|
|
|
| Stochastic inversion of surface wave dispersion curves based on Bayesian theory |
LIU Hui1( ), LI Jing1,2( ), LI Jing1,2( ), ZENG Zhao-Fa1, WANG Tian-Qi1 ), ZENG Zhao-Fa1, WANG Tian-Qi1 |
1. College of Geo-exploration Science and Technology,Jilin University,Changchun 130021,China
2. Key Laboratory of Geophysical Exploration Equipment,Ministry of Education (Jilin University),Changchun 130026,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Surface wave dispersion curve inversion is an important geophysical method for obtaining the velocity and thickness distribution of underground shear wave.Conventional linear inversion methods,such as iterative least squares,relying on the initial model and multiple solution,are easy to fall into local minimum and low inversion accuracy.The stochastic inversion method based on Bayesian theory is a nonlinear inversion method which can integrate prior information.This method does not need initial model,only uses prior information to sample the model randomly,and selects and accepts the appropriate inversion model according to the probability distribution.It achieves the accurate estimation of the detail information.In this paper,the authors present a Bayesian Markov Monte Carlo (MCMC) stochastic inversion method based on GPR data constraints to invert the Rayleigh-waves dispersion curve.In the inversion process,by randomly changing the model parameters and calculating the likelihood function of the dispersion curve and the actual dispersion curve,researchers can choose whether to accept the new model parameters,repeat this process continuously,and finally get the best fitting result with the actual dispersion curve and the posterior probability density distribution of the VS solution.The typical numerical model test and field seismic data demonstrate that,compared with the conventional unconstrained stochastic inversion,the proposed method can effectively reduce the multiple solution and improve the efficiency and accuracy.
|
|
Received: 09 March 2020
Published: 20 August 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
LI Jing
E-mail: 177344303@qq.com;ljwy1209@163.com
|
|
|
|
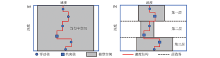
|
Model parameterization using Voronoi nuclei
a—1 layer model without constraints;b—3 layer model with GPR constraints
|
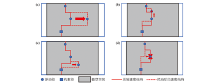
|
Illustration of four possible perturbations to a current model
a—change vs of a nuclcus;b—move a nuclcus to a different depth;c—give birth to a new floating nucleus;d—remove a floating nucleus
|
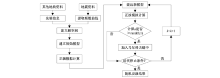
|
Basic flowchart of surface wave stochastic inversion
|

| 层序号 | 层厚度/m | vs/(m·s-1) | vp/vs | 密度/(g·cm-3) | vs约束/(m·s-1) | | 1 | 2 | 400 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 | | 2 | 5 | 600 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 | | 3 | 8 | 800 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 | | 4 | 15 | 1200 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 |
|
4-layer vs incremental model parameters
|
|
Fundamental dispersion curve inversion of four-layer vs increasing model
a—inversion results without constraints;b—inversion results with prior constraints;c—dispersion curves of the best fitting model and true model for unconstrained inversion;d—dispersion curves of the best fitting model and the true model with prior constraint inversion;e—misfit iteration curve
|

| 层序号 | 层厚度/m | vs/(m·s-1) | vp/vs | 密度/(g·cm-3) | vs约束/(m·s-1) | | 1 | 2 | 600 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 | | 2 | 15 | 800 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 | | 3 | 8 | 400 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 | | 4 | 5 | 1200 | 2 | 1.8 | 300~1300 |
|
4-layer model with low velocity interlayer
|
|
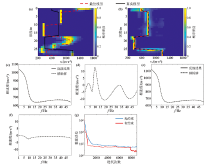
Fundamental dispersion curve inversion of low-velocity layer model
a—stochastic inversion results without constraints;b—stochastic inversion results with prior constraints;c—dispersion curve of the best fitting model and true model for unconstrained inversion;d—error of dispersion curve for unconstrained inversion;e—dispersion curves of the best fitting model and the true model with prior constraint inversion;f—error of dispersion curve with prior constraint inversion;g—misfit iteration curve
|
|
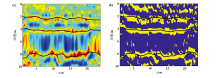
Processed GPR profile(a)and GPR layer recognition results based on Convolutional Neural Networks(b)
|
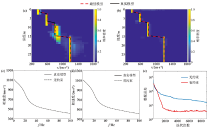
|
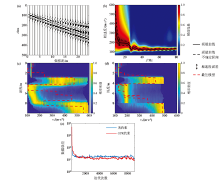
Inversion results of real surface wave data
a—one shot gather of 13th shot;b—extracted dispersion curve;c—unconstrained stochastic inversion result;d—stochastic inversion with GPR constrained;e—iterations
|
|
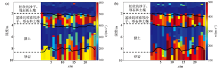
Comparison of quasi-two-dimensional profile inversion results
a—2D velocity profile of unconstrained stochastic inversion;b—2D velocity profile of GPR constrained stochastic inversion
|
| [1] |
李庆春, 邵广周, 刘金兰, 等. 瑞雷面波勘探的过去、现在和未来[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2006,28(3):74-77.
