|
|
|
| Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method |
XUE Dong-Xu1( ), LIU Cheng1( ), LIU Cheng1( ), GUO Fa1, WANG Jun2, XU Duo-Xun1, YANG Sheng-Fei1, ZHANG Pei1 ), GUO Fa1, WANG Jun2, XU Duo-Xun1, YANG Sheng-Fei1, ZHANG Pei1 |
1. Xi’an Center of Mineral Resources Survey, China Geological Survey, Xi’an 710100, China
2. School of Geophysics and Information Technology, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Despite abundant geothermal reserves of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, long-term exploitation has decreased the water temperatures and yields of its existing geothermal wells year by year. Hence, there is an urgent need to explore new potential geothermal resources in the geothermal field. Since the known geothermal wells in the geothermal field are significantly controlled by faults, investigating the deep fault propagation holds critical significance for exploring the geothermal field’s potential geothermal resources. Due to the method limitations and the topographic influence, identifying thermal control faults through conventional geological route investigation or large-scale engineering is not applicable to the geothermal field. Therefore, a new technical method combining the penetrating soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric (CSAMT) method was employed in this study to find concealed faults and delineate potential geothermal areas. Based on the measured surface soil radon concentration anomaly data and the subsurface electrical structure model derived from the CSAMT data inversion, this study inferred six new concealed faults on the basis of corroborating the known faults, predicted two potential geothermal areas, and built a conceptual model for the Tangyu geothermal field. As revealed by the results, the soil radon concentrations at concealed faults are much higher than the regional background value, and the concealed faults are located in the low-resistivity fracture zones as indicated by the apparent resistivity results based on CSAMT data inversion. Besides, the two potential geothermal areas spread from 450~750 m and 850~1 150 m on the profile, respectively, at depths of approximately 250~300 m. This study concludes that the geothermal field resides in a low-resistivity region with soil radon anomalies three times the regional background value. The results of this study provide a reference for the subsequent sustainable production and utilization of potential geothermal resources in the region.
|
|
Received: 03 January 2023
Published: 27 October 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
LIU Cheng
E-mail: 18645810303@163.com;liuchenghj@163.com
|
|
|
|
3,20] )
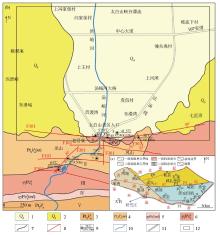
1—the Quaternary Holocene; 2—the upper Pleistocene of the Quaternary system; 3—plagioclase amphibolite gneiss; 4—mixed lithic gneiss; 5—ylonitic granite; 6—gneiss granite; 7—stratigraphic boundary; 8—fracture structure; 9—geothermal wells; 10—river system; 11—road; 12—research area
">
|
Geotectonic location map of the study area (a) and geological sketch (b) (modified from literature [3,20] )
1—the Quaternary Holocene; 2—the upper Pleistocene of the Quaternary system; 3—plagioclase amphibolite gneiss; 4—mixed lithic gneiss; 5—ylonitic granite; 6—gneiss granite; 7—stratigraphic boundary; 8—fracture structure; 9—geothermal wells; 10—river system; 11—road; 12—research area
|

| 采样点编号 | 采样位置 | 井深/m | 空气氡浓度/
(Bq·m-3) | 水中氡含量/
(Bq·L-1) | 238U含量
(μg·L-1) | 226Ra含量/
(Bq·L-1) | | 1号井 | 太白山国家森林公园 | 300 | 20.85 | 18.5 | 7.58 | 0.100 | | 2号井 | 眉县汤峪疗养院 | 400.18 | 22.15 | 12.4 | 57.70 | 0.074 | | 6号井 | 太白山青园山庄温泉 | 400 | 19.95 | 30.2 | 0.47 | 0.027 | | 7号井 | 眉县汤峪温泉 | 350 | 59.45 | 19.4 | 3.15 | 0.054 | | 1 | 居民家自来水 | | 9.82 | 2.7 | | | | 2 | 居民家自来水 | | 8.05 | 2.4 | | |
|
Detection result of radioactivity index of Tangyu geothermal hot spring in Mei County
|

| 类别 | 岩石名称 | 标本数量 | η/% | ρs/(Ω·m) | | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | | 沉积岩 | 砂岩 | 14 | 3.01 | 0.44 | 1.93 | 31191 | 1872 | 9136 | | 断层角砾岩 | 9 | 5.76 | 1.61 | 3.23 | 80973 | 831 | 25433 | | 变质岩 | 斜长角闪岩 | 11 | 3.16 | 1.23 | 1.94 | 39914 | 1802 | 13352 | | 大理岩 | 5 | 2.94 | 0.88 | 1.97 | 90850 | 5803 | 33743 | | 片麻岩 | 246 | 6.17 | 0.94 | 2.40 | 37474 | 587 | 5448 | | 侵入岩 | 花岗岩 | 45 | 7.92 | 0.26 | 3.27 | 26149 | 863 | 6043 |
|
Statistics of stratum physical characteristics in the study area[32]
|
|
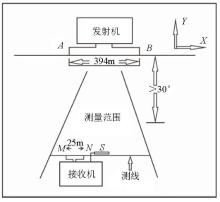
Planar diagram of scalar CSAMT measuring device
|
|
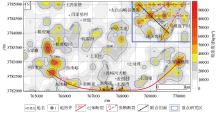
Plan view of soil radon concentration in the study area
|
|
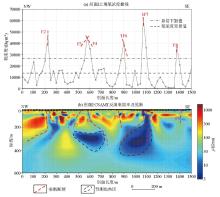
Joint profile comprehensive Ⅰ interpretation inference map
|
|
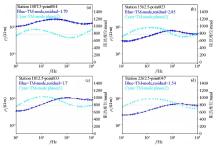
Apparent resistivity and impedance phase curves of typical measuring points
|
|
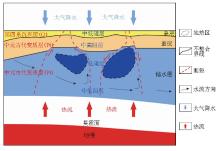
Conceptual model of Tangyu geothermal field in Mei County
|
| [1] |
王贵玲, 刘彦广, 朱喜, 等. 中国地热资源现状及发展趋势[J]. 地学前缘, 2020, 27(1):1-9.
|
| [1] |
Wang G L, Liu Y G, Zhu X, et al. The status and development trend of geothermal resources in China[J]. Earth Science Froniters, 2020, 27(1):1-9.
|
| [2] |
王贵玲, 张薇, 梁继运, 等. 中国地热资源潜力评价[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4):449-459.
|
| [2] |
Wang G L, Zhang W, Liang J Y, et al. Evaluation of geothermal resources potential in China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4):449-459.
|
| [3] |
张鹏, 端木合顺, 端木辉, 等. 陕西省眉县汤峪地热田地质特征与成因分析[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2014, 37(1):27-33.
|
| [3] |
Zhang P, Duanmu H S, Duanmu H, et al. Geological characteristics and cause analysis for Tangyu geothermal field in Mei Country,Shaanxi Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2014, 37(1):27-33.
|
| [4] |
马岩, 张保建, 闫金凯, 等. 雄安新区深部储热构造探测研究与地热井优选技术[J]. 地球学报, 2022, 43(5):699-710.
|
| [4] |
Ma Y, Zhang B J, Yan J K, et al. Deep geothermal reservoir structure detection and geothermal well optimization technology in Xiongan new area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2022, 43(5):699-710.
|
| [5] |
Jiang G Z, Hu S B, Shi Y Z, et al. Terrestrial heat flow of continental China:Updated dataset and tectonic implications[J]. Tectonophysics, 2019, 753:36-48.

|
| [6] |
邓亚仁, 任战利, 任文波. 关中地区地热分布控制因素与地热开发前景[J]. 西部大开发:土地开发工程研究, 2017, 2(11):19-27.
|
| [6] |
Deng Y R, Ren Z L, Ren W B. Geothermal distribution control factors and geothermal prospect in Guanzhong region[J]. Western Development:Land Development Project Research, 2017, 2(11):19-27.
|
| [7] |
张健, 董淼, 王蓓羽, 等. 陕西关中盆地地热资源及壳幔温度结构的地球物理分析[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2021, 43(1):150-163.
|
| [7] |
Zhang J, Dong M, Wang B Y, et al. Geophysical analysis of geothermal resources and temperature structure of crust and upper mantle beneath Guanzhong basin of Shaanxi,China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2021, 43(1):150-163.
|
| [8] |
洪增林, 张银龙, 周阳. 关中盆地南部山前中深层地热资源赋存特征及应用[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(5):1224-1235.
