|
|
|
| Evaluation of the primary soil fertility indices for the agricultural area of Yongqing County, Hebei Province |
HU Qing-Hai1,2( ), LI Jun-Hua1,3, WANG Xue-Qiu1,2( ), LI Jun-Hua1,3, WANG Xue-Qiu1,2( ), YI Ming-Xuan3, WU Hui1,2, TIAN Mi1,2 ), YI Ming-Xuan3, WU Hui1,2, TIAN Mi1,2 |
1. Key Laboratory of Geochemical Exploration, Ministry of Natural Resources, Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
2. International Centre on Global-Scale Geochemistry, United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization, Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Langfang 065000, China
3. Langfang Natural Resources Comprehensive Survey Center, China Geological Survey, Langfang 065000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Yongqing County, as a pivotal pollution-free vegetable production base in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, has made significant contributions to ensuring the food safety of this region. However, there has been no systematic and comprehensive evaluation of Yongqing County's soil fertility, hindering the sustainable development of its green food industry. This study collected 338 soil samples from the arable layer (depth: 0~20 cm) throughout the county, including 155 from dry land, 84 from vegetable plots, and 99 from garden plots. Four soil nutrient elements including organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus and potassium were determined using these samples. The results show that: The average contents of organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus, and rapidly available potassium in the soil samples from Yongqing County's arable layer were 5.29×10-3, 0.78×10-3, 41.8×10-6, and 197×10-6, respectively. The soil fertility generally exhibited deficient organic matter and total nitrogen and abundant available phosphorus and potassium. In addition, the soil fertility of Yongqing County was graded and evaluated according to China's agricultural standard Green food-Environmental quality for production area (NY/T 391—2021). For land-use types like dry land, vegetable and garden plots, their organic matter and total nitrogen contents were mostly at level Ⅲ, and available phosphorus and potassium contents were primarily at level Ⅰ. The soil nutrient contents differed significantly in spatial distributions. Specifically, Longhuzhuang, Liujie, and Yangmazhuang townships in the southwest generally had higher soil nutrient contents than Caojiawu Township, Hancun and Lilancheng towns in the northeast. To efficiently develop the green food industry, Yongqing County needs to apply fertilizers scientifically and properly according to land-use types and actual planting situations and considering the soil texture and natural geographical factors. The specific measures are as follows: increasing the organic matter and total nitrogen contents in the soil by applying more organic and nitrogen fertilizers; applying more phosphate and potassium fertilizers to soil lacking available phosphorus and potassium, otherwise, the application of such fertilizers should be controlled.
|
|
Received: 27 November 2022
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
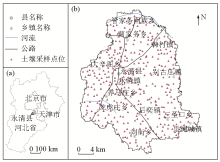
|
Regional location(a) and distribution of soil fertility survey sites(b) in Yongqing County
|

