|
|
|
| Flux of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet precipitation and their effects on farmland soil: A case study of Chongzhou,Sichuan |
YE Jiao-Long( ), ZHONG Hong-Mei, XU Zheng-Qiang, MA Chan-Hua ), ZHONG Hong-Mei, XU Zheng-Qiang, MA Chan-Hua |
| Sichuan Institute of Nuclear Geology Survey, Chengdu 610061, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract It shows that atmospheric deposition is one of the main sources of soil heavy metal pollution. In order to find out the effects of atmospheric wet and dry deposition on farmland soil, the accumulation of heavy metals in farmland soil was analysed by monitoring the dry and wet deposition in the study area and testing the heavy metal content, estimating the dry and wet deposition flux, heavy metal change rate and potential ecological risk assessment. The results showed that the heavy metal content of dry and wet sediment exceeded the content of Cd, Pb and Zn in the surrounding soil, and Cd and Zn exceeded the soil pollution screening value of agricultural land by 2.25 times and 1.09 times;The annual flux of heavy metal elements in the dry and wet precipitation of the atmosphere is smaller than the national average, and the sedimentation flux order is Zn>Cr>Pb>Cu>Ni>As>Cd>Hg, the annual sedimentation flux of Zn is the highest, and the sedimentation flux of Cd is low. The geo-accumulation index showed that in the atmospheric dust, Cd reached extremely high pollution level, followed by Hg, Pb, there was no As and Ni pollution. The heavy metals with the most significant impact of atmospheric dry and wet sediment on soil were Cd and Zn, with an increase of 0.421 mg/kg and 104.653 mg/kg after one year, and the annual change rates reached 0.138% and 0.146%, which indicated that the atmospheric deposition was one of the most important sources of the heavy metal Cd and Zn in the farmland soil. The sedimentation flux of Cd is low, but its content exceeded the standard the most, and caused the most significant changes in the soil environment, which needs to be paid attention to.
|
|
Received: 26 March 2024
Published: 22 July 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distribution map of atmospheric dry and wet deposition monitoring samples
|

| | As | Hg | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 湿物质 | 最大值 | 0.00059 | - | 0.00027 | 0.07544 | 0.00672 | 0.00156 | 0.01920 | 0.32167 | | 最小值 | - | - | 0.00008 | 0.00276 | 0.00089 | 0.00033 | 0.00073 | 0.01148 | | 平均值 | 0.00046 | - | 0.00012 | 0.01288 | 0.00308 | 0.00063 | 0.00376 | 0.05807 | | 干物质 | 最大值 | 6.65358 | 0.16257 | 1.99882 | 62.99439 | 50.64183 | 20.86872 | 163.72294 | 420.90655 | | 最小值 | 1.21612 | 0.04969 | 0.55682 | 15.32678 | 12.19508 | 5.02972 | 20.35649 | 102.76901 | | 平均值 | 2.46887 | 0.10948 | 1.35057 | 41.21737 | 32.86500 | 13.38574 | 66.39179 | 271.63615 | | 研究区土壤平均值 | 11.72 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 93.54 | 38.46 | 33.97 | 41.86 | 104.50 | | 四川省土壤背景值 | 10.4 | 0.061 | 0.079 | 79 | 31.1 | 32.6 | 30.9 | 86.5 | | 风险筛选值 | 35 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 200 | 200 | 100 | 120 | 250 |
|
The content of heavy metals deposed by dry and wet precipitation in the study area mg/kg
|

