|
|
|
| A preliminary study of Se-rich soil in the Shizuishan area, Ningxia and its potential for application |
WANG Zhi-Qiang( ), YANG Jian-Feng( ), YANG Jian-Feng( ), SHI Tian-Chi ), SHI Tian-Chi |
| Geophysical and Geochemical Survey Institute of the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, Yinchuan 750004, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the statistical analysis of the Se distribution in 8,835 soil samples and 240 sets of crop-root soil samples, as well as related survey data in the Shizuishan area of Ningxia, this study summarized the element geochemical characteristics of the local Se-rich soil and explored the development and utilization prospects of the soil and related issues. The study results are as follows. ① The newly delineated Se-rich land (soil with Se content of ≥0.222×10-6; local standard of Ningxia) covers a total area of more than 1,000 km2, including more than 25% of Se-rich farmland, and the effective Se content is mostly over 10% of Se in the soil; ② The Se-rich soil has pH of greater than 7.5 and organic matter content of less than 10.26%, without heavy metal pollution. There are significant positive correlations between the Se content and the contents of organic matter, B, Mn, Mo, Cu, and Zn and a negative correlation between the Se content and pH; ③ The correlation coefficient between effective Se and Se in the soil is r = 0.39, and those between effective Se and OM, CEC, and N are 0.33 to 0.5; ④ Among the 10 types of Se-rich agricultural products (i.e., Se-rich wheat) obtained in Se-enrich soil through spot check, the wheat has been proven to have the strongest capacity to absorb Se, with an average bioconcentration coefficient of 0.12; ⑤ Since the unique Se-rich soil resources in this area is of great value in development and utilization, it is necessary to strengthen the R&D of characteristic Se-rich crops (i.e., wheat, rice, wolfberry, and grape) and the development of relevant Se-rich standards through scientific research and reasonable planning.
|
|
Received: 26 July 2021
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YANG Jian-Feng
E-mail: nxw12@163.com;623552149@qq.com
|
|
|
|
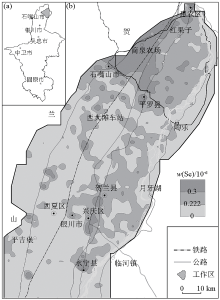
|
Regional location (a) and distribution of Se-riched soil (b) in the study areas
|

| 检测项目 | 检测方法 | 检出限 | 检出限要求 | 大米、
稻谷 | 脱水
蔬菜 | | Pb | 石墨炉原子吸收光谱法 | 0.005 | 0.1 | 0.1 | | Cd | 石墨炉原子吸收光谱法 | 0.003 | 0.10 | 0.03 | | Hg | 原子荧光光谱法 | 0.0001 | 0.010 | 0.005 | | As | 电感耦合等离子体质谱法 | 0.005 | 0.3 | 0.3 | | Cu | 火焰原子吸收光谱法 | 0.02 | 1.0 | 1.0 | | Zn | 火焰原子吸收光谱法 | 0.4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | | Ni | 石墨炉原子吸收光谱法 | 0.004 | 0.1 | 0.1 | | Cr | 石墨炉原子吸收光谱法 | 0.01 | 0.5 | 0.2 | | F | 离子色谱法 | 0.05 | 1.0 | 1.0 | | Se | 氢化物原子荧光光谱法 | 0.005 | 0.005 | 0.005 |
