|
|
|
| Genetic analysis of dolomites in the Sinian Dengying Formation on the periphery of the Huangling anticline, western Hubei Province |
LI Hao-Han1,2( ), ZHANG Cong1,2( ), ZHANG Cong1,2( ), LI Wen-Zheng3,4, ZHANG Chun-He1,2, ZHANG Yuan1,2, WANG Zi1,2, CHEN Wei-Kun1,2, FANG Rong-Hui1,2 ), LI Wen-Zheng3,4, ZHANG Chun-He1,2, ZHANG Yuan1,2, WANG Zi1,2, CHEN Wei-Kun1,2, FANG Rong-Hui1,2 |
1. Oil and Gas Survey, China Geological Survey, Beijing 100083, China
2. State Key Laboratory of Continental Shale Oil, Daqing 163712, China
3. Hangzhou Research Institute of Geology, PetroChina, Hangzhou 310023, China
4. Key Laboratory of Carbonate Reservoirs, China National Petroleum Corporation, Hangzhou 310023, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract A suite of dolomite-dominated carbonate reservoirs is developed in the Sinian Dengying Formation in the Huangling anticline in the eastern part of the intracratonic rift, western Hubei Province. Investigating the formation environment and genetic mechanism of dolomites is crucial for determining the developmental mechanism of carbonate reservoirs and facilitating conventional oil and gas exploration in the study area. This study employed various analytical techniques, including cast thin sections, cathodoluminescence thin sections, field emission scanning electron microscopy, carbon and oxygen isotope analyses of carbonate rocks, major and trace element analyses, whole-rock mineral analyses, and determination of the degree of order of dolomite. Using these techniques, this study analyzed the chemical composition and mineralogical characteristics of dolomites from the Dengying Formation on the periphery of the Huangling anticline. Furthermore, this study explored the formation environment, developmental mechanism, and modification process of dolomites. The results indicate that the dolomites from the Dengying Formation contained the same proportions of CaO and MgO molecules and low Sr content, aligning with the characteristics of penecontemporaneous dolomites. The analytical results of trace elements and carbon and oxygen isotopes confirm that the dolomites formed in a marine environment with low Fe and Mn contents. The average paleoseawater salinity (Z) of 128.41, average temperature of 21.32 ℃, and average diagenetic temperature of 49.36 ℃ created the favorable environmental conditions for forming penecontemporaneous dolomites. Additionally, the dolomite from the Dengying Formation exhibited significantly lower δ18O compared to the Dengyingian seawater, degrees of order ranging from 0.61 to 0.99, and a peak frequency distribution between 0.8 and 0.9, indicating that the dolomite experienced a progressively deepening burial modification process. The whole-rock mineral analyses reveal that the content of dolomite was positively correlated with its degree of order, suggesting that a high degree of dolomitization corresponded to a higher degree of order during burial modification. Therefore, this study holds that dolomites in the Dengying Formation were originally formed by penecontemporaneous dolomite. Through prolonged burial modification, micritic dolomite with a low degree of order experienced recrystallization, gradually transitioning into very finely crystalline/finely crystalline dolomite, accompanied by an elevated degree of order. Ultimately, dolomites of a penecontemporaneous-burial modification origin formed in the study area.
