络对储层孔隙度的预测研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(4):1548-1555.
|
| [13] |
Yang L Q, Chen W, Cha P. Prediction and application of reservoir porosity by convolutional neural network[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(4):1548-1555.
|
| [14] |
武中原, 张欣, 张春雷, 等. 基于LSTM循环神经网络的岩性识别方法[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2021, 33(3):120-128.
|
| [14] |
Wu Z Y, Zang X, Zhang C L, et al. Lithology identification based on LSTM recurrent neural network[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2021, 33(3):120-128.
|
| [15] |
周恒, 张春雷, 张欣, 等. 基于胶囊网络的碳酸盐岩储层岩性识别方法[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2021, 32(5):685-694.
|
| [15] |
Zhou H, Zhang C L, Zhang X, et al. Lithology identification method of carbonate reservoir based on capsule network[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2021, 32(5):685-694.
|
| [16] |
王逸宸, 柳林涛, 许厚泽. 基于卷积神经网络识别重力异常体[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(2):394-400.
|
| [16] |
Wang Y C, Liu L T, Xu H Z. The identification of gravity anomaly body based on the convolutional neural network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(2):394-400.
|
| [17] |
梁立锋, 刘秀娟, 张宏兵, 等. 超参数对GRU-CNN混合深度学习弹性阻抗反演影响研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1):133-139.
|
| [17] |
Liang L F, Liu X J, Zhang H B, et al. A study of the effect of hyperparameters GRU-CNN hybrid deep learning EI inversion[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1):133-139.
|
|
|
|

