|
|
|
| Numerical simulation of MT tipper response based on 3D fault models |
LIN Xing-Long1( ), GU Guan-Wen1,2,3( ), GU Guan-Wen1,2,3( ), NIU Xing-Guo4, WU Ye1,2,3, WANG Shun-Ji1, WANG Ying-Jie1, CAO Lai1 ), NIU Xing-Guo4, WU Ye1,2,3, WANG Shun-Ji1, WANG Ying-Jie1, CAO Lai1 |
1. School of Earthquake Sciences,Institute of Disaster Prevention,Sanhe 065201,China
2. Hebei Key Laboratory of Earthquake Dynamics,Sanhe 065201,China
3. Langfang Key Laboratory of Earth Exploration and Information Technology,Sanhe 065201,China
4. Inner Mongolia Nonferrous Geology and Mining (Group) Geophysical Exploration Co.,Ltd.,Hohhot 010010,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The tipper vector,a significant parameter in magnetotelluric(MT) sounding,is applicable to infer fault structures that cause lateral inhomogeneity of media.Subsurface faults typically exhibit three-dimensionality and complexity.To reveal the MT tipper response characteristics in 3D fault models,this study conducted numerical simulations of the MT tipper response in 3D fault models based on the vector finite element method.First,the validity of the 3D tipper forward modeling program was verified through theoretical model calculations and comparisons with previous finite element results.Subsequently,four typical 3D models for vertical,normal,reverse,and strike-slip faults were employed for forward modeling,obtaining the response characteristics of the real part,imaginary part,amplitude,and phase of the tipper.The simulation results are as follows:(1) In two polarization modes,the response characteristics of the real part,imaginary part,and amplitude of the tipper effectively reflect the properties,strikes,and dip directions of the four different faults while indicating the location of the laterally inhomogeneous boundaries,thus serving as a significant basis for discriminating fault types and characteristics;(2)In contrast,the relatively complex response characteristics of the phase fail to effectively mirror the fault characteristics.
|
|
Received: 29 March 2024
Published: 26 February 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
45])
">
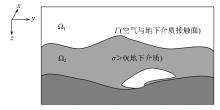
|
Section diagram of numerical modeling domain for 3D MT(revised to Shi et al.[45])
|
48])
a—domain subdivision;b—location of electric field components
">
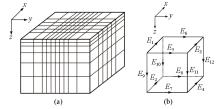
|
Domain subdivision of the vector finite element method(according to Nam et al.[48])
a—domain subdivision;b—location of electric field components
|
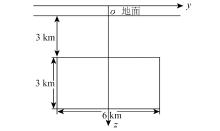
|
Schematic diagram of the central low-resistance model
|

|
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the electric field component of the 2D prism model (1 Hz)
a—plot of the real part of the Ex component;b—imaginary plot of the Ex component
|
|
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the horizontal magnetic field component of the 2D prism model (1 Hz)
a—plot of the real part of the Hy component;b—imaginary plot of the Hy component
|
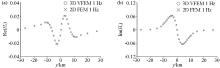
|
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the perpendicular magnetic field component of the 2D prism model (1 Hz)
a—plot of the real part of the Hz component;b—imaginary plot of the Hz component
|
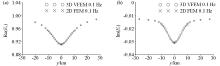
|
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the electric field component of the 2D prism model (0.1Hz)
a—plot of the real part of the Ex component;b—imaginary plot of the Ex component
|
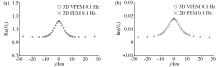
|
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the horizontal magnetic field component of the 2D prism model (0.1 Hz)
a—plot of the real part of the Hy component;b—imaginary plot of the Hy component
|
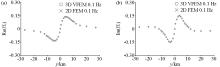
|
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the perpendicular magnetic field component of the 2D prism model (0.1 Hz)
a—plot of the real part of the Hz component;b—imaginary plot of the Hz component
|
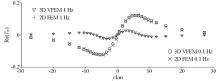
|
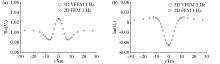
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the tipper response real part of the 2D prism model
|
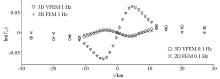
|
Comparison of the 2D finite element numerical solution and the 3D vector finite element numerical solution of the tipper response imaginary part of the 2D prismatic model
