|
|
|
| Audiomagnetotelluric data: Influence of terrain and the inversion considering terrain |
CHENG Zheng-Pu( ), GUO Shu-Jun( ), GUO Shu-Jun( ), WEI Qiang, ZHOU Le, LEI Ming, LI Shu ), WEI Qiang, ZHOU Le, LEI Ming, LI Shu |
| Center for Hydrogeology and Environmental Geology Survey, China Geological Survey, Baoding 071000, China |
|
|
|
|
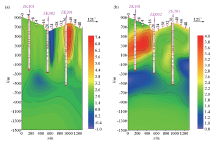
Abstract This study designed a group of 2D peak-valley comprehensive terrain models with different widths and slopes and investigated the influence of differently undulating terrains in mountainous areas on the audiomagnetotelluric (AMT) data and corresponding distortion characteristics from seven aspects, namely polarization modes, frequency, positions of measurement points, the width of a mountain top, the elevation difference and slope of terrain, and phase curves. The results are as follows. The transverse magnetic mode (TM mode) is more susceptible to terrain than the transverse electric mode (TE mode). The undulating terrain has little influence on the high-frequency parts of AMT data but has a great influence on their low-frequency parts. The apparent resistivity and phase of different frequency points at a measurement point reflect the comprehensive influence of all terrains within the skin depth level rather than just the influence of a single mountain peak or valley near the measurement point. Measurement points located at the mountain peaks are more easily affected by terrains than those in the valleys. Moreover, narrower mountain tops correspond to greater elevation differences of terrain, and steeper terrain exerts greater influence. In addition, the comparison of the 2D_TE results of the inversion considering and not considering terrains show that the 2D inversion considering terrains can effectively eliminate the influence of terrain. The 2D inversion considering terrains was carried out for measured AMT data. As indicated by the inversion results, the 2D inversion considering terrains can effectively eliminate the false high and low resistance anomalies and relieve the "hanging surface" phenomenon of signals, and the results corresponded well with the horizons with encountered manganese of three boreholes.
|
|
Received: 26 January 2022
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
GUO Shu-Jun
E-mail: czp1990@126.com;279464376@qq.com
|
|
|
|
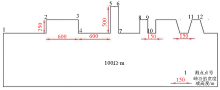
|
Schematic diagram of peak valley terrain model A
|

| 序号 | 频率/Hz | 序号 | 频率/Hz | 序号 | 频率/Hz | | 1 | 9135.5500 | 19 | 288.8914 | 37 | 9.1356 | | 2 | 7540.5210 | 20 | 238.4522 | 38 | 7.5405 | | 3 | 6223.9780 | 21 | 196.8195 | 39 | 6.224 | | 4 | 5137.2970 | 22 | 162.4556 | 40 | 5.1373 | | 5 | 4240.3470 | 23 | 134.0915 | 41 | 4.2403 | | 6 | 3500.0000 | 24 | 110.6797 | 42 | 3.5000 | | 7 | 2888.9150 | 25 | 91.3555 | 43 | 2.8889 | | 8 | 2384.5220 | 26 | 75.4052 | 44 | 2.3845 | | 9 | 1968.1950 | 27 | 62.2398 | 45 | 1.9682 | | 10 | 1624.5560 | 28 | 51.3730 | 46 | 1.6246 | | 11 | 1340.9150 | 29 | 42.4035 | 47 | 1.3409 | | 12 | 1106.7970 | 30 | 35.0000 | 48 | 1.1068 | | 13 | 913.5550 | 31 | 28.8891 | 49 | 0.9136 | | 14 | 754.0521 | 32 | 23.8452 | 50 | 0.7541 | | 15 | 622.3978 | 33 | 19.6820 | 51 | 0.6224 | | 16 | 513.7297 | 34 | 16.2456 | 52 | 0.5137 | | 17 | 424.0347 | 35 | 13.4092 | 53 | 0.4240 | | 18 | 350.0000 | 36 | 11.0680 | 54 | 0.3500 |
|
The forward sampling frequency by Model A
|
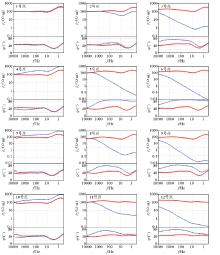
|
The forward apparent resistivity and phase curves of TE and TM by model A(red circle is TE curve, blue triangle is TM curve)
|
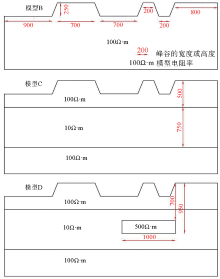
|
Schematic diagram of peak valley terrain model with gradual edge change
|
|
2D_TE inversion apparent resistivity profile of model B, C and D
a—2D_TE inversion apparent resistivity profile by without terrain of model B; b—2D_TE inversion apparent resistivity profile by without terrain of model C; c—2D_TE inversion apparent resistivity profile by without terrain of model D; d—2D_TE inversion apparent resistivity profile by with terrain of model B; e—2D_TE inversion apparent resistivity profile by with terrain of model C; f—2D_TE inversion apparent resistivity profile by with terrain of model D
|
|
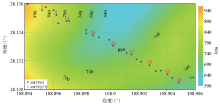
Actual AMT survey line deployment
|

