|
|
|
| Deep structural characteristics of the Yagan fault zone in northeastern Ejina Banner, Inner Mongolia: Evidence from magnetotelluric sounding |
WANG Wen-Jie1,2( ), CHEN Lei1( ), CHEN Lei1( ), LEI Cong-Cong1, SHI Xiao-Feng1, YANG Biao1, WANG Wen-Bao1, SUN Da-Peng1, XU Hao-Qing1 ), LEI Cong-Cong1, SHI Xiao-Feng1, YANG Biao1, WANG Wen-Bao1, SUN Da-Peng1, XU Hao-Qing1 |
1. Hohhot General Survey of Natural Resources Center, China Geological Survey, Hohhot 010200, China
2. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract There exists a continued debate concerning the spatial distribution and deep structural characteristics of the Yagan fault zone in northeastern Ejina Banner, Inner Mongolia. Adhering to the known-to-unknown research approach, this study completed five magnetotelluric sounding (MT) profiles. First, it delved into the relationship between the electrical structure characteristics of a MT profile (MT01) on the west side of the study area and the geological structure information of the Yagan fault zone within the profile. In terms of electrical characteristics, the Yagan fault zone was determined as a resistivity gradient zone characterized by northward dip, high dip angles, and deep depths. Based on these characteristics, and combined with the inversion interpretation results of four MT profiles (MT02~MT05) on the east side, this study identified the deep positions and structural characteristics of the Yagan fault zone within all the MT profiles. Moreover, it determined the major electrical directions of all the MT profiles using the impedance tensor decomposition technique, and the spatial trend of the Yagan fault zone based on the two-dimensional inversion interpretation results. As revealed by the results, the Yagan fault zone within the study area exhibits an overall nearly EW strike at the shallow surface and a strike of NE45° in the deep part, with an average width of approximately 6.8 km. It is a reverse fault with a gradual arc deflection to the north from west to east, manifesting a generally northward dip direction, dip angles ranging from 60° to 67°, and a fault depth of about 20 km. The obtained deep electrical structure model effectively reveals the deep structural characteristics of the study area. providing certain reference significance for the study of regional tectonic evolution
|
|
Received: 10 November 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
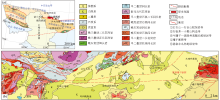
|
Geotectonic location and geological and structural schematic map of the study area
a—geotectonic location of the study area; b—schematic map of geological structure of the study area
|

| 岩性 | 时代 | 地层 | 代号 | 样品数/块 | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | | 砂岩 | 白垩纪 | 巴音戈壁组 | K1by | 15 | 813 | 4145 | 1758 | | 花岗岩 | 晚三叠世 | 侵入岩 | ηγT3 | 15 | 200 | 3106 | 1340 | | 流纹岩 | 二叠纪 | 雅干火山岩 | P1yg | 15 | 555 | 2180 | 1042 | | 玄武岩 | 二叠纪 | 金塔组 | P2j | 12 | 632 | 1215 | 1009 | | 砂质板岩 | 二叠纪 | 双堡塘组 | P2sb | 15 | 5241 | 8233 | 6658 | | 闪长岩 | 二叠纪 | 侵入岩 | δP1 | 12 | 340 | 2590 | 552 | | 花岗岩 | 二叠纪 | 侵入岩 | δγP1 | 15 | 1336 | 4560 | 2379 | | 辉长岩 | 二叠纪 | 侵入岩 | νP1 | 15 | 620 | 2370 | 1363 | | 石英砂岩 | 石炭纪 | 绿条山组 | C1l | 15 | 345 | 3222 | 1711 | | 大理岩 | 石炭纪 | 绿条山组 | C1l | 11 | 254 | 976 | 558 | | 英安岩 | 石炭纪 | 白山组 | C1-2b | 14 | 1104 | 1513 | 1218 | | 花岗岩 | 石炭纪 | 侵入岩 | C1l | 16 | 260 | 2258 | 1266 | | 闪长岩 | 石炭纪 | 侵入岩 | δοC2 | 15 | 627 | 2413 | 1113 | | 花岗闪长岩 | 晚泥盆世 | 侵入岩 | γδD3 | 14 | 635 | 1540 | 892 | | 结晶灰岩 | 泥盆纪 | 西屏山组 | D3x | 13 | 70 | 1874 | 695 | | 花岗岩 | 新元古代 | 侵入岩 | ηγPt3 | 15 | 1028 | 1583 | 1591 |
|
Statistical result of conductivity properties of rock in research area
|
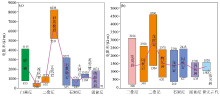
|
Resistivity characteristics of various rocks in the research area
a—apparent resistivity characteristics of formation rock; b—apparent resistivity characteristics of intrusive rocks