| | As | Hg | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | 2020年12月~
2021年11月 | 最小值 | 0.136 | 0.006 | 0.05 | 1.261 | 1.095 | 0.358 | 1.5 | 8.202 | | 最大值 | 0.336 | 0.027 | 0.181 | 26.826 | 5.906 | 1.733 | 15.227 | 97.089 | | 均值 | 0.242 | 0.017 | 0.122 | 6.218 | 3.035 | 1.080 | 5.474 | 31.785 | | 标准差 | 0.060 | 0.006 | 0.039 | 6.831 | 1.329 | 0.372 | 3.497 | 21.245 | | 2004年8月~2005年8月成都经济区[5] | 最小值 | 0.38 | 0.01 | 0.64 | - | - | - | 11.00 | 35.84 | | 最大值 | 11.74 | 0.50 | 10.28 | - | - | - | 320.15 | 1423.87 | | 均值 | 2.77 | 0.10 | 1.77 | - | - | - | 45.95 | 147.83 | | 标准差 | 2.45 | 0.09 | 1.74 | - | - | - | 56.16 | 286.01 | | 全国平均值 | 2.45 | 0.036 | 0.48 | 15.08 | 13.09 | 5.9 | 22.99 | 70.11 |
|
The flux of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet deposition mg/(m2·a)
|
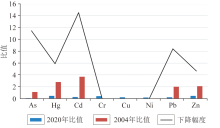
|
Comparison of flux changes of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition
|
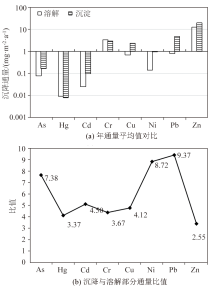
|
The ratio of the precipitation to the dissolved fraction of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition
|
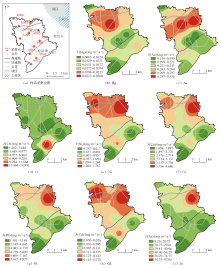
|
Geochemical map of annual flux of atmospheric heavy metal deposition of dry and wet
|

| 元素 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | | As | -2.51 | -0.06 | -1.64 | | Hg | 0.29 | 2.00 | 1.36 | | Cd | 3.4 | 5.25 | 4.57 | | Cr | -1.78 | 0.26 | -0.5 | | Cu | -0.77 | 1.29 | 0.52 | | Ni | -2.11 | -0.06 | -0.84 | | Pb | -0.02 | 2.99 | 1.46 | | Zn | 0.83 | 2.87 | 2.11 |
|
Geo-accumulation index of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition
|
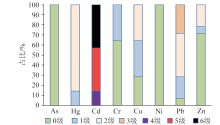
|
Features of geo-accumulation index
|

| 采样点 | As | Hg | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | | A001 | 11.718 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.601 | 38.465 | 33.966 | 41.875 | 104.637 | | A002 | 11.716 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.661 | 38.478 | 33.965 | 41.934 | 104.693 | | A003 | 11.716 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.520 | 38.463 | 33.961 | 41.873 | 104.672 | | A004 | 11.719 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.540 | 38.467 | 33.968 | 41.880 | 104.649 | | A005 | 11.718 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.540 | 38.477 | 33.969 | 41.902 | 105.063 | | A006 | 11.718 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.537 | 38.468 | 33.968 | 41.878 | 104.639 | | A007 | 11.716 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.549 | 38.472 | 33.963 | 41.896 | 104.716 | | A008 | 11.718 | 0.170 | 0.420 | 93.535 | 38.465 | 33.968 | 41.871 | 104.590 | | A009 | 11.712 | 0.170 | 0.420 | 93.487 | 38.447 | 33.949 | 41.850 | 104.565 | | A010 | 11.715 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.511 | 38.452 | 33.957 | 41.864 | 104.662 | | A011 | 11.716 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.523 | 38.459 | 33.961 | 41.869 | 104.613 | | A012 | 11.721 | 0.170 | 0.420 | 93.543 | 38.465 | 33.970 | 41.867 | 104.545 | | 最小值 | 11.712 | 0.170 | 0.420 | 93.487 | 38.447 | 33.949 | 41.850 | 104.545 | | 最大值 | 11.721 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.661 | 38.478 | 33.970 | 41.934 | 105.063 | | 平均值 | 11.717 | 0.170 | 0.421 | 93.541 | 38.463 | 33.963 | 41.877 | 104.653 |
|
The amount of changes of heavy metals in the soil after one year of dry and wet precipitation mg/kg
|