| 岩性名称 | 地层代号 | 样点数(点) | 电阻率平均值/(Ω·m) | 极化率平均值/% | | 粘土 | Q | 28 | 115.42 | 2.05 | | 白云岩 | ∈2+3ls、∈1q | 52 | 2508.71 | 1.79 | | 灰岩 | ∈1q | 38 | 4579.28 | 1.86 | | 砂岩、粉砂岩 | ∈1p、∈1b、Qbq | 40 | 1614.33 | 1.93 | | 粉砂质页岩 | Nh1d1 | 35 | 551.35 | 2.38 | | 碳质页岩 | Nh1d1 | 33 | 24.24 | 22.05 | | 冰碛砾岩 | Nh2n | 37 | 1500.73 | 2.93 | | 板岩 | Qbbh | 41 | 1707.68 | 2.53 | | 硅质岩 | Z1l | 40 | 4050.97 | 1.77 | | 含砾砂岩、含砾粉砂岩 | Nh2n、Nh1t | 35 | 1732.58 | 2.17 | | 粉砂质粘土岩、页岩 | Nh1d2 | 61 | 983.86 | 3.12 | | 块状锰矿石 | Nh1d1 | 31 | 22.66 | 10.42 | | 变余砂岩 | Qbbh | 26 | 1748.09 | 2.40 |
|
Statistics of physical properties of rocks and ores in the exploration area
|
|
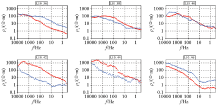
Apparent resistivity curve of measuring points on the peak of measured AMT profile(red circle is TE curve, blue triangle is TM curve)
|
|
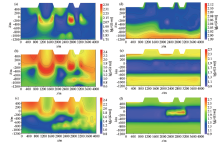
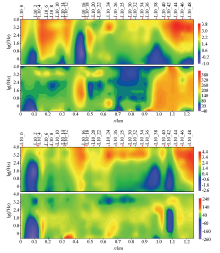
Apparent resistivity and phase pseudo section of measured AMT profile (upper: TE mode; down: TM mode)
|
|
2D_TEinversion results of AMT line in a mountainous area of manganese ore without terrain(a) and with terrain(b)
|
| [1] |
Wannamaker P E, Stodt J A, Rijo L. Two dimensional topographic responses in magnetotellurics modeled using finite-elements[J]. Geophysics, 1986, 51(11):2131-2144.

|
| [2] |
Redding R P, Jiracek G R. Topographic modeling and correction in magnetotelluric,Technical program and biographies[C]// 54th Annual International Meeting, 1984:44-47.
|
| [3] |
Andrieux P, Wightman W. The so-called static corrections in magnetotelluric measurements, technical program and biographies[C]// 54th Annual international Meeting, 1984:43.
|
| [4] |
Chouteau M, Bouchard K. Two-dimensional terrain correction in magnetotelluric survey[J]. Geophysics, 1988, 53(6):854-862.

|
| [5] |
Baranwal V C, Franke A, Borner R U. Unstructured grid based 2D inversion of plan wave EM data for models including topography[J]. Proceedings of IAGAWG1.2 on Electromagnetic Induction in the Earth, 2006, S3(12):1-5.
|
| [6] |
Myung J N, Hee J K, Yoonho S. 3D magnetotelluric modeling including surface topography[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2007, 55(2):277-287.

