|
|
|
| The spatial variations of elements and element associations in the primary geochemical halos:A case study of the Zhajiatongna gold deposit in Qinghai province |
HOU Zhen-Guang1( ), YUAN Zhao-Xian2( ), YUAN Zhao-Xian2( ) ) |
1. No. 5 Exploration Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources, Qinghai Bureau of Geological Exploration and Mineral Development, Xining 810008, China
2. Institute of Resource and Environmental Engineering, Hebei GEO University, Shijiazhuang 050031, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The primary geochemical halos, which exist in nearly all types of deposits, especially in hydrothermal deposits, serve as an essential geochemical indicator for deep prospecting. Many studies have been presently carried out on the elemental enrichment/depletion and component zoning in primary geochemical halos. However, there is a lack of reports on the spatial variations of elements and associated elements. This study collected geochemical data from 2,279 samples of the boreholes in the Zhajiatongna gold deposit and then calculated the enrichment factors and conducted a multivariate analysis to characterize the spatial variations of elements and element associations of the deposit. The element associations representing the components of surrounding rocks and mineralized components were extracted from all samples including surrounding rock samples, mineralized surrounding rock samples, and ore samples. They reflect that the deposit was formed by the superposition of mineralized components on the components of surrounding rocks in essence. Moreover, high-medium- and medium-low-temperature element associations were extracted from the ore samples, and high- and medium-low-temperature metallogenic element associations were extracted from the mineralized surrounding rock samples, indicating mineral precipitation mechanisms and the differences in the precipitation time and space. As suggested by the results, the primary geochemical halos of the Zhajiatongna deposit show the following variations from the periphery to the mineralization center: the mineralization-related elements generally exhibit an increasing trend in terms of enrichment degree and the number of enriched element types quantitatively, and the high-medium-temperature-medium-low-temperature and high-temperature-medium-low-temperature metallogenic element associations are superimposed on the surrounding rocks - mineralized element associations.
|
|
Received: 12 August 2021
Published: 17 August 2022
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
YUAN Zhao-Xian
E-mail: up.hzg@126.com;sdyzx86@126.com
|
|
|
|
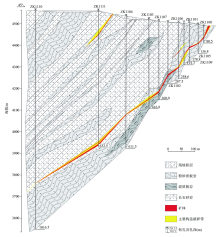
|
Sketches of gold orebodies and wall rocks in the profile of No.11 prospecting line
|

| 元素 | Ag | As | Au | Cu | Hg | Mo | Pb | Sb | Sn | W | Zn | | 方法 | ES | AF | ICP-MS | ICP-MS | AF | ICP-MS | ICP-MS | AF | ES | ICP-MS | ICP-MS | | 检出限 | 20 | 0.33 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.15 | 0.85 | 0.046 | 0.85 | 0.3 | 4 |
|
Analyticalmethods and the limits of detection for the elements
|

| 围岩 | 矿化围岩 | 矿石 | | 粉砂质板岩 | 含黄铁矿化粉砂质板岩、含黄铁矿化碎裂岩化粉砂质板岩、含黄铁矿化毒砂矿化粉砂质板岩 | 金矿石 | | 泥质板岩 | 含黄铁矿化泥质板岩、含黄铁矿化碎裂岩化泥质板岩、含黄铁矿化毒砂矿化泥质板岩 | | 长石砂岩 | 含黄铁矿化长石砂岩、含黄铁矿化碎裂岩化长石砂岩、含黄铁矿化毒砂矿化长石砂岩、含黄铁矿化毒砂矿化碎裂岩化长石砂岩 |
|
Lithological classification of the primary halo samples from the Zhajiatongna deposit
|
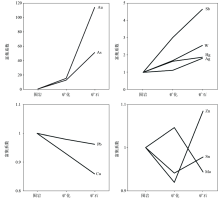
|
Variationsin elemental enrichment factor of mineralized wall rock and ore relative to unmineralized wall rock
|