| 土壤养分要素 | 有机质/10-3 | 全氮/10-3 | 有效磷/10-6 | 速效钾/10-6 | | 级别 | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | | 旱地 | >15 | 10~15 | <10 | >1.0 | 0.8~1.0 | <0.8 | >10 | 5~10 | <5 | >120 | 80~120 | <80 | | 菜地 | >30 | 20~30 | <20 | >1.2 | 1.0~1.2 | <1.0 | >40 | 20~40 | <20 | >150 | 100~150 | <100 | | 园地 | >20 | 15~20 | <15 | >1.0 | 0.8~1.0 | <0.8 | >10 | 5~10 | <5 | >100 | 50~100 | <50 |
|
Soil fertility grading standard of green food production area
|

| 用地类型 | 养分类别 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 中位数 | 标准偏差 | 变异系数/% | | 研究区 | 有机质/10-3 | 5.29 | 13.50 | 0.91 | 4.64 | 2.83 | 53.6 | | 全氮/10-3 | 0.78 | 3.18 | 0.09 | 0.74 | 0.35 | 45.2 | | 有效磷/10-6 | 41.80 | 554.00 | 0.39 | 15.50 | 68.90 | 165 | | 速效钾/10-6 | 197 | 1439.0 | 43.9 | 146.0 | 156.0 | 78.8 | | 旱地 | 有机质/10-3 | 5.44 | 12.60 | 1.54 | 4.87 | 2.81 | 51.7 | | 全氮/10-3 | 0.76 | 1.70 | 0.09 | 0.76 | 0.26 | 34.4 | | 有效磷/10-6 | 22.50 | 319.70 | 0.69 | 11.90 | 37.20 | 166 | | 速效钾/10-6 | 161.4 | 857.0 | 43.9 | 134.0 | 101.0 | 62.5 | | 菜地 | 有机质/10-3 | 6.07 | 13.50 | 0.91 | 5.58 | 3.15 | 51.8 | | 全氮/10-3 | 0.98 | 3.20 | 0.37 | 0.87 | 0.44 | 44.5 | | 有效磷/10-6 | 89.40 | 554.00 | 3.63 | 59.50 | 99.70 | 112 | | 速效钾/10-6 | 283.0 | 1439.0 | 87.2 | 215.0 | 213.0 | 75.2 | | 园地 | 有机质/10-3 | 4.26 | 11.50 | 1.42 | 3.67 | 2.08 | 48.7 | | 全氮/10-3 | 0.63 | 3.00 | 0.12 | 0.59 | 0.31 | 49.6 | | 有效磷/10-6 | 31.40 | 500.00 | 0.39 | 11.30 | 56.40 | 180 | | 速效钾/10-6 | 174.0 | 1081.0 | 50.2 | 135.0 | 128.0 | 73.9 |
|
Statistics of soil nutrients of various land-use types in Yongqing County
|

| 指标 | 级别 | | Ⅰ | Ⅱ | Ⅲ | Ⅳ | Ⅴ | Ⅵ | | 有机质/10-3 | >40 | 30~40 | 20~30 | 10~20 | 6~10 | <6 | | 全氮/10-3 | >2 | 1.5~2 | 1~1.5 | 0.75~1 | 0.5~0.75 | <0.5 | | 有效磷/10-6 | >40 | 20~40 | 10~20 | 5~10 | 3~5 | <3 | | 速效钾/10-6 | >200 | 150~200 | 100~150 | 50~100 | 30~50 | <30 |
|
Classification standards for the second national soil census
|
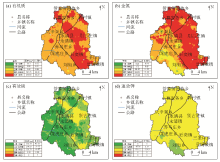
|
Geochemical map of organic matter(a), total nitrogen(b), available phosphorus(c) and available potassium(d) in surface soils in Yongqing County
|

| 土地利用类型 | 土壤养分要素 | 各级别样品数(占比) | | Ⅲ | Ⅱ | Ⅰ | 合计/个 | | 旱地 | 有机质 | 142 (92%) | 13 (8%) | 0 (0) | 155 | | 全氮 | 88 (57%) | 43 (28%) | 24 (15%) | 155 | | 有效磷 | 22 (14%) | 46 (30%) | 87 (56%) | 155 | | 速效钾 | 10 (6%) | 50 (32%) | 95 (61%) | 155 | | 菜地 | 有机质 | 84 (100%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 84 | | 全氮 | 57 (68%) | 6 (7%) | 21 (25%) | 84 | | 有效磷 | 25 (30%) | 10 (12%) | 49 (58%) | 84 | | 速效钾 | 5 (6%) | 20 (24%) | 59 (70%) | 84 | | 园地 | 有机质 | 99 (100%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 99 | | 全氮 | 83 (84%) | 12 (12%) | 4 (4%) | 99 | | 有效磷 | 24 (24%) | 19 (19%) | 56 (57%) | 99 | | 速效钾 | 1 (0) | 24 (24%) | 74 (75%) | 99 |
|
Soil fertility grading statistics of all sampling sites in different land-use types
|

| 乡镇 | 有机质
均值/
10-3 | 全氮均
值/
10-3 | 有效磷
均值/
10-6 | 速效钾
均值/
10-6 | 样本数 | | 龙虎庄乡 | 7.50 | 0.98 | 70.10 | 320.0 | 22 | | 刘街乡 | 9.90 | 1.17 | 41.10 | 315.0 | 25 | | 养马庄乡 | 5.67 | 0.91 | 53.10 | 213.0 | 15 | | 大辛阁乡 | 3.73 | 0.69 | 24.20 | 142.0 | 5 | | 永清镇 | 4.92 | 0.81 | 46.20 | 187.0 | 87 | | 后奕镇 | 6.48 | 0.74 | 33.10 | 165.0 | 17 | | 曹家务乡 | 3.90 | 0.67 | 43.10 | 152.0 | 43 | | 管家务乡 | 2.76 | 0.80 | 53.50 | 199.0 | 10 | | 三圣口乡 | 4.44 | 0.52 | 29.40 | 150.0 | 33 | | 韩村镇 | 4.65 | 0.66 | 37.10 | 144.0 | 21 | | 别古庄镇 | 4.58 | 0.61 | 15.50 | 152.0 | 20 | | 里澜城镇 | 4.51 | 0.67 | 22.30 | 160.0 | 27 |
|
Average statistics of soil fertility contents of the main towns in Yongqing County
|
| [1] |
孟娟. 河北平原区无公害蔬菜基地土壤质量评价研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2009.
