|
|
|
| Application of the mobile form indicators ingeochemical prospecting of hydrocarbons in Yubei area, Tarim Basin |
LI Wu( ), WANG Guo-Jian, JIANG Tao, ZOU Yu, LUO Xin, GUO Jia-Qi, TANG Yu-Ping, CHEN Zhe-Chun ), WANG Guo-Jian, JIANG Tao, ZOU Yu, LUO Xin, GUO Jia-Qi, TANG Yu-Ping, CHEN Zhe-Chun |
| Wuxi Research Institute of Petroleum Geology, Petroleum Exploration and Production Research Institute, SINOPEC, Wuxi 214126, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Yubei area in Tarim Basin is characterized by complex geological conditions and desert land form with widely distributed mobile sand dunes. Seismic signals are severely attenuated in the area due to the absorption by desert surface, leading to a low signal-noise ratio and low resolution of data and thereby making hydrocarbon exploration difficult. The method using mobile forms for geochemical prospecting of hydrocarbons is not affected by the desert land form and can detect information of underlying hydrocarbons in adirect, rapid, and economic manner. The mobile form indicators of free hydrocarbon gas, headspace gas, fluorescence spectra, and microorganisms were selected for the geochemical prospecting of hydrocarbons in the Yubei area, Tarim Basin. The results are as follows. The anomaly zones of the methane,butane oxidizing bacteria and the integrated indicators (entropy) can effectively indicate the hydrocarbon-bearing scope of the area controlled by Well Yubei-1. Based on the spatial combination and configuration relationship of the anomaly zones of these indicators, six favorable zones of geochemical anomalieswere delineated, and their integrated anomalous levels were determined. Among these favorable zones, the tectonoclastic zone of Well Yebue-1 is the most favorable target area for hydrocarbon exploration, followed by the marginal regions of the tectonoclastic zone. These results provide a geochemical basis for further deployment of hydrocarbon exploration in the Yuebei area, Tarim Basin.
|
|
Received: 04 March 2021
Published: 28 June 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
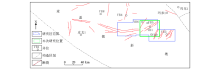
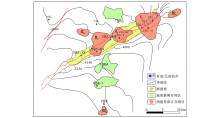
Geological structure and well location distribution in the study area
|
|
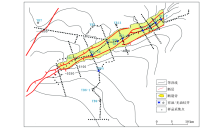
Distribution of the sampling profiles in the geochemical exploration
|

| 参数 | BOB/(CFU·108) | MOB/(CFU·108) | F360/int | /(μL·L-1) | YC1/(μL·L-1) | WC1/(μL·L-1) | W /(μL·L-1) | | C | 0.91 | 3.43 | 28.43 | 0.64 | 4.41 | 5.52 | 0.26 | | S | 4.33 | 9.16 | 45.35 | 0.70 | 2.51 | 1.30 | 0.10 | | V | 4.75 | 2.67 | 1.59 | 1.09 | 0.56 | 0.23 | 0.38 |
|
Data statistics of the geochemical indicators used in the structure zone in Well Yubei-1 area
|

| 指标 | WC1 | | YC1 | | MOB | BOB | F360 | | WC1 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | 0.205 | 1.000 | | | | | | | YC1 | 0.211 | -0.015 | 1.000 | | | | | | | 0.078 | 0.022 | 0.576 | 1.000 | | | | | MOB | 0.072 | 0.087 | -0.049 | -0.096 | 1.000 | | | | BOB | -0.019 | 0.040 | -0.056 | -0.038 | 0.061 | 1.000 | | | F360 | -0.065 | -0.048 | -0.060 | -0.064 | 0.036 | 0.056 | 1.000 |
|
Correlation matrix of the geochemical indicators used in Yubei area
|
|
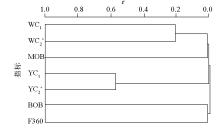
Diagram showing the clustering spectrums ofthe geochemical indicators used in the study area
|
|
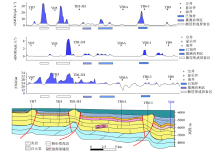
Schematic diagram showing the YB7—YB5—YB9 geological profiles in Well Yubei area and anomaly distribution of the geochemical indicators
|
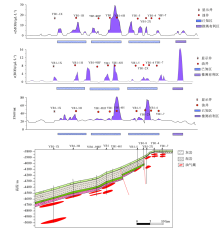
|
Schematic diagram showing the YB1-1X—YB1-7 geological profile in Well Yubei area and anomaly distribution of the geochemical indicators
|
|
Evaluation result of the geochemical anomalous zones in Yubei study area
|
| [1] |
李志明, 宋喜林, 张长江. 游离烃技术在沙漠覆盖区构造含油气评价中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2002, 26(5):344-346.
|
| [1] |
Li Z M, Song X L, Zhang C J. The application of the free hydrocarbon technique to the evaluation of oil and gas potential of structures in desert areas[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2002, 26(5):344-346.
|
| [2] |
任春, 夏响华, 王国建. 内蒙古沙漠覆盖区油气化探应用实例[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(8):25-27.
