|
|
|
| Accessing the distribution and ecological risks of heavy metals in soil in Hong’an County, Hubei Province through ecological geological surveys |
JU Zi-Long( ), QIN Zhi-Jun, Wan Xiang( ), QIN Zhi-Jun, Wan Xiang( ), YUAN Hang, ZHANG Xiao-Bo, WANG Deng ), YUAN Hang, ZHANG Xiao-Bo, WANG Deng |
| Hubei Geological Survey, Wuhan 430034, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study selected the Jinsha Lake and the Miersi Industry Park as key survey areas to study the distribution of heavy metals in soil in Hong’an County, Hubei Province. Samples were collected from surface soil and vertical soil profiles to assay the contents of eight heavy metals, i.e., Cu, Pb, Zn, Cr, Ni, Cd, As, and Hg. Both the single factor pollution index method and the potential ecological hazard index method were used to assess the distribution and the ecological risk of heavy metals. The study results are as follows:The average contents of the above eight heavy metals were 21.48×10-6, 21.75×10-6, 63.60×10-6, 53.24×10-6, 20.25×10-6, 0.13×10-6, 5.44×10-6, and 0.04×10-6,respectively. The cumulative Cu, Cr, Ni, and Cd are relatively enriched in the soil and their pollution is slight. The heavy metals show distinct distribution patterns. Minor pollution exists in the Gaoqiao-Yongjiahe basic-ultrabasic melange zone and around the Miershi Industrial Park, while severe pollution exists in Mn-Co mineralized points scattered in the northeastern Baliwan. Pb and Hg are enriched in the surface layer but decrease in the deep layer, Cr and Ni show an inverse trend, while other elements show indistinct distribution patterns. Cd and Hg have high potential ecological risk individually in the soil in the surveyed areas. The comprehensive ecological risk assessment based on Cd and Hg shows that the surrounding area of the Jinsha Lake Chengguan Town, the basic-ultrabasic melange zone, the surrounding area of the Miersi Industrial Park, and the Baliwan manganese-cobalt mineralization zone are areas with moderate potential ecological risks, where ecological supervision and protection should be strengthened. This study can provide a scientific basis for later ecological management in Hongan. It also serves as a good soil reference for other ecological geological surveys.
|
|
Received: 16 July 2021
Published: 17 August 2022
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Wan Xiang
E-mail: zilongcug@163.com;wxzgdz@hotmail.com
|
|
|
|
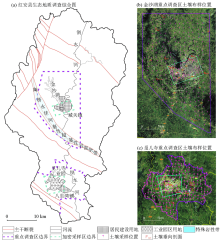
|
Overview of study area and the distribution of sampling points
|

| 元素 | 土地
类型 | 土壤环境质量标准(GB 15168—2018) | 湖北省
背景
值[21,25] | | pH≤5.5 | 5.5<pH
≤6.5 | 6.5<pH
≤7.5 | pH>7.5 | | Cu | 其他 | 50 | 60 | 100 | 100 | 30.7 | | 果园 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 200 | | Pb | 其他 | 70 | 90 | 120 | 170 | 26.7 | | 水田 | 80 | 100 | 140 | 240 | | Zn | 所有 | 200 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 83.6 | | Cr | 其他 | 150 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 86 | | 水田 | 250 | 250 | 300 | 350 | | Ni | 所有 | 60 | 70 | 100 | 190 | 26.9 | | Cd | 其他 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.17 | | 水田 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | | As | 其他 | 40 | 40 | 30 | 25 | 12.3 | | 水田 | 30 | 30 | 25 | 20 | | Hg | 其他 | 1.3 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 3.4 | 0.08 | | 水田 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 1 |
|
Reference value of heavy metal contents in single factor index method10-6
|
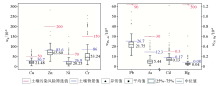
|
Statistics for soil heavy metal contents in the study area
|