|
| [1] |
Meng J. Study on soil quality eEvaluation of non-environmental pollution vegetable base in plain area of Hebei[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2009.
|
| [2] |
骆东奇, 白洁, 谢德体. 论土壤肥力评价指标和方法[J]. 土壤与环境, 2002, 11(2):202-205.
|
| [2] |
Luo D Q, Bai J, Xie D T. Research on evaluation norm and method of soil fertility[J]. Soil and Environmental Sciences, 2002, 11(2):202-205.
|
| [3] |
孔祥斌, 刘灵伟, 秦静, 等. 基于农户行为的耕地质量评价指标体系构建的理论与方法[J]. 地理科学进展, 2007, 26(4):75-85.
|
| [3] |
Kong X B, Liu L W, Qin J, et al. Theory and methodology for the construction of arable land quality evaluation system based on household behaviors[J]. Progress in Geography, 2007, 26(4):75-85.
|
| [4] |
康日峰, 任意, 吴会军, 等. 26年来东北黑土区土壤养分演变特征[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(11):2113-2125.
|
| [4] |
Kang R F, Ren Y, Wu H J, et al. Changes in the nutrients and fertility of black soil over 26 years in Northeast China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(11):2113-2125.
|
| [5] |
朱永磊. 河北主要土壤肥力质量时空变异及评价研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2014.
|
| [5] |
Zhu Y L. Studies on temporal and spatial variability of the major soil fertility in Hebei Province[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2014.
|
| [6] |
李菊梅, 王朝辉, 李生秀. 有机质、 全氮和可矿化氮在反映土壤供氮能力方面的意义[J]. 土壤学报, 2003, 40(2):232-238.
|
| [6] |
Li J M, Wang Z H, Li S X. Significance of soil organic matter,total N and mineralizable nitrogen in reflectiong soil N supplying capacity[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2003, 40(2):232-238.
|
| [7] |
郭巨秋. 河北省苹果园土壤养分状况与变化研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2020.
|
| [7] |
Guo J Q. Study on soil nutrient status and change of apple orchard in Hebei Province[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2020.
|
| [8] |
纪梦梦, 吴晓刚, 吴欣欣, 等. 过量施肥对设施菜田土壤菌群结构及N2O产生的影响[J]. 微生物学通报, 2018, 45(6):1323-1332.
|
| [8] |
Ji M M, Wu X G, Wu X X, et al. Effect of overuse nitrogen fertilizer on bacterial community and N2O emission from greenhouse soil[J]. Microbiology China, 2018, 45(6):1323-1332.
|
| [9] |
肖阳. 农业绿色发展背景下我国化肥减量增效研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2018.
|
| [9] |
Xiao Y. Reduction and efficiency of chemical fertilizer under the background of agricultural green development in China:An empirical study of Henan Province[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018.
|
| [10] |
NY/T 391—2021 绿色食品产地环境质量标准[S].
|
| [10] |
NY/T 391—2021 Green food-environmental quality for production area[S].
|
| [11] |
魏晓涵. 永清县设施蔬菜发展现状及融入京津冀农业协同的对策研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2015.
