|
|
|
| Geochemical evaluation of surface soil nutrients in eastern Maqin County, Qinghai Province, China |
ZHANG Hao1,2( ), NIU Yao1,2, ZHANG Hai-Xu1,2, SHA Hui-Lan1,2 ), NIU Yao1,2, ZHANG Hai-Xu1,2, SHA Hui-Lan1,2 |
1. The Fifth Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province, Xining 810003, China
2. Engineering Technology Research Center for Selenium-Rich Resource Utilization of Qinghai Province, Xining 810003, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Maqin County, an important county of animal husbandry in Qinghai Province, hosts more than 13 million mu of naturally available grassland and rich forage resources. In 2022, a 1∶250 000 land (grassland) quality geochemical survey was carried out in the eastern part of Maqin County. This survey represents the first large-scale land quality survey of grassland in the Qingnan region of Qinghai Province, setting a model exemplary role. Based on nutrient content in plants from the surface soil in the survey area, this study assessed the abundance and deficiency of various nutrient elements. The results indicate that soils in the survey area are dominated by first- and second-grade soils in terms of comprehensive geochemical grades of soil nutrients, accounting for 91.68% of the total area. In contrast, third- and fourth-grade soils collectively represent 8.33%, with no fifth-grade soils identified. The generally rich nutrients in the soils provide a solid foundation for the development of plateau-specific agriculture and animal husbandry. The results of this study provide essential foundational information for the planning and utilization of local grasslands, the development of agriculture and animal husbandry with local features, and the restoration of degraded pastures.
|
|
Received: 19 April 2024
Published: 22 July 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
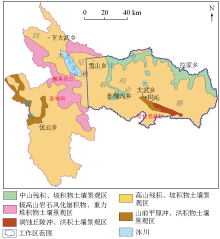
|
Soil landscape zoning map of Maqin County
|
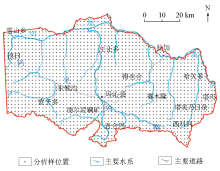
|
Analyzing sample bitmaps
|

元素/
指标 | 分析
方法 | 要求
检出限 | 方法
检出限 | 报出
率/% | 重复性检验
合格率/% | | N | VOL | 20 | 20 | 100 | 100 | | P | XRF | 10 | 10 | 100 | 100 | | K2O | ICP-AES | 0.05* | 0.05* | 100 | 100 | | 有机质 | VOL | 0.1* | 0.02* | 100 | 100 | | CaO | ICP-AES | 0.05* | 0.05* | 100 | 100 | | MgO | ICP-AES | 0.05* | 0.05* | 100 | 100 | | S | VOL | 30 | 30 | 100 | 95.50 | | TFe2O3 | XRF | 0.05* | 0.05* | 100 | 100 | | Co | ICP-MS | 1 | 1 | 100 | 100 | | V | ICP-AES | 5 | 3 | 100 | 100 | | Ge | ICP-MS | 0.1 | 0.1 | 100 | 98.26 | | B | ES | 1 | 1 | 100 | 99.13 | | Mo | ICP-MS | 0.3 | 0.2 | 100 | 98.26 | | Mn | ICP-AES | 10 | 10 | 100 | 100 | | Cu | ICP-MS | 1 | 1 | 100 | 97.39 | | Zn | XRF | 4 | 4 | 100 | 100 |
|
Results of soil sample element testing
|