|
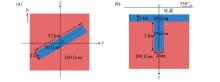
|
Schematic diagram of upright fault model extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—schematic diagram of the x-y plane;b—schematic diagram of a profile perpendicular to the fault trend
|
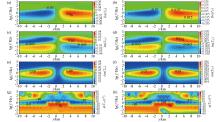
|
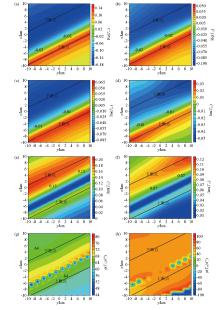
Schematic of a upright fault dip profile extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—Tzx tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;b—Tzy tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;c—Tzx tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;d—Tzy tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;e—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzx tipper;f—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzy tipper;g—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzx tipper;h—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzy tipper
|
T z y tipper plane;c—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzx tipper plane;d—contour map of the imaginary part of the tipper plane;e—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzx tipper plane;f—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzy tipper plane;g—contour map of the phase part of the Tzx tipper plane;h—contour map of the phase part of the Tzy tipper plane
">
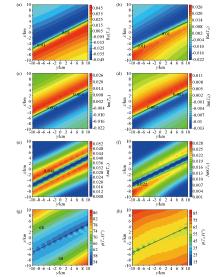
|
Contour map of the tilt plane of a upright fault extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60° at a frequency of 0.1 Hz
a—contour map of the real part of the Tzx tipper plane;b—contour map of the real part of the tipper plane;c—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzx tipper plane;d—contour map of the imaginary part of the tipper plane;e—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzx tipper plane;f—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzy tipper plane;g—contour map of the phase part of the Tzx tipper plane;h—contour map of the phase part of the Tzy tipper plane
|
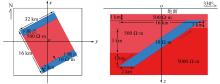
|
Schematic diagram of normal fault model extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—schematic diagram of the x-y plane;b—schematic diagram of a profile perpendicular to the fault trend
|
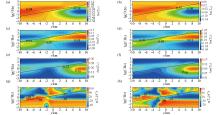
|
Pseudo-section diagram of a normal fault dip extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—Tzx tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;b—Tzy tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;c—Tzx tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;d—Tzy tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;e—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzx tipper;f—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzy tipper;g—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzx tipper;h—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzy tipper
|

|
Contour map of the tipper plane of a normal fault extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60° at a frequency of 0.1 Hz
a—contour map of the real part of the Tzx tipper plane;b—contour map of the real part of the Tzy tipper plane;c—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzx tipper plane;d—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzy tipper plane; e—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzx tipper plane;f—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzy tipper plane;g—contour map of the phase part of the Tzx tipper plane;h—contour map of the phase part of the Tzy tipper plane
|
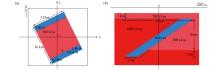
|
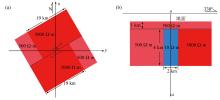
Schematic diagram of reverse fault model extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—schematic diagram of the x-y plane;b—schematic diagram of a profile perpendicular to the fault trend
|
|
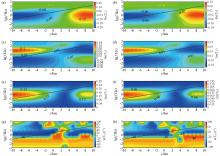
Pseudo-section diagram of a reverse fault dip extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—Tzx tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;b—Tzy tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;c—Tzx tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;d—Tzy tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;e—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzx tipper;f—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzy tipper;g—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzx tipper;h—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzy tipper