|
| [11] |
Wei X H. Yongqing facilities vegetables developping status and agricultural integration strategies of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei circle[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2015.
|
| [12] |
郭丽羡, 邵岩, 王永江, 等. 永清县蔬菜产业发展现状及展望[J]. 蔬菜, 2019(8):38-41.
|
| [12] |
Guo L X, Shao Y, Wang Y J, et al. Current situation and prospect of vegetable industry in Yongqing County[J]. Vegetables, 2019(8):38-41.
|
| [13] |
刘佳. 京津冀地区葡萄园土壤养分分布特征及绿色施肥技术研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2021.
|
| [13] |
Liu J. Study on soil nutrient distribution characteristics and green fertilization technology of grape garden in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2021.
|
| [14] |
王双双. 河北省设施蔬菜土壤质量调查及改良技术研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2019.
|
| [14] |
Wang S S. Investigation on soil quality of vegetable field in Hebei Province research on improvement technology[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2019.
|
| [15] |
孟祥林. 京津冀协同发展背景下“广域永清城市团”发展构想[J]. 北方工业大学学报, 2021, 33(3):82-90.
|
| [15] |
Meng X L. “Wide-Area Yongqing City Group”development ideas under the background of the coordinated development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei[J]. North China Univ.of Tech., 2021, 33(3):82-90.
|
| [16] |
江勇, 付梅臣, 杜春艳, 等. 基于DPSIR模型的生态安全动态评价研究——以河北永清县为例[J]. 资源与产业, 2011, 13(1):61-65.
|
| [16] |
Jiang Y, Fu M C, Du C Y, et al. A case study on Yongqing county:Dynamic assessment of ecological safety based on DPSIR model[J]. Resources & Ndustries, 2011, 13(1):61-65.
|
| [17] |
DZ/T 0295—2016 土地质量地球化学评价规范[S].
|
| [17] |
DZ/T 0295—2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment[S].
|
| [18] |
NY/T 1121.6—2016 土壤检测第6部分:土壤有机质的测定[S].
|
| [18] |
NY/T 1121.6—2016 Soil testing Part 6:Method for determination of soil organic matter[S].
|
| [19] |
HJ 717—2014 土壤质量全氮的测定凯氏法[S].
|
| [19] |
HJ 717—2014 Soil quality-determination of total nitrogen-modified Kjeldahl method[S].
|
| [20] |
LY/T 1232—2015 森林土壤磷的测定[S].
|
| [20] |
LY/T 1232—2015 Phosphorus determination methods of forest soils[S].
|
| [21] |
LY/T 1234—2015 森林土壤钾的测定[S].
|
| [21] |
LY/T 1234—2015 Potassium determination methods of forest soils[S].
|
| [22] |
黄先飞, 王莉霞, 龚宁, 等. 剑河县水田及旱地的土壤肥力特征与评价[J]. 西南农业学报, 2020, 33(7):1510-1516.
|
| [22] |
Huang X F, Wang L X, Gong N, et al. Soil fertility characteristics and evaluation of paddy field and dry land in Jianhe County[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 33(7):1510-1516.
|
| [23] |
孙彦铭, 黄少辉, 刘克桐, 等. 土壤肥力差异对冀中南山前平原与低平原夏玉米产量的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2022, 38(35):35-42.
|
| [23] |
Sun Y M, Huang S H, Liu K T, et al. Effects of soil fertility difference on summer maize yield in piedmont plain and low plain in Central and Southern Hebei[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2022, 38(35):35-42.
|
| [24] |
高新昊, 刘苹, 刘兆辉, 等. 寿光设施菜地土壤养分累积与农产品硝酸盐污染研究[J]. 江西农业学报, 2013, 25(6):125-128,136.
|
| [24] |
Gao X H, Liu P, Liu Z H, et al. Studies on soil nutrient accumulation in protected vegetable land and nitrate pollution of agricultural products in Shouguang City[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2013, 25(6):25-128,136.
|
| [25] |
王倩姿, 王书聪, 张书贵, 等. 潮土区菜田土壤肥力现状评价[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2020, 37(5):645-653.