|
| [1] |
Li Q C, Shao G Z, Liu J L, et al. Past,present and future of Rayleigh surface wave exploration[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences & Environment, 2006,28(3):74-77.
|
| [2] |
张立, 刘争平. 水平层状介质中基阶瑞利面波椭圆极化特征数值分析与研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013,56(5):1686-1695,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130526.
|
| [2] |
Zhang L, Liu Z P. A study of the elliptic polarization characteristics of fundamental mode Rayleigh wave based on numerical simulation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013,56(5):1686-1695,doi: 10.6038/cjg20130526.
|
| [3] |
夏江海, 高玲利, 潘雨迪, 等. 高频面波方法的若干新进展[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015,58(8):2591-2605,doi: 10.6038/cjg20150801.
|
| [3] |
Xia J H, Gao L L, Pan Y D, et al. New findings in high frequency surface wave method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015,58(8):2591-2605,doi: 10.6038/cjg20150801.
|
| [4] |
Li J, Hanafy S. Skeletonized inversion of surface wave:Active source versus controlled noise comparison[J]. Interpretation, 2016,4(3):11-19.
|
| [5] |
石耀霖, 金文. 面波频散反演地球内部构造的遗传算法[J]. 地球物理学报, 1995,38(2):189-198.
|
| [5] |
Shi Y L, Jin W. Genetic algorithms inversion of lithospheric structure from surface wave dispersion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1995,38(2):189-198.
|
| [6] |
Park C B, Miller R D, Xia J. Multichannel analysis of surface waves[J]. Geophysics, 1999,64(3):800-808.
|
| [7] |
Xia J H, Miller R D, Park C B. Estimation of near-surface shear-wave velocity by inversion of Rayleigh waves[J]. Geophysics, 1999,64(3):691-700.
|
| [8] |
Song X H, Gu H M, Liu J P. Occam's inversion of high-frequency Rayleigh wave dispersion curves for shallow engineering applications[C]// Wuhan:Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Environmental and Engineering Geophysics (ICEEG), 2006: 124-130.
|
| [9] |
鲁来玉, 张碧星, 汪承灏. 基于瑞利波高阶模式反演的实验研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006,49(4):1082-1091.
|
| [9] |
Lu L Y, Zhang B X, Wang C H. Experiment and inversion studies on Rayleigh wave considering higher modes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2006,49(4):1082-1091.
|
| [10] |
罗银河, 夏江海, 刘江平, 等. 基阶与高阶瑞利波联合反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2008,51(1):242-249.
|
| [10] |
Luo Y H, Xia J H, Liu J P, et al. Joint inversion of fundamental and higher mode Rayleigh waves[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2008,51(1):242-249.
|
| [11] |
Beaty K S, Schmitt D R, Sacchi M. Simulated annealing inversion of multimode Rayleigh wave dispersion curves for geological structure[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2002,151(2):622-631.
