|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of coal seams in the Yimin Formation in the Yimin Basin |
Li Bin1( ), Zhang Yue-Heng2, Hong Lian-Han1, Yuan Jing-Yi1, Gao Ting1, Dong Zhen-Guo2 ), Zhang Yue-Heng2, Hong Lian-Han1, Yuan Jing-Yi1, Gao Ting1, Dong Zhen-Guo2 |
1. Shool of Geography and Tourism, Hanshan Normal University, Chaozhou 521014, China
2. Shenhua Geological Exploration Co., Ltd., Beijing 102211, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Yimin Formation hosts shallow and stable coal seams, which are rich in coal resources and suitable for open-pit mining. To ascertain the distributions of coal seams in the Yimin Formation and reveal the coal accumulation patterns, it holds critical geological significance to identify the provenance setting and coal-forming environment using geochemical methods. This study systematically collected coal samples from drilling cores in the study area for testing and analysis of coal quality.Furthermore, this study reconstructed the paleogeographic information and sedimentary environment during the formation of coal seams for comprehensive research. The results show that:(1) The coal seams of the Yimin Formation are primarily composed of lignite, with durain being the dominant component, followed by fusain. Their coal samples exhibited average vitrinite reflectance (R0) of 0.37%, average oil content of 7.66% in raw coal, and average total sulfur content of 1.32%; (2) The average CIA value of 58.45 suggests that the source area experienced primary to moderate weathering. The average w(Si)/w(Al) ratio of 2.72 indicates that minerals in the coal originated from terrestrial argillaceous sediments. The ash index (K) of 0.34 implies that the coal seams formed in a low-level peat swamp environment. The w(Sr)/w(Cu), w(Sr)/w(Ba), w(Mg)/w(Al) (m), and w(Ca)/w(Fe) (n) ratios signify warm and humid paleoclimate, significant evaporation, and high salinity of ancient water bodies during the coal seam sedimentation stage. The Sr, Ba, and w(Ba)/w(Ga) values denote that the coal seams resulted from continental sedimentation. The w(V)/[w(V)+w(Ni)], w(V)/w(Cr), w(Ni)/w(Co), and w(V)/w(Sc) ratios demonstrate that the coal seams formed under anoxic reducing conditions. This study posited that the early sedimentary stage of the Yimin Formation saw the reduced continental faulted basin, humid climate, and lake siltation, forming a peat swamp environment in the deltaic plain, thus creating favorable conditions for coal generation and accumulation.
|
|
Received: 18 August 2023
Published: 08 January 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
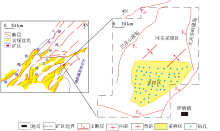
|
The structural outline of Hailar settlement area and sample location
|
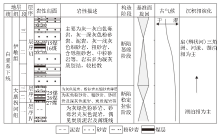
|
The comprehensive histogram of lower Cretaceous coal bearing strata
