|
|
|
| A Res-UNet network-based method for borehole-to-surface electrical resistivity inversion |
ZHOU Nan1( ), WANG Zhi1( ), WANG Zhi1( ), FANG Si-Nan2, ZHANG Yu-Zhe1 ), FANG Si-Nan2, ZHANG Yu-Zhe1 |
1. School of Electronic Information and Electrical Engineering, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, China
2. College of Geophysics and Petroleum Resources, Yangtze University, Wuhan 430100, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Traditional resistivity inversion methods tend to rely on the initial inversion model selected, get stuck in local minima, and be time-consuming. To address these issues, this study proposed a real-time resistivity inversion method based on the Res-UNet neural network. First, a significantly expanded forward response dataset was generated using the Gmsh software. Then, inversion experiments were carried out based on appropriate network parameters determined according to data characteristics. The experimental results indicate that the Res-UNet algorithm can fully dig the data characteristics and rapidly produce resistivity images that align with the electrical properties of strata. The experiments on the dataset for resistivity forward modeling yielded a mean squared error between the predicted values and the forward responses of 0.019 44, and those on the test set yielded a mean squared error of 0.075 8, suggesting improved imaging results compared to traditional inversion methods. Furthermore, the proposed method achieved encouraging results in the inversion calculations of simulation models, enabling rapid and accurate inversion of the location and morphologies of subsurface anomalies while exhibiting a strong noise resistance. This study provides a new method and philosophy for mapping the relationship between resistivity data and the actual geoelectric structures.
|
|
Received: 01 April 2024
Published: 26 February 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
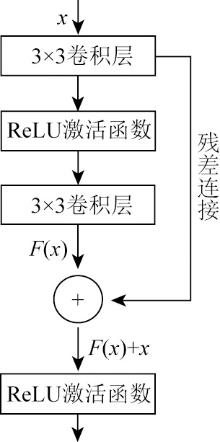
|
The diagram of residual block
|
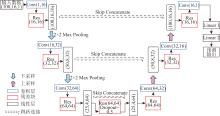
|
Res-UNet network structure
|

| Conv1 | Res1 | Conv2 | Res2 | Conv3 | Res3 | | 1 | Conv(1,4) | Res(4,4) | Conv(4,16) | Res(16,16) | Conv(16,32) | Res(32,32) | | 2 | Conv(1,16) | Res(16,16) | Conv(16,32) | Res(32,32) | Conv(32,64) | Res(64,64) | | 3 | Conv(1,32) | Res(32,32) | Conv(32,64) | Res(64,64) | Conv(64,128) | Res(128,128) | | 4 | Conv(1,64) | Res(64,64) | Conv(64,128) | Res(128,128) | Conv(128,256) | Res(256,256) |
|
Encoder section with different channel numbers
|
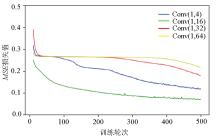
|
Compare mean squared error (MSE) values for different channel numbers
|

|
Schematic diagram of square anomaly body well-earth secondary device model
|
|
Flow Chart of Random Batch Modeling Based on Gmsh
|

| 异常体类型 | 异常体
尺寸/m | 样本数
量/个 | 异常体电率/
(Ω·m) | 围岩电阻率/
(Ω·m) | | 正方形异常体 | 12×12 | 1 000 | 10~100
300~1 000 | 200 | | 长方形异常体 | 16×8 | 1 000 | | 阶梯型异常体 | 3层9×3 | 1 000 | | 正方形 | 12×12 | 1 500 | | 阶梯型 | 3层9×3 | | 层状 | 100×20 | 1 500 | | 阶梯型 | 3层9×3 |
|
Parameters of anomalous body models
|
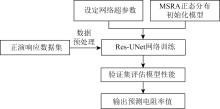
|
Res-UNet network inversion process
|
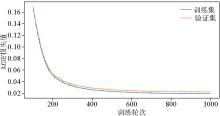
|
Res-UNet network loss curve graph
|