| 指标 | 一等 | 二等 | 三等 | 四等 | 五等 | 上限值 | | 丰富 | 较丰富 | 中等 | 较缺乏 | 缺乏 | 超限 | | 有机质 | 含量/(g·kg-1) | >40 | >30~40 | >20~30 | >10~20 | ≤10 | / | | 面积/km2 | 5 260.52 | 514.31 | 330.24 | 170.03 | 24.90 | / | | 比例/% | 83.50 | 8.16 | 5.24 | 2.70 | 0.40 | / | | 全氮 | 含量/(g·kg-1) | >2.0 | >1.5~2.0 | >1.0~1.5 | >0.75~1.0 | ≤0.75 | / | | 面积/km2 | 5 558.47 | 401.26 | 220.06 | 72.39 | 47.82 | / | | 比例/% | 88.23 | 6.37 | 3.49 | 1.15 | 0.76 | / | | 全磷 | 含量/(g·kg-1) | >1.0 | >0.8~1.0 | >0.6~0.8 | >0.4~0.6 | ≤0.4 | / | | 面积/km2 | 2314.64 | 2211.65 | 1475.94 | 281.65 | 16.12 | / | | 比例/% | 36.74 | 35.11 | 23.43 | 4.47 | 0.26 | / | | 全钾 | 含量/(g·kg-1) | >25 | >20~25 | >15~20 | >10~15 | ≤10 | / | | 面积/km2 | 95.50 | 3972.44 | 2223.04 | 9.02 | 0 | / | | 比例/% | 1.52 | 63.05 | 35.29 | 0.14 | 0 | / | | 氧化钙 | 含量/% | >5.54 | >2.68~5.54 | >1.16~2.68 | >0.42~1.16 | ≤0.42 | / | | 面积/km2 | 725.63 | 1633.68 | 3657.91 | 282.78 | 0 | / | | 比例/% | 11.52 | 25.93 | 58.06 | 4.49 | 0 | / | | 氧化镁 | 含量/% | >2.15 | >1.70~2.15 | >1.20~1.70 | >0.70~1.20 | ≤0.70 | / | | 面积/km2 | 253.55 | 2919.31 | 3075.14 | 52.00 | 0 | / | | 比例/% | 4.02 | 46.34 | 48.81 | 0.83 | 0 | / | | 硫 | 含量/(g·kg-1) | >343 | >270~343 | >219~270 | >172~219 | ≤172 | ≥2000 | | 面积/km2 | 4970.30 | 640.71 | 427.68 | 176.66 | 56.65 | 28 | | 比例/% | 78.89 | 10.17 | 6.79 | 2.80 | 0.90 | 0.44 |
|
Classification and statistics of major and secondary nutrient indicators in soil
|
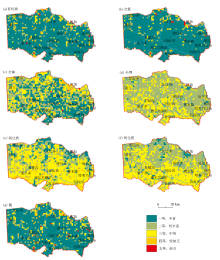
|
Geochemical grade of nutrient elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in soil
|

| 指标 | 一等 | 二等 | 三等 | 四等 | 五等 | 超限 | | 丰富 | 较丰富 | 中等 | 较缺乏 | 缺乏 | | 氧化铁 | 含量/% | >5.30 | >4.60~5.30 | >4.15~4.60 | >3.40~4.15 | ≤3.40 | / | | 面积/km2 | 4039.79 | 1907.55 | 293.10 | 55.56 | 4.00 | / | | 比例/% | 64.12 | 30.28 | 4.65 | 0.88 | 0.06 | / | | 钴 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >15 | >13~15 | >11~13 | >8~11 | ≤8 | / | | 面积/km2 | 415.65 | 2808.22 | 2727.64 | 340.49 | 8.00 | / | | 比例/% | 6.60 | 44.57 | 43.30 | 5.40 | 0.13 | / | | 钒 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >96 | >84~96 | >75~84 | >63~75 | ≤63 | / | | 面积/km2 | 593.13 | 3331.74 | 1951.35 | 395.78 | 28.00 | / | | 比例/% | 9.41 | 52.88 | 30.97 | 6.28 | 0.44 | / | | 锗 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >1.5 | >1.4~1.5 | >1.3~1.4 | >1.2~1.3 | ≤1.2 | / | | 面积/km2 | 482.02 | 1219.11 | 2156.03 | 1492.14 | 950.70 | / | | 比例/% | 7.65 | 19.35 | 34.22 | 23.68 | 15.09 | / | | 硼 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >65 | >55~65 | >45~55 | >30~45 | ≤30 | ≥3000 | | 面积/km2 | 3604.11 | 2126.33 | 521.57 | 47.99 | 0 | / | | 比例/% | 57.21 | 33.75 | 8.28 | 0.76 | 0.00 | / | | 钼 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >0.85 | >0.65~0.85 | >0.55~0.65 | >0.45~0.55 | ≤0.45 | ≥4 | | 面积/km2 | 2003.75 | 3985.90 | 226.35 | 64.00 | 20.00 | / | | 比例/% | 31.81 | 63.27 | 3.59 | 1.02 | 0.32 | / | | 锰 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >700 | >600~700 | >500~600 | >375~500 | ≤375 | ≥1500 | | 面积/km2 | 2954.33 | 2604.47 | 586.16 | 135.04 | 20.00 | / | | 比例/% | 46.89 | 41.34 | 9.30 | 2.14 | 0.32 | / | | 铜 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >29 | >24~29 | >21~24 | >16~21 | ≤16 | ≥50 | | 面积/km2 | 839.67 | 3212.77 | 1763.03 | 470.46 | 6.07 | 8 | | 比例/% | 13.33 | 51.00 | 27.98 | 7.47 | 0.10 | 0.13 | | 锌 | 含量/(mg·kg-1) | >84 | >71~84 | >62~71 | >50~62 | ≤50 | ≥200 | | 面积/km2 | 521.34 | 3161.50 | 2227.07 | 377.95 | 2.07 | 10.07 | | 比例/% | 8.28 | 50.18 | 35.35 | 6.00 | 0.03 | 0.16 |
