|
|
|
| Delimitation of natural Se-rich land in Sanhe Town, Haidong City, Qinghai Province, China |
ZHANG Ya-Feng( ), Yao Zhen( ), Yao Zhen( ), ZHU Ming-Xia, MA Qiang, SHEN Xiao, WANG Shuai, HE Lian-Zhen, DAI Lu ), ZHU Ming-Xia, MA Qiang, SHEN Xiao, WANG Shuai, HE Lian-Zhen, DAI Lu |
| The Fifth Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province, Xining 810099, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the 1∶50 000~1∶2 000 land quality geochemical survey data and the requirements of the Delimitation and the Logo for Natural Selenium-enriched Land (DZ/T 0380—2021), this study evaluated the selenium (Se) content, environmental quality, fertility quality, and irrigation water quality of soil in Sanhe Town, Ping'an District, Haidong City, Qinghai Province. The evaluation results show that: (1) The soil in Sanhe Town was alkaline; (2) The soil Se content ranged from 0.093×10-6 to 1.938×10-6, averaging 0.425×10-6; (3) The Cd, Hg, Pb, and Cr contents in the soil were all below the risk screening values of soil for agricultural land, while the As content in the soil in the southern portion of the study area was higher than its risk screening value; (4) The quality of irrigation water met the standard specified in the Green Food-Environmental Quality for Production Area (NY/T 391—2013), and the soil fertility was characterized by rich available phosphorus and potassium, and moderate nitrogen and organic matter. Based on the above evaluation results, this study delimited contiguous natural green Se-rich land of 40.46 km2, including 12% directly usable arable land (4.76 km2), and 88% potentially usable grassland (7.84 km2) and forest land (27.86 km2). They are distributed primarily in six villages, including Zhangqizhai, Luotuobao, Xicun, Dongcun, Qixinzhuang, and Sanhe villages. Considering the Se-rich industry planning and local conditions, this study proposed developing Se-rich planting in arable land and Se-rich animal husbandry by utilizing natural Se-rich forage in forest land and grassland.
|
|
Received: 11 April 2023
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
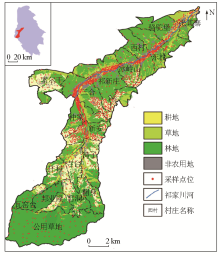
|
Schematic representation of land use type and soil sampling location in the study area
|

| 成土母质 | Se含量/10-6 | 土壤类型 | Se含量/10-6 | 土地利用类型 | Se含量/10-6 | 地貌类型 | Se含量/10-6 | | 第四系冲洪积物 | 0.490 | 灰钙土 | 0.548 | 耕地 | 0.478 | 河流阶地 | 0.490 | | 第四系风成黄土 | 0.184 | 栗钙土 | 0.355 | 草地 | 0.345 | 中低山丘陵 | 0.262 | | 西宁群泥岩风化物 | 0.361 | 黑钙土 | 0.210 | 林地 | 0.343 | | | | 民和组砂泥岩风化物 | 0.252 | 灰褐土 | 0.307 | 非农用地 | 0.391 | | | | 磨石沟组砂岩风化物 | 0.296 | 高山草甸土 | 0.294 | | | | | | 六道沟群火山岩风化物 | 0.294 | | | | | | |
|
Index for classification of selenium-rich land types
|

| 富硒土地类型 | 土壤类型 | pH | Se阀值/10-6 | 条件 | | 绿色富硒地 | 中酸性土壤 | pH≤7.5 | ≥0.40 | 重金属元素镉、汞、砷、铅和铬含量符合GB 15618—2018标准;农田灌溉水水质和土壤肥力满足NY/T 391—2013要求 | | 碱性土壤 | pH>7.5 | ≥0.30 | | 无公害富硒地 | 中酸性土壤 | pH≤7.5 | ≥0.40 | 重金属元素镉、汞、砷、铅和铬含量符合GB 15618—2018标准;灌溉水同时满足NY/T 5010—2016要求 | | 碱性土壤 | pH>7.5 | ≥0.30 | | 一般富硒地 | 中酸性土壤 | pH≤7.5 | ≥0.40 | 重金属元素镉、汞、砷、铅和铬含量符合GB 15618—2018标准 |
|
Index for classification of selenium-rich land types[13]
|
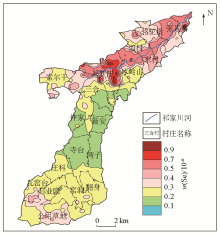
|
Soil Se geochemical distribution in the study area