| 元素 | 全体数据 | 围岩数据 | 矿化围岩数据 | 矿石数据 | | F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | F1 | F2 | | As | 0.86 | -0.06 | -0.11 | 0.86 | -0.84 | 0.38 | 0.79 | -0.33 | | Au | 0.78 | -0.07 | -0.11 | 0.81 | -0.84 | 0.07 | 0.84 | -0.10 | | Cu | -0.06 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.01 | 0.90 | 0.15 | -0.20 | 0.55 | | Hg | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.30 | 0.79 | 0.43 | 0.20 | 0.67 | | Mo | 0.05 | 0.20 | 0.21 | 0.12 | -0.02 | -0.71 | | | | Pb | 0.08 | 0.43 | 0.59 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 0.46 | -0.31 | 0.39 | | Sb | 0.56 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.88 | -0.01 | 0.69 | | Sn | -0.09 | 0.67 | 0.65 | -0.02 | 0.66 | -0.54 | -0.46 | -0.11 | | W | 0.42 | -0.02 | 0.26 | 0.68 | -0.48 | -0.11 | 0.83 | -0.01 | | Zn | 0.01 | 0.81 | 0.80 | -0.01 | 0.90 | 0.27 | -0.04 | 0.69 |
|
Loadings of elements in the two biggest factors of the four sets of data
|
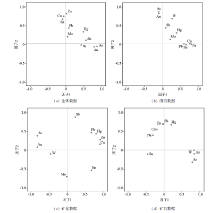
|
The loading plots of the two biggest factors of the four sets of data
|
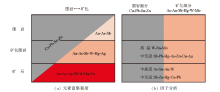
|
Sketch map of zonation of elements and element associations in the primary halo of the Zhajiatongna deposit
|
| [1] |
刘崇民. 金属矿床原生晕研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(10):1528-1538.
|
| [1] |
Liu C M. Progress in studies on primary halos of ore deposit[J]. Acta Geologicasinica, 2006, 80(10):1528-1538.
|
| [2] |
李惠, 禹斌, 李德亮, 等. 化探深部预测新方法综述[J]. 矿产勘查, 2010, 1(2):156-160.
|
| [2] |
Li H, Yu B, Li D L, et al. Summary of new methods on deep prediction of geochemical exploration[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2010, 1(2):156-160.
|
| [3] |
邵跃. 热液矿床岩石测量(原生晕法)找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.
|
| [3] |
Shao Y. Rock prospecting of hydrothermal deposit(primary halo method)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1997.
|
| [4] |
欧阳宗圻, 李惠, 刘汉忠. 典型有色金属矿床地球化学异常模式[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1990.
|
| [4] |
Ouyang Z Q, Li H, Liu H Z. Geochemical anomaly models for typical nonferrous metal deposits[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1990.
|
| [5] |
史长义, 汪彩芳. 区域次生地球化学负异常模型及其意义[J]. 物探与化探, 1995, 19(2):104-113.
|
| [5] |
Shi C Y, Wang C F. The regional secondary geochemical negative anomaley model and its significance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1995, 19(2):104-113.
|
| [6] |
朴寿成, 刘树田, 连长云, 等. 地球化学负异常及其找矿意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 1996, 32(2):46-50.
|
| [6] |
Piao S C, Liu S T, Lian C Y, et al. Geochemical negative anomaly and its prospecting significances[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1996, 32(2):46-50.
|
| [7] |
Goldberg I S, Abramson G Y, Los V L. Depletion and enrichment of primary haloes:Their importance in the genesis of and exploration for mineral deposits[J]. Geochemistry:Exploration,Environment,Analysis, 2003, 3(3):281-293.

|
| [8] |
徐明钻, 朱立新, 马生明, 等. 多重分形模型在区域地球化学异常分析中的应用探讨[J]. 地球学报, 2010, 31(4):611-618.
|
| [8] |
Xu M Z, Zhu L X, Ma S M, et al. A tentative discussion on the application of multi-fractal models to the analysis of regional geochemical anomalies[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2010, 31(4):611-618.
|
| [9] |
马生明, 朱立新, 刘海良, 等. 甘肃北山辉铜山铜矿地球化学异常结构研究[J]. 地球学报, 2011, 32(4):405-412.
|
| [9] |
Ma S M, Zhu L X, Liu H L, et al. A study of geochemical anomaly structure of the Huitongshan copper deposit in Beishan Area,Gansu Province[J]. Acta GeoscienticaSinica, 2011, 32(4):405-412.
|
| [10] |
Goldberg I S, Abramson G Y, Haslam C O, et al. Depletion and enrichment zones in the Bendigo gold field:A possible source of gold and implications for exploration[J]. Economic Geology, 2007, 102(4):745-753.

|
| [11] |
Beus A A, Grigorian S V. Geochemical exploration methods for mineral deposits[M]. Wilmette: Applied Publishing Ltd, 1977.
|
| [12] |
Yate Z. Geochemical exploration for deeply hidden ore in southeastern Hubei Province[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1989, 33(1):135-144.

|
| [13] |
Konstantinov M M, Strujkov S F. Application of indicator halos(signs of ore remobilization)in exploration for blind gold and silver deposits[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1995, 54(1):1-17.

|
| [14] |
黄转莹, 路润安. 陕西省凤县铅硐山大型铅锌矿床原生异常分带及分带指数[J]. 地质与勘探, 2003, 39(3):39-44.
|
| [14] |
Huang Z Y, Lu R A. Zoning characteristics and index of primary geochemical anomalies in Qiandongshan Pb-Zn deposit,Shaanxi Province,China[J]. Geology And Prospecting, 2003, 39(3):39-44.
|
| [15] |
Liu L M, Peng S L. Prediction of hidden ore bodies by synthesis of geological,geophysical and geochemical information based on dynamic model in Fenghuangshan ore field,Tongling district,China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2004, 81(1):81-98.