| 累积时间/a | As | Hg | Cd | Cr | Cu | Ni | Pb | Zn | | 1 | -0.027 | 0.022 | 0.138 | 0.001 | 0.009 | -0.020 | 0.040 | 0.146 | | 3 | -0.082 | 0.066 | 0.414 | 0.003 | 0.026 | -0.061 | 0.121 | 0.439 | | 5 | -0.136 | 0.110 | 0.689 | 0.004 | 0.043 | -0.102 | 0.201 | 0.731 | | 10 | -0.271 | 0.220 | 1.375 | 0.009 | 0.085 | -0.203 | 0.401 | 1.460 | | 20 | -0.539 | 0.439 | 2.740 | 0.018 | 0.170 | -0.403 | 0.800 | 6.913 | | 50 | -1.328 | 1.087 | 6.769 | 0.049 | 0.422 | -0.992 | 1.979 | 7.188 | | 100 | -2.592 | 2.138 | 13.280 | 0.105 | 0.839 | -1.934 | 3.890 | 14.110 |
|
The annual variation rate of heavy metals in soil caused by atmospheric dry and wet deposition
|
| [33] |
Zhang G Z. Influence of atmospheric deposition on heavy metal pollution in farmland soil in Bohai Rim region and its control countermeasures[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu Agricultural University, 2019.
|
| [34] |
龚香宜, 祁士华, 吕春玲, 等. 福建省兴化湾大气重金属的干湿沉降[J]. 环境科学研究, 2006, 19(6):31-34.
|
| [34] |
Gong X Y, Qi S H, Lv C L, et al. Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals to Xinghua Bay,Fujian Province[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2006, 19(6):31-34.
|
| [35] |
Rühling Å. A European survey of atmospheric heavy metal deposition in 2000-2001[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2002, 120(1):23-25.
|
| [36] |
Tasdemir Y, Kural C. Atmospheric dry deposition fluxes of trace elements measured in Bursa,Turkey[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2005, 138(3):462-472.
|
| [37] |
De P Pereira P A, Lopes W A, Carvalho L S, et al. Atmospheric concentrations and dry deposition fluxes of particulate trace metals in Salvador,Bahia,Brazil[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(36):7837-7850.
|
| [38] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部.土地质量地球化学评价规范:DZ/T 0295—2016[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [38] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People’s Republic of China.Determination of land quality geochemical evaluation:DZ/T 0295—2016[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2016.
|
| [39] |
Dai L J, Wang L Q, Li L F, et al. Multivariate geostatistical analysis and source identification of heavy metals in the sediment of Poyang Lake in China[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018,621:1433-1444.
|
| [40] |
Wu W, Wu P, Yang F, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and human health risks in urban soils around an electronics manufacturing facility[J]. Science of The Total Environment, 2018,630:53-61.
|
| [41] |
Cai K, Li C, Na S. Spatial distribution,pollution source,and health risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric depositions:A case study from the sustainable city of Shijiazhuang,China[J]. Atmosphere, 2019, 10(4):222.
|
| [42] |
国家环境保护局, 中国环境监测总站. 中国土壤元素背景值[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社,1990:334-379.
|
| [42] |
Environmental Protection Administration, China Environmental Monitoring Station. Background values of soil elements in China[S]. Beijing: Environmental Science Press of China,1990:334-379.
|
| [43] |
生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局. 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准:GB 15618—2018[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
|
| [43] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment,State Administration for Market Supervision and Administration. Soil environmental quality Risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land:GB 15618—2018[S].Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2018.