|

| 煤层 | 煤质特征 | 显微组分 | 类型指数
TI值 | 镜惰比
V/I | 反射率
R0/% | | FCad/% | Mad/% | Ad/% | Vdaf/% | 透光率
PM | 镜质
组V/% | 半镜
质组/% | 惰性
组I/% | 壳质
组E/% | 矿物质/% | | 15-5下 | 23.79 | 10.72 | 19.13 | 46.36 | 35 | 59.93 | | 0.59 | 0.66 | 38.83 | -45.21 | 101.58 | 0.34 | | 16-1 | 23.23 | 9.80 | 20.33 | 46.64 | 36 | 55.27 | | 7.05 | 0.77 | 35.40 | -48.12 | 7.84 | 0.36 | | 16-2下 | 27.10 | 9.82 | 17.10 | 45.98 | 36 | 75.71 | | 1.59 | 0.50 | 22.08 | -58.12 | 47.62 | 0.38 | | 16-3上 | 30.37 | 8.70 | 16.29 | 44.64 | 37 | 62.64 | 2.52 | 1.37 | 0.46 | 34.85 | -48.12 | 45.72 | 0.39 | | 16-3 | 33.30 | 12.01 | 11.49 | 43.20 | 41 | 72.15 | 9.14 | 6.69 | 0.56 | 11.46 | -60.52 | 10.78 | 0.39 |
|
The coal quality characteristics and macerals
|

| 煤层 | w(C)/% | w(H)/% | w(O)/% | w(N)/% | w(S)/% | H/C原子比 | O/C原子比 | | 15-5下 | 72.09 | 4.78 | 22.41 | 0.68 | 1.04 | 0.07 | 0.31 | | 16-1 | 69.95 | 4.43 | 24.67 | 0.8 | 1.71 | 0.07 | 0.33 | | 16-2 | 70.11 | 4.82 | 24.24 | 0.71 | 1.00 | 0.06 | 0.32 | | 16-3上 | 71.02 | 4.69 | 23.22 | 0.79 | 1.16 | 0.07 | 0.31 | | 16-3 | 72.05 | 4.63 | 22.82 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.06 | 0.35 |
|
The elemental composition and atomic ratio of coal
|

| 煤层 | 腐殖酸 | 苯萃取物产率/% | 低温干馏/% | | Tar.ad | CR.ad | Water.ad | 气体损失 | | 15-5下 | 14.34 | 0.50 | 7.07 | 59.64 | 19.47 | 15.00 | | 16-1 | 13.66 | 0.72 | 7.68 | 60.87 | 18.39 | 14.00 | | 16-2下 | 16.68 | 0.74 | 9.47 | 61.95 | 20.43 | 13.84 | | 16-3上 | 17.00 | 0.69 | 7.22 | 62.20 | 15.34 | 15.24 | | 16-3 | 17.20 | 1.65 | 6.84 | 63.54 | 15.34 | 14.62 |
|
The raw coal tar yield at low temperature dry distillation 600 ℃
|

| 煤层 | 煤灰元素/% | 酸性氧化物
(SiO2 +
Al2O3)/% | 碱性氧化物
(Fe2O3+
CaO+MgO)/% | w(Fe2O3)/
w(Al2O3) | 煤厚/m | | SiO2 | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | SO3 | | 15-5下 | 47.03 | 4.65 | 19.57 | 10.87 | 2.72 | 0.85 | 7.51 | 66.60 | 18.24 | 0.24 | 2.83 | | 16-1 | 49.14 | 6.54 | 19.51 | 8.28 | 2.11 | 0.78 | 6.87 | 68.65 | 16.93 | 0.34 | 2.64 | | 16-2下 | 47.73 | 4.87 | 16.30 | 10.86 | 1.82 | 0.73 | 8.49 | 64.03 | 17.55 | 0.30 | 3.16 | | 16-3上 | 45.04 | 8.47 | 16.06 | 14.53 | 2.37 | 1.70 | 7.80 | 61.10 | 25.37 | 0.53 | 7.50 | | 16-3 | 39.64 | 11.50 | 13.15 | 15.59 | 2.58 | 1.81 | 7.22 | 52.79 | 29.67 | 0.87 | 21.50 | | 平均值 | 45.72 | 7.21 | 16.92 | 12.03 | 2.32 | 1.17 | 7.58 | 62.63 | 21.55 | 0.45 | 7.53 |
|
The main element content of coal ash
|

| 煤层 | 样号 | Sc | V | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Ga | Rb | Sr | Mo | Ba | Th | U | | 15上 | M6 | 4.42 | 30.50 | 11.20 | 1.31 | 4.59 | 5.11 | 1.30 | 0.49 | 257.00 | 0.12 | 137.00 | 2.12 | 0.76 | | M5 | 0.20 | 28.40 | 8.41 | 2.29 | 7.00 | 5.37 | 1.08 | 0.53 | 156.00 | 0.34 | 75.60 | 0.75 | 0.14 | | M4 | 4.74 | 38.40 | 22.50 | 0.92 | 3.13 | 29.60 | 5.22 | 2.30 | 244.00 | 0.71 | 153.00 | 6.94 | 2.28 | | 16下 | M3 | 2.60 | 