| 重金属 | 以湖北省土壤背景值为参考 | 以GB15618—2018为参考 | | 超标个数 | 超标率 | 单因子污染指数
最小值~最大值(平均值) | 超标个数 | 超标率 | 单因子污染指数
最小值~最大值(平均值) | | Cu | 107 | 14.59% | 1~5.21/(1.37) | 10 | 1.48% | 1.07~3.2/(1.43) | | Pb | 79 | 10.81% | 1~8.31/(1.26) | 1 | 0.14% | 3.1 | | Zn | 170 | 23.11% | 1~13.77/(1.28) | 1 | 0.27% | 1.41~5.75/(3.58) | | Cr | 88 | 11.89% | 1~2.95/(1.47) | 19 | 2.57% | 1~1.69/(1.26) | | Ni | 158 | 21.49% | 1~9.03/(1.6) | 15 | 2.16% | 1.04~4.05/(1.42) | | Cd | 107 | 14.59% | 1~191.17/(2.75) | 14 | 2.03% | 1~9.33/(8.66) | | As | 32 | 4.46% | 1~6.17/(1.63) | 1 | 0.27% | 1.02~1.9/(1.46) | | Hg | 65 | 8.78% | 1~7.68/(1.57) | 0 | 0 | |
|
Statistics of heavy metals exceeding the standard in the survey area
|
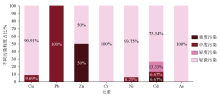
|
Pollution assessment of heavy metal content exceeding standard in study area
|
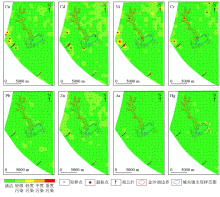
|
Distribution of heavy meatal pollution assessment and samples exceeding standard in Jinshahu investigation area
|
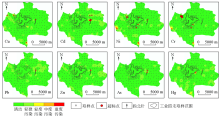
|
Distribution of heavy meatal pollution assessment and samples exceeding standard in Miersi investigation area
|

| 项目 | Cu | Pb | Zn | Cr | Ni | Cd | As | Hg | | 最小值/10-6 | 9.35 | 8.27 | 41.70 | 7.25 | 4.48 | 0.03 | 2.26 | 0.004 | | 最大值/10-6 | 90.40 | 52.80 | 234.00 | 122.00 | 69.60 | 0.71 | 43.30 | 0.13 | | 平均值/10-6 | 32.87 | 22.73 | 97.58 | 53.82 | 27.07 | 0.22 | 13.46 | 0.04 | | 变异系数/% | 81.27 | 48.10 | 61.91 | 60.41 | 73.11 | 101.51 | 78.07 | 78.43 | | 湖北省背景值/10-6 | 30.70 | 26.70 | 83.60 | 86.00 | 26.90 | 0.17 | 12.30 | 0.08 | | 背景值倍数 | 1.07 | 0.85 | 1.17 | 0.63 | 1.01 | 1.32 | 1.09 | 0.50 |
|
Statistics of soil heavy metal content in vertical profile
|
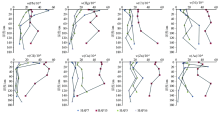
|
Soil profiles for heavy metal contents
|
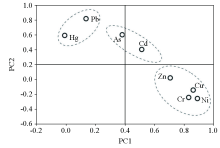
|
Principal components analysis for soil heavy metal content in study area
|

| 单项生态风险因子(Ei) | 综合生态风险指数(RI) | | 等级 | 得分 | 等级 | 得分 | | 低生态风险 | <40 | 低生态风险 | <150 | | 中等生态风险 | 40~80 | 中等生态风险 | 150~300 | | 较高生态风险 | 80~160 | 较高生态风险 | 300~600 | | 高生态风险 | >160 | 高生态风险 | >600 |
|
Evaluation criteria of potential ecological hazard derived from heavy metal
|
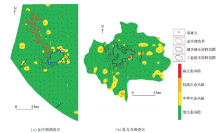
|
Ecological risk distribution in the study area
|
| [1] |
徐夕博, 吕建树, 徐汝汝. 山东省沂源县土壤重金属来源分布及风险评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(9):216-223.
|
| [1] |
Xu X B, Lyu J S, Xu R R. Source spatial distribution and risk assessment of heavy metals in Yiyuan county of Shandong Province[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(9):216-223.
|
| [2] |
吕建树, 张祖陆, 刘洋, 等. 日照市土壤重金属来源解析及环境风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2012(7):109-122.
|
| [2] |
Lyu J S, Zhang Z L, Liu Y, et al. Sources identification and hazardous risk delineation of heavy metals contamination in Rizhao City[J] Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012(7):109-122.
|
| [3] |
戴彬, 吕建树, 战金成, 等. 山东省典型工业城市土壤重金属来源、空间分布及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2015, 36(2):507-515.
|
| [3] |
Dai B, Lyu J S, Zhan J C, et al. Assessment of sources,spatial distribution and ecological risk of heavy metals in soils in a typical industry-based city of Shandong Province,Eastern China[J] .Environmental Science, 2015, 36(2):507-515.
|
| [4] |
周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 等. 云南省镇雄县土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [4] |
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang C W, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong County,Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1358-1366..