|
Classification and statistics of geochemical grades of micronutrients and beneficial elements
|
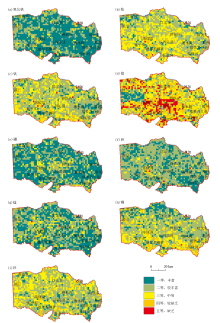
|
Geochemical grade map of trace nutrient element indicators in soil
|

| 一等 | 二等 | 三等 | 四等 | 五等 | | f养综 | ≥4.5 | <4.5~3.5 | <3.5~2.5 | <2.5~1.5 | <1.5 | | 含义 | 丰富 | 较丰富 | 中等 | 较缺乏 | 缺乏 | | 面积/km2 | 2325.19 | 3450.32 | 450.27 | 74.22 | 0 | | 占比/% | 36.91 | 54.77 | 7.15 | 1.18 | 0 |
|
Statistical table of comprehensive geochemical grades of soil nutrients
|
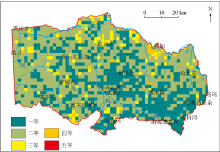
|
Comprehensive geochemical grade map of soil nutrients in the work area
|
| [1] |
李梦佳. 重庆市典型血橙基地土地质量地球化学评价与分析[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2021.
|
| [1] |
Li M J. Geochemical evaluation and analysis of land quality in typical blood orange base in Chongqing[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021.
|
| [2] |
罗亚勇, 孟庆涛, 张静辉, 等. 青藏高原东缘高寒草甸退化过程中植物群落物种多样性、生产力与土壤特性的关系[J]. 冰川冻土, 2014, 36(5):1298-1305.
|
| [2] |
Luo Y Y, Meng Q T, Zhang J H, et al. Species diversity and biomass in relation to soil properties of alpine meadows in the eastern Tibetan Plateau in different degradation stages[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2014, 36(5):1298-1305.
|
| [3] |
任学敏, 杨改河, 朱雅, 等. 环境因子对太白山高山植被物种组成和丰富度的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(23):6993-7003.
|
| [3] |
Ren X M, Yang G H, Zhu Y, et al. Effect of environmental variables on species composition and richness of alpine vegetation in Taibai Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(23):6993-7003.
|
| [4] |
崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 石少坚, 等. 石家庄污灌区土壤元素评价[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(6):1753-1759.
|
| [4] |
Cui X T, Luan W L, Shi S J, et al. The evaluation of soil elements in topsoil of the sewage irrigation area in Shijiazhuang[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(6):1753-1759.
|
| [5] |
杨佳宾, 黄海峰. 上海市土地整治区土壤环境因子与草本植物群落分析研究[J]. 上海国土资源, 2022, 43(1):40-44,74.
|
| [5] |
Yang J B, Huang H F. Research on soil environmental factors and herbaceous community of land consolidate area in Shanghai[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2022, 43(1):40-44,74.
|
| [6] |
郭莉, 杨忠芳, 阮起和, 等. 北京市平原区土壤中硒的含量和分布[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):859-864.
|
| [6] |
Guo L, Yang Z F, Ruan Q H, et al. Content and distribution of selenium in soil of Beijing Plain[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):859-864.
|
| [7] |
江晓龙. 基于主成分和聚类分析的永泰县土壤养分地球化学综合评价[C]// 山东省地质学会. 华东六省一市地学科技论坛文集,2023:580-585.