|
Elements detected line and its testing methods for some phyto-samples10-6
|

| 参数 | Se | Mn | Cu | Zn | Cd | Hg | As | Pb | Cr | 有机质 | pH | | 最小值 | 0.018 | 4.69 | 7.44 | 0.91 | 0.03 | 0 | 2.90 | 11.40 | 2.86 | 0.06 | 6.88 | | 最大值 | 1.800 | 1500.00 | 49.08 | 138.60 | 0.58 | 0.65 | 19.77 | 50.00 | 93.21 | 10.26 | 10.40 | | 平均值 | 0.260 | 597.60 | 22.54 | 65.56 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 11.98 | 21.57 | 60.69 | 1.50 | 8.61 | | 标准差 | 0.120 | 124.80 | 5.00 | 14.43 | 0.06 | 0.02 | 3.04 | 3.47 | 11.92 | 0.68 | 0.31 | | 变异系数 | 0.46 | 0.21 | 0.22 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 0.73 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.04 |
|
Statistics of Se and other elemental geochemical distributive parameters in soil in Shizuishan areas
|
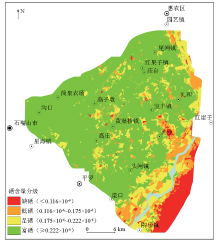
|
Distribution of Se-riched soil in the Shizuishan areas
|

| 指标 | 相关系数 | | 指标 | 相关系数 | | 指标 | 相关系数 | | Li | 0.803 | | N | 0.514 | | Ge | 0.256 | | Mo | 0.693 | | F | 0.505 | | MgO | 0.148 | | B | 0.648 | | 阳离子交换量 | 0.500 | | S | 0.119 | | 有机质 | 0.642 | | Mn | 0.444 | | As | 0.069 | | TFe2O3 | 0.622 | | K2O | 0.434 | | 全盐量 | -0.030 | | Pb | 0.582 | | Cd | 0.398 | | CaO | -0.035 | | Zn | 0.56 | | P | 0.329 | | pH | -0.382 | | Cr | 0.529 | | I | 0.290 | | | | | Co | 0.516 | | Hg | 0.275 | | | |
|
Table of correlation between soil selenium and soil physical and chemical indexes(n=8835)
|

| 作物 | 土壤Se | 土壤Se均值 | 土壤有效Se | 有效Se均值 | 有效度/% | 作物Se | 作物Se均值 | Se生物
富集系数 | 富硒作物
样占比/% | | 玉米(40) | 0.12~0.31 | 0.252 | 0.0024~0.0268 | 0.0140 | 5.56 | 0.013~0.041 | 0.0225 | 0.089 | 2.50 | | 小麦(30) | 0.10~0.48 | 0.261 | 0.0042~0.0178 | 0.0116 | 4.44 | 0.011~0.167 | 0.0453 | 0.174 | 33.33 | | 稻籽(30) | 0.10~0.28 | 0.182 | 0.0045~0.0221 | 0.0127 | 6.98 | 0.011~0.076 | 0.0288 | 0.158 | 13.33 | | 葡萄(20) | 0.17~0.42 | 0.272 | 0.0029~0.0196 | 0.0113 | 4.15 | 0.009~0.021 | 0.0152 | 0.056 | 40.00 | | 枸杞(15) | 0.17~0.48 | 0.289 | 0.0072~0.0261 | 0.0158 | 5.47 | 0.013~0.024 | 0.0160 | 0.055 | 40.00 | | 苜蓿(15) | 0.19~0.72 | 0.370 | 0.0053~0.0245 | 0.0136 | 3.68 | 0.010~0.024 | 0.0163 | 0.044 | 66.67 | | 芹菜(15) | 0.22~0.34 | 0.263 | 0.0099~0.0171 | 0.0129 | 4.91 | 0.014~0.040 | 0.0213 | 0.081 | 46.67 | | 西红柿(15) | 0.21~0.76 | 0.405 | 0.0019~0.0254 | 0.0116 | 2.86 | 0.008~0.020 | 0.0105 | 0.026 | 26.67 | | 芥蓝(15) | 0.08~0.41 | 0.246 | 0.0043~0.0275 | 0.0109 | 4.43 | 0.009~0.032 | 0.0180 | 0.073 | 33.33 | | 韭葱(15) | 0.18~0.28 | 0.254 | 0.0088~0.0212 | 0.0131 | 5.16 | 0.013~0.029 | 0.0181 | 0.071 | 46.67 |
|
Se distribution of main plant foods and its cultivated soil in the Shizuishan areas
|
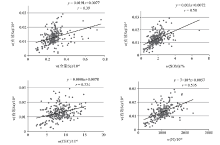
|
Scatter plots of effective selenium content vs Se, SOM, CEC and N in root soil
|