|
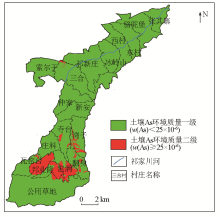
|
Environmental quality grading map of soil As in the study area
|

| 项目 | 绿色食品灌溉水
水质要求 | 实测值 | | 值域(n=3) | 评价结果 | | pH | 5.5~8.5 | 7.8~8.1 | 满足 | | 总汞 | ≤0.001 | <2.5×10-6 | 满足 | | 总镉 | ≤0.005 | <0.6×10-4 | 满足 | | 总砷 | ≤0.05 | 0.00123~0.00166 | 满足 | | 总铅 | ≤0.1 | <0.7×10-4 | 满足 | | 六价铬 | ≤0.1 | <0.9×10-4 | 满足 | | 氟化物 | ≤2.0 | 0.04~0.07 | 满足 | | 化学需氧量 | ≤60 | 0.57~1.62 | 满足 | 粪大肠菌群/
(个·L-1) | ≤10 000 | 1080~3660 | 满足 |
|
Statistical of irrigation water quality in the study area mg·L-1
|

| 指标 | 等级 | 标准值域 | 各级样品数 | 各级比例/% | 有机质
/10-3 | Ⅰ | >15 | 57 | 35.6 | | Ⅱ | 10~15 | 52 | 32.5 | | Ⅲ | <10 | 51 | 31.9 | 全氮
/10-3 | Ⅰ | >1.0 | 86 | 53.7 | | Ⅱ | 0.8~1.0 | 36 | 22.5 | | Ⅲ | <0.8 | 38 | 23.8 | 有效磷
/10-6 | Ⅰ | >10 | 148 | 92.5 | | Ⅱ | 5~10 | 9 | 5.6 | | Ⅲ | <5 | 3 | 1.9 | 速效钾
/10-6 | Ⅰ | >120 | 148 | 92.5 | | Ⅱ | 80~120 | 12 | 7.5 | | Ⅲ | <80 | 0 | 0 |
|
Statistical of soil fertility index(n=160)
|
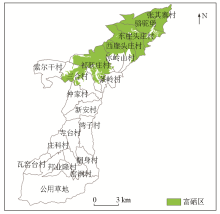
|
Natural selenium-rich land zoning in the study area
|
| [1] |
齐玉薇, 史长义. 硒的生态环境与人体健康[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2005, 22(2):63-66.
|
| [1] |
Qi Y W, Shi C Y. Se ecological environment and human boby health[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2005, 22(2):63-66.
|
| [2] |
李家熙, 张光弟, 葛晓立, 等. 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.
|
| [2] |
Li J X, Zhang G D, Ge X L, et al. Prediction and geochemical environmental chatacter of human Selenium imbalances[M]. Beijing: The Geological Publishing House, 2000.
|
| [3] |
尹红星, 张殊佳, 邓学仿, 等. 硒的抗肿瘤作用研究综述[J]. 大连大学学报, 2008, 29(6):18-25.
|
| [3] |
Yin H X, Zhang S J, Deng X F, et al. Areview of the antitumoreffect of selenium[J]. Journal of Dalian University, 2008, 29(6):18-25.
|
| [4] |
赵少华, 宇万太, 张璐, 等. 环境中硒的生物地球化学循环和营养调控及分异成因[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(10):1197-1203.
|
| [4] |
Zhao S H, Yu W T, Zhang L, et al. Biogeochemical cycling of selenium nutrition adjustment and differentiation canuse in environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(10):1197-1203.
|
| [5] |
谭见安. 中国人民共和国地方病与环境图集[M]. 北京: 科学出版社,1989.
|
| [5] |
Tan J A. The atlas of endemic diseases and theirenvironments in the People's Republie of China[M]. Beijing: Science Press,1989.
|
| [6] |
谭见安. 生命元素硒的地域分异与健康[J]. 中国地方病学杂志, 1996(2):67.
|
| [6] |
Tan J A. The regional differentiation and health of the life element selenium[J]. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 1996(2):67.
|
| [7] |
全国国土资源标准化技术委员会. DZ/T 0295—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2016.
|
| [7] |
National Technical Committee for Land and Resources Standardization. DZ/T 0295—2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment[S]. Beijing: Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China, 2016.
|
| [8] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海东部碱性土壤中硒的形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [8] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Speciation of selenium in alkaline soils in eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [9] |
马强, 张亚峰, 黄强, 等. 青海省富硒土壤标准探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):772-780.