20.90 | 6.85 | 1.58 | 3.35 | 2.30 | 1.32 | 0.62 | 46.00 | 1.97 | 74.70 | 0.24 | 0.17 | | M2 | 1.47 | 18.40 | 10.10 | 1.51 | 3.54 | 12.00 | 1.14 | 0.42 | 117.00 | 0.28 | 274.00 | 0.78 | 0.22 | | M1 | 6.14 | 16.90 | 13.80 | 4.22 | 3.57 | 14.50 | 3.76 | 6.04 | 96.30 | 1.55 | 191.00 | 3.70 | 1.00 | | 平均值 | 3.26 | 25.58 | 12.14 | 1.97 | 4.20 | 11.48 | 2.30 | 1.73 | 152.72 | 0.83 | 150.88 | 2.42 | 0.76 | | 地壳克拉克值 | 22 | 135 | 100 | 25 | 75 | 55 | 15 | 90 | 375 | 1.5 | 425 | 9.6 | 2.7 | | 富集系数Ef | 0.15 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.02 | 0.41 | 0.55 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.28 | 中国煤
(侏罗系—白垩系)[6] | 3 | 13 | 12 | 8 | 11 | 9 | 4 | 7 | 79 | 2 | 150 | 4 | 2 | | 世界褐煤[6] | 3.86 | 37.38 | 54.53 | 32.01 | 54.17 | 35.32 | 5.22 | 32.64 | 206.82 | 6.18 | 249.91 | 3.3 | 6.06 |
|
The treace element content of coal ash [5] 10-6
|
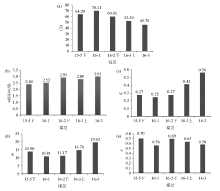
|
Characteristics of CIA value(a), w(Si)/w(Al) value(b), K value(c), m value(d) and n value(e) of coal groups 15 and 16 of Yimin Formation
|
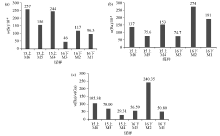
|
The contents of Sr(a),Ba(b) and w(Ba)/w(Ga) value(c) characteristics of coal groups 15 and 16 of Yimin Formation
|
|
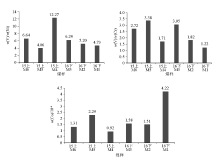
Characteristics of V/Ni value, V/Cr value and Co value of coal groups 15 and 16 of Yimin Formation
|
|
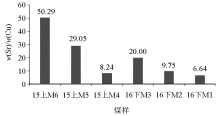
w(Sr)/w(Cu) value characteristics of coal groups 15 and 16 of Yimin Formation
|
|
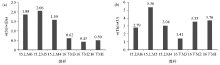
w(Sr)/w(Ba) value(a) and w(Th)/w(U) value(b) characteristics of coal groups 15 and 16 of Yimin Formation
|
|
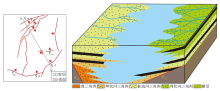
Sedimentary evolution model of Damoguaihe Formation and Yimin Formation
|
| [1] |
张云鹤, 邵龙义, 孙钦平, 等. 海拉尔盆地旧桥凹陷伊敏组层序——古地理及聚煤特征[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(4):177-187.
|
| [1] |
Zhang Y H, Shao L Y, Sun Q P, et al. Sequence-paleogeography and coal accumulation features of Jiuqiao Sag Yimin Formation in Hailaer Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(4):177-187.
|
| [2] |
余坤, 屈争辉, 薛志文, 等. 二连盆地胜利煤田构造特征及成因机制[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(6):59-66,73.
|
| [2] |
Yu K, Qu Z H, Xue Z W, et al. Structural characteristics and genetic mechanism of Shengli coalfield in Erlian Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(6):59-66,73.
|
| [3] |
王东东, 邵龙义, 张强, 等. 二连盆地群下白垩统含煤地层聚煤特征分析[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2013, 42(2):257-265.
|
| [3] |
Wang D D, Shao L Y, Zhang Q, et al. Analysis of coal-accumulating characteristics in the lower Cretaceous coal-containing strata of the Erlian Basin Group[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2013, 42(2):257-265.
|
| [4] |
李春柏. 海拉尔盆地油气勘探历程与启示[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2021, 42(3):374-380.