| 样号 | 粮食 | 根系土 | | | Se | Cd | Hg | As | Pb | Cr | Cu | Zn | Se | Se-B | pH | SOM | | 稻籽 | 0.076 | 0.0076 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.1870 | 未检出 | 52.1 | 25.1 | 0.24 | 0.0119 | 8.59 | 1.25 | | 稻籽 | 0.050 | 0.0031 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0689 | 未检出 | 53.2 | 17.4 | 0.25 | 0.0196 | 8.33 | 6.84 | | 稻籽 | 0.044 | 0.0038 | 0.0034 | 未检出 | 0.0816 | 未检出 | 20.2 | 19.2 | 0.20 | 0.0116 | 7.98 | 1.31 | | 稻籽 | 0.043 | 0.0022 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0508 | 未检出 | 20.4 | 13.0 | 0.17 | 0.0103 | 8.17 | 1.06 | | 小麦 | 0.167 | 0.0095 | 未检出 | 0.020 | 0.0214 | 未检出 | 6.52 | 20.8 | 0.24 | 0.0177 | 9.17 | 1.91 | | 小麦 | 0.083 | 0.0172 | 0.0064 | 0.303 | 0.4570 | 0.2800 | 21.6 | 26.4 | 0.27 | 0.0132 | 8.56 | 2.40 | | 小麦 | 0.074 | 0.0102 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0179 | 0.0405 | 5.41 | 24.2 | 0.44 | 0.0178 | 8.41 | 3.49 | | 小麦 | 0.073 | 0.0149 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0120 | 未检出 | 5.54 | 20.2 | 0.48 | 0.0130 | 8.52 | 2.06 | | 小麦 | 0.052 | 0.0111 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0167 | 0.0429 | 6.40 | 21.0 | 0.27 | 0.0102 | 8.56 | 1.79 | | 小麦 | 0.047 | 0.0119 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0120 | 未检出 | 5.44 | 17.5 | 0.29 | 0.0131 | 8.41 | 2.28 | | 小麦 | 0.045 | 0.0152 | 0.0171 | 0.0085 | 0.0509 | 0.0830 | 11.7 | 27.0 | 0.24 | 0.0119 | 8.47 | 2.06 | | 小麦 | 0.044 | 0.0194 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0295 | 0.0724 | 4.98 | 14.8 | 0.31 | 0.0073 | 8.72 | 1.03 | | 小麦 | 0.042 | 0.0100 | 未检出 | 未检出 | 0.0166 | 0.0410 | 6.43 | 24.2 | 0.27 | 0.0110 | 8.52 | 1.97 | | 小麦 | 0.040 | 0.0089 | 0.0082 | 未检出 | 0.0095 | 0.0501 | 7.11 | 17.8 | 0.35 | 0.0147 | 8.63 | 1.85 |
|
Testing results of element content of some Se-riched foods and its soil samples in the Shizuishan areas
|

| 资源属性 | 主要特征 | 代表性参数 | 影响因素或其他 | | 富硒土壤分布 | 石嘴山及所属银川平原存在大片优质富硒土地,富硒土地占比超过已调查面积的67%,其中包含大面积的耕地 | 土壤Se含量范围介于(0.0018~1.8)×10-6,平均含量0.26×10-6,与全国土壤硒平均含量相当;土壤硒有效度约为5%,高于国内多数地区 | 与贺兰山煤系地层关系密切,是黄河中上游地区代表性的天然富硒土壤之一 | | 产出环境 | 碱性土壤环境下的多个土类同时相对富硒,富硒土类包含灌淤土、灰钙土、盐土、潮土等,土壤Se分布不均衡 | pH>7.5,w(SOM)<10.26%,土壤Se同有效Se的相关系数r=0.39;重金属元素含量低 | 土壤Se同SOM、B、Mo、Mn、Cu、Zn、Pb、Cr等存在显著正相关性 | | 与农作物关系 | 在富硒区分析稻籽、小麦、玉米、葡萄、苜蓿、芹菜等10种天然富硒作物,以小麦吸收土壤Se能力最强。粮食样品与土壤Se之间存在较显著正相关性,但其与土壤有效Se相关性却不明显 | 麦籽Se生物富集系数最高达到0.71、平均值为0.174,天然富硒小麦样品占比达到33.33% | 富硒稻米样品占比低于小麦,可能同部分抽查样品未落在真正富硒土壤区有关,土壤富硒是农作物富硒的前提或物质基础 | | 利用前景或潜力 | 大面积开发利用还没有真正开始,天然富硒小麦、稻米可作为最基本的开发产品,目前的天然富硒稻米选区不够理想 | 通过调整种植规划、改良土壤,提高天然富硒稻米占比(现为13.33%) | 调整规划、优选品种、改良土壤(有机质与酸碱度等),提高富硒土壤利用效率 |
|
Basic features of Se-riched soil resources in the Shizuishan areas
|
| [1] |
Tan J A, Huang Y J. Selenium in geo-ecosystem and its relations to endemic diseases in China[J]. Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 1991, 57(59-68):59-68.