|
| [5] |
常文静, 李枝坚, 周妍姿, 等. 深圳市不同功能区土壤表层重金属污染及其综合生态风险评价[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(3):999-1007.
|
| [5] |
Chang W J, Li Z J, Zhou Y Z, et al. Heavy metal pollution and comprehensive ecological risk assessment of surface soil in different functional areas of Shenzhen,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(3):999-1007.
|
| [6] |
施宸皓, 王云燕, 柴立元, 等. 洞庭湖湿地周围表层土壤重金属污染及其人体健康风险评价[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2020, 30(1):150-161
|
| [6] |
Shi C H, Wang Y Y, Chai L Y, et al. Assessment of heavy metal and human health risk in surface soils around Dongting Lake wetland,China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2020, 30(1):150-161.
|
| [7] |
王宇珊, 刘成坚, 陈晓燕, 等. 垃圾焚烧厂周边土壤的重金属污染风险评价[J]. 华南师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 52(5):57-64.
|
| [7] |
Wang Y S, Liu C J, Chen X Y, et al. Pollution risk assessments of heavy metals in soils around a municipal solid waste incinerator[J]. Journal of South China Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2020, 52(5):57-64.
|
| [8] |
郭平, 谢忠雷, 李军, 等. 长春市土壤重金属污染特征及其潜在生态风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2005, 25(1):108-112.
|
| [8] |
Guo P, Xie Z L, Li J, et al. Specificity of heavy metal pollution and the ecological hazard in urban soils of Changchun City[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2005, 25(1):108-112.
|
| [9] |
聂洪峰, 肖春蕾, 戴蒙, 等. 生态地质调查工程进展与主要成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(1):1-12.
|
| [9] |
Nie H F, Xiao C L, Dai M, et al. Progresses and main achievements of eco-geological survey project[J] Geological Survey of China, 2021, 8(1):1-12.
|
| [10] |
陈树旺, 邢德和, 丁秋红, 等. 生态地质调查评价——以辽宁铁岭地区为例[J]. 地质与资源, 2012, 21(6):540-545.
|
| [10] |
Chen S W, Xing D H, Ding Q H, et al. Eco-geological survey and evaluation:A case study of Tieling area,Liaoning Province[J]. Geology and Resources, 2012, 21(6):540-545.
|
| [11] |
李金发. 为生态文明服务的地质调查工作[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2014, 28(1):1-4.
|
| [11] |
Li J F. Geological survey for ecological civilization[J]. Resources Environment and Engineering, 2014, 28(1):1-4.
|
| [12] |
徐黎. 生态环境地质调查进展与展望[J]. 世界有色金属, 2019, 1(3):248-250.
|
| [12] |
Xu L. Progress and prospect of eco-environmental geological survey[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2019, 1(3):248-250.
|
| [13] |
刘洪, 黄瀚霄, 欧阳渊, 等. 基于地质建造的土壤地质调查及应用前景分析——以大凉山区西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(1):91-105.
|
| [13] |
Liu H, Huang H X, Ouyang Y, et al. Soils geologic investigation in Daliangshan,Xichang,Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2020, 40(1):91-105.
|
| [14] |
王京彬, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 等. 基于地质建造的生态地质调查方法——以河北省承德市国家生态文明示范区综合地质调查为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1611-1624.
|
| [14] |
Wang J B, Wei X F, Zhang H Q, et al. The eco-geological survey based on geological formation,exemplified by integrated geological survey of National Ecological Civilization Demonstration Area in Chengde City,Hebei Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1611-1624.
|
| [15] |
严明书, 黄剑, 何忠庠, 等. 地质背景对土壤微量元素的影响——以渝北地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(1):199-205,219.
|
| [15] |
Yan M S, Huang J, He Z Y, et al. The influence of geological background on trace elements of soil:A case study of Yubei area[J]. Geophysical and Geo-chemical Exploration, 2018, 42(1) :199-205,219.
|
| [16] |
朱彩云, 白洁润, 顾国洪. 母质演化与质地对土壤养分的影响[J]. 现代农业, 2014, 1(6):32-33.
|
| [16] |
Zhu C Y, Bai J Y, Gu G H. Effects of parent material evolution and texture on soil nutrients[J]. Modern Agriculture, 2014, 1(6):32-33.
|
| [17] |
张腾蛟, 刘洪, 欧阳渊, 等. 中高山区土壤成土母质理化特征及主控因素初探——以西昌市为例[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2020, 40(1):106-114.
|
| [17] |
Zhang T J, Liu H, Ouyang Y, et al. A preliminary discussion on the physical and chemical characteristics and main controlling factors of soil and parent material in the middle and high mountain area-Take Xichang as an example[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2020, 40(1):106-114.