|
| [7] |
Jiang X L. Comprehensive evaluation of soil nutrient geochemistry in Yongtai County based on principal component and cluster analysis[C]// Geological Society of Shandong Province. Proceedings of Geoscience Science and Technology Forum of six provinces and one city in East China,2023:580-585.
|
| [8] |
庞绪贵. 山东省东部特色农业区及典型生态区地球化学环境研究与评价[R]. 山东省地质调查院, 2012.
|
| [8] |
Pang X G. Study and evaluation of geochemical environment of characteristic agricultural area and typical ecological area in eastern Shandong Province[R]. Shandong Institute of Geological Survey, 2012.
|
| [9] |
段中华. 基于土壤及植物生物标记物的高寒草甸退化研究[D]. 西宁: 青海大学, 2018.
|
| [9] |
Duan Z H. Study on degradation of alpine meadow based on soil and plant biomarkers[D]. Xining: Qinghai University, 2018.
|
| [10] |
付嵩, 丁玉进, 张新远, 等. 青海省民和县新民—李二堡地区土壤养分地球化学特征分析[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(5) :1103-1108.
|
| [10] |
Fu S, Ding Y J, Zhang X Y, et al. Geochemical Characteristics of Soil Nutrients in Xinmin-Lierbao Area of Minhe County,Qinghai Province[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(5) :1103-1108.
|
| [11] |
邓远文, 黄仕宗, 沈和明, 等. 甘洛县坪坝乡松树坪村土壤养分地球化学特征与评价[J]. 科学技术创新, 2020(14):153-154.
|
| [11] |
Deng Y W, Huang S Z, Shen H M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and evaluation of soil nutrients in Songshuping Village,Pingba Township,Ganluo County[J]. Scientific and Technological Innovation, 2020(14):153-154.
|
| [12] |
刘亮, 张杰, 张杰琼, 等. 四川旺苍县化龙乡土地质量及生态农业建设[J]. 矿产勘查, 2020, 11(12):2601-2609.
|
| [12] |
Liu L, Zhang J, Zhang J Q, et al. Land quality and ecological agriculture construction in Hualong Township of Wangcang County,Sichuan Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2020, 11(12):2601-2609.
|
| [13] |
薛增忍, 薛占业, 杨自成. 山西芮城县河滩芦笋土壤养分状况调查与分析[J]. 中国园艺文摘, 2012, 28(9):8-9.
|
| [13] |
Xue Z R, Xue Z Y, Yang Z C. Investigation and analysis on soil nutrient status of asparagus in Ruicheng County,Shanxi Province[J]. Chinese Horticulture Abstracts, 2012, 28(9):8-9.
|
| [14] |
黎玉国, 伍正菊. 土壤有机质类型及永胜县土壤有机质含量分析[J]. 农业与技术, 2014, 34(5):4.
|
| [14] |
Li Y G, Wu Z J. Types of soil organic matter and analysis of soil organic matter content in Yongsheng County[J]. Agriculture and Technology, 2014, 34(5):4.
|
| [15] |
周勇, 贾建忠, 狄小东, 等. 喷播植生纤维对西北干旱区沙土理化性质影响研究[J]. 价值工程, 2023, 42(9):116-118.
|
| [15] |
Zhou Y, Jia J Z, Di X D, et al. Effects of sprayying planting fiber on physicochemical properties of sandy soil in arid area of northwest China[J]. Value Engineering, 2023, 42(9):116-118.
|
| [16] |
张弛. 钾肥对植物生长的影响[J]. 中国农资, 2012(36):24.
|
| [16] |
Zhang C. The effects of potassium fertilizer on plant growth were relaxed[J]. Chinese Agricultural Materials, 2012(36):24.
|
| [1] |
LI Yong-Chun, SU Ri-Li-Ge, ZHOU Wen-Hui, TAI Su-Ri-Ga-La, CHEN Guo-Dong, WANG Yong-Liang, GAO Qi, ZHANG Xiang, ZHANG Dong. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of soil in Hulu River Basin in the southern mountainous region of Ningxia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4): 999-1010. |
| [2] |
HOU Jin-Kai, SONG Yan-Bin, ZHU Rui-Zhen, XIN Feng-Pei, ZHOU Jian-Chuan, LU Fu-Lan, YAO Jie. Selenium speciation in surface soil in Yaling Town, Yichuan County—Xiaodian Town,Ruyang County in Luoyang City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2): 511-517. |
|
|
|
|