| 异常体大小 | 异常体中心
节点坐标 | 异常体电阻
率/(Ω·m) | 背景电阻率/
(Ω·m) | | 模型一 | 正方形12 m×12 m | (39,-29) | ρ=500 | 200 | | 模型二 | 长方形16 m×8 m | (42,-42) | ρ=100 | | 模型三 | 正方形12 m×12 m
阶梯形3层9 m×3 m | (20,-30)
(80,-50) | ρ1=100
ρ2=1 000 | | 模型四 | 层状100 m×20 m
阶梯形3层9 m×3 m | (50,-70)
(43,-39) | ρ1=500
ρ2=1 000 |
|
Single anomaly model parameters
|
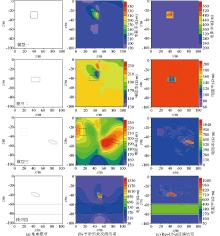
|
Inversion result comparison chart
|
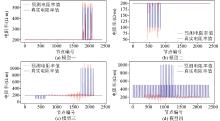
|
Comparison chart of res-UNet predicted values and true apparent resistivity values
|
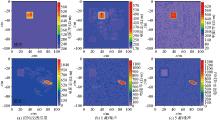
|
Adding Gaussian white noise to the inversion results
|
| [1] |
蔡军涛, 阮百尧, 赵国泽, 等. 复电阻率法二维有限元数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2007, 50(6):1869-1876.
|
| [1] |
Cai J T, Ruan B Y, Zhao G Z, et al. Two-dimensional modeling of complex resistivity using finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2007, 50(6):1869-1876.
|
| [2] |
苏洲, 胡文宝. 二维大地电磁正演中的无网格算法[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(6):1024-1028,1039.
|
| [2] |
Su Z, Hu W B. Meshless algorithm in two-dimensional electromagnetic forward calculation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(6):1024-1028,1039.
|
| [3] |
王智, 方思南, 姜匡义, 等. 基于非结构化网格的井地电阻率法三维正演模拟及异常特征研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(4):1620-1630.
|
| [3] |
Wang Z, Fang S N, Jiang K Y, et al. Research on 3D hole-to-surface resistivity forward modeling and anomaly based on unstructured meshes[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(4):1620-1630.
|
| [4] |
任政勇, 汤井田. 基于局部加密非结构化网格的三维电阻率法有限元数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(10):2627-2634.
|
| [4] |
Ren Z Y, Tang J T. Finite element modeling of 3-D DC resistivity using locally refined unstructured meshes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(10):2627-2634.
|
| [5] |
Tang J T, Wang F Y, Ren Z Y. 2.5D DC resistivity modeling by adaptive finite-element with unstructured triangulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(3):708-716.
|
| [6] |
张宇哲, 孟麟, 王智. 基于Gmsh的起伏地形下井—地直流电法正演模拟[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(1):182-190.
|
| [6] |
Zhang Y Z, Meng L, Wang Z. Forward modeling of well-ground direct current resistivity method for undulating terrain based on Gmsh[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1):182-190.
|
| [7] |
Constable S C, Parker R L, Constable C G. Occam’s inversion:A practical algorithm for generating smooth models from electromagnetic sounding data[J]. Geophysics, 1987, 52(3):289-300.
|
| [8] |
Smith J T, Booker J R. Rapid inversion of two- and three-dimensional magnetotelluric data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 1991, 96(B3):3905-3922.
|
| [9] |
Chen X B, Zhao G Z, Tang J, et al. The adaptive regularized inversion algorithm(ARIA) for magnetotelluric data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2005, 48(4):1005-1016.
|
| [10] |
黄俊革, 阮百尧. 直流电阻率测深中二维与三维反演结果的对比与分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2004, 28(5):447-450.
|
| [10] |
Huang J G, Ruan B Y. An analytical comparison between 2d and 3d inversions in dc resistivity sounding[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 28(5):447-450.
|
| [11] |
刘斌, 李术才, 李树忱, 等. 基于不等式约束的最小二乘法三维电阻率反演及其算法优化[J]. 地球物理学报, 2012, 55(1):260-268.
|
| [11] |
Liu B, Li S C, Li S C, et al. 3D electrical resistivity inversion with least-squares method based on equality constraint and its computation efficiency optimization[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2012, 55(1):260-268.
|
| [12] |
王智, 潘和平, 骆玉虎, 等. 基于不等式约束的井地电阻率法三维非线性共轭梯度反演研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016, 31(1):360-370.
|
| [12] |
Wang Z, Pan H P, Luo Y H, et al. 3-D hole-to-surface resistivity inversion with nonlinear conjugate gradients method under the constraint of inequality[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016, 31(1):360-370.
|
| [13] |
刘征宇, 庞永昊, 张凤凯, 等. 基于多尺度边缘特征的深度学习电阻率反演方法[J]. 岩土力学, 2023, 44(11):3299-3306.
|
| [13] |
Liu Z Y, Pang Y H, Zhang F K, et al. Deep learning resistivity inversion method based on multi-scale edge features[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2023, 44(11):3299-3306.
|
| [14] |
安鹏, 曹丹平. 基于深度学习的测井岩性识别方法研究与应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(3):1029-1034.
|
| [14] |
An P, Cao D P. Research and application of logging lithology identification based on deep learning[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(3):1029-1034.
|
| [15] |
夏文鹤, 朱喆昊, 韩玉娇, 等. 电阻率测井成像图井壁裂缝智能识别与分割方法[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2023, 58(5):1042-1052.
|
| [15] |
Xia W H, Zhu Z H, Han Y J, et al. Intelligent identification and segmentation method of wellbore fractures in resistivity logging imaging map[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2023, 58(5):1042-1052.
|
| [16] |
Anomohanran O, Orhiunu M E. Assessment of groundwater occurrence in Olomoro,Nigeria using borehole logging and electrical resistivity methods[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2018, 11(9):1-9.
|
| [17] |
Park G, Park S, Kim J H. Estimating the existence probability of cavities using integrated geophysics and a neural network approach[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 2010, 36(9):1161-1167.
|
| [18] |
张凌云, 刘鸿福. ABP法在高密度电阻率法反演中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(1):227-233.
|
| [18] |
Zhang L Y, Liu H F. The application of ABP method in high-density resistivity method inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(1):227-233.
|
| [19] |
高明亮, 于生宝, 郑建波, 等. 基于 IGA 算法的电阻率神经网络反演成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016, 59(11):4372-4382.
|
| [19] |
Gao M L, Yu S B, Zheng J B, et al. Research of resistivity imaging using neural network based on immune genetic algorithm[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016, 59(11):4372-4382.
|
| [20] |
Phueakim K, Amatyakul P, Vachiratienchai C. An attempt to use convolutional neural network to recover layered-earth structure from electrical resistivity tomography survey[J]. Journal of Physics:Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2023, 2653(1):012044.
|
| [21] |
He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]// Las Vegas:2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).NV,USA.IEEE,2016:770-778.
|
| [22] |
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net:Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[M]// Lecture Notes in Computer science. Cham: Springer International Publishing,2015:234-241.
|
| [23] |
Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, et al. Dropout:A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting.[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1):1929-1958.
|
| [24] |
He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, et al. Delving deep into rectifiers:Surpassing human-level performance on imagenet classification[C]// Santiago:2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV).Chile.IEEE,2015:1026-1034.
|
|
|
|