|
| [12] |
Song X, Gu H, Zhang X, et al. Pattern search algorithms for nonlinear inversion of high-frequency Rayleigh-wave dispersion curves[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2008,34(6):611-624.
|
| [13] |
Song X, Tang L, Lyu X, et al. Application of particle swarm optimization to interpret Rayleigh wave dispersion curves[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2012,84(9):1-13,doi: 10.1016/j.jappgeo.2012.05.011.
|
| [14] |
蔡伟, 宋先海, 袁士川, 等. 基于萤火虫和蝙蝠群智能算法的瑞雷波频散曲线反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018,60(6):2409-2420,doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0322.
|
| [14] |
Cai W, Song X H, Yuan S C, et al. Inversion of Rayleigh wave dispersion curves based on firefly and bat algorithms[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018,60(6):2409-2420,doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0322.
|
| [15] |
于东凯, 宋先海, 江东威, 等. 改进蜂群算法及其在面波频散曲线反演中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018,61(4):1482-1495,doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0424.
|
| [15] |
Yu D K, Song X H, Jiang D W, et al. Improvement of Artificial Bee Colony and its application in Rayleigh wave inversion[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018,61(4):1482-1495,doi: 10.6038/cjg2018L0424.
|
| [16] |
于东凯, 宋先海, 张学强, 等. 蚱蜢算法在瑞雷波频散曲线反演中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2019,54(2):288-301,doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2019.02.007.
|
| [16] |
Yu D K, Song X H, Zhang X Q, et al. Rayleigh wave dispersion inversion based on grasshopper optimization algorithm[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2019,54(2):288-301,doi: 10.13810/j.cnki.issn.1000-7210.2019.02.007.
|
| [17] |
Aki K. Space and time spectra of stationary stochastic waves, with special reference to microtremors[J]. Bull. Earth. Res. Inst., 1957,35:415-456.
|
| [18] |
徐佩芬, 李世豪, 凌甦群, 等. 利用SPAC法估算地壳S波速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2013,56(11):3846-3854.
|
| [18] |
Xu P F, Li S H, Ling S Q. Application of SPAC method to estimate the crustal S-wave velocity structure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2013,56(11):3846-3854.
|
| [19] |
张宝龙, 李志伟, 包丰, 等. 基于微动方法研究五大连池火山区尾山火山锥浅层剪切波速度结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 2016,59(10):3662-3673.
|
| [19] |
Zhang B L, Li Z W, Bao F. Shallow shear-wave velocity structures under the Weishan volcanic cone in Wudalianchi volcano field by microtremor survey[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2016,59(10):3662-3673.
|
| [20] |
Dettmer J, Dosso S E, Holland C W. Trans-dimensional geoacoustic inversion[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2010,128(6):3393-3405,doi: https:// doi.org/10.1121/ 1.3500674.
|
| [21] |
Maraschini M, Foti S. A Monte Carlo multimodal inversion of surface waves[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2010,182(3):66,doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-246X.2010.04703.x.1557-15
|
| [22] |
Denison D, Holmes C, Mallik B, et al. Bayesian methods for nonlinear classification and regression[M]. Chichester:John Wiley, 2002.
|
| [23] |
Qin T, Zhao Y, Hu S, et al. An interactive integrated interpretation of GPR and Rayleigh wave data based on the genetic algorithm[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 2019: 1-26,doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-019-09543-x.
|
| [24] |
Li J, Chen Y Q, Schuster G. Separation of multi-mode surface waves by supervised machine learning methods[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 2019,doi: 10.1111/1365-2478.12927.
|
| [25] |
Wang Y R. The geotechnical investigation report of Hongxueyaju in Huainan[R]. Anhui Hydrological Engineering Survey and Research Institute, 2013: 1-13,doi: https://wenku.baidu.com/view/dbf3624a3968011ca200913f.html.
|
|
|
|