|
| [2] |
Rayman M. The importance of selenium to human health[J]. Lancet, 2000, 356(9225): 233-241.
|
| [3] |
Zhu J M, Wang N, Li S H, et al. Distribution and transport of selenium in Yutangba,China: Impact of human activities[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2008, 392(23): 252-261.

|
| [4] |
Qin H B, Zhu Z M, Liang L, et al. The bioavailability of selenium and risk assessment for human selenium poisoning in high-Se areas, China[J]. Environment International, 2013, 52: 66-74.

|
| [5] |
Wang J, Li H R, Yang L S, et al. Distribution and translocation of selenium from soil to highland barley in the Tibetan Plateau Kashin-Beck disease area[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2017, 39(1): 221-229.
|
| [6] |
王金达, 于君宝, 张学林. 黄土高原土壤中硒等元素的地球化学特征[J]. 地理科学, 2000, 20(5): 469-473.
|
| [6] |
Wang J D, Yu J B, Zhang X L. Geochemical characteristics of selenium and other elements in Loess Plateau Soil[J]. Geoscience, 2000, 20(5): 469-473.
|
| [7] |
杨忠芳, 余涛, 侯青叶, 等. 海南岛农田土壤 Se 的地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5): 837-849.
|
| [7] |
Yang Z F, Yu T, Hou Y Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in farmland of Hainan Island[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5): 837-849.
|
| [8] |
吴跃东, 向钒, 马玲, 等. 安徽石台大山地区硒的地球化学研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2017, 27(4): 53-59.
|
| [8] |
Wu Y D, Xiang F, Ma L, et al. The geochemistry study of selenium in the stone mountain area of Anhui province[J]. Journal Mineral Petrol, 2017, 27(4): 53-59.
|
| [9] |
姬丙艳, 沈骁, 姚振, 等. 青海柴达木盆地绿洲农业区硒地球化学特征——以诺木洪绿洲为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(1): 199-206.
|
| [9] |
Ji B Y, Shen X, Yao Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in the oasis agricultural area of Qaidam Basin, Qinghai Province: Exemplified by Nomhon oasis[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1): 199-206.
|
| [10] |
时章亮, 金立新, 廖超, 等. 四川雷波县重点耕地区土壤硒含量特征及其成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(5): 1253-1260.
|
| [10] |
Shi Z L, Jin L X, Liao C, et al. Content characteristics and genesis of soil selenium in important cultivated areas of Leibo County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5): 1253-1260.
|
| [11] |
韩伟, 王乔林, 宋云涛, 等. 四川省沐川县北部土壤硒地球化学特征与成因探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1): 215-222.
|
| [11] |
Han W, Wang Q L, Song Y T, et al. Geochemical characteristics and genesis of selenium in soil in northern Muchuan County,Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 215-222.
|
| [12] |
肖高强, 宗庆霞, 向龙洲, 等. 云南省盈江县旧城—姐冒地区土壤和农产品硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(2): 412-418.