|
|
Received: 16 August 2024
Published: 07 August 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
14])
">
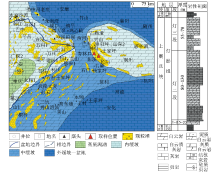
|
Lithofacies palaeogeographic map and stratigraphy of Dengying Formation in study area (modified from Li et al.[14])
|
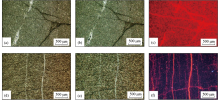
|
Thin-section characteristics of dolomite lithofacies in Dengying Formation
a—micropohograph of sample No.QLK-23 under plane polarized light; b—micropohograph of sample No.QLK-23 under perpendicular polarized ligh; c—micropohograph of sample No.QLK-23 under cathode light; d—micropohograph of sample No.QLK-11 under plane polarized light; e—micropohograph of sample No.QLK-11 under perpendicular polarized ligh; f—micropohograph of sample No.QLK-11 under cathode light
|
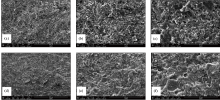
|
Scanning electron microscope photo of dolomite in Dengying Formation
a—full view of Sample QLK-23 reveals euhedral calcite crystals with well-developed intercrystalline pores (×500); b—enlarged view of part (a) shows euhedral calcite crystals, predominantly rhombic dodecahedra, with well-developed intercrystalline pores (×1000); c—further enlargement of part (b) exhibits the presence of well-developed intercrystalline pores in calcite (×2000); d—full view of Sample QLK-11 displays euhedral calcite crystals with well-developed intercrystalline pores (×500); e—enlarged view of part (d) depicts euhedral calcite crystals, mainly rhombic dodecahedra, with well-developed intercrystalline pores (×1000); f—further enlargement of part (e) showcases the existence of well-developed intercrystalline pores in calcite at a higher magnification level(×2000)
|

序
号 | 样品编号 | 岩性 | 微量元素含量/10-6 | 主量元素含量/% | 碳氧同位素 | Sr
光谱 | Sr
质谱 | Mn | Fe | w(Fe)/
w(Mn) | w(Mn)/
w(Sr) | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | MgO | δC13/
PDB,‰ | δO18/
PDB,‰ | 古盐度指
标(Z) | 古海水温
度T/℃ | 成岩温
度T/℃ | | 1 | QLK-01 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 61.94 | 86.6 | 97.70 | 357.78 | 3.66 | 1.13 | 0.50 | 0.18 | 32.37 | 23.08 | -2.29 | -6.55 | 119.35 | 17.96 | 45.57 | | 2 | QLK-02 | 纹层状泥质泥晶白云岩 | 149.91 | 99.5 | 94.20 | 5374.44 | 57.05 | 0.95 | 6.82 | 1.81 | 27.51 | 20.80 | 1.89 | -7.45 | 127.46 | 21.9 | 50.19 | | 3 | QLK-03 | 粉—泥晶硅质灰岩 | 479.53 | 43 | 190.10 | 62.22 | 0.33 | 4.42 | 13.29 | 0.06 | 26.33 | 20.03 | 3.54 | -5.45 | 131.84 | 13.42 | 40 | | 4 | QLK-04 | 粒屑粉—泥晶灰岩 | 2683.77 | 1361 | 34.20 | / | 0.00 | 0.03 | 1.52 | 0.05 | 53.66 | 1.48 | 2.65 | -6.3 | 129.59 | 16.9 | 44.29 | | 5 | QLK-05 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 2462.38 | 77.1 | 169.90 | 147.78 | 0.87 | 2.20 | 0.68 | 0.10 | 32.57 | 23.07 | 3.83 | -6.65 | 131.83 | 18.39 | 46.08 | | 6 | QLK-06 | 细晶含灰白云岩 | 1994.75 | 67.1 | 216.80 | 132.22 | 0.61 | 3.23 | 0.72 | 0.09 | 32.64 | 22.74 | 5.03 | -5.39 | 134.92 | 13.19 | 39.7 | | 7 | QLK-07 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 1090.57 | 90.5 | 166.90 | 482.22 | 2.89 | 1.84 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 32.68 | 20.55 | 3.89 | -6.56 | 132 | 18 | 45.62 | | 8 | QLK-08 | 粉—细晶白云岩 | 2573.67 | 63.2 | 144.10 | 4106.67 | 28.50 | 2.28 | 5.58 | 1.58 | 27.91 | 18.56 | 3.81 | -5.99 | 132.12 | 15.61 | 42.72 | | 9 | QLK-09 | 粉—细晶白云岩 | 1620.55 | 1528.4 | / | 38.89 | / | / | 0.45 | 0.08 | 54.03 | 1.38 | 3.77 | -5.27 | 132.4 | 12.71 | 39.1 | | 10 | QLK-10 | 泥—粉晶云质灰岩 | 984.39 | 397.6 | 2.50 | 15.56 | 6.22 | 0.01 | 3.77 | 0.15 | 50.88 | 1.63 | 1.61 | -8.22 | 126.5 | 25.44 | 54.2 | | 11 | QLK-11 | 粉—细晶灰质白云岩 | 1463.82 | 1149.4 | 19.40 | / | 0.00 | 0.02 | 2.23 | 0.08 | 54.13 | 0.63 | 3.68 | -6.07 | 131.81 | 15.94 | 43.12 | | 12 | QLK-12 | 粉—细晶灰质白云岩 | 664.52 | 73.9 | 139.80 | 70.00 | 0.50 | 1.89 | 4.43 | 0.16 | 30.83 | 22.19 | 2.82 | -7.95 | 129.12 | 24.18 | 52.79 | | 13 | QLK-13 | 粉—细晶白云质灰岩 | 1192.04 | 117.3 | 116.80 | 2107.78 | 18.05 | 1.00 | 1.28 | 0.34 | 32.33 | 19.40 | 3.07 | -7.08 | 130.06 | 20.26 | 48.28 | | 14 | QLK-14 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 1308.22 | 684.5 | 337.10 | 124.44 | 0.37 | 0.49 | 2.51 | 0.21 | 39.91 | 14.44 | 1.03 | -9.78 | 124.54 | 33.09 | 62.47 | | 15 | QLK-15 | 粉—细晶云质灰岩 | 861.54 | 2027.9 | 10.70 | 7.78 | 0.73 | 0.01 | 17.43 | 0.16 | 40.02 | 1.73 | 1.31 | -9.7 | 125.15 | 32.68 | 62.04 | | 16 | QLK-16 | 粉晶含灰白云岩 | 1702.04 | 36.6 | 68.40 | 31.11 | 0.45 | 1.87 | 0.16 | 0.05 | 32.54 | 23.31 | 2.93 | -6.95 | 129.84 | 19.68 | 47.61 | | 17 | QLK-17 | 粉—细晶白云岩 | 2327.16 | 2073.7 | 12.70 | 140.00 | 11.02 | 0.01 | 1.79 | 0.14 | 51.02 | 3.33 | 3.53 | -6.08 | 131.5 | 15.98 | 43.18 | | 18 | QLK-18 | 粉晶白云岩 | 1841.99 | 64.3 | 87.50 | 248.89 | 2.84 | 1.36 | 0.13 | 0.06 | 32.92 | 22.77 | 2.95 | -6.81 | 129.95 | 19.08 | 46.89 | | 19 | QLK-19 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 62.49 | 1687.1 | 19.50 | 7.78 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 14.35 | 0.11 | 41.48 | 2.47 | 2.48 | -7.81 | 128.49 | 23.54 | 52.06 | | 20 | QLK-20 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 57.44 | 95.8 | 99.90 | 132.22 | 1.32 | 1.04 | 0.31 | 0.16 | 33.45 | 22.37 | 1.23 | -8.04 | 125.82 | 24.6 | 53.26 | | 21 | QLK-21 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 63.87 | 857.5 | 204.50 | 4876.67 | 23.85 | 0.24 | 16.56 | 2.99 | 32.59 | 4.55 | 2.16 | -7.86 | 127.81 | 23.77 | 52.32 | | 22 | QLK-22 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 81.86 | 1029.4 | 106.40 | 1796.67 | 16.89 | 0.10 | 6.73 | 1.03 | 45.38 | 2.38 | 2.35 | -7.8 | 128.23 | 23.49 | 52.01 | | 23 | QLK-23 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 60.23 | 173.1 | 154.50 | 248.89 | 1.61 | 0.89 | 1.23 | 0.21 | 32.77 | 22.10 | 0.87 | -7.57 | 125.31 | 22.44 | 50.81 | | 24 | QLK-24 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 102.88 | 73.9 | 101.40 | 256.67 | 2.53 | 1.37 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 32.74 | 23.12 | 1.18 | -7.04 | 126.21 | 20.08 | 48.08 | | 25 | YX-01 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 54.88 | 100.1 | 207.80 | 7.78 | 0.04 | 2.08 | 0.75 | 0.06 | 32.89 | 22.87 | 3.35 | -6.25 | 131.05 | 16.69 | 44.04 | | 26 | YX-02 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 42.51 | 936.3 | 24.50 | 116.67 | 4.76 | 0.03 | 2.41 | 0.14 | 52.39 | 1.25 | 1.97 | -6.85 | 127.92 | 19.25 | 47.1 | | 27 | YX-03 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 87.58 | 283.7 | 7.10 | / | 0.00 | 0.03 | 1.24 | 0.05 | 54.06 | 1.28 | 1.55 | -4.17 | 128.4 | 8.54 | 33.64 | | 28 | YX-04 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 82.75 | 92.1 | 76.70 | 132.22 | 1.72 | 0.83 | 0.67 | 0.10 | 32.61 | 23.06 | 1.95 | -8.34 | 127.14 | 26.01 | 54.83 | | 29 | YX-05 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 64.72 | 46.4 | 178.70 | 85.56 | 0.48 | 3.85 | 25.64 | 0.06 | 20.82 | 17.36 | -1.28 | -8.6 | 120.4 | 27.25 | 56.2 | | 30 | YX-06 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 