|
|
|
| The application of magnetotelluric sounding to geothermal resources assessment in Yinchuan Basin |
Huai-Liang ZHU1, Bo-Wen XU1( ), Zhi-Long LIU1, Feng SHI1, Yu-Qi XIN1, Xue-Gang CAO2, Guo-Qiang Cheng2 ), Zhi-Long LIU1, Feng SHI1, Yu-Qi XIN1, Xue-Gang CAO2, Guo-Qiang Cheng2 |
1. Tianjin Geothermal Exploration and Development-Designing Institute, Tianjin 300250,China
2. Ningxia Institute of Geological Engineering,Yinchuan 750004,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract As a kind of clean and continuous energy, geothermal resources will play an enormous role in the development of China’s economy. In this study, data processing and analysis included calculation of 2D skewness and electric strike of the MT profile, and NLCG 2D inversion was performed on TM data, which consisted of 51 measurement points from line L1 and line L2 in western area of Yinchuan Basin. The result shows that the western margin of the Yinchuan Basin can be divided into three layers from top to bottom:low-resistivity layer, relatively high-resistivity layer and low-resistivity layer. Combined with the known geothermal geological data, the authors hold that Hongliugou Formation of Neogene is the principal heat reservoir and exploitation bed, followed by Qingshuiying Formation of Palaeogene and Ganhegou Formation of Neogene. The result shows that using MT method can well delineate the range of deep geothermal reservoir in the Yinchuan Basin and that MT method is suitable for exploring buried geothermal resources in deep plain.
|
|
Received: 08 October 2018
Published: 15 August 2019
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Bo-Wen XU
E-mail: 15222699756@163.com
|
|
|
|
|
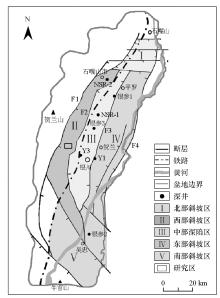
Present-day structural framework of the Yinchuan basin
|
|
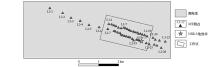
MT stations along the profil from L1 and L2 profiles
|
|
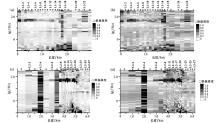
Two-dimensional deviation degree pseudo-section of L1 and L2 lines
a—L1 line Swift skewness;b—L1 line Bahr skewness; c—L2 line Swift skewness;d—L2 line Bahr skewness
|

|
Rose diagram showing analysis result of L1 , L2 lines electrical principal axes
|
|
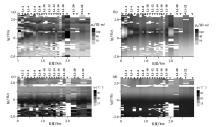
Comparison of resistivity section and phase section before and after L1 profile inversion
a—measured apparent resistivity;b—predicted resistivity;c—measured impedance phase;d—predicted impedance phase.
|
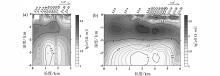
|
Two-dimensional inversion electrical structure model of MT data for L1(a) , L2(b) 〗lines
|
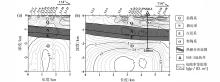
|
Inversion of resistivity Section and its Geological interpretation by L1 (a), L2 (b) lines
|

| 地层 | 层厚/m | 底深/m | 主要岩性 | 划分依据 | | 第四系 | 910 | 910 | 深灰色砾岩、砂砾岩、含砾砂岩、粗砂岩、细砂岩夹粉砂质泥岩、泥灰岩,泥灰岩中含有贝壳化石 | 沉积物结构疏松,胶结程度差,钻进速率快 | | 新近系 | 干河
沟组 | 324 | 1234 | 深灰色、灰白色、土黄色砾岩、含砾粗砂岩、中-粗砂岩夹少量泥质粉砂岩 | 钻遇干河沟组顶部黄绿色粉砂岩 | 红柳
沟组 | 220 | 1454 | 黄绿色、褐灰色、土黄色砂砾岩与泥质灰岩、粉砂质泥岩互层 | 钻遇红柳沟组顶部深灰色泥质灰岩 | | 古近系 | 清水
营组 | 166 | 1620 | 灰绿色、棕红色、黄褐色泥岩、泥质粉砂岩与灰色砂砾岩不等厚互层 | 钻遇清水营组顶部红褐色泥岩层 | | 奥陶系 | 米钵
山组 | 780 | 2400 | 上部为灰绿色、黄褐色泥质板岩为主,下部为长石石英砂岩为主夹薄层灰岩、角砾岩 | 钻遇米钵山组顶部深灰色板岩,未钻穿 |
|
Stratigraphic system and main lithological distribution revealed by Well NSR-3
|
| [1] |
严烈宏, 王利 . 银川盆地地热系统[M]. 银川: 宁夏人民出版社, 2002.
|
| [1] |
Yan L H, Wang L. Geothermal system in Yinchuan Basin[M]. Yinchuan: Ningxia People’s Publishing House, 2002.
|
| [2] |
高亮, 陈海波, 李向宝 , 等. 综合电磁法在银川盆地地热资源勘查中的应用[J]. 山东理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2013,27(3):62-66.
|
| [2] |
Gao L, Chen H B, Li X B , et al. Application of integrated electromagnetic methods in exploration of geothermal resource in Yinchuan Basin[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Technology:Natural Science Edition, 2013,27(3):62-66.