|
| [7] |
徐世浙, 赵生凯. 地形对大地电磁勘探的影响[J]. 西北地震学报, 1985, 7(4):69-78.
|
| [7] |
Xu S Z, Zhao S K. The topographic effects on magnetotelluric response[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1985, 7(4):69-78.
|
| [8] |
徐世浙, 李予国, 刘斌. 大地电磁Hx型波二维地形改正的方法与效果[J]. 地球物理学报, 1997, 40(6):842-846.
|
| [8] |
Xu S Z, Li Y G, Liu B. Method and effect of two-dimensional terrain correction of magnetotelluric Hx wave[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1997, 40(6):842-846.
|
| [9] |
陈小斌. MT 二维正演计算中地形影响的研究[J]. 石油物探, 2000, 39(3):112-120.
|
| [9] |
Chen X B. On the research of the influence of terrain to MT 2D forward computation[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2000, 39(3):112-120.
|
| [10] |
赵广茂, 李桐林, 王大勇, 等. 基于二次场二维起伏地形 MT 有限元数值模拟[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2008, 35(6):1055-1059.
|
| [10] |
Zhao G M, Li T L, Wang D Y, et al. Secondary field-based two-dimensional topographic numerical simulation in magnetoteillurics by finite element method[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth ScienceEdition, 2008, 35(6):1055-1059.
|
| [11] |
刘晓甲, 汤井田, 王琪琪. 大地电磁法的地形效应[J]. 中国科技信息, 2019, 603(8):90-93.
|
| [11] |
Liu X J, Tang J T, Wang Q Q. Topographic effect of magnetotelluric method[J]. China Science and Technology Information, 2019, 603(8):90-93.
|
| [12] |
孙鸿雁. 可控源音频大地电磁法地形影响及校正方法的对比研究与应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2005.
|
| [12] |
Sun H Y. Topographic effect in CSAMT & compare of terrain correction methods[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2005.
|
| [13] |
周茜茜. 大地电磁正演数值模拟及反演效果对比分析[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019.
|
| [13] |
Zhou Q Q. Comparative analysis of forward numerical simulation and inversion effect of magnetotelluric[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2019.
|
| [14] |
晋光文, 赵国泽, 徐常芳, 等. 二维倾斜地形对大地电磁资料的影响与地形校正[J]. 地震地质, 1998, 20(4):454-458.
|
| [14] |
Jin G W, Zhao G Z, Xu C F, et al. The affection and correction on magnetotelluric response data for inclination two dimension terrain[J]. Seismology and Geology, 1998, 20(4):454-458.
|
| [15] |
王绪本, 李永年, 高永才. 大地电磁测深二维地形影响及其校正方法研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 1999, 21(4):327-332.
|
| [15] |
Wang X B, Li Y N, Gao Y C. Two dimensional topographic responses in magneto-telluric sounding and its correction methods[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 21(4):327-332.
|
| [16] |
张翔, 胡文宝, 严良俊, 等. 大地电磁测深中的地形影响与校正[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1999, 21(1):37-41.
|
| [16] |
Zhang X, Hu W B, Yan L J, et al. Effects and correction of topography in magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 1999, 21(1):37-41.
|
| [17] |
张翔, 胡文宝. 带地形的大地电磁测深联合二维反演[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1999, 34(2):190-196.
|
| [17] |
Zhang X, Hu W B. Joint 2D inversion of magnetotelluric sounding data having landform effect[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1999, 34(2):190-196.
|
| [18] |
吴頔, 辛慧翠, 卜传新. 附加列插值法在起伏地形条件下二维大地电磁正演中的研究与应用[J]. 承德石油高等专科学校学报, 2019, 21(6):35-40.
|
| [18] |
Wu D, Xin H C, Pu C X. Research and application of improved interpolation method in MT 2D forward computation with terrain[J]. Journal of Chengde Petroleum College, 2019, 21(6):35-40.
|
| [19] |
顾观文, 李桐林. 基于矢量有限元的带地形大地电磁三维反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2020, 63(6):337-353.
|
| [19] |
Gu G W, Li T L. Three-dimensional magnetotelluric inversion with surface topography based on the vector finite element method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(6):337-353.
|
| [20] |
胡祖志, 何展翔, 孙卫斌, 等. 一种改进的大地电磁地形校正方法及相关问题探讨[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2008, 43(3):343-348.
|
| [20] |
Hu Z Z, He Z X, Sun W B, et al. An improved MT topographic correction method and discussion on relative issues[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2008, 43(3):343-348.
|
| [21] |
冈崎金雄, 吉村, 雄三郎, 等. 大地电磁法中有关地形影响的研究[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 1987(1):80-90.
|
| [21] |
Gang Q J X, Ji C, Xiong S L, et al. Study on topographic influence in magnetotelluric method[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 1987(1):80-90.
|
| [22] |
王绪本, 周军, 李海蓉, 等. 二维大地电磁静位移估算及其在隧道勘探中的应用[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2014, 31(8):20-26.
|
| [22] |
Wang X B, Zhou J, Li H R, et al. The estimation of two dimensional magnetotelluric static shift and its application in the tunnel exploration[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2014, 31(8):20-26.
|
| [23] |
孙鸿雁, 李金铭, 林天亮. 地形影响校正反演方法对比[C]// 中国地质学会勘探地球物理学术交流会,中国地质学会, 2006.
|
| [23] |
Sun H Y, Li J M, Lin T L. Comparison of topographic influence correction and inversion methods[C]// Symposium on Exploration Geophysics of China Geological Society,Geological Society of China, 2006.
|
| [24] |
王佳龙, 张宝松, 陈基炜, 等. 大地电磁测深不同反演方法的应用效果对比——以安徽皖江地区页岩气调查为例[J]. 华东地质, 2020, 41(1):79-87.
|
| [24] |
Wang J L, Zhang B S, Chen J W, et al. Comparison of application effect of magnetotelluric sounding using different inversion methods in shale gas investigation in Wanjiang area of Anhui Province[J]. East China Geology, 2020, 41(1):79-87.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Bao-Feng, WANG Qi-Nian, GUO Xin, GUAN Da-Wei, CHEN Tong-Gang, FANG Wen. Gravity survey and audio magnetotellurics-based insights into the deep structures and geothermal resource potential of the Rucheng Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1147-1156. |
| [2] |
XUE Dong-Xu, LIU Cheng, GUO Fa, WANG Jun, XU Duo-Xun, YANG Sheng-Fei, ZHANG Pei. Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1169-1178. |
|
|
|
|