57.01 | 39.1 | 140.90 | 225.56 | 1.60 | 3.60 | 0.29 | 0.06 | 32.36 | 23.23 | 1.96 | -8.06 | 127.3 | 24.69 | 53.36 | | 31 | YX-07 | 粉—泥晶含硅白云岩 | 37.75 | 49.2 | 256.60 | 70.00 | 0.27 | 5.22 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 32.56 | 22.62 | / | / | / | / | / | | 32 | YX-08 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 36.41 | 82.8 | 73.10 | 342.22 | 4.68 | 0.88 | 29.55 | 0.12 | 19.56 | 16.47 | 3 | -8.83 | 129.05 | 28.36 | 57.41 | | 33 | YX-09 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 43.43 | 79.2 | 154.20 | 85.56 | 0.55 | 1.95 | 1.09 | 0.05 | 32.08 | 22.28 | 2.65 | -8.41 | 128.54 | 26.34 | 55.2 | | 34 | YX-10 | 泥—粉晶白云岩 | 61.82 | 1128.6 | 12.20 | 303.33 | 24.86 | 0.01 | 24.17 | 0.24 | 31.96 | 4.81 | 3.38 | -7.98 | 130.25 | 24.32 | 52.95 | | 35 | YX-11 | 粉—泥晶白云岩 | 67.23 | 76.2 | 201.30 | 70.00 | 0.35 | 2.64 | 8.10 | 0.08 | 28.51 | 21.23 | 1.74 | -8.1 | 126.83 | 24.88 | 53.57 | | 36 | YX-12 | 粒屑粉—泥晶白云岩 | 71.48 | 1354.8 | 0.80 | 85.56 | 106.94 | 0.00 | 6.29 | 0.12 | 46.72 | 3.24 | 2.29 | -7.72 | 128.15 | 23.13 | 51.59 | | 37 | YX-13 | 含粒屑粉—泥晶白云岩 | 32.58 | 787.3 | 55.90 | 93.33 | 1.67 | 0.07 | 0.95 | 0.11 | 54.04 | 1.37 | 0.73 | -7.31 | 125.15 | 21.27 | 49.47 | | 38 | YX-14 | 粉—细晶白云岩 | 79.11 | 9.5 | 9.50 | 202.22 | 21.29 | 1.00 | 3.76 | 0.21 | 50.34 | 1.78 | 2.91 | -8.27 | 129.14 | 25.68 | 54.46 |
|
Data of major elements, trace elements and carbon and oxygen isotopes of Youxi and Qinglinkou profiles in the western Hubei region
|

序
号 | 样品
编号 | 矿物含量/% | 白云石
有序度 | | 方解石 | 白云石 | 石英 | 钾长石 | 斜长石 | | 1 | QLK-01 | 14 | 86 | / | / | / | 0.67 | | 2 | QLK-02 | / | 68 | 24 | 8 | / | 0.61 | | 3 | QLK-03 | / | 99 | 1 | / | / | 0.99 | | 4 | QLK-04 | 3 | 90 | 5 | / | 2 | / | | 5 | QLK-05 | / | 99 | / | / | 1 | / | | 6 | QLK-06 | 10 | 86 | 4 | / | / | / | | 7 | QLK-07 | / | 90 | 10 | / | / | 0.82 | | 8 | QLK-08 | / | 87 | 13 | / | / | 0.74 | | 9 | QLK-09 | 17 | 83 | / | / | / | 0.74 | | 10 | QLK-10 | / | 97 | / | 2 | 1 | / | | 11 | QLK-11 | 6 | 93 | / | / | 1 | / | | 12 | QLK-12 | / | 86 | 11 | 3 | / | 0.57 | | 13 | QLK-13 | / | 93 | / | 7 | / | / | | 14 | QLK-14 | 14 | 86 | / | / | / | 0.76 | | 15 | QLK-15 | / | 85 | / | 15 | / | 0.77 | | 16 | QLK-16 | / | 96 | 4 | / | / | / | | 17 | QLK-17 | / | 89 | 11 | / | / | / | | 18 | QLK-18 | / | 85 | 10 | / | 5 | / | | 19 | QLK-19 | / | 85 | 15 | / | / | 0.82 | | 20 | QLK-20 | / | 92 | / | 8 | / | 0.78 | | 21 | QLK-21 | / | 98 | / | 1 | 1 | 0.9 | | 22 | QLK-22 | / | 96 | 4 | / | / | 0.85 | | 23 | QLK-23 | / | 93 | 6 | 1 | / | 0.81 | | 24 | QLK-24 | / | 95 | 4 | 1 | / | 0.85 | | 25 | YX-01 | / | 100 | / | / | / | 0.9 | | 26 | YX-02 | / | 99 | 1 | / | / | 0.96 | | 27 | YX-03 | / | 89 | 1 | / | 10 | / | | 28 | YX-04 | / | 96 | 4 | / | / | 0.85 | | 29 | YX-05 | / | 96 | 2 | 2 | / | 0.83 | | 30 | YX-06 | 2 | 93 | / | 5 | / | 0.8 | | 31 | YX-07 | / | 90 | 10 | / | / | 0.84 | | 32 | YX-08 | 6 | 80 | 10 | 4 | / | 0.79 | | 33 | YX-09 | / | 91 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0.82 | | 34 | YX-10 | / | 94 | 5 | 1 | / | 0.83 | | 35 | YX-11 | / | 94 | / | 5 | 1 | 0.84 | | 36 | YX-12 | / | 93 | 2 | 5 | / | 0.88 | | 37 | YX-13 | / | 99 | / | 1 | / | 0.97 | | 38 | YX-14 | / | 100 | / | / | / | 0.94 |
|
Mineral content and dolomite ordering data
|
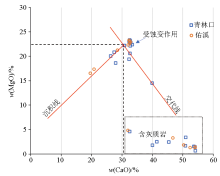
|
Relationship between CaO and MgO contents
|
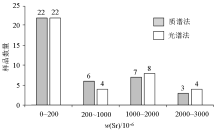
|