|
| [1] |
Kapusta P, Stanek M, Szarek-Łukaszewska G, et al. Long-term moss monitoring of atmospheric deposition near a large steelworks reveals the growing importance of local non-industrial sources of pollution[J]. Chemosphere, 2019,230:29-39.
|
| [2] |
Deng Y, Jiang L H, Xu L F, et al. Spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in contaminated paddy fields:A case study in Xiangtan City,Southern China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2019,171:281-289.
|
| [3] |
王增辉. 鲁西南平原区大气干湿沉降元素输入通量及来源浅析:以巨野县为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4):839-846.
|
| [3] |
Wang Z H. An analysis of the input flux and source of elements in dry and wet atmospheric deposition of southwest plain of Shandong:A case study of Juye County[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4):839-846.
|
| [4] |
张夏, 刘斌, 肖柏林, 等. 重庆主城大气降尘中重金属污染特征及评价[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12):5288-5294.
|
| [4] |
Zhang X, Liu B, Xiao B L, et al. Pollution characteristics and assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric deposition in core urban areas,Chongqing[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12):5288-5294.
|
| [5] |
汤奇峰, 杨忠芳, 张本仁, 等. 成都经济区As等元素大气干湿沉降通量及来源研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2007, 14(3):213-222.
|
| [5] |
Tang Q F, Yang Z F, Zhang B R, et al. A study of elements flux and sources from atmospheric bulk deposition in the Chengdu Economic Region[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(3):213-222.
|
| [6] |
陈雅丽, 翁莉萍, 马杰, 等. 近十年中国土壤重金属污染源解析研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(10):2219-2238.
|
| [6] |
Chen Y L, Weng L P, Ma J, et al. Review on the last ten years of research on source identification of heavy metal pollution in soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(10):2219-2238.
|
| [7] |
王梦梦, 原梦云, 苏德纯. 我国大气重金属干湿沉降特征及时空变化规律[J]. 中国环境科学, 2017, 37(11):4085-4096.
|
| [7] |
Wang M M, Yuan M Y, Su D C. Characteristics and spatial-temporal variation of heavy metals in atmospheric dry and wet deposition of China[J]. China Environmental Science, 2017, 37(11):4085-4096.
|
| [8] |
黄春雷, 宋金秋, 潘卫丰. 浙东沿海某地区大气干湿沉降对土壤重金属元素含量的影响[J]. 地质通报, 2011, 30(9):1434-1441.
|
| [8] |
Huang C L, Song J Q, Pan W F. Impact of dry and wet atmospheric deposition on content of heavy metals in soils along coastal areas of eastern Zhejiang Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2011, 30(9):1434-1441.
|
| [9] |
栾慧君, 塞古, 徐蕾, 等. 徐州北郊大气降尘重金属污染特征与风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(11):4679-4687.
|
| [9] |
Luan H J, Sai G, Xu L, et al. Characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals from atmospheric deposition in northern suburban of Xuzhou[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(11):4679-4687.
|
| [10] |
孙锐, 周晓芳, 陈阳, 等. 正定矩阵因子模型解析鄂尔多斯高原煤矿土壤重金属来源[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2021, 21(16):6937-6943.
|
| [10] |
Sun R, Zhou X F, Chen Y, et al. Positive definite matrix factor model analysis of the source of heavy metals in coal mine soils in the Ordos Plateau[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(16):6937-6943.
|
| [11] |
叶娇珑, 袁宏, 马婵华, 等. 成都平原某农田区大气降尘重金属含量特征及生态风险评价[J]. 四川环境, 2023, 42(3):65-71.
|
| [11] |
Ye J L, Yuan H, Ma C H, et al. Characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in atmospheric dust in a farmland area in Chengdu Plain[J]. Sichuan Environment, 2023, 42(3):65-71.
|
| [12] |
环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[R]. [2014-04-17]. https://www.gov.cn/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm.