|
| [12] |
Xiao G Q, Zong Q X, Xiang L Z, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils and agricultural products in the Jiucheng-Jiemao area,Yingjiang County,Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(2): 412-418.
|
| [13] |
高宇, 刘志坚. 宁夏长山头富硒区土壤硒地球化学特征研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(6): 628-633.
|
| [13] |
Gao Y, Liu Z J. Geochemical characteristics of soil selenium in selenium-rich area in Changshantou,Ningxia Province[J]. Earth and Environmen, 2017, 45(6): 628-633.
|
| [14] |
黄子龙, 林清梅, 范汝海. 广西全州县富硒土壤地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(2): 381-385.
|
| [14] |
Huang Z L, Lin Q M, Fan R H. Geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soil in Quanzhou County of Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2): 381-385.
|
| [15] |
廖启林, 崔晓丹, 黄顺生, 等. 江苏富硒土壤元素地球化学特征及主要来源[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [15] |
Liao Q L, Cui X D, Huang S S, et al. Element geochemistry of selenium-enriched soil and its main sources in Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [16] |
刘永贤, 陈锦平, 潘丽萍, 等. 浔郁平原富硒土壤成因及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤, 2018, 50(6): 1139-1144.
|
| [16] |
Liu Y X, Chen J P, Pan L P, et al. Studies on causes and influential factors of selenium-rich soil in Xunyu Plain[J]. Soils, 2018, 50(6): 1139-1144.
|
| [17] |
乔新星, 晁旭, 任蕊, 等. 陕西关中富硒土壤研究及开发利用——以三原—阎良地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 45(1): 230-238.
|
| [17] |
Qiao X X, Chao X, Ren R, et al. Research,development and utilization of selenium-rich soil of Shaanxi: A case study of Sanyuan-Yanliang area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 230-238.
|
| [18] |
文帮勇, 张涛亮, 李西周, 等. 江西龙南地区富硒土壤资源开发可行性研究[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(1):256-263.
|
| [18] |
Wen B Y, Zhang T L, Li X Z, et al. A feasibility study of selenium-rich soil development in Longnan County of Jiangxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(1): 256-263.
|
| [19] |
吴兴盛. 福建省武平县富硒土壤特征及成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3): 778-784.
|
| [19] |
Wu X S. Characteristics and genesis of selenium-rich soil in Wuping area,Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3):778-784.
|
| [20] |
宁夏回族自治区质量技术监督局. DB64/T 1220—2016宁夏富硒土壤标准[S].
|
| [20] |
The Quality and Technology Supervision Bureau of Ningxia Province. DB64/T 1220—2016 Selenium-enriched soil standards of Ningxia[S].
|
| [21] |
戴慧敏, 宫传东, 董北, 等. 东北平原土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 2015, 52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [21] |
Dai H M, Gong C D, Dong B, et al. Distribution of soil selenium in the northeast china plain and its influencing factors[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2015, 52(6):1356-1364.
|
| [22] |
杨良策, 李明龙, 杨廷安, 等. 湖北省恩施市表层土壤硒含量分布特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2015, 29(6): 825-829.
|
| [22] |
Yang L C, Li M L, Yang T A, et al. Study on distribution characteristics of selenium content of surface soil and its influencing factors in Enshi City,Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment &Engineering, 2015, 29(6): 825-829.
|
| [23] |
迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等. 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274.
|
| [23] |
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution of selenium and its influencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5): 1262-1274.
|
| [24] |
廖启林, 任静华, 许伟伟, 等. 江苏宜溧富硒稻米产区地质地球化学背景[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(5):1791-1802.
|
| [24] |
Liao Q L, Ren J H, Xu W W, et al. Geological and geochemical background of Se-rich rice production in Yili area, Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43 (5):1791-1802.
|
| [25] |
吴俊. 福建省寿宁县土壤硒分布特征及影响因素[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6): 1167-1176.
|
| [25] |
Wu J. The distribution of soil selenium in Shouning County of Fujian Province and its influencing factors[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6): 1167-1176.