|
| [18] |
湖北省红安县地方志编纂委员会. 红安县志 1990-2007[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社, 2016.
|
| [18] |
The Compilation Committee of Local Chronicles of Hong'an County,Hubei. Hong'an County records 1990-2007[M]. Wuhan: Wuhan University Press, 2016
|
| [19] |
周豪. 西大别康家湾构造混杂岩带锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学特征及其地质意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2017.
|
| [19] |
Zhou H. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Kanjiawan tectonic melange belt of Western Dabie and it is geological significance[D]. Beijing: China University of Geoscience(Beijing), 2017.
|
| [20] |
杨振, 丁启燕, 宋万营. 湖北省土壤重金属污染健康风险评价[J]. 国外医学:医学地理分册, 2018, 39(3):181-187.
|
| [20] |
Yang Z, Ding Q Y, Song W Y. Assessment on health risk of heavy metal pollution in soil of Hubei Province[J]. Foreign Medical Sciences Section of Medgeography, 2018, 39(3):181-187.
|
| [21] |
黄赫, 周勇, 刘宇杰, 等. 基于多源环境变量和随机森林的农用地土壤重金属源解析——以襄阳市襄州区为例[J]. 环境科学学报, 2020, 40(12):4548-4558.
|
| [21] |
Huang H, Zhou Y, Liu Y J, et al. Source analysis of heavy metals in farmland and based on environmental variables and random forest approach:District of Xiangzhou District in Xiangyang City[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2020, 40(12):4548-4558.
|
| [22] |
孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 甘凤伟, 等. 承德市滦河流域土壤重金属地球化学基线厘定及其累积特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8):3753-3763.
|
| [22] |
Sun H Y, Wei X F, Gan F W. Determination of heavy metal geochemical baseline values and its accumulation in soils of the Luanhe River Basin,Chengde[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8):3753-3763.
|
| [23] |
黄凯, 张雪娇, 冯媛, 等. 河南某尾矿库土壤重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 环境影响评价, 2018, 40(1):78-83.
|
| [23] |
Huang K, Zhang X J, Feng Y, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in a Tailing pond of Henan[J]. Environmental Impact Assessment, 2018, 40(1):78-83.
|
| [24] |
张慧, 郑志志, 马鑫鹏, 等. 哈尔滨市土壤表层重金属污染特征及来源辨析[J]. 环境科学研究, 2017, 30(10):1597-1606.
|
| [24] |
Zhang H, Zeng Z Z, Ma X P, et al. Sources and pollution characteristics of heavy metals in surface soils of Harbin City[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2017, 30(10) :1597-1606.
|
| [25] |
李向阳, 吴疆, 刘洪强. 鄂东南5种森林土壤重金属含量及污染评价[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39(10):103-108.
|
| [25] |
Li X Y, Wu J, Liu H Q. Concentration and ecology risk assessment of heavy metal in five forest soils in southeastern Hubei province[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forest & Technology, 2019, 39(10):103-108.
|
| [26] |
刘文慧, 李湘凌, 章康宁, 等. 基于改进Håkanson法的水稻根系土壤重金属生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(11):2613-2620.
|
| [26] |
Liu W H, Li X L, Zhang K N, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in paddy soil based on improved Hakanson method[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences, 2020, 33(11):2613-2620.
|
| [27] |
王玉军, 吴同亮, 周东美, 等. 农田土壤重金属污染评价研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017, 36(12):2365-2378.
|
| [27] |
Wang Y J, Wu T L, Zhou D M, et al. Advances in soil heavy metal pollution evaluation based on bibliometrics analysis[J]. Journal of Agro-environment Science, 2017, 36(12):2365-2378.
|
| [28] |
阿吉古丽·马木提, 麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 艾尼瓦尔·买买提. 新疆焉耆县耕地土壤重金属垂直分布特征与污染风险[J]. 水土保持研究, 2018, 25(2):367-373.
|
| [28] |
Ajiguli M, Maimaitituerxun A, Ainiwaer M. Vertical distribution characteristics and risk assessment of soil heavy metal contamination of farmlands in Yanqi County,Xinjiang[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2018, 25(2):367-373.
|
| [29] |
麦麦提吐尔逊·艾则孜, 阿吉古丽·马木提, 艾尼瓦尔·买买提, 等. 博斯腾湖流域绿洲农田土壤重金属污染及潜在生态风险评价[J]. 地理学报, 2017, 72(9):1680-1694.