|
| [4] |
Li C B. Petroleum exploration history and enlightenment in Hailar Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2021, 42(3):374-380.
|
| [5] |
梁虎珍, 曾凡桂, 相建华, 等. 伊敏褐煤中微量元素的地球化学特征及其无机—有机亲和性分析[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2013, 41(10):1173-1183.
|
| [5] |
Liang H Z, Zeng F G, Xiang J H, et al. Geochemical characteristics and inorganic-organic affinity of the trace elements in Yimin lignite[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2013, 41(10):1173-1183.
|
| [6] |
唐修义, 黄文辉. 中国煤中微量元素[M]. 北京: 商务出版社, 2004.
|
| [6] |
Tang X Y, Huang W H. Trace elements in coal of China[M]. Beijing: The Commercial Press, 2004.
|
| [7] |
屈晓荣, 李俊, 孙彩蓉, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东缘柳林地区煤系泥页岩稀土元素地球化学特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(4):1083-1093.
|
| [7] |
Qu X R, Li J, Sun C R, et al. Geochemistry characteristics of rare earth elements in the late Paleozoic black shale from eastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(4):1083-1093.
|
| [8] |
黄文辉, 万欢, 杜刚, 等. 内蒙古自治区胜利煤田煤—锗矿床元素地球化学性质研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(4):56-64.
|
| [8] |
Huang W H, Wan H, Du G, et al. Research on elemental geochemical characteristics of coal-Ge deposit in Shengli coalfield,Inner Mongolia,China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(4):56-64.
|
| [9] |
韦恒叶. 古海洋生产力与氧化还原指标——元素地球化学综述[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2012, 32(2):76-88.
|
| [9] |
Wei H Y. Productivity and redox proxies of palaeo-oceans:An overview of elementary geochemistry[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2012, 32(2):76-88.
|
| [10] |
李玉坤, 李广. 吐哈盆地沙尔湖煤田煤质煤岩特征及煤相分析[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2019, 47(5):198-205.
|
| [10] |
Li Y K, Li G. Analysis on quality,petrography and facies of coal seam in Shaerhu Coalfield of Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2019, 47(5):198-205.
|
| [11] |
王绍清, 孙翊博, 沙玉明. 不同聚煤区内富氢煤有机地球化学特征研究[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2018, 46(9):233-238.
|
| [11] |
Wang S Q, Sun Y B, Sha Y M. Study on organic geochemical features of rich hydrogen coal in different coal accumulation areas[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2018, 46(9):233-238.
|
| [12] |
杜刚, 夏斌, 秦胜利, 等. 内蒙古胜利煤田共生锗矿与成煤沼泽微环境的成因关系[J]. 煤炭学报, 2008, 33(4):405-409.
|
| [12] |
Du G, Xia B, Qin S L, et al. Genetic relationship of Ge-coal deposit in Shengli Coalfield and micro-environment of coal-forming swamp[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2008, 33(4):405-409.
|
| [13] |
董振国, 赵伟, 郭军军, 等. 胜利煤田胜利组褐煤地球化学特征及古环境地质意义[J]. 煤炭科学技术, 2020, 48(11):172-181.
|
| [13] |
Dong Z G, Zhao W, Guo J J, et al. Geochemical characteristics of lignite from Shengli Formation and Paleo-environmental geological significance in Shengli Coalfield[J]. Coal Science and Technology, 2020, 48(11):172-181.
|
| [14] |
黄文辉, 久博, 李媛. 煤中稀土元素分布特征及其开发利用前景[J]. 煤炭学报, 2019, 44(1):287-294.
|
| [14] |
Huang W H, Jiu B, Li Y. Distribution characteristics of rare earth elements in coal and its prospects on development and exploitation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(1):287-294.
|
| [15] |
岳立孝, 石彦强. 沁水煤田玉溪井田煤系沉积环境及聚煤规律[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2017, 29(12):50-54,71.
|
| [15] |
Yue L X, Shi Y Q. Coal measures sedimentary environment and coal accumulation pattern in Yuxi minefield,Qinshui coalfield[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2017, 29(12):50-54,71.