|

|
Location of magnetotelluric sounding profiles in the research area
|
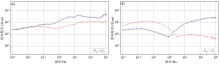
|
Observation curve of typical magnetotelluric station
a—magnetotelluric observation curve of magmatic rock mass on the northwest side of the survey area; b—magnetotelluric observation curve of Central Basin area
|
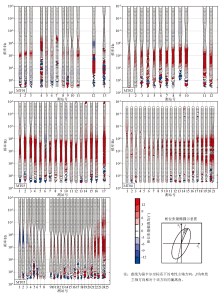
|
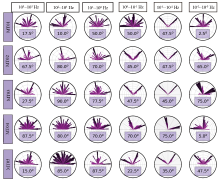
The skewness of MT01~MT05 profiles using phase tensor decomposition technique
|
|
Rose diagrams of strike analysis results
|
|
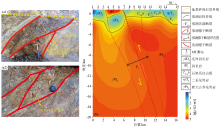
Photos of Yagan fault (a1)、(a2) and 2D inversion results of MT01 (b)
|
|
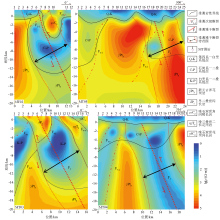
2D inversion results of MT02-MT05 profile
|

| 剖面 | 边缘位置
(MT测站号) | 宽度/km | 中心断裂位置
(MT测站号) | 倾向/(°) | 倾角/(°) | 断层类型 | 最佳电性主轴方
向(10-1~10-2 Hz) | | MT01 | 3~9 | 6 | 6 | 50° | 55°~65° | 逆断层 | 47.5° | | MT02 | 4~10 | 6 | 6 | 0° | 62°~65° | 逆断层 | 47.5° | | MT03 | 3~9 | 6 | 6 | 0° | 60°~68° | 逆断层 | 45° | | MT04 | 8~16 | 8 | 11 | 316° | 65°~70° | 逆断层 | 75° | | MT05 | 13~20 | 7 | 18 | 300° | 62°~68° | 逆断层 | 35° | | 均值 | - | 6.8 | - | 350° | 60°~67° | - | - |
|
Summary of structural characteristics of the inferred Yagan fault zone
|
|
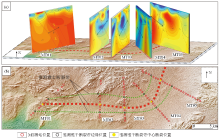
The 2D electrical structure characteristics an inferred strike of Yagan fault zone on shallow surface
a—the electrical structure of the Yagan fault zone (3D display); b—inferred strike of Yagan fault zone on shallow surface
|
| [1] |
王文杰, 雷聪聪, 薄海军, 等. 组合物探方法在浅覆盖区1∶50 000区域地质调查中的应用——以额济纳旗地区为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2022, 44(2):235-244.
|
| [1] |
Wang W J, Lei C C, Bo H J, et al. Application of composite geophysical exploration method in 1∶50,000 regional geological survey in shallow coverage area-taking Ejina banner area as an example[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 44(2):235-244.
|
| [2] |
郑荣国, 吴泰然, 张文, 等. 阿拉善地块北缘雅干花岗岩体地球化学、地质年代学及其对区域构造演化制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(8):2665-2675.
|
| [2] |
Zheng R G, Wu T R, Zhang W, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Yagan granite in the northern margin of the Alxa Block:Constraints on the tectonic evolution of the southern Altaids[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(8):2665-2675.
|
| [3] |
吴泰然, 何国琦. 内蒙古阿拉善地块北缘的构造单元划分及各单元的基本特征[J]. 地质学报, 1993, 67(2):97-108.
|
| [3] |
Wu T R, He G Q. Tectonic units and their fundamental characteristics on the northern margin of the Alxa Block[J]. Acta Geological Sinica, 1993, 67(2):97-108.
|
| [4] |
王青玉. 雅干幅K-48-13 拐子湖幅K-48-19 1∶20万区域地质调查报告[R]. 甘肃地质局地质力学区测队,1981.
|
| [4] |
Wang Qing Yu. Yakan Area K-48-13 Guaizi Lake area K-48-19 1∶200,000 regional Geological survey report[R]. Geomechanical area Survey Team,Gansu Geological Bureau,1981.
|
| [5] |
Badarch G, Dickson Cunningham W, Windley B F. A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:Implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2002, 21(1):87-110.
|
| [6] |
潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1):1-16,255,17-28.
|
| [6] |
Pan G T, Xiao Q H, Lu S N, et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(1):1-16,255,17-28.
|
| [7] |
魏文博. 我国大地电磁测深新进展及瞻望[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2002, 17(2):245-254.
|
| [7] |
Wei W B. New advance and prospect of magnetotelluric sounding (MT) in China[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2002, 17(2):245-254.
|
| [8] |
杨文采, 金胜, 张罗磊, 等. 青藏高原岩石圈三维电性结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(3):817-827.
|
| [8] |
Yang W C, Jin S, Zhang L L, et al. The three-dimensional resistivity structures of the lithosphere beneath the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(3):817-827.
|
| [9] |
李波, 金胜, 叶高峰, 等. 中亚造山带东段岩石圈电性结构特征及其构造涵义[J]. 现代地质, 2023, 37(1):15-30.