Histogram of Sr elemental content distribution
|
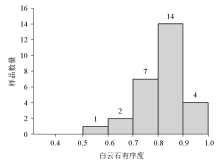
|
Histogram of dolomite orderliness distribution(n=28)
|
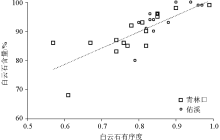
|
Relationship between dolomite content and dolomite orderliness
|
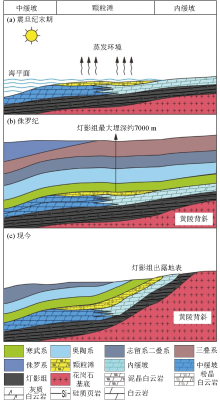
|
Genetic model of dolomite in the Sinian Dengying Formation on the periphery of Huangling anticline
a—under the environment of high-salinity seawater under intense evaporation conditions during the Sinian Dengying Stage, dolomite rapidly crystallized to form micritic dolomite with a low degree of order;b—at the end of the Jurassic, the burial depth of the Dengying Formation reached its maximum, the dolomite underwent deep burial transformation and recrystallization to form silt-crystalline dolomite with a high degree of order;c—during the uplifting process, the Dengying Formation was exposed on the earth's surface and underwent transformation
|
| [1] |
杜金虎, 邹才能, 徐春春, 等. 川中古隆起龙王庙组特大型气田战略发现与理论技术创新[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3):268-277.
|
| [1] |
Du J H, Zou C N, Xu C C, et al. Theoretical and technical innovations in strategic discovery of a giant gas field in Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation of central Sichuan paleo-uplift,Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3):268-277.
|
| [2] |
邹才能, 杜金虎, 徐春春, 等. 四川盆地震旦系—寒武系特大型气田形成分布、资源潜力及勘探发现[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3):278-293.
|
| [2] |
Zou C N, Du J H, Xu C C, et al. Formation, distribution,resource potential and discovery of the Sinian-Cambrian giant gas field,Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3):278-293.
|
| [3] |
晋达, 杜浩坤, 孟凡冰, 等. 普光地区长兴组生物礁储层分布预测[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(1):50-58.
|
| [3] |
Jin D, Du H K, Meng F B, et al. The prediction of reef reservoir distribution in Changxing Formation of Puguang area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1):50-58.
|
| [4] |
李忠权, 刘记, 李应, 等. 四川盆地震旦系威远—安岳拉张侵蚀槽特征及形成演化[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2015, 42(1):26-33.
|
| [4] |
Li Z Q, Liu J, Li Y, et al. Formation and evolution of Weiyuan-Anyue extension-erosion groove in Sinian system,Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(1):26-33.
|
| [5] |
李双建, 高平, 黄博宇, 等. 四川盆地绵阳—长宁凹槽构造演化的沉积约束[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2018, 39(5):889-898.
|
| [5] |
Li S J, Gao P, Huang B Y, et al. Sedimentary constraints on the tectonic evolution of Mianyang-Changning trough in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2018, 39(5):889-898.
|
| [6] |
汪泽成, 赵文智, 胡素云, 等. 克拉通盆地构造分异对大油气田形成的控制作用——以四川盆地震旦系—三叠系为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(1):9-23.
|
| [6] |
Wang Z C, Zhao W Z, Hu S Y, et al. Control of tectonic differentiation on the formation of large oil and gas fields in craton basins:A case study of Sinian-Triassic of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(1):9-23.
|
| [7] |
赵文智, 魏国齐, 杨威, 等. 四川盆地万源—达州克拉通内裂陷的发现及勘探意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(5):659-669.
|
| [7] |
Zhao W Z, Wei G Q, Yang W, et al. Discovery of Wanyuan-Dazhou intracratonic rift and its exploration significance in the Sichuan basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(5):659-669.
|
| [8] |
李茜, 朱光有, 张志遥. 超深层白云岩成因与规模储层控制因素——以四川盆地震旦系灯影组和寒武系龙王庙组为例[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2024, 54(7):2389-2418.
|
| [8] |
Li X, Zhu G Y, Zhang Z Y. Genesis of ultra-deep dolostone and controlling factors of large-scale reservoir:A case study of the Sinian Dengying Formation and the Cambrian Longwangmiao Formation in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Scientia Sinica:Terrae, 2024, 54(7):2389-2418.
|
| [9] |
唐军, 刘沁园, 赖强, 等. 白云岩声电各向异性实验测量及分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(6):1492-1499.
|
| [9] |
Tang J, Liu Q Y, Lai Q, et al. Experimental measurement and analysis of the acoustic-electrical anisotropy of dolomites[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6):1492-1499.
|
| [10] |
王坤, 王铜山, 汪泽成, 等. 华北克拉通南缘长城系裂谷特征与油气地质条件[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(5):504-517.
|
| [10] |
Wang K, Wang T S, Wang Z C, et al. Characteristics and hydrocarbon geological conditions of the Changchengian rifts in the southern North China Craton[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(5):504-517.
|
| [11] |
谭秀成, 何如意, 杨文杰, 等. 四川盆地武胜—潼南地区中二叠统茅口组二段下亚段白云岩薄储层成因及分布模式[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2025, 52(1):1-16.
|
| [11] |
Tan X C, He R Y, Yang W J, et al. Origin and distribution model of thin dolomite reservoir in the lower sub-member of Mao 2 member of middle Permian Maokou Formation in Wusheng-Tongnan area,Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2025, 52(1):1-16.
|
| [12] |
许文龙, 袁海锋, 肖钦仁, 等. 川西地区中二叠统栖霞组白云岩成因——以江油通口栖霞组剖面为例[J/OL]. 天然气地球科学,1-31[2025-02-17].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20241220.1608.004.html.
|
| [12] |
Xu W L, Yuan H F, Xiao Q R, et al. Genesis of dolomites of the Middle Permian Qixia Formation in western Sichuan Basin:A case study of the Qixia Formation section of Tongkou,Jiangyou[J/OL]. Natural Gas Geoscience,1-31 [2025-02-17].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/62.1177.TE.20241220.1608.004.html.
|
| [13] |
汪泽成, 刘静江, 姜华, 等. 中—上扬子地区震旦纪陡山沱组沉积期岩相古地理及勘探意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1):39-51.
|
| [13] |
Wang Z C, Liu J J, Jiang H, et al. Lithofacies paleogeography and exploration significance of Sinian Doushantuo depositional stage in the middle-Upper Yangtze region,Sichuan Basin,SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1):39-51.
|
| [14] |
李文正, 张建勇, 李浩涵, 等. 鄂西—渝东地区克拉通内裂陷分布特征及油气勘探意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(5):675-685.
|
| [14] |
Li W Z, Zhang J Y, Li H H, et al. Distribution characteristics of intracratonic rift and its exploration significance in western Hubei and eastern Chongqing area[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(5):675-685.
|
| [15] |
翟刚毅, 包书景, 王玉芳, 等. 古隆起边缘成藏模式与湖北宜昌页岩气重大发现[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(4):441-447.
|
| [15] |
Zhai G Y, Bao S J, Wang Y F, et al. Reservoir accumulation model at the edge of Palaeohigh and significant discovery of shale gas in Yichang area,Hubei Province[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(4):441-447.
|
| [16] |
翟刚毅, 包书景, 庞飞, 等. 武陵山复杂构造区古生界海相油气实现重大突破[J]. 地球学报, 2016, 37(6):657-662,795.
|
| [16] |
Zhai G Y, Bao S J, Pang F, et al. Breakthrough of the natural gas of Paleozoic marine strata in Wuling Mountain complex tectonic zone[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2016, 37(6):657-662,795.
|
| [17] |
陈科, 翟刚毅, 包书景, 等. 华南黄陵隆起构造演化及其对页岩气保存的控制作用[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(1):161-172.
|
| [17] |
Chen K, Zhai G Y, Bao S J, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Huangling uplift and its control effect on shale gas preservation in South China[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(1):161-172.
|
| [18] |
李浩涵, 陈科, 包书景, 等. 鄂西黄陵背斜南翼震旦系陡山沱组有利目标区页岩气资源潜力评价[J]. 石油实验地质, 2019, 41(1):31-37.
|
| [18] |
Li H H, Chen K, Bao S J, et al. Evaluation of shale gas resources of the Sinian Doushantuo Formation in the southern Huangling anticline,western Hubei Province[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2019, 41(1):31-37.
|
| [19] |
李浩涵, 宋腾, 陈科, 等. 鄂西地区(秭地2井)震旦纪地层发现页岩气[J]. 中国地质, 2017, 44(4):812-813.