|
| [16] |
秦身钧, 陆青锋, 吴士豪, 等. 重庆中梁山晚二叠世煤有机地球化学特征[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(7):1973-1982.
|
| [16] |
Qin S J, Lu Q F, Wu S H, et al. Organic geochemistry of the Late Permian Coal from the Zhongliangshan mine,Chongqing[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(7):1973-1982.
|
| [17] |
孙莎莎, 姚艳斌, 吝文. 鄂尔多斯盆地南缘铜川地区油页岩元素地球化学特征及古湖泊水体环境[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2015, 34(3):642-645.
|
| [17] |
Sun S S, Yao Y B, Lin W. Elemental geochemical characteristics of the oil shale and the paleo-lake environment of the Tongchuan area,southern Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2015, 34(3):642-645.
|
| [18] |
王双杰, 王金喜, 李世龙. 平朔矿区安太堡煤矿9#煤的有机地球化学特征[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2014, 26(12):20-23.
|
| [18] |
Wang S J, Wang J X, Li S L. Organic geochemical characteristics of coal No.9 in Antaibao coalmine,Pingshuo mining area[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2014, 26(12):20-23.
|
| [19] |
刘国, 姚忠岭, 董淑丽. 呼和诺尔特大型煤田地质特征及沉积环境分析[J]. 产业与科技论坛, 2012, 11(4):122-123.
|
| [19] |
Liu G, Yao Z L, Dong S L. Geological characteristics and sedimentary environment analysis of Huhe Nuoerte large coalfield[J]. Industrial & Science Tribune, 2012, 11(4):122-123.
|
| [20] |
张运周, 徐胜林, 陈洪德, 等. 川东北旺苍地区栖霞组地球化学特征及其古环境意义[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(2):210-217.
|
| [20] |
Zhang Y Z, Xu S L, Chen H D, et al. Geochemical characteristics and paleo-environmental implications of middle Permian Qixia Formation in Wangcang,northern Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(2):210-217.
|
| [21] |
徐晓琴. 内蒙古胜利煤田0-1孔煤中微量元素地球化学特征[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2017, 36(6):933-940.
|
| [21] |
Xu X Q. Trace element geochemical features of the coals in 0-1 borehole of the Shengli coal field in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2017, 36(6):933-940.
|
| [22] |
徐发. 内蒙古新巴尔虎左旗诺门罕煤田地质背景及沉积环境聚煤规律分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2010, 24(5):440-444.
|
| [22] |
Xu F. Geological background and analysis on coal accumulating law in sedimentary environment of Nomonhan coal field in Inner Mongolian new Barag left Banner[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2010, 24(5):440-444.
|
| [23] |
王善博, 杨君, 李建国, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地西缘宁东地区侏罗系含铀地层元素地球化学特征[J]. 煤田地质与勘探, 2018, 46(6):19-25,32.
|
| [23] |
Wang S B, Yang J, Li J G, et al. Elemental geochemical characteristics of Jurassic uranium-bearing strata in Ningdong Area,western Ordos Basin[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2018, 46(6):19-25,32.
|
| [24] |
焦叶红. 呼山煤盆地伊敏组煤层特征及聚煤环境分析[J]. 中国煤炭, 2013, 39(10):31-34,70.
|
| [24] |
Jiao Y H. Analysis on characteristics of Yimin Formation coal seam in Hushan coal basin and coal accumulating environment[J]. China Coal, 2013, 39(10):31-34,70.
|
| [25] |
张才利, 高阿龙, 刘哲, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7油层组沉积水体及古气候特征研究[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(4):582-587.
|
| [25] |
Zhang C L, Gao A L, Liu Z, et al. Study of character on sedimentary water and palaeoclimate for Chang7 oil layer in Ordos Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(4):582-587.
|
| [26] |
万欣. 呼和诺尔盆地伊敏组含煤特征分析[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2010, 22(5):23-28.
|
| [26] |
Wan X. Coal-bearing characteristic analysis of yimin formation in Hohnur Basin,Inner Mongolia[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2010, 22(5):23-28.
|
|
|
|