|
| [9] |
Li B, Jin S, Ye G F, et al. Lithospheric electrical structure of eastern segment of Central Asian Orogenic Belt and its tectonic implications[J]. Geoscience, 2023, 37(1):15-30.
|
| [10] |
侯征, 陈雄, 于长春, 等. 山东齐河—禹城地区深部地质构造特征——来自大地电磁的证据[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(3):1070-1081.
|
| [10] |
Hou Z, Chen X, Yu C C, et al. Characteristics of the geological deep structure in QiHe-Yucheng Area of Shandong:Evidence from magnetotelluric method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(3):1070-1081.
|
| [11] |
Maswah F, Suryantini, Srigutomo W, et al. Magnetotelluric data analysis using phase tensor and tipper strike to determine geoelectrical strike in "DKH" geothermal field[J]. IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 732(1):012014.
|
| [12] |
李尔頔, 罗润林, 徐志峰. 大地电磁测深不同极化模式测深曲线特征在探测断裂中的应用[J]. 矿产与地质, 2017, 31(1):124-130.
|
| [12] |
Li E D, Luo R L, Xu Z F. Application of curve features under different polarization modes of magnetotelluric sounding in the detection of faults[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2017, 31(1):124-130.
|
| [13] |
许第桥, 李茂. 二连盆地宽频大地电磁法数据精细反演处理研究——以满都拉图地区的数据为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(4):994-1001.
|
| [13] |
Xu D Q, Li M. Fine inversion of the broadband magnetotelluric data of the Erlian Basin:A case study of the Mandulatu Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4):994-1001.
|
| [14] |
张昭, 殷全增, 张龙飞, 等. 综合物探技术在深部碳酸盐岩热储探测中的应用研究——以雄安新区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(4):926-935.
|
| [14] |
Zhang Z, Yin Q Z, Zhang L F, et al. Application of the integrated geophysical exploration technology in the exploration of deep carbonate geothermal reservoirs:A case study of the Xiongan New Area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4):926-935.
|
| [15] |
吴旭亮, 李茂. 基于AMT的龙首山成矿带西岔地段马路沟断裂带深部发育特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5):1180-1186.
|
| [15] |
Wu X L, Li M. Deep occurrence characteristics of the Malugou fault zone in the Xicha section of the Longshoushan metallogenic belt determined based on AMT[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5):1180-1186.
|
| [16] |
李英宾. 可控源音频大地电磁测量对腾格尔坳陷东北缘下白垩统赛汉组砂体的识别及其地质意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3):616-623.
|
| [16] |
Li Y B. The identification of the sand body of lower Cretaceous Saihan Formation on the northeastern margin of Tengger depression by controlled source audio frequency magnetotelluric survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3):616-623.
|
| [17] |
陈大磊, 王润生, 贺春艳, 等. 综合地球物理探测在深部空间结构中的应用——以胶东金矿集区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(1):70-77.
|
| [17] |
Chen D L, Wang R S, He C Y, et al. Application of integrated geophysical exploration in deep spatial structures:A case study of Jiaodong gold ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1):70-77.
|
| [18] |
彭明涛, 王磊, 曾明勇, 等. 综合物探方法在川东高陡断褶带隐伏断层勘探中的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):882-889.
|
| [18] |
Peng M T, Wang L, Zeng M Y, et al. The application of integrated geophysical prospecting to the exploration of buried faults in the high and steep fault-fold zone in eastern Sichuan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):882-889.
|
| [19] |
仇根根, 方慧, 吕琴音, 等. 武夷山北段及相邻区深部电性构造与成矿分析:基于三维大地电磁探测结果[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(4):775-785.
|
| [19] |
Qiu G G, Fang H, Lyu Q Y, et al. Deep electrical structures and metallogenic analysis in the north section of Wuyishan Mountains and its adjacent areas:Based on three-dimensional magnetotelluric sounding results[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(4):775-785.
|
| [20] |
虎新军, 陈晓晶, 仵阳, 等. 综合地球物理技术在银川盆地东缘地热研究中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(4):845-853.
|
| [20] |
Hu X J, Chen X J, Wu Y, et al. Application of comprehensive geophysical exploration in geothermal resources on the eastern margin of Yinchuan Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4):845-853.
|
| [21] |
伍显红, 许第桥, 李茂. 宽频大地电磁法在二连盆地铀矿资源评价中的试验应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(4):830-837.
|
| [21] |
Wu X H, Xu D Q, Li M. An application test of broadband magnetotelluric method(BMT)for the evaluation of uranium resources in the Erlian Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4):830-837.
|
| [1] |
HAO She-Feng, TIAN Shao-Bing, MEI Rong, PENG Rong-Hua, LI Zhao-Ling. Exploring electromagnetic noise suppression technologies for magnetotelluric sounding in high-interference ore districts[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1): 162-174. |
| [2] |
Dai-Li XU, Bao-Shan TANG, Wen-Bo WEI. Electrical structure characteristics of Longmen fault zone and its adjacent areas[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(1): 17-27. |
|
|
|
|