|
| [3] |
汪琪, 赵志鹏, 尹秉喜 , 等. 电磁测深MT法在平原深部地热调查中的应用[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2016,16(6):782-787.
|
| [3] |
Wang Q, Zhao Z P, Yin B X , et al. The application of Magnetotelluric sounding(MT)method to deep geothermal investigation in plain[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2016,16(6):782-787.
|
| [4] |
Chen L, Booker J R, Jones A G , et al. Electrically conductive crust in Southern Tibet from INDEPTH Magnetotelluric surveying[J]. Science, 1996,274(5293):1694-1696.
|
| [5] |
Wei W B, Unsworth M J, Jones A G , et al. Detection of widespread fluids in the Tibetan crust by magnetotelluric studies[J]. Science, 2001,292(5517):716-719.
|
| [6] |
Unsworth M J, Jones A G, Wei W B , et al. Crustal rheology of the Himalaya and Southern Tibet inferred from magnetotelluric data[J]. Nature, 2005,438(7064):78-81.
|
| [7] |
Tikhonov A N . On determining electrical characteristics of the deep layers of the Earth’s crust[J]. Doklady, 1950,73(2):295-297.
|
| [8] |
Cagniard L . Basic theory of the magneto-telluric method of geophysical prospecting[J]. Geophysics, 1953,18(3):605-635.
|
| [9] |
钟大赉, 丁林 . 青藏高原的隆起过程及其机制探讨[J]. 中国科学( D辑):地球科学, 1996,26(4):289-295.
|
| [9] |
Zhong D L, Ding L . The discussion for the uplifting and the formation mechanism of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Science in China(Series D), 1996,26(4):289-295.
|
| [10] |
赵红格, 刘池洋, 王锋 , 等. 贺兰山隆升时限及其演化[J]. 中国科学( D辑):地球科学, 2007,37(S1):185-192.
|
| [10] |
Zhao H G, Liu H Y, Wang F , et al. Constraints the uplift age and the evolution of the Helan Mountain[J]. Science in China(Series D), 2007,37(S1):185-192.
|
| [11] |
黄兴富, 施炜, 李恒强 , 等. 银川盆地新生代构造演化:来自银川盆地主边界断裂运动学的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 2013,20(4):199-210.
|
| [11] |
Huang X F, Shi W, Li H Q , et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Yinchuan Basin:Constraints from the deformation of its boundary faults[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013,20(4):199-210.
|
| [12] |
侯旭波, 尹克敏, 林中凯 , 等. 银川盆地构造反转及其演化与叠合关系分析[J]. 高校地质学报, 2014,20(2):277-285.
|
| [12] |
Hou X B, Yin K M, Lin Z K , et al. The study of tectonic inversion,evolution,and superposition of Yinchuan Basin[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2014,20(2):277-285.
|
| [13] |
Egbert G D, Booker J R . Robust estimation of geomagnetic transfer functions[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 1986,87(1):173-194.
|
| [14] |
Groom R W, Bailey R C . Decomposition of magnetotelluric impedance tensors in the presence of Local three-Dimensional galvanic distortion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1989,94(B2):1913-1925.
|
| [15] |
Rodi W, Mackie R L . Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2001,66(1):174-187.
|
| [16] |
Chen Q, Li W H, Hao S L , et al. Carbon isotope evidence for Ordovician marine hydrocarbon source rocks in Ordos Basin,North China[J]. Energy Exploration and Exploitation, 2011,29(3):267-289.
|
| [17] |
李文厚, 陈强, 李智超 , 等. 鄂尔多斯地区早古生代岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 2012,14(1):85-100.
|
| [17] |
Li W H, Chen Q, Li Z C , et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Early Paleozoic in Ordos area[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2012,14(1):85-100.
|
| [18] |
郭彦如, 赵振宇, 付金华 , 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶纪层序岩相古地理[J]. 石油学报, 2012,33(2):95-109.
|
| [18] |
Guo Y R, Zhao Z Y, Fu J H , et al. Sequence lithofacies Palaeogeography of the Ordovician in Ordos Basin,China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012,33(2):95-109.
|
| [19] |
马占荣, 白海峰, 刘宝宪 , 等. 鄂尔多斯西部地区中-晚奥陶世克里摩里期-乌拉力克期岩相古地理[J]. 古地理学报, 2013,15(6):751-764.
|
| [19] |
Ma Z R, Bai H F, Liu B X , et al. Lithofacies palaeogeography of the Middle-Late Ordovician Kelimoli and Wulalike Ages in western Ordos area[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2013,15(6):751-764.
|
| [20] |
宁夏回族自治区地质矿产局. 宁夏回族自治区岩石地层[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1996.
|
| [20] |
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Ninxia Hui Autonomous region. Stratigraphy (Lithostratic) of Ningxia Hui Autonomous region[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1996.
|
| [1] |
CHEN Da-Lei, WANG Run-Sheng, HE Chun-Yan, WANG Xun, YIN Zhao-Kai, YU Jia-Bin. Application of integrated geophysical exploration in deep spatial structures: A case study of Jiaodong gold ore concentration area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 70-77. |
| [2] |
WANG Jia-Long, DI Bing-Ye, ZHANG Bao-Song, ZHAO Dong-Dong. The application of audio frequency magnetotelluric method to the geothermal exploration: A case study of Huangniqiao area, Ninghua County, Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 576-582. |
|
|
|
|