|
|
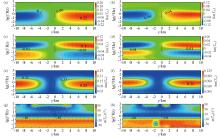
Contour map of the tipper plane of a reverse fault extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60° at a frequency of 0.1 Hz
a—contour map of the real part of the Tzx tipper plane;b—contour map of the real part of the Tzy tipper plane;c—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzx tipper plane;d—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzy tipper plane;e—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzx tipper plane;f—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzy tipper plane;g—contour map of the phase part of the Tzx tipper plane;h—contour map of the phase part of the Tzy tipper plane
|
|
Schematic diagram of strike-slip fault model extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—schematic diagram of the x-y plane;b—schematic diagram of a profile perpendicular to the fault trend
|
|
Pseudo-section diagram of a strike-slip fault dip extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°
a—Tzx tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;b—Tzy tipper real part pseudo-section diagram;c—Tzx tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;d—Tzy tipper imaginary part pseudo-section diagram;e—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzx tipper;f—pseudo-section diagram of the amplitude of the Tzy tipper;g—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzx tipper;h—pseudo-section diagram of the phase of the Tzy tipper
|
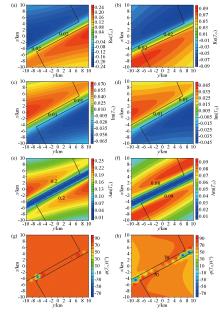
|
Contour map of the tipper plane of a strike-slip fault extending in the direction of north-northeast at 60°at a frequency of 0.1 Hz
a—contour map of the real part of the Tzx tipper plane;b—contour map of the real part of the Tzy tipper plane;c—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzx tipper plane;d—contour map of the imaginary part of the Tzy tipper plane;e—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzx tipper plane;f—contour map of the amplitude part of the Tzy tipper plane;g—contour map of the phase part of the Tzx tipper plane;h—contour map of the phase part of the Tzy tipper plane
|
| [1] |
Červ V, Pek J, Praus O. Long period magnetotelluric studies in the western part of the bohemian massif[J]. Seismology and Geology,2001,23(2):166-177.
|
| [2] |
Chen J, Dosso H W, Kang S. EM induction in elongated conductors normal to a coastline with application to geomagnetic measurements in Nigeria[J]. Journal of Geomagnetism and Geoelectricity, 1997, 49(11):1401-1414.
|
| [3] |
Garcia X, Ledo J, Queralt P. 2D inversion of 3D magnetotelluric data:The Kayabe dataset[J]. Earth,Planets and Space, 1999, 51(10):1135-1143.
|
| [4] |
刘彦涛, 彭莉红, 孙栋华, 等. 基于三维有限元的航空大地电磁倾子响应特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1329-1337.
|
| [4] |
Liu Y T, Peng L H, Sun D H, et al. Research on response characteristics of airborne magnetotelluric tipper based on three-dimensional finite element[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1329-1337.
|
| [5] |
Patra H P, Mallick K. Geosounding principles[M]. Amstedam Oxford New York: Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company,1980:253-259.
|
| [6] |
朱仁学. 断层的大地电磁响应的研究[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 1999, 29(3):290-294.
|
| [6] |
Zhu R X. Study of MT responses of fault[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 1999, 29(3):290-294.
|
| [7] |
李学民, 曹俊兴, 贺桃娥. 断层构造的大地电磁响应曲线变化特征的研究[J]. 天然气工业, 2004, 24(7):42-44,57-135.
|
| [7] |
Li X M, Cao J X, He T E. Research on the change characteristics of MT response curves of fault structure[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2004, 24(7):42-44,57-135.
|
| [8] |
苗景春, 阮帅, 张悦. 音频大地电磁测深法对正、逆断层的精细解释[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(4):681-686.
|
| [8] |
Miao J C, Ruan S, Zhang Y. The application of the audio magnetotelluric sounding method to the precise interpretation of normal and reverse faults[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(4):681-686.
|
| [9] |
冯建新, 杨天春, 王燕龙, 等. 隐伏地质构造的大地电磁有限单元法正演模拟[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(1):137-144.
|
| [9] |
Feng J X, Yang T C, Wang Y L, et al. Magnetotelluric forward modelling for underground geologic structures by finite element method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(1):137-144.
|
| [10] |
梁霄, 艾林, 吴仁学. 三维断层模型的MT正演响应及极化模式分析[J]. 中国锰业, 2016, 34(4):32-34.
