|
|
|
| Selenium background values and their responses to soil factors along the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau |
MA Qiang1,2( ), QIANG Xiao-Nong3( ), QIANG Xiao-Nong3( ), WU Jin-Hong1, DAI Lu1,2, HE Lian-Zhen1,2, WANG Shuai1,2, MA Nan1,2 ), WU Jin-Hong1, DAI Lu1,2, HE Lian-Zhen1,2, WANG Shuai1,2, MA Nan1,2 |
1. The Fifth Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province, Xining 810099, China
2. Engineering Technology Research Center for Selenium-rich Resource Utilization of Qinghai Province, Xining 810099, China
3. Haixi Prefecture Natural Resources Comprehensive Survey Center, Delingha 817099, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study aims to determine the selenium (Se) background values of oils along the northern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and serve the utilization of Se-rich resources, as well as the prevention and control of Se deficiency risks. To this end, this study systematically collected 8 273 surface soil samples and 2 190 deep soil samples, analyzed and tested the Se content and other relevant indicators, and examined the response relationships between soil Se and factors such as soil type and physicochemical properties. The results indicate that the surface and deep soils exhibit Se background values of 0.188×10-6 and 0.153×10-6, respectively. High Se background values are identified in the Menyuan Basin, the Xining Basin, the northern part of Qinghai Lake, and the Lagrange and Daban mountains. The highest Se background values occur in soils with the weathering materials of red and coal-bearing clastics of the Paleogene Xining Group as parent materials. The Se background values exhibit a negative correlation with pH and a positive correlation with the contents of organic matter and iron-aluminum oxides. Se in soils tends to accumulate in woodlands, grasslands, peat-rich marsh soils, and meadow soils. The study posits that the soil-forming parent materials with Se background values, including red and coal-bearing clastics of the Paleogene Xining Group, serve as the primary factor controlling the formation of Se-rich soils, and the secondary controlling factors include carbon-rich forests, grasslands, meadow soils, and marsh soils. The transportation by water streams and sedimentary transformation of these controlling factors contribute to the formation of the spatial distribution pattern of localized Se enrichment in the soils of the northern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau.
|
|
Received: 24 April 2024
Published: 07 August 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
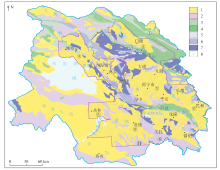
|
Geological sketch map of the study area
1—Cenozoic;2—Mesozoic;3—late Paleozoic;4—early Paleozoic;5—Neoproterozoic;6—Mesoproterozoic;7—Paleoproterozoic;8—sampling points;①—Corridor south Mountain;②—Menyuan Basin;③—Daban Mountain;④—Qinghai Lake Basin;⑤—Xining Basin;⑥—Minhe Basin;⑦—Laji Mountain;⑧—Gonghe Basin;⑨—Guide Basin;⑩—Nanshan,Qinghai;11—Heka Mountain
|
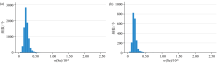
|
Histograms of surface (a) and deep (b) soil data in the study area
|

| 指标 | 原数据(N) | 最大值(Max) | 最小值(Min) | 均值($\stackrel{-}{X}$) | 变异系数(CV) | 剔除数(N2) | 中位数(M) | 背景值 | 全国土壤背景值[11] | | 表层 | 8273 | 2.307 | 0.017 | 0.199 | 0.50 | 283 | 0.186 | 0.188 | 0.17 | | 深层 | 2190 | 2.275 | 0.037 | 0.169 | 0.64 | 109 | 0.151 | 0.153 | 0.26 |
|
Statistics of geochemical parameters of Se content in soil
|
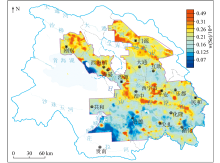
|
Geochemical distribution of Se in the top soil
|
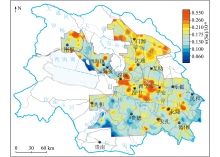
|
Geochemical distribution of Se in the deep soil
|

| 成土母质 | 表层 | 深层 | | 样本数 | Se均值/10-6 | 样本数 | Se均值/10-6 | | 第四系沉积物 | 2751 | 0.19±0.78 | 679 | 0.16±0.83 | | 碎屑岩类风化物 | 3509 | 0.19±0.10 | 939 | 0.17±0.93 | | 火成岩类风化物 | 1148 | 0.24±0.12 | 331 | 0.20±0.16 | | 变质岩类风化物 | 865 | 0.22±0.90 | 241 | 0.18±0.14 |
|
Soil Se content of different parent materials
|

| 指标 | Se | S | pH | Corg | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | | Se | