|
|
|
| Comprehensive application of borehole log data of the Pulang copper deposit, Yunnan Province |
YANG Chao-Yi1,2( ), ZHU Qian-Kun1,2, JIE Shao-Peng3, KONG Chui-Ai1,2, SHA You-Cai1,2, ZHONG Zhi-Yong1,2, SHEN Qi-Wu1,2, CHEN Zhi-Jun2,4, MA Huo-Lin2,3( ), ZHU Qian-Kun1,2, JIE Shao-Peng3, KONG Chui-Ai1,2, SHA You-Cai1,2, ZHONG Zhi-Yong1,2, SHEN Qi-Wu1,2, CHEN Zhi-Jun2,4, MA Huo-Lin2,3( ) ) |
1. Yunnan Diqing Non-ferrous Metal Co., Ltd., Shangri-La 674400, China
2. Practical Teaching and Innovative Talents Training Base in the Pulang Copper Deposit, Shangri-La 674400, China
3. Institute of Geophysics and Geomatics, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan 430074, China
4. School of Earth Sciences, China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), Wuhan 430074, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The copper mineralized bodies and orebodies of the Pulang copper deposit in Yunnan Province are mainly distributed in the Pulang complex porphyry body and were formed through complex multi-stage development. This study aims to detail the geophysical response and fractures of copper reservoirs and provide detailed orebody characteristics, fractures, and horizon burial depth to be referenced in the exploration and exploitation of the Pulang copper deposit. First, the borehole-log data in the Pulang copper deposit were sampled for comprehensive evaluation. Then, in combination with the drilling reports and data on partial core samples, this study analyzed the log response characteristics and fractures and identified the lithology of the Pulang copper deposit using mathematical statistics, three-dimensional cross plots, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and fracture parameter calculation. The log response characteristics of the three major strata of quartz monzonite porphyries, quartz diorite porphyrites, and hornstones in the study area are as follows. The hornstone strata have relatively high resistivity, followed by the quartz diorite porphyrite strata and the quartz monzonite porphyry strata in sequence. The resistivity decreases significantly at the intervals with fractures occurring or at the relatively fractured intervals. The quartz monzonite porphyry strata have a relatively high charge rate (polarization rate) of up to about 10%. The hornstone strata have relatively high radioactive intensity than the quartz diorite porphyrite strata and the quartz monzonite porphyry strata. CNNs were used to identify and analyze the lithology of the three major types of strata based on log data, with an accuracy rate of 97.94%. Finally, this study identified fractures in these strata using dual laterolog data. The resistivity significantly decreases at intervals with fractures occurring and differs greatly between deep and shallow lateral resistivity. The quartz monzonite porphyry strata with a high copper grade have relatively low resistivity and relatively well-developed high-angle fractures. The results of this study are of significance for the identification of ore body characteristics and the exploitation of ore bodies in the Pulang copper deposit.
|
|
Received: 23 March 2022
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
MA Huo-Lin
|
|
|
|
10])
">
|
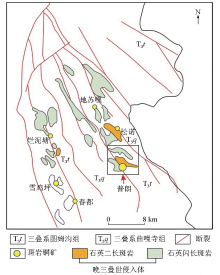
Tectonic and geological map of the study area(modified from reference[10])
|
|
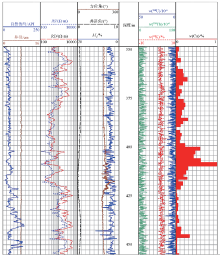
Comprehensive logging results of well ZK18XX
|
|
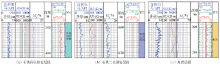
The logging curves of quartz diorite porphyrite, quartz monzonite porphyry and hornstone formation
|
|
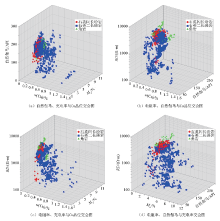
Three-dimensional cross plot of three logging parameters and copper grade for three lithological formations
|

| 岩性 | 自然伽马/API | Ma/% | RD/(Ω·m) | w(Cu)/% | | 分布范围(平均值) | 分布范围(平均值) | 分布范围(平均值) | 分布范围(平均值) | 石英二
长斑岩 | 31~203(135) | 1.9~10.1(4.1) | 204~2931(1223) | 0.3~1.2(0.42) | 石英闪
长玢岩 | 107~219(159) | 0.9~3.9(2.8) | 1302~3901(2015) | 0.33~0.39(0.36) | | 角岩 | 116~238(173) | 2.3~4.7(3.1) | 1537~5972(3180) | 0.32~0.52(0.39) |
|
Characteristics of logging response and copper grade parameters for three lithologies
|
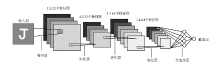
|
Convolutional neural network structure schematic
|

| 岩性 | CAL/cm | GR/API | RD/(Ω·m) | RS/(Ω·m) | Ma/% | w(40K)/% | w(232Th)/10-6 | w(238U)/10-6 | Label | | 角岩 | 8.4 | 195.3 | 5343.6 | 2122.7 | 4.5 | 2.9 | 12.4 | 5.6 | 0 | | 8.4 | 201.2 | 5343.6 | 2182.5 | 4.7 | 3.1 | 18.8 | 9.1 | 0 | | 8.4 | 170.2 | 5000.0 | 2182.5 | 4.7 | 2.1 | 13.0 | 10.4 | 0 | | 8.3 | 175.3 | 4638.3 | 2302.5 | 4.6 | 4.5 | 0.3 | 8.9 | 0 | | 8.5 | 194.8 | 4638.3 | 2405.9 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 31.3 | 8.5 | 0 | | 8.6 | 198.3 | 4810.1 | 2405.9 | 4.3 | 1.9 | 26.8 | 1.0 | 0 | | 8.4 | 190.6 | 5972.9 | 2270.1 | 4.5 | 5.2 | 9.9 | 11.0 | 0 | | 8.5 | 201.5 | 5972.9 | 2256.6 | 4.3 | 3.0 | 1.3 | 25.9 | 0 | | 8.4 | 187.6 | 4710.3 | 2256.6 | 4.3 | 0.7 | 15.2 | 11.2 | 0 | | 8.4 | 175.9 | 4227.2 | 1883.8 | 4.1 | 8.5 | 9.9 | 1.1 | 0 | | 石英二长斑岩 | 7.7 | 100.5 | 300.1 | 116.7 | 8.2 | 1.7 | 7.5 | 3.4 | 1 | | 7.7 | 98.6 | 300.1 | 116.7 | 9.0 | 1.4 | 8.3 | 2.8 | 1 | | 7.7 | 100.5 | 269.5 | 130.7 | 9.0 | 1.4 | 5.7 | 2.6 | 1 | | 7.7 | 106.2 | 269.5 | 130.7 | 9.0 | 1.4 | 5.1 | 3.3 | 1 | | 7.7 | 106.2 | 256.6 | 112.6 | 7.3 | 1.8 | 4.9 | 6.7 | 1 | | 7.7 | 104.3 | 346.4 | 229.7 | 7.0 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 5.5 | 1 | | 7.7 | 104.3 | 287.6 | 241.9 | 6.2 | 2.5 | 6.8 | 4.7 | 1 | | 7.7 | 108.1 | 287.6 | 241.9 | 6.2 | 2.8 | 10.6 | 4.1 | 1 | | 7.7 | 100.5 | 244.7 | 222.7 | 4.6 | 3.3 | 11.9 | 7.0 | 1 | | 7.7 | 98.6 | 244.7 | 222.7 | 4.6 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 6.4 | 1 | | 石英闪长玢岩 | 9.7 | 147.2 | 2301.8 | 1237.4 | 3.2 | 3.5 | 1.6 | 14.1 | 2 | | 9.9 | 161.8 | 2167.1 | 1348.2 | 3.5 | 3.4 | 4.8 | 3.5 | 2 | | 9.8 | 178.8 | 2117.9 | 1385.7 | 3.6 | 3.2 | 2.8 | 12.7 | 2 | | 9.7 | 140.8 | 1988.1 | 1495.9 | 3.4 | 3.9 | 2.6 | 4.8 | 2 | | 9.9 | 148.5 | 1899.8 | 1514.2 | 3.3 | 3.8 | 14.4 | 0.5 | 2 | | 9.8 | 157.6 | 1783.3 | 1548.3 | 3.2 | 1.5 | 14.7 | 6.4 | 2 | | 9.9 | 161.9 | 1745.4 | 1622.9 | 3.2 | 4.7 | 11.8 | 2.1 | 2 | | 9.8 | 210.4 | 1717.8 | 1686.4 | 3.1 | 1.9 | 3.2 | 15.0 | 2 | | 9.8 | 134.5 | 1699.8 | 1828.1 | 3.1 | 3.9 | 13.1 | 5.7 | 2 | | 9.8 | 171.4 | 1691.3 | 1910.7 | 3.0 | 5.4 | 25.6 | 5.8 | 2 |
|
CNN training sample set partial data
|

| 真实类别 | 预测类别 | | 角岩 | 石英二长斑岩 | 石英闪长玢岩 | 总计 | | 角岩 | 296 | 2 | 2 | 300 | | 石英二长斑岩 | 0 | 306 | 3 | 309 | | 石英闪长玢岩 | 7 | 5 | 300 | 312 | | 总计 | 303 | 313 | 305 | 921 |
|
CNN confusion matrix for lithology prediction
|
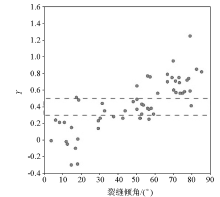
|
Cross plot of Y value and fracture dip angle
|

| Y值范围 | 裂隙类型 | 倾角范
围/(°) | 判断
点数 | 判断正
确点数 | 判断正
确率/% | | Y≤0.3 | 低角度缝 | 0~30 | 20 | 14 | 70.0 | | 0.3<Y≤0.5 | 倾斜裂缝 | 30~60 | 15 | 13 | 86.7 | | Y>0.5 | 高角度缝 | 60~90 | 22 | 19 | 86.4 |
|
Statistical table for judging fracture type by Y value
|

| 倾角范围/(°) | 频数/条 | 占比/% | | 0~15 | 3 | 0.76 | | 15~30 | 31 | 7.81 | | 30~45 | 56 | 14.11 | | 45~60 | 65 | 16.37 | | 60~75 | 143 | 36.02 | | 75~90 | 99 | 24.94 | | 总计 | 397 | 100 |
|
Dip Angle data of ZK18XX ore-bearing veins
|
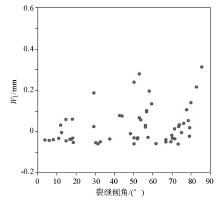
|
Cross plot of Wl and fracture dip angle
|
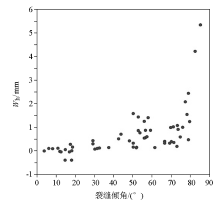
|
Cross plot of Wh and fracture dip angle
|
| [1] |
范玉华, 李文昌. 云南普朗斑岩铜矿床地质特征[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(2): 352-362.
|
| [1] |
Fan Y H, Li W C. Geological characteristics of the Pulang porphyry copper deposit, Yunnan[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(2): 352-362.
|
| [2] |
潘和平, 马火林, 蔡柏林, 等. 地球物理测井与井中物探[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.
|
| [2] |
Pan H P, Ma H L, Cai B L, et al. Principles of Geophysical Logging and Well Geophysical Exploration[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009.
|
| [3] |
袁桂琴, 熊盛青, 孟庆敏, 等. 地球物理勘查技术与应用研究[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(11): 1744-1805.
|
| [3] |
Yuan G Q, Xiong S Q, Meng Q M, et al. Application research of geophysical prospecting techniques[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(11): 1744-1805.
|
| [4] |
樊彦超. 地球物理测井技术在金属矿勘查中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属, 2018(15): 129-130.
|
| [4] |
Fan Y C. Application of geophysical logging technology in metal ore exploration[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2018(15): 129-130.
|
| [5] |
周新鹏, 项彪, 邹长春, 等. 南岭地区多金属矿NLSD-2孔综合地球物理测井研究[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(4): 686-694.
|
| [5] |
Zhou X P, Xiang B, Zou C C, et al. Integrated geophysical logging study on the borehole NLSD-2 of the polymetallic ore in the Nanling District[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(4): 686-694.

|
| [6] |
郭建宏, 杜婷, 张占松, 等. 基于支持向量机与地球物理测井资料的煤体结构识别方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3):768-777.
|
| [6] |
Guo J H, Du T, Zhang Z S, et al. The coal structure identification method based on support vector machine and geophysical logging data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3):768-777.
|
| [7] |
Konate A A, Pan H P, Ma H L, et al. Use of spectral gamma ray as a lithology guide for fault rocks: A case study from the Wenchuan Earthquake Fault Scientific Drilling project Borehole 4 (WFSD-4)[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2017, 128: 75-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2017.06.038.

|
| [8] |
Xu Z X, Ma W, Peng L, et al. Deep learning of rock images for intelligent lithology identification[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2021, 154: 104799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cageo.2021.104799.

|
| [9] |
陈钢花, 梁莎莎, 王军, 等. 卷积神经网络在岩性识别中的应用[J]. 测井技术, 2019, 43(2): 129-134.
|
| [9] |
Chen G H, Liang S S, Wang J, et al. Application of convolutional neural network in lithology identification[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2019, 43(2): 129-134.
|
| [10] |
Yang L Q, He W Y, Gao X, et al. Mesozoic multiple magmatism and porphyry-skarn Cu-polymetallic systems of the Yidun Terrane, Eastern Tethys: Implications for subduction- and transtension-related metallogeny[J]. Gondwana Research, 2018, 62: 144-162. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gr.2018.02.009.

|
| [11] |
李文昌, 曾普胜. 云南普朗超大型斑岩铜矿特征及成矿模型[J]. 成都理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 34(4): 436- 446.
|
| [11] |
Li W C, Zeng P S. Characteristics and metallogenic model of the Pulang super large porphyry copper deposit in Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition, 2007, 34(4):436-446.
|
| [12] |
李文昌, 余海军, 尹光候. 西南”三江”格咱岛弧斑岩成矿系统[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(4): 1129-1144.
|
| [12] |
Li W C, Yu H J, Yin G H. Porphyry metallogenic system of Geza arc in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(4): 1129-1144.
|
| [13] |
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.726791.

|
| [14] |
Sibbit A M, Faivre Q. The dual laterolog response in fractured rocks[C]// Dallas:SPWLA 26th Annual Logging Symposium, 1985: 17-20.
|
| [1] |
WANG Zong-Ren, WEN Chang, XIE Kai, SHENG Guan-Qun, HE Jian-Biao. Reservoir lithology identification method based on multi-scale time-frequency-space feature combination[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 81-90. |
| [2] |
LIU Wei-Nan, ZHANG Chao-Mo, ZHU Lin-Qi, HU Song, KONG Zheng, DENG Rui. A new method for TOC logging evaluation in shale gas for horizontal well[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 423-431. |
|
|
|
|