|
| [8] |
Hong Z L, Zhang Y L, Zhou Y. Research on the modes of occurrence and application of geothermal resources in the middle and deep layers of the piedmont area in Southern Guanzhong basin[J], Geology in China, 2019, 46(5):1224-1235.
|
| [9] |
张胜, 刘晓华, 李文超. 关中地区地热分布控制因素与地热开发前景[J]. 资源节约与环保, 2019(10):116.
|
| [9] |
Zhang S, Liu X H, Li W C. Geothermal distribution control factors and geothermal development prospects in Guanzhong region[J]. Resource Conservation and Environmental Protecion, 2019(10):116.
|
| [10] |
李兆雨, 李永项, 李文厚, 等. 汾渭盆地古近系—新近系沉积特征[J]. 地质科学, 2021, 56(4):1120-1133.
|
| [10] |
Li Z Y, Li Y X, Li W H, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of Paleogene-Neogene in Fenwei basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2021, 56(4):1120-1133.
|
| [11] |
李富, 周洪福, 唐文清, 等. 物化探方法在隐伏活动断裂探测中综合研究——以安宁河秧财沟断裂为例[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(3):1199-1205.
|
| [11] |
Li F, Zhou H F, Tang W Q, et al. Comprehensive study of geophysical and geochemical methods in detecting buried active faults:Taking the Yangcaigou fault in Anning river as an example[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(3):1199-1205.
|
| [12] |
张晓亮, 白凌燕, 倪敬波, 等. 北京平原区隐伏断裂与氡浓度响应关系[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(2):344-351.
|
| [12] |
Zhang X L, Bai L Y, Ni J B, et al. Relationship between concealed faults and radon concentration in plain areas of Beijing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2):344-351.
|
| [13] |
陈松, 庞凯旋, 陈长敬, 等. 基于音频大地电磁测深和高密度电法的城市隐伏断裂联合探测[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2020, 17(4):470-477.
|
| [13] |
Chen S, Pang K X, Chen C J, et al. Joint detection of urban buried faults with audio magnetotelluric sounding and high density resistivity method[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2020, 17(4):470-477.
|
| [14] |
朱怀亮, 胥博文, 刘志龙, 等. 大地电磁测深法在银川盆地地热资源调查评价中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(4):718-725.
|
| [14] |
Zhu H L, Xu B W, Liu Z L, et al. The application of magnetotelluric sounding to geothermal resources assessment in Yinchuan basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(4):718-725.
|
| [15] |
吴奇, 许立青, 李三忠, 等. 华北地块中部活动构造特征及汾渭地堑成因探讨[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(4):104-114.
|
| [15] |
Wu Q, Xu L Q, Li S Z, et al. Active tectonics in the Central North China block and the cause of the formation of the Fenwei graben[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(4):104-114.
|
| [16] |
李承东, 赵利刚, 许雅雯, 等. 北秦岭宽坪岩群变质沉积岩年代学及地质意义[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(5):992-1010.
|
| [16] |
Li C D, Zhao L G, Xu Y W, et al. Chronology of metasedimentary rocks from Kuanping group complex in North Qinling belt and its geological significance[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(5):992-1010.
|
| [17] |
闫全人, 王宗起, 陈隽璐, 等. 北秦岭斜峪关群和草滩沟群火山岩成因的地球化学和同位素约束、SHRIMP年代及其意义[J]. 地质学报, 2007, 81(4):488-500,583-584.
|
| [17] |
Yan Q R, Wang Z Q, Chen X L, et al. Tectonic setting and SHRIMP age of volcanic rocks in the Xieyuguan and Caotangou groups:Implications for the north Qinling orogenic belt[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2007, 81(4):488-500,583-584.

|
| [18] |
王海杰, 陈丹玲, 任云飞, 等. 北秦岭构造带与华北板块关系探讨:来自宽坪杂岩变碎屑岩锆石U-Pb年代学与变质作用证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(5):1489-1514.
|
| [18] |
Wang H J, Chen D L, Ren Y F, et al. The relationship between the North Qinlin Belt and the North China Craton:Constrains from zircon U-Pb geochronology and metamorphism of metaclastic rocks from the Kuanping Complex[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(5):1489-1514.