|
| [10] |
Liang X, Ai L, Wu R X. An analysis of MT forward modeling and different polarization modes in 3D fault model[J]. China’s Manganese Industry, 2016, 34(4):32-34.
|
| [11] |
欧阳承新, 王时平, 全德辉, 等. 高频大地电磁测深在断层构造探测中的应用研究[J]. 世界地震工程, 2007, 23(3):138-141.
|
| [11] |
Ouyang C X, Wang S P, Quan D H, et al. Application of the high frequency magnetotelluric sounding to faults[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 2007, 23(3):138-141.
|
| [12] |
肖兵, 余成华, 徐俊, 等. 城市断层深部结构大地电磁阵列探测[J]. 城市勘测, 2011(3):159-163.
|
| [12] |
Xiao B, Yu C H, Xu J, et al. Prospecting of the deep tructure of city fault with magnetotelluric method sounding[J]. Urban Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2011(3):159-163.
|
| [13] |
武毅, 封绍武, 王亚清. 应用大地电磁法TE、TM模式勘查构造裂隙水[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(3):329-332.
|
| [13] |
Wu Y, Feng S W, Wang Y Q. The technological application of TE and TM mode to the prospecting for structural fissure water[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(3):329-332.
|
| [14] |
张振宇, 王绪本, 方慧. 龙门山构造带中段大地电磁测深研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(3):377-381.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Z Y, Wang X B, Fang H. A study of magnetotelluric sounding in the middle segment of the longmensham structural belt[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(3):377-381.
|
| [15] |
徐志敏, 辛会翠, 谭新平, 等. 强电磁干扰区大地电磁远参考技术试验效果分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(3):560-568.
|
| [15] |
Xu Z M, Xin H C, Tan X P, et al. An analysis of the experimental result of MT remote reference technique in strong electromagnetic interference region[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(3):560-568.
|
| [16] |
刘战. 音频大地电磁法在探测断层发育区中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2019, 16(5):730-736.
|
| [16] |
Liu Z. Application of audio magnetotelluric method to detecting fault area[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2019, 16(5):730-736.
|
| [17] |
于建华, 夏方华, 张志强, 等. 基于大地电磁测深的平原区隐伏断裂构造研究——以天津蔡公庄乡等四幅区调为例[J]. 矿产勘查, 2023, 14(7):1161-1173.
|
| [17] |
Yu J H, Xia F H, Zhang Z Q, et al. Study on concealed fault structure in plain area based on magnetotelluric sounding:Taking Caigongzhuang Township and other four regional surveys in Tianjin as an example[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2023, 14(7):1161-1173.
|
| [18] |
吴頔, 严家斌, 贺文根. 倾子对异常体的分辨能力及影响因素研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2012, 27(6):2656-2663.
|
| [18] |
Wu D, Yan J B, He W G. Study on distinguishing to anomalous bodies by tipper & influencing factor of tipper[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2012, 27(6):2656-2663.
|
| [19] |
Parkinson W D. Directions of rapid geomagnetic fluctuations[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 1959, 2(1):1-14.
|
| [20] |
Schmucker U. Anomalies of geomagnetic variations in the southwestern United States[M]. Berkeley: University of California Press,1970.
|
| [21] |
Vozoff K. The magnetotelluric method in the exploration of sedimentary basins[J]. Geophysics, 1972, 37(1):98-141.
|
| [22] |
Zhdanov M S, Varentsov I M, Weaver J T, et al. Methods for modelling electromagnetic fields Results from COMMEMI—The international project on the comparison of modelling methods for electromagnetic induction[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 1997, 37(3/4):133-271.
|
| [23] |
胡文宝, 苏朱刘, 陈清礼, 等. 倾子资料的特征及应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1997, 32(2):202-213,304.
|
| [23] |
Hu W B, Su Z L, Chen Q L, et al. Character of tipper data and the application[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1997, 32(2):202-213,304.