|
| [12] |
Ministry of Environmental Protection,Ministry of Land and Resources. Report on the national general survey of soil contamination[R]. [2014-04-17]. https://www.gov.cn/foot/2014-04/17/content_2661768.htm.

|
| [13] |
生态环境部. 2021 年中国生态环境状况公报[R]. [2022-05-26]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-05/28/content_5692799.htm.

|
| [13] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. Report on the China’s ecological and environmental conditions[R]. [2022-05-26]. https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2022-05/28/content_5692799.htm.

|
| [14] |
米雅竹, 梁家妮, 周俊, 等. 典型冶炼厂大气沉降区农田耕层土壤重金属(Cd、Cu、Pb)输入输出平衡研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2024, 61(5):1339-1348.
|
| [14] |
Mi Y Z, Liang J N, Zhou J, et al. Input and output balance of heavy metals (Cd,Cu,Pb) in arable soils in atmospheric deposition area of typical smelter[J]. China Industrial Economics, 2024, 61(5):1339-1348.
|
| [15] |
张国忠, 黄威, 潘月鹏, 等. 河北典型农田大气重金属干沉降通量及来源解析[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2019, 27(8):1245-1254.
|
| [15] |
Zhang G Z, Huang W, Pan Y P, et al. Dry deposition flux of atmospheric heavy metals and its source apportionment in a typical farmland of Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2019, 27(8):1245-1254.
|
| [16] |
蔡柯柯, 赵志强, 蒙丽, 等. 重庆市秀山县北部大气干湿沉降重金属元素分布特征及来源分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(1):237-244.
|
| [16] |
Cai K K, Zhao Z Q, Meng L, et al. Distribution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals from dry and wet atmospheric deposition in northern XiushanCounty,Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1):237-244.
|
| [17] |
Pacyna J M, Pacyna E G, Aas W. Changes of emissions and atmospheric deposition of mercury,lead,and cadmium[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2009, 43(1):117-127.
|
| [18] |
Conko K M, Rice K C, Kennedy M M. Atmospheric wet deposition of trace elements to a suburban environment,Reston,Virginia,USA[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(24):4025-4033.
|
| [19] |
Sakata M, Tani Y, Takagi T. Wet and dry deposition fluxes of trace elements in Tokyo Bay[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(23):5913-5922.
|
| [20] |
Castillo S, de la Rosa J D, Sánchez de la Campa A M, et al. Heavy metal deposition fluxes affecting an Atlantic coastal area in the southwest of Spain[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2013,77:509-517.
|
| [21] |
Aas W, Shao M, Jin L, et al. Air concentrations and wet deposition of major inorganic ions at five non-urban sites in China,2001-2003[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2007, 41(8):1706-1716.
|
| [22] |
Rossini P, Matteucci G, Guerzoni S. Atmospheric fall-out of metals around the murano glass-making district (Venice,Italy)[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2010, 17(1):40-48.
|
| [23] |
Weerasundara L, Amarasekara R W K, Magana-Arachchi D N, et al. Microorganisms and heavy metals associated with atmospheric deposition in a congested urban environment of a developing country:Sri Lanka[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2017,584:803-812.
|
| [24] |
Davis B S, Birch G F. Spatial distribution of bulk atmospheric deposition of heavy metals in metropolitan Sydney,Australia[J]. Water,Air,& Soil Pollution, 2011, 214(1):147-162.
|
| [25] |
Sabin L D, Schiff K C. Dry atmospheric deposition rates of metals along a coastal transect in southern California[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2008, 42(27):6606-6613.
|
| [26] |
杨忠平, 卢文喜, 龙玉桥. 长春市城区重金属大气干湿沉降特征[J]. 环境科学研究, 2009, 22(1):28-34.
|
| [26] |
Yang Z P, Lu W X, Long Y Q. Atmospheric dry and wet deposition of heavy metals in Changchun City,China[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2009, 22(1):28-34.
|
| [27] |
王艳, 刘晓环, 金玲仁, 等. 泰山地区湿沉降中重金属的空间分布[J]. 环境科学, 2007, 28(11):2562-2568.
|
| [27] |
Wang Y, Liu X H, Jin L R, et al. Spatial variations of heavy metals in precipitation at mount Taishan Region[J]. Environmental Science, 2007, 28(11):2562-2568.
|
| [28] |
潘月鹏, 王跃思, 杨勇杰, 等. 区域大气颗粒物干沉降采集及金属元素分析方法[J]. 环境科学, 2010, 31(3):553-559.
|
| [28] |
Pan Y P, Wang Y S, Yang Y J, et al. Determination of trace metals in atmospheric dry deposition with a heavy matrix of PUF by inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy after microwave digestion[J]. Environmental Science, 2010, 31(3):553-559.
|
| [29] |
Pan Y P, Wang Y S. Atmospheric wet and dry deposition of trace elements at 10 sites in Northern China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2015, 15(2):951-972.
|
| [30] |
张小敏, 张秀英, 钟太洋, 等. 中国农田土壤重金属富集状况及其空间分布研究[J]. 环境科学, 2014, 35(2):692-703.
|
| [30] |
Zhang X M, Zhang X Y, Zhong T Y, et al. Spatial distribution and accumulation of heavy metal in arable land soil of China[J]. Environmental Science, 2014, 35(2):692-703.
|
| [31] |
杨昱祺, 王小策, 孙淑蕊, 等. 不同农业用地类型对土壤性质和土壤环境的影响——以北京市延庆县为例[J]. 水土保持通报, 2014, 34(5):313-316,321.
|
| [31] |
Yang Y Q, Wang X C, Sun S R, et al. Effects of different agricultural land use types on soil properties and soil environment:A case study in Yanqing County of Beijing City[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 34(5):313-316,321.
|
| [32] |
Meng W Q, Wang Z W, Hu B B, et al. Heavy metals in soil and plants after long-term sewage irrigation at Tianjin China:A case study assessment[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2016,171:153-161.
|
| [33] |
张国忠. 环渤海区域大气沉降对农田土壤重金属污染的影响及其防治对策研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃农业大学, 2019.
|
| [1] |
HAN Bing, HUANG Yong, LI Huan, AN Yong-Long. Distributions, enrichment characteristics, and sources of heavy metals in soils in Fangshan District, Beijing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 820-833. |
| [2] |
JIANG Yu-Xiong, WEN Mei-Lan, PAN Qi-Ming, JIANG Bo-Chang, WANG Zhong-Wei. The migration,transformation and ecological effects of heavy metals in soil-cropsystem in Lipu, Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 858-867. |
|
|
|
|