|
| [19] |
李晓, 秦江锋, 周旭晨, 等. 秦岭群混合岩中花岗质脉体成因及锆石结晶机理[J]. 西安科技大学学报, 2022, 42(4):733-741.
|
| [19] |
Li X, Qin J F, Zhou X C, et al. Petrogenesis of the leucogranite veins and zircon crystallization process in the Qinling magmatic complex[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Science and Technology, 2022, 42(4):733-741.
|
| [20] |
尚海敏, 于进庆, 王文科, 等. 关中盆地秦岭山前地下热水的循环机理[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2015, 42(4):150-155,170.
|
| [20] |
Shang H M, Yu J Q, Wang W K, et al. Circulating mechanism of geothermal fluids in the submountain region of the Southern Guanzhong basin[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(4):150-155,170.
|
| [21] |
周阳, 洪增林, 张卉, 等. 关中盆地浅层地热能赋存规律及资源量估算[J]. 中国地质调查, 2020, 7(2):21-29.
|
| [21] |
Zhou Y, Hong Z L, Zhang H, et al. Occurrence rules and resource estimation of shallow geothermal energy in Guanzhong basin[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2020, 7(2):21-29.
|
| [22] |
校培喜, 张俊雅, 王洪亮, 等. 北秦岭太白岩体岩石谱系单位划分及侵位时代确定[J]. 西北地质科学, 2000, 21(2):37-45.
|
| [22] |
Xiao P X, Zang J Y, Wang H L, et al. Subdivision of rock series units and determination of intrusion age of Taibai rock mass in North Qinling[J]. Northwest Geoscience, 2000, 21(2):37-45.
|
| [23] |
王敬宇. 北秦岭宽坪群浅变质沉积岩沉积时代、物质源区和构造背景[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.
|
| [23] |
Wang J Y. Depositional age, Provenance and tectonic setting of the Kuanping group in the North Qinling orogenic belt, China[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2019.
|
| [24] |
张志华, 赖绍聪, 秦江锋. 北秦岭太白山晚中生代正长花岗岩成因及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2014, 30(11):3242-3254.
|
| [24] |
Zhang Z H, Lai S C, Qin J F. Petrogenesis and its geological significance of the Late Mesozoic syengranite from the Taibai mountain,North Qinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2014, 30(11):3242-3254.
|
| [25] |
侯建军, 韩慕康, 张保增, 等. 秦岭北麓断裂带晚第四纪活动的地貌表现[J]. 地理学报, 1995, 50(2):138-146.
|
| [25] |
Hou J J, Han M K, Zhang B Z, et al. Geomorphic expressions of the activity alone North Qinling piedmont fault zone in the Late Quaternary Period[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1995, 50(2):138-146.
|
| [26] |
王泽龙. 北京市小汤山地区地温场特征及地下热水成因模式分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2007.
|
| [26] |
Wang Z L. Characteristics of the geothermal field and formation of the thermal groudwater in the Xiaotangshan area of Beijing[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2007.
|
| [27] |
柯柏林. 北京市平原区北部孙河断裂的地热地质特征[J]. 现代地质, 2009, 23(1):43-48.
|
| [27] |
Ke B L. Geothermal and geological features of Sunhe fault in the Northern part of Beijing plain[J]. Geoscience, 2009, 23(1):43-48.
|
| [28] |
毛翔, 汪新伟, 郭世炎, 等. 高阳地热田及邻区地热资源形成机制[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(2):273-280.
|
| [28] |
Mao X, Wang X W, Guo S Y, et al. Genetic mechanism of geothermal resources in the Gaoyang geothermal field and adjacent areas[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(2):273-280.
|
| [29] |
黄理善, 侯一俊, 陈远荣, 等. 基于物探-化探技术快速精确定位评价城市及周边隐伏断层——以广西桂林市临桂区为例[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(3):929-942.
|
| [29] |
Huang L S, Hou Y J, Chen Y R, et al. Rapid and accurate positioning concealed fault using geophysical and geochemical techniques in cities and surrounding areas—A case study of Lingui district,Guilin City,Guangxi[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(3):929-942.
|
| [30] |
张志勇, 王强. 新沂土壤中氡浓度的放射性调查研究[J]. 能源技术与管理, 2014, 39(2):186-188.
|
| [30] |
Zhang Z Y, Wang Q. Radiological investigation study of radon concentration in Xinyi soil[J]. Energy Technology and Management, 2014, 39(2):186-188.
|
| [31] |
马永, 高冰莹, 金大利, 等. 宝坻断裂土壤氡气观测技术与应用[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 2019, 39(7):756-759.
|
| [31] |
Ma Y, Gao B Y, Jin D L, et al. Technique and application of soil radon observation in the Baodi fault[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 2019, 39(7):756-759.
|
| [32] |
刘亮, 梁斌, 燕中林, 等. 龙泉山断裂带隐伏断层氡气特征及其活动性分析[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2019, 39(2):45-53.
|
| [32] |
Liu L, Liang B, Yan Z L, et al. Soil gas radon and fault activity in the Longquanshan fault zone,Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2019, 39(2):45-53.
|
| [33] |
Chen J, Ford K L. A study on the correlation between soil radon potential and average indoor radon potential in Canadian cities[J]. Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2017, 166(1):152-156.