|
| [24] |
Ledo J, Gabàs A, Marcuello A. Static shift levelling using geomagnetic transfer functions[J]. Earth,Planets and Space, 2002, 54(5):493-498.
|
| [25] |
Berdichevsky M N, Dmitriev V I, Golubtsova N S, et al. Magnetovariational sounding:New possibilities[J]. Izvestiya,Physics of the Solid Earth, 2003, 39(9):701-727.
|
| [26] |
Pedersen L B, Bastani M, Dynesius L. Groundwater exploration using combined controlled-source and radiomagnetotelluric techniques[J]. Geophysics, 2005, 70(1):G8-G15.
|
| [27] |
陈小斌, 赵国泽, 詹艳, 等. 磁倾子矢量的图示分析及其应用研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2004, 11(4):626-636.
|
| [27] |
Chen X B, Zhao G Z, Zhan Y, et al. Analysis of tipper visual vectors and its application[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2004, 11(4):626-636.
|
| [28] |
余年, 王绪本, 阚瑷珂, 等. 倾子和视倾子的研究及在断裂解释中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2007, 4(4):275-281.
|
| [28] |
Yu N, Wang X B, Kan A K, et al. Study on tipper and apparent tipper & application in fault interpretaion[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2007, 4(4):275-281.
|
| [29] |
陈清礼, 胡文宝, 李金铭, 等. 埋藏球体的倾子响应特征分析[J]. 石油天然气学报, 2007, 29(3):75-78,505.
|
| [29] |
Chen Q L, Hu W B, Li J M, et al. Characteristics of tipper response of buried sphere[J]. Journal of Oil and Gas Technology, 2007, 29(3):75-78,505.
|
| [30] |
柳建新, 甘佳雄, 童孝忠, 等. 板状体MT倾子响应的二维有限元模拟与定性分析[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2012, 34(5):541-547,500-501.
|
| [30] |
Liu J X, Gan J X, Tong X Z, et al. Finite element simulation and qualitative analysis of two-dimensional MT tipper response of tabular body[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 34(5):541-547,500-501.
|
| [31] |
吴頔. 二维及三维倾子响应和异常体识别[D]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2012.
|
| [31] |
Wu D. 2D and 3D tilt response and distinguishing to anomalous bodies[D]. Changsha: Central South University, 2012.
|
| [32] |
余年, 胡祥云, 王绪本, 等. 大地电磁二维倾子和视倾子模拟及其应用研究[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 2014, 49(2):268-275.
|
| [32] |
Yu N, Hu X Y, Wang X B, et al. Two-dimensional magnetotelluric tipper and apparent tipper:Simulation and application[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2014, 49(2):268-275.
|
| [33] |
田郁, 胡祥云, 乐彪. 倾子在地球物理断裂构造解释中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(6):1237-1244.
|
| [33] |
Tian Y, Hu X Y, Yue B. The application of tipper to geophysical fault interpretation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(6):1237-1244.
|
| [34] |
Wannamaker P E. Advances in three-dimensional magnetotelluric modeling using integral equations[J]. Geophysics, 1991, 56(11):1716.
|
| [35] |
Mackie R L, Madden T R, Wannamaker P E. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric modeling using difference equations—Theory and comparisons to integral equation solutions[J]. Geophysics, 1993, 58(2):215-226.
|
| [36] |
Mitsuhata Y, Uchida T. 3D magnetotelluric modeling using the T-Ω finite-element method[J]. Geophysics, 2004, 69(1):108-119.
|
| [37] |
徐凯军, 李桐林, 张辉, 等. 利用积分方程法的大地电磁三维正演[J]. 西北地震学报, 2006, 28(2):104-107.
|
| [37] |
Xu K J, Li T L, Zhang H, et al. Three dimentional magnetotelluric forward modeling using integral equation[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 2006, 28(2):104-107.
|
| [38] |
谭捍东, 余钦范, John Booker, 等. 大地电磁法三维交错采样有限差分数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2003, 46(5):705-711.