|
| [26] |
余飞, 张风雷, 张永文, 等. 重庆典型农业区土壤硒地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(4): 830-838.
|
| [26] |
Yu F, Zhang F L, Zhang Y W, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influential factors of soil selenium in typical agricultural area,Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4): 830-838.
|
| [27] |
周墨, 陈国光, 张明, 等. 赣南地区土壤硒元素地球化学特征及其影响因素研究: 以青塘—梅窖地区为例[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1301.
|
| [27] |
Zhou M, Chen G G, Zhang M, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of selenium in soils of south Jiangxi province: A typical area of Qingtang-Meijiao[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(6): 1292-1301.
|
| [28] |
牛雪, 何锦, 庞雅婕, 等. 三江平原西部土壤硒分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45 (1): 223-229.
|
| [28] |
Nin X, He J, Pang Y J, et al. Distribution feature of soil selenium in west Sanjiang plain and its influencing factors[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 223-229.
|
| [29] |
王志强, 杨建锋, 魏丽馨, 等. 石嘴山地区碱性土壤硒地球化学特征及生物有效性[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(1):229-237.
|
| [29] |
Wang Z Q, Yang J F, Wei L X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and bioavailability of selenium in alkaline soil of Shizuishan area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 229-237.
|
| [30] |
成晓梦, 马荣荣, 彭敏, 等. 中国大宗农作物及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤标准建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6): 1367-1372.
|
| [30] |
Cheng X M, Ma R R, Peng M, et al. Characteristics of selenium in crops and roots in China and recommendations for selenium-enriched soil standards[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1367-1372.
|
| [31] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海东部碱性土壤中硒的形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43 (5): 1138-1144.
|
| [31] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of Se speciation of alkaline soil in eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5): 1138-1144.
|
| [32] |
Deng X F, Liu K Z, Li M F, et al. Difference of selenium uptake and distribution in the plant and selenium form in the grains of rice with foliar spray of selenite or selenate at different stages[J]. Field Crop Research, 2017, 211:165-171.

|
| [33] |
商靖敏, 罗维, 吴光红, 等. 洋河流域不同土地利用类型土壤硒(Se)分布及影响因素[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(1): 301-308.
|
| [33] |
Shang J M, Luo W, Wu G H, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of soil selenium (Se)in different land use types in the Yanghe River Basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2015, 36 (1):301-308.
|
| [34] |
陈锦平, 刘永贤, 曾成城, 等. 降雨对土壤硒迁移转化的影响研究进展[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(6): 1909-1915.
|
| [34] |
Chen J P, Liu Y X, Zeng C C, et al. Research advances in the effects of rainfall on soil selenium migration and transformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(6): 1909-1915.
|
| [35] |
田义超, 黄远林, 张强, 等. 北部湾钦江流域土壤侵蚀及其硒元素流失评估[J]. 中国环境科学, 2019, 39(1):257-273.
|
| [35] |
Tian Y C, Huang Y L, Zhang Q, et al. Soil erosion and selenium loss in Qinjiang River Basin in Beibu Gulf coastal zone[J]. China Environmental Science, 2019, 39(1): 257-273.
|
| [36] |
张栋, 张妮, 侯振安, 等. 石灰性土壤硒含量与小麦籽粒硒相关性研究[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2016, 34(5): 152-157.
|
| [36] |
Zhang D, Zhang N, Hou Z A, et al. Study on correlation between selenium content in calcareous soil and selenium in wheat[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2016, 34 (5): 152-157.
|
| [1] |
HU Xin-Jun, CHEN Xiao-Jing, WU Yang, BAI Ya-Dong, ZHAO Fu-Yuan. An analysis of the fault framework in southern Ningxia based on geophysical data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 916-925. |
| [2] |
ZHANG Ya-Feng, JI Bing-Yan, SHEN Xiao, YAO Zhen, MA Qiang, WANG Shuai, HE Lian-Zhen, HAN Wei-Ming. Formation mechanisms and significance of saline-lacustrine Se-rich soils in the Xining Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 470-476. |
|
|
|
|