|
| [19] |
Li H H, Song T, Chen K, et al. The discovery of shale gas from Sinian Formation at ZD-2 well in western Hubei[J]. Geology in China, 2017, 44(4):812-813.
|
| [20] |
王宗哲, 杨杰东, 孙卫国. 扬子地台震旦纪海水碳同位素的变化[J]. 高校地质学报, 1996, 2(1):112-120.
|
| [20] |
Wang Z Z, Yang J D, Sun W G. Carbon isotope record of sinian seawater in Yangtze platform[J]. Geological Journal of Universitiesf, 1996, 2(1):112-120.
|
| [21] |
Kaufman A J, Knoll A H. Neoproterozoic variations in the C-isotopic composition of seawater:Stratigraphic and biogeochemical implications[J]. Precambrian Research, 1995, 73(1-4):27-49.
|
| [22] |
Kaufman A J, Jacobsen S B, Knoll A H. The Vendian record of Sr and C isotopic variations in seawater:Implications for tectonics and paleoclimate[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1993, 120(3-4):409-430.
|
| [23] |
钟倩倩, 黄思静, 邹明亮, 等. 碳酸盐岩中白云石有序度的控制因素——来自塔河下古生界和川东北三叠系的研究[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2009, 21(3):50-55.
|
| [23] |
Zhong Q Q, Huang S J, Zou M L, et al. Controlling factors of order degree of dolomite in carbonate rocks:A case study from Lower Paleozoic in Tahe Oilfield and Triassic in northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2009, 21(3):50-55.
|
| [24] |
黄思静, Qing H R, 胡作维, 等. 封闭系统中的白云石化作用及其石油地质学和矿床学意义——以四川盆地东北部三叠系飞仙关组碳酸盐岩为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(11):2955-2962.
|
| [24] |
Huang S J, Qing H R, Hu Z W, et al. Closed-system dolomitization and the significance for petroleum and economic geology:An example from Feixianguan carbonates,Triassic NE Sichuan basin of China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(11):2955-2962.
|
| [25] |
方少仙, 侯方浩, 董兆雄. 上震旦统灯影组中非叠层石生态系兰细菌白云岩[J]. 沉积学报, 2003, 21(1):96-105.
|
| [25] |
Fang S X, Hou F H, Dong Z X. Non-stromatoltite ecologic system cyanobacteria dolostone in dengying formation of upper-sinian[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2003, 21(1):96-105.
|
| [26] |
孙健, 董兆雄, 郑琴. 白云岩成因的研究现状及相关发展趋势[J]. 海相油气地质, 2005, 10(3):25-30.
|
| [26] |
Sun J, Dong Z X, Zheng Q. Study actuality and trend on origin of dolostone[J]. Marine Origin Petoleum Geology, 2005, 10(3):25-30.
|
| [27] |
何勇, 刘波, 刘红光, 等. 塔里木盆地西北缘通古孜布隆剖面下奥陶统蓬莱坝组白云石化流体来源及白云岩成因分析[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2018, 54(4):781-791.
|
| [27] |
He Y, Liu B, Liu H G, et al. Origin of Mg-rich-fluids and dolomitization of lower Ordovician penglaiba formation at tongguzibulong outcrop in the northwestern margin of Tarim basin[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 2018, 54(4):781-791.
|
| [28] |
郑剑锋, 沈安江, 刘永福, 等. 塔里木盆地寒武—奥陶系白云岩成因及分布规律[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2011, 32(6):600-604.
|
| [28] |
Zheng J F, Shen A J, Liu Y F, et al. Genesis and distribution of the Cambro-Ordovician dolomite in Tarim Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2011, 32(6):600-604.
|
| [29] |
陈永权, 周新源, 赵葵东, 等. 塔里木盆地中寒武统泥晶白云岩红层的地球化学特征与成因探讨[J]. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14(4):583-592.
|
| [29] |
Chen Y Q, Zhou X Y, Zhao K D, et al. Geochemical research on middle Cambrian red dolostones in Tarim Basin:Implications for dolostone genesis[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2008, 14(4):583-592.
|
| [30] |
黄思静, 李小宁, 兰叶芳, 等. 海水胶结作用对碳酸盐岩石组构的影响:以四川盆地东北部三叠系飞仙关组为例[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 44(12):5007-5018.
|
| [30] |
Huang S J, Li X N, Lan Y F, et al. Influences of marine cementation on carbonate textures:A case of Feixianguan carbonates of Triassic,NE Sichuan Basin[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2013, 44(12):5007-5018.