|
| [25] |
Wang Q Z, Wang S C, Zhang S G, et al. Evaluation on fertility status of fluvo-aquic soil in a vegetable field[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2020, 37(5):645-653.
|
| [26] |
乔德波. 施用有机肥对设施菜地土壤养分、重金属含量及其分布特征的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2014.
|
| [26] |
Qiao D B. Effects of organic fertilizer application on the accumulation and distribution of nutrients and heavy metals in greenhouse vegetable system[D]. Shengyang: Shengyang Agricultural University, 2014.
|
| [27] |
张绪美, 沈文忠, 胡青青. 太仓市郊大棚菜地土壤盐分累积与分布特征研究[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(5):987-991.
|
| [27] |
Zhang X M, Shen W Z, Hu Q Q. Accumulation and regional distribution of salinity in greenhouse soils in Taicang suburban area[J]. Soils, 2017, 49(5):987-991.
|
| [28] |
周建斌, 翟丙年, 陈竹君, 等. 设施栽培菜地土壤养分的空间累积及其潜在的环境效应[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2004, 23(2):332-335.
|
| [28] |
Zhou J B, Zhai B N, Chen Z J, et al. Nutrient accumulations in soil profiles under canopy vegetable cultivation and their potential environmental impacts[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2004, 23(2):332-335.
|
| [29] |
王柳, 张福墁, 高丽红. 京郊日光温室土壤养分特征的研究[J]. 中国农业大学学报, 2003, 8(1):62-66.
|
| [29] |
Wang L, Zhang F M, Gao L H. Characteristics of soil nutrients in solar greenhouse in Beijing suburb[J]. Journal of China Agricultural University, 2003, 8(1):62-66.
|
| [30] |
俞巧钢, 孙万春, 叶静. 有机肥替代化肥对橘园土壤培肥及果实产量品质的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2023, 40(4):755-762.
|
| [30] |
Yu Q G, Sun W C, Ye J, et al. Effects of organic manure substituting chemical fertilizer on soil fertility and fruit yield and quality in citrus orchard[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2023, 40(4):755-762.
|
| [31] |
赵丽. 区域土地利用空间格局与统筹研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2008.
|
| [31] |
Zhao L. Research on the spatial structure of land-use planning at the overall area:A case of Yongqing County[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2008.
|
| [32] |
单燕, 李水利, 李茹, 等. 陕西省玉米土壤肥力与施肥效应评估[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6):1430-1437.
|
| [32] |
Shan Y, Li S L, Li R, et al. Analysis of soil fertility and fertilizer efficiency of maize field in Shannxi[J]. Acta Pedlolgica Sinica, 2015, 52(6):1430-1437.
|
| [33] |
聂扬眉, 步连燕, 陈文峰, 等. 高量秸秆还田配施芽孢杆菌对沙化土壤细菌群落及肥力的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(9):5176-5185.
|
| [33] |
Nie Y M, Bu L Y, Chen W F, et al. Effect of returning high amount of straw and applying bacillus on bacterial community and fertility of desertification soil[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(9):5176-5185.
|
| [34] |
解文艳, 周怀平, 杨振兴, 等. 山西省农田土壤肥力现状及近10年变化特征[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022, 306(10):1-10.
|
| [34] |
Xie W Y, Zhou H P, Yang Z X, et al. Current situation and change characteristics in recent 10 years of farmland soil fertility in Shanxi province based on location monitoring[J]. Soil and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2022, 306(10):1-10.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Mian, ZHANG Chun-Guan, ZHAO Min, ZHONG Zhen-Hua, YUAN Bing-Qiang, ZHOU Lei, HAN Mei. An integrated data quality evaluation of Earth magnetic anomaly grid EMAG2v3 and global gravimetric database V29: A case study of the Aegir ridge in the Arctic[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1410-1416. |
| [2] |
REN Rui, ZHANG Zhi-Min, WANG Hui, CHEN Ji-Ping, QIAO Xin-Xing, LIANG Dong-Li. Exploring selenium enrichment criteria for soils in the Guanzhong area, Shaanxi Province: A case study of wheat[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1354-1360. |
|
|
|
|