|
| [2] |
Ren C, Xia X H, Wang G J. An application case of geochemical exploration technique in desert areas of Inner Mongolia[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(8): 25-27.
|
| [3] |
蒋涛, 汤玉平, 吴向华, 等. 油气化探在低渗透油气资源勘探中的应用——以英南2气藏、鄂尔多斯盆地某油藏为例[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(4):790-797.
|
| [3] |
Jiang T, Tang Y P, Wu X H, et al. Application of the oil and gas geochemical exploration in low permeability oil and gas resources exploration: Take Yingnan 2 Gas Reservoir and an Ordos Oil Field as examples[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(4): 790-797.
|
| [4] |
陈浙春, 程同锦, 汤玉平, 等. 油气化探在塔里木盆地油气勘探中的应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(1):59-63.
|
| [4] |
Chen Z C, Cheng T J, Tang Y P, et al. Application results of oil and gas geochemical technique in oil and gas exploration in Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(1): 59-63.
|
| [5] |
蒋涛, 仵永强, 汤玉平, 等. 地球化学烃场效应及影响化探异常的凶素[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(2):280-285.
|
| [5] |
Jiang T, Wu Y Q, Tang Y P, et al. Hydrocarbon geochemical field effects and influencing factor in oil and gas geochemical exploration[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(2): 280-285.
|
| [6] |
蒋涛, 汤玉平, 吴向华, 等. 油气化探在低渗透油气资源勘探的应用[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2013, 24(4):790-797.
|
| [6] |
Jiang T, Tang Y P, Wu X H, et al. Application of the oil and gas geochemical exploration in low permeability oil and gas resources exploration[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2013, 24(4): 790-797.
|
| [7] |
蒋涛, 赵克斌, 荣发准, 等. 油气藏烃类垂向微渗漏及近地表化探异常的油气地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(5):901-908.
|
| [7] |
Jiang T, Zhao K B, Rong F Z, et al. Vertical micro-migration of hydrocarbons from subsurface reservoirs and geological significance in near-surface geochemical exploration for oil and gas[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(5): 901-908.
|
| [8] |
岳勇, 罗少辉. 塔里木盆地玉北地区构造特征及对奥陶系成藏输导体系的控制[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5):20-30.
|
| [8] |
Yue Y, Luo S H. Structural characteristics and their control over Ordovician hydrocarbon migration pathway system in Yubei area, Tarim Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 20-30.
|
| [9] |
乔桂林, 郑和荣, 余腾孝, 等. 塔里木盆地玉北地区断裂带控藏特征研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2018, 40(5):662-668.
|
| [9] |
Qiao G L, Zheng H R, Yu T X, et al. Fault belt reservoir controls in Yubei area,Tarim Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2018, 40(5): 662-668.
|
| [10] |
蒋涛, 荣发准, 陈浙春, 等. 民和盆地和松辽盆地化探工区顶空气指标数据特征对比和分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2007, 18(5):760-763.
|
| [10] |
Jiang T, Rong F Z, Chen Z C, et al. Comparison and analyses of geochemical prospecting index in Minhe and Shongliao Basins[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2007, 18(5): 760-763.
|
| [11] |
王国建, 汤玉平, 唐俊红, 等. 断层对烃类微渗漏主控作用及异常分布影响的实验模拟研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(1):21-27.
|
| [11] |
Wang G J, Tang Y P, Tang J H, et al. Experimental simulation of the effect of faults on vertical hydrocarbon microseepage[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(1):21-27.
|
| [12] |
王国建, 唐俊红, 汤玉平, 等. 油气藏上方地层中不同赋存态微渗漏轻烃特征初步模拟实验研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2):261-266.
|
| [12] |
Wang G J, Tang J H, Tang Y P, et al. Simulation of microseepage of light hydrocarbon of different occurrence states in strata above reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(2): 261-266.
|
| [13] |
刘运黎. 似源组构异常在油气化探中的应用[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2003, 24(2):184-186.
|
| [13] |
Liu Y L. Application of source similar fabric anomaly analysis in petroleum geochemical exploration[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2003, 24(2): 184-186.
|
| [14] |
徐翔军, 刘玉梅, 郭少斌. 非常规综合物化探油气预测研究[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2002, 32(4):349-352.
|
| [14] |
Xu X J, Liu Y M, Guo S B. Studied on the prediction of oil and gas of unconventional integrated geophysical and geochemical method[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2002, 32(4):349-352.
|
| [1] |
WAN Tai-Ping, ZHANG Li, LIU Han-Liang. Regional geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prospect area prediction of strategic mineral antimony in the Eerguna block, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1179-1188. |
| [2] |
ZHENG Xu-Ying, XU Ke-Wei, GU Lei, WANG Guo-Jian, LI Guang-Zhi, GUO Jia-Qi, ZOU Yu, BORJIGIN Tenger. Distribution of microorganisms in the typical geothermal field environment and its significance for geothermal exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1127-1136. |
|
|
|
|