|
| [31] |
何莹, 鲍志东, 沈安江, 等. 塔里木盆地牙哈—英买力地区寒武系—下奥陶统白云岩形成机理[J]. 沉积学报, 2006, 24(6) :806-818.
|
| [31] |
He Y, Bao Z D, Shen A J, et al. The Genetic Mechanism of Dolostones of the Cambrian-Lower Ordovician in Yaha-Yingmaili Region,Tarim Basin:Dolomitization through deep buried hydrothermal fluid[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2006, 24(6):806-818.
|
| [32] |
李文正, 张建勇, 郝毅, 等. 川东南地区洗象池组碳氧同位素特征、古海洋环境及其与储集层的关系[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(2):487-500.
|
| [32] |
Li W Z, Zhang J Y, Hao Y, et al. Characteristics of carbon and oxygen isotopic,paleoceanographic environment and their relationship with reservoirs of the Xixiangchi Formation,southeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(2):487-500.
|
| [33] |
贺训云, 寿建峰, 沈安江, 等. 白云岩地球化学特征及成因:以鄂尔多斯盆地靖西马五段中组合为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3) :375-384.
|
| [33] |
He X Y, Shou J F, Shen A J, et al. Geochemical characteristics and origin of dolomite:A case study from the middle assemblage of Majiagou Formation Member 5 of the west of Jingbian gas field,Ordos Basin,North China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3) :375-384.
|
| [34] |
韩林. 白云岩成因分类的研究现状及相关发展趋势[J]. 中国西部油气地质, 2006, 2(4):50-56.
|
| [34] |
Han L. Research status and related development trends of genetic classification of dolomite[J]. West China Petroleum Geosciences, 2006, 2(4):50-56.
|
| [35] |
赵俊兴, 陈洪德, 张锦泉, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地中部马五段白云岩成因机理研究[J]. 石油学报, 2005, 26(5):38-41,47.
|
| [35] |
Zhao J X, Chen H D, Zhang J Q, et al. Genesis of dolomite in the fifth member of Majiagou Formation in the middle Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26(5):38-41,47.
|
| [36] |
强子同. 碳酸盐岩储层地质学[M]. 东营: 石油大学出版社,1998.
|
| [36] |
Qiang Z T. Carbonate reservoir geology[M]. Dongying: China University of Petroleum Press,1998.
|
| [37] |
Allan J R, Wiggins W D. Dolomite reservoirs:Geochemical techniques for evaluating origin and distribution[M]. Tulsa: AAPG,1996:36-129.
|
| [38] |
曾理, 万茂霞, 彭英. 白云石有序度及其在石油地质中的应用[J]. 天然气勘探与开发, 2004, 27(4):64-66,72-85.
|
| [38] |
Zeng L, Wan M X, Peng Y. Dolomite sequentiality and its application to petroleum geology[J]. Natural Cas Exploraiton & Development, 2004, 27(4):64-66,72-85.
|
| [39] |
胡俊杰, 李琦, 陈若瑜, 等. 羌塘盆地中、下二叠统碳酸盐岩白云石有序度控制因素研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2014, 34(2):91-95.
|
| [39] |
Hu J J, Li Q, Chen R Y, et al. Research on the controlling factors of order degree of dolomite in carbonate rocks of middle and Lower Permian series in Qiangtang Basin[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2014, 34(2):91-95.
|
| [40] |
张杰, Brian Jones, 张建勇. 不同埋藏深度交代白云石晶体结构及其对白云岩储层研究的意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(3):21-28.
|
| [40] |
Zhang J, Jones B, Zhang J Y. Crystal structure of replacement dolomite with different buried depths and its significance to study of dolomite reservoir[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(3):21-28.
|
| [41] |
翟刚毅, 王玉芳, 刘国恒, 等. 鄂西地区震旦系—寒武系页岩气成藏模式[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(5):696-713.
|
| [41] |
Zhai G Y, Wang Y F, Liu G H, et al. Accumulation model of the Sinian-Cambrian shale gas in western Hubei Province,China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(5):696-713.
|
| [1] |
TIAN Liao-Dong, LONG Deng-Hong, YANG Tao, LIU Hai, MA Min-Xiong, JIANG Hong-Ying. Extracting geological mineral information from regional geochemical exploration data: A case study of the Gaoqiao area in Huixian County, Gansu Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(4): 768-777. |
| [2] |
CHAI Chen-Hui, QIN Yue-Qiang, LI Peng-Yuan, XIN Kai, WANG Jian-Min, YIN Jia-Le, LI Chao-Qun, YUAN Ning-Bo, GUO Dong, SUN Yu-Fei. Soil geochemical characteristics and prospecting orientations in the Bishan area, Xianghuang Banner, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(4): 778-789. |
|
|
|
|