|
| [16] |
Ghavami-Riabi R, Theart H F, De Jager C. Detection of concealed Cu-Zn massive sulfide mineralization below eolian sand and a calcrete cover in the eastern part of the Namaqua Metamorphic Province,South Africa[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2008, 97(2/3):83-101.

|
| [17] |
Wang C M, Carranza E J, Zhang S T, et al. Characterization of primary geochemical haloes for gold exploration at the Huanxiangwa gold deposit,China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 24:40-58.
|
| [18] |
Zheng C J, Luo X R, Wen M L, et al. Axial primary halo characterization and deep orebody prediction in the Ashele copper-zinc deposit,Xinjiang,NW China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 213:106509.

|
| [19] |
李惠, 张国义, 王支农, 等. 构造叠加晕法在预测金矿区深部盲矿中的应用效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2003, 27(6):438-440.
|
| [19] |
Li H, Zhang G Y, Wang Z N, et al. The effect of applying structural superimposed halos to the prognosis of deep blind orebodies in the gold ore district[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 27(6):438-440.
|
| [20] |
李惠, 禹斌, 李永才, 等. 热液型矿床深部盲矿预测的构造叠加晕实用理想模型及其意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(5):889-897.
|
| [20] |
Li H, Yu B, Li Y C, et al. A new practical ideal model of structural superimposed halos for prediction of deep blind hydrothermal deposits and its significance[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(5):889-897.
|
| [21] |
王文, 李鹏, 夏有清, 等. 东昆仑大场金矿田扎家同哪矿床地质特征及找矿方向[J]. 青海大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 30(5):60-68.
|
| [21] |
Wang W, Li P, Xia Y Q, et al. Geological features and prospecting orientation of Zhajiatongna deposit in Dachang golden orefield of Eastern Kunlun mountain[J]. Journal of Qinghai University:Nature Science Edition, 2012, 30(5):60-68.
|
| [22] |
袁兆宪, 侯振广, 任志栋, 等. 金属元素形成原生晕能力定量评价——以青海省扎家同哪金矿为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(1):292-300.
|
| [22] |
Yuan Z X, Hou Z G, Ren Z D, et al. Quantitative evaluation of the ability of elements in forming primary halos:A case study of the Zhajiatongna gold deposit,Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1):292-300.
|
| [23] |
刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.
|
| [23] |
Liu Y J, Cao L M, Li Z L, et al. Element geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984.
|
| [24] |
Thompson J F, Sillitoe R H, Baker T, et al. Intrusion-related gold deposits associated with tungsten-tin provinces[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 1999, 34(4):323-334.

|
| [25] |
刘建明, 周渝峰, 付仁平, 等. 杂多酸络合物及其与热液成矿元素组合的关系[J]. 矿物岩石, 1994, 4(4):76-84.
|
| [25] |
Liu J M, Zhou Y F, Fu R P, et al. Heteropolyacide complexes in relationship to hydrothermal paragenesis of ore elements[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 1994, 4(4):76-84.
|
| [26] |
刘家军, 刘光智, 廖延福, 等. 甘肃寨上金矿床中白钨矿矿体的发现及其特征[J]. 中国地质, 2008, 35(6):1113-1120.
|
| [26] |
Liu J J, Liu G Z, Liao Y F, et al. Discovery and significance of scheelite orebodies in the Zhaishang gold deposit,southern Gansu[J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(6):1113-1120.
|
| [27] |
Grigoryeva T A, Sukneva L S. Effects of sulfur and of antimony and arsenic sulfide on the solubility of gold[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica, 1981, 18:153-158.
|
| [28] |
Akhmedzhanova G M, Nekrasov I Y, Tikhomirova V I, et al. Solubility of gold in sulfide-arsenide solutions at 200-300 ℃[J]. Earth Science Sections, 1998, 300(3):189-191.
|
| [29] |
丁清峰, 王冠, 孙丰月, 等. 青海省曲麻莱县大场金矿床成矿流体演化:来自流体包裹体研究和毒砂地温计的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 26(12):3709-3719.
|
| [29] |
Ding Q F, Wang G, Sun F Y, et al. Ore-forming fluid evolution of Dachang gold deposit in Qumalai County,Qinghai Province:Evidence from fluid inclusion study and arsenopyrite geothermometer[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(12):3709-3719.
|
| [1] |
YUAN Zhao-Xian, HOU Zhen-Guang, REN Zhi-Dong, LIU Yong-Le, ZHANG Da-Ming, ZHANG Jian-Ping. Quantitative evaluation of the ability of elements in forming primary halos: A case study of the Zhajiatongna gold deposit, Qinghai Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 292-300. |
| [2] |
LI Huan, HUANG Yong, ZHANG Qin-Rui, JIA San-Man, XU Guo-Zhi, YE Bei-Bei, HAN Bing. Soil geochemical characteristics and influencing factors in Beijing Plain[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(2): 502-516. |
|
|
|
|