|
| [34] |
程业勋. 环境中氡及其子体的危害与控制[J]. 现代地质, 2008, 22(5):857-868.
|
| [34] |
Cheng Y X. Hazard and control measures of radon and its progenies in the environment[J]. Geoscience, 2008, 22(5):857-868.
|
| [35] |
张利明, 凌丹丹. 激电测量在秦岭山前构造研究中的应用[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2019, 31(1):160-165.
|
| [35] |
Zhang L M, Ling D D. Application of excitation measurements in the study of mountain front tectonics in the Qinling mountains[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2019, 31(1):160-165.
|
| [36] |
孙中任, 杨殿臣, 赵雪娟. 综合物探方法寻找深部地下水[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(1):52-57.
|
| [36] |
Sun Z R, Yang D C, Zhao X J. The application of integrated geophysical methods to the prospecting for deep geothermal resource[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(1):52-57.
|
| [37] |
孙海川, 刘永亮, 邵程龙. 综合物探在海石湾地区地热勘查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(2):290-297.
|
| [37] |
Sun H C, Liu Y L, Shao C L. The application of integrated geophysical exploration to geothermal exploration in Haishiwan area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(2):290-297.
|
| [38] |
Miklyaev P S, Petrova T B. Study of abnormal seasonal variations in the radon exhalation rate in a fault zone[J]. Geochemistry International, 2021, 59(4):435-447.
|
| [39] |
李杰彪, 周志超, 云龙, 等. 基于土壤氡气测量识别甘肃北山南缘隐伏断裂[J]. 地质学报, 2022, 96(6):2240-2250.
|
| [39] |
Li J B, Zhou Z C, Yun L, et al. Indentification of hadden faults based on soil radon measurement in the southern margin of the Beishan area,Gansu Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2022, 96(6):2240-2250.
|
| [40] |
Teuku A S. Identification of Lembang fault,West-Java Indonesia by using controlled source audio-magnetotelluric (CSAMT)[J]. Aip Conference Proceedings, 2017, 1861(1):030002.
|
| [41] |
Hou, D Y, Xue G Q, Zhou N N, et al. Comparison between different apparent resistivity definitions of CSAMT[J]. Journal of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 2019, 24(1):119-127.
|
| [42] |
任小庆, 余鸿, 罗娜宁, 等. CSAMT法在福建省惠安地热勘查中的应用[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2):515-523.
|
| [42] |
Ren X Q, Yu H, Luo N N, et al. Application of CSAMT in geothermal exploration in Hui’an,Fujian Province[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(2):515-523.
|
| [43] |
任文波. 渭河盆地中深层地热资源特征及开发利用[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2019.
|
| [43] |
Ren W B. Characteristics and development of geothermal resources in the middle and deep layers of the Weihe basin[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2019.
|
| [44] |
穆根胥, 李锋, 闫文中, 等. 关中盆地地热资源赋存规律及开发利用关键技术[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.
|
| [44] |
Mu G X, Li F, Yan W Z, et al. Geothermal resource fugacity law and key technology for development and utilization in the Guanzhong basin[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016.
|
| [45] |
孙红丽. 关中盆地地热资源赋存特征及成因模式研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
|
| [45] |
Sun H L. The bearing features and genetic model for geothermal resources in Guanzhong basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2015.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Bao-Feng, WANG Qi-Nian, GUO Xin, GUAN Da-Wei, CHEN Tong-Gang, FANG Wen. Gravity survey and audio magnetotellurics-based insights into the deep structures and geothermal resource potential of the Rucheng Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1147-1156. |
| [2] |
YANG Tian-Chun, HU Feng-Ming, YU Xi, FU Guo-Hong, LI Jun, YANG Zhui. Analysis and application of the responses of the frequency selection method of telluric electricity field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1010-1017. |
|
|
|
|