|
| [9] |
Ma Q, Zhang Y F, Huang Q, et al. Discussion on the standard of selenium-rich soil in Qinghai province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):772-780.
|
| [10] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海省海东市平安区土壤Se的地球化学特征[J]. 地球与环境, 2019, 47(1):74-80.
|
| [10] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Geochemical Characteristics of Se in Soil of the Pinaan District,Haidong City,Qinghai Province[J]. Earth and Environment, 2019, 47(1):74-80.
|
| [11] |
周国华. 富硒土地资源研究进展与评价方法[J]. 岩矿测试, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [11] |
Zhou G H. Research progress of selenium-enriched land resources and evaluation methods[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2020, 39(3):319-336.
|
| [12] |
姬丙艳, 许光, 张亚峰, 等. 青海东部生态地球化学成果及经济效益示范[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2020.
|
| [12] |
Ji B Y, Xu G, Zhang Y F, et al. Demonstration of ecological geochemistry achievements and economic benefits in eastern Qinghai[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2020.
|
| [13] |
全国自然资源与国土空间规划标准化技术委员会. DZ/T 0380—2021天然富硒土地划定与标识[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国自然资源部, 2021.
|
| [13] |
National Technical Committee for the Standardization of Natural Resources and Territorial Spatial Planning. DZ/T 0380—2021 Delineation and identification of natural selenium-rich land[S]. Beijing: Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China, 2021.
|
| [14] |
王惠艳, 曾道明, 郭志娟, 等. 天然富硒土地划定的富硒阈值[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1):333-342.
|
| [14] |
Wang H Y, Zeng D M, Guo Z J, et al. Selenium threshold for the delimitation of natural selenium-enriched land[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1):333-342.
|
| [15] |
张亚峰, 姬丙艳, 沈骁, 等. 西宁盆地咸水湖相沉积型富硒土壤的形成机理及意义[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(2):470-476.
|
| [15] |
Zhang Y F, Ji B Y, Shen X, et al. Formation mechanism and significance of saltwater lacustrine sedimentary selenium-rich soil in Xining Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2):470-476.
|
| [16] |
中华人民共和国农业农村部. NY/T 391—2013绿色食品产地环境质量[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2013.
|
| [16] |
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 391—2021 Green food-environmental quality for production area[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2021.
|
| [17] |
中华人民共和国农业农村部. NY/T 5010—2016无公害农产品种植业产地环境条件[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021.
|
| [17] |
Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 5010—2016 Pollution-free agricultural products-environmental conditions of plantation production areas[J]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2016.
|
| [18] |
全国国土资源标准化技术委员会地质矿产试验测试分析技术委员会. DZ/T 0130.6—2006地质矿产实验室测试质量管理规范第6部分:水样分析[S]. 北京: 中华人民共和国国土资源部, 2006.
|
| [18] |
National Land and Resources Standardization Technical Committee Geology and Mineral Resources Experimental Testing and Analysis Technical Committee. DZ/T 0130.6—2006 The specification of testing quality management for geological laboratories-Pant 6:Water analysis[S]. Beijing: Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China, 2006.
|
| [19] |
奚小环, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 基于大数据的中国土壤背景值与基准值及其变化特征研究——写在《中国土壤地球化学参数》出版之际[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1095-1108.
|
| [19] |
Xi X H, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. Big data based studies of the variation features of Chinese soil’s background value versus reference value:A paper written on the occasion of Soil Geochemical Parameters of China’s publication[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1095-1108.
|
| [20] |
生态环境部土壤环境管理司, 科技标准司.GB 15618—2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)[S]. 北京: 生态环境部国家市场监督管理总局, 2018.
|
| [20] |
Department of Soil Environmental Management and Division of Scientific and Technical Standards in the Ministry of Ecology and Environment. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land(pilot)[S]. Beijing: Ministry of Ecology and Environment State Administration for Market Regulation, 2018.
|
| [1] |
MA Qiang, ZHANG Ya-Feng, HUANG Qiang, JI Bing-Yan, Miao Guo-Wen, MA Feng-Juan, MA Ying. Exploring the standards of Se-rich soil in Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 772-780. |
| [2] |
WANG Zhi-Qiang, YANG Jian-Feng, WEI Li-Xin, SHI Tian-Chi, CAO Yuan-Yuan. Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil in Shizuishan area, Ningxia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 229-237. |
|
|
|
|