|
| [38] |
Tan H D, Yu Q F, Booker J, et al. Magnetotelluric three-dimensional modeling using the staggered-grid finite difference method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2003, 46(5):705-711.
|
| [39] |
顾观文, 吴文鹂, 李桐林. 大地电磁场三维地形影响的矢量有限元数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2014, 44(5):1678-1686.
|
| [39] |
Gu G W, Wu W L, Li T L. Modeling for the effect of magnetotelluric 3D topography based on the vector finite-element method[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2014, 44(5):1678-1686.
|
| [40] |
殷长春, 张博, 刘云鹤, 等. 面向目标自适应三维大地电磁正演模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(1):327-336.
|
| [40] |
Yin C C, Zhang B, Liu Y H, et al. A goal-oriented adaptive algorithm for 3D magnetotelluric forward modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(1):327-336.
|
| [41] |
林昌洪, 谭捍东, 佟拓. 倾子资料三维共轭梯度反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2011, 54(4):1106-1113.
|
| [41] |
Lin C H, Tan H D, Tong T. Three-dimensional conjugate gradient inversion of tipper data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(4):1106-1113.
|
| [42] |
田郁, 乐彪. 复杂异常体模型下的三维MT倾子正演模拟[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):1021-1029.
|
| [42] |
Tian Y, Yue B. Forward modeling of MT tipper based on 3D complex anomalous body model[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):1021-1029.
|
| [43] |
严家斌, 胡涛, 林旭, 等. 基于电场矢量有限元三维高频大地电磁倾子响应与感应矢量研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(1):123-136.
|
| [43] |
Yan J B, Hu T, Lin X, et al. Three-dimensional high-frequency electromagnetic tipper response and induction vectors based on the electric field vector finite element[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(1):123-136.
|
| [44] |
顾观文, 李桐林. 基于矢量有限元的带地形大地电磁三维反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(6):2449-2465.
|
| [44] |
Gu G W, Li T L. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion with surface topography based on the vector finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(6):2449-2465.
|
| [45] |
Shi X, Utada H, Wang J, et al. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric forward modelling using vector finite element method combined with divergence corrections(VFE++)[R]// Hyderbad:17th IAGA WG1.2 Workshop on electromagnetic Induction in the Earth, 2004.
|
| [46] |
Mackie R L, Smith J T, Madden T R. Three-dimensional electromagnetic modeling using finite difference equations:The magnetotelluric example[J]. Radio Science, 1994, 29(4):923-935.
|
| [47] |
Siripunvaraporn W, Egbert G, Lenbury Y. Numerical accuracy of magnetotelluric modeling:A comparison of finite difference approximations[J]. Earth,Planets and Space, 2002, 54(6):721-725.
|
| [48] |
Nam M J, Kim H J, Song Y, et al. 3D magnetotelluric modelling including surface topography[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 55(2):277-287.
|
| [49] |
徐世浙. 地球物理中的有限单元法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1994.
|
| [49] |
Xu S Z. Finite element method in Geophysics[M]. Beijing: Sci-ence Press,1994.
|
| [50] |
金建铭. 电磁场有限元方法[M]. 王建国,译. 西安: 西安电子科技大学出版社,1998:176-189.
|
| [50] |
Jin J M. Electromagnetic field finite element method[M]. Wang J G,tran. Xi'an: Xidian University Press,1998:176-189.
|
| [51] |
Newman G A, Alumbaugh D L. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion using non-linear conjugate gradients[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2000, 140(2):410-424.
|
| [52] |
顾观文, 武晔, 石砚斌. 基于矢量有限元的大地电磁快速三维正演研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(6):1387-1398.
|
| [52] |
Gu G W, Wu Y, Shi Y B. Research on fast three-dimensional forward algorithm of magnetotelluric sounding based on vector finite element[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(6):1387-1398.
|
| [53] |
Wannamaker P E, Stodt J A, Rijo L. PW2D finite element program for solution of magnetotelluric responses of two-dimensional earth resistivity structure.User documentation[J]. User Documentation,1985.
|
|
|
|