|
| [29] |
Maimaitituerxun A, Ajiguli M, Ainiwaer M, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and its potential ecological risks of farmland soils of oasis in Bosten Lake Basin[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2017, 72(9):1680-1694.
|
| [30] |
刘昭, 周宏, 陈丽, 等. 鄂西典型锰矿区河流表层沉积物中重金属的空间分布特征与污染评价[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2020, 27(3):114-121.
|
| [30] |
Liu Z, Zhou H, Chen L, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of heavy metals in river surface sediments in a manganese mining area,Western Hubei[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2020, 27(3):114-121.
|
| [31] |
任军, 刘方, 朱健, 等. 锰矿废渣区苔藓物种多样性及其重金属污染监测[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2020, 20(6):2398-2407.
|
| [31] |
Ren J, Liu F, Zhu J, et al. Diversity of the bryophytes and heavy metal pollution monitoring in manganese ore waste area[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2020, 20(6):2398-2407.
|
| [32] |
张炜华, 于瑞莲, 杨玉杰, 等. 厦门某旱地土壤垂直剖面中重金属迁移规律及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2019, 40(8):3765-3773.
|
| [32] |
Zhang W H, Yu R L, Yang Y J, et al. Migration and source analysis of heavy metals in vertical soil profiles of the drylands of Xiamen City[J]. Environmental Science, 2019, 40(8):3765-3773.
|
| [33] |
苏耀明, 陈志良, 雷国建, 等. 多金属矿区土壤重金属垂向污染特征及风险评估[J]. 生态环境学报, 2016, 25(1):130-134.
|
| [33] |
Su Y M, Chen Z L, Lei G J, et al. Vertical pollution characteristic and ecological risk assessment of heavy metal of soil profiles in polymetallic ore mine[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2016, 25(1):130-134.
|
| [34] |
刘银飞, 孙彬彬, 贺灵. 福建龙海土壤垂向剖面元素分布特征[J]. 物探与化探, 40(4):713-721.
|
| [34] |
Liu Y F, Sun B B, He L. Vertical distribution of elements in soil profiles in Longhai,Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(4) :713-721.
|
| [35] |
马溪平, 李法云, 肖鹏飞, 等. 典型工业区周围土壤重金属污染评价及空间分布[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2007, 39(2):326-329.
|
| [35] |
Ma X P, Li F Y, Xiao P F, et al. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and characteristics of its spatial distribution in soil near the typical industry area[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2007, 39(2):326-329.
|
| [36] |
王关玉, 吴月照. 山东省土壤中元素含量与母质的关系[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 1992, 28(4):475-485.
|
| [36] |
Wang G Y, Wu Y Z. Relationship between element content and parent material in soil of Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Peking University:Natural Science Edition, 1992, 28(4):475-485.
|
| [37] |
麦尔耶姆·亚森, 买买提·沙吾提, 尼格拉·塔什甫拉提, 等. 渭干河—库车河绿洲土壤重金属分布特征与生态风险评价[J]. 农业工程学报, 2017, 33(20):226-233.
|
| [37] |
Maieryemu Y, Mamat S, Nigela T, et al. Distribution of heavy metal pollution and assessment of its potential ecological risks in Ugan-Kuqa River Delta of Xinjiang[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2017, 33(20):226-233.
|
| [38] |
杨安, 邢文聪, 王小霞, 等. 西藏中部河流、湖泊表层沉积物及其周边土壤重金属来源解析及风险评价[J]. 中国环境科学, 2020, 40(10):4557-4567.
|
| [38] |
Yang A, Xing W C, Wang X X, et al. Source and risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of rivers,lakes and their surrounding soils in central Tibet[J]. China Environmental Science, 2020, 40(10):4557-4567.
|
| [39] |
宋波, 杨子杰, 张云霞, 等. 广西西江流域土壤镉含量特征及风险评估[J]. 环境科学, 2018, 39(4):446-458.
|
| [39] |
Song B, Yang Z J, Zhang Y X, et al. Accumulation of Cd and its risks in the soils of the Xijiang River drainage basin in Guangxi[J]. Environmental Science, 2018, 39(4):446-458.
|
| [1] |
XUE Dong-Xu, LIU Cheng, GUO Fa, WANG Jun, XU Duo-Xun, YANG Sheng-Fei, ZHANG Pei. Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1169-1178. |
| [2] |
FAN Hai-Yin, SONG Rui-Rui, YU Lin-Song, TENG Yong-Bo, WAN Fang, ZHANG Xiu-Wen, LI Sheng-Yu, ZHAO Chuang. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of groundwater in a typical chemical industry park in northwestern Shandong, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1326-1335. |
|
|
|
|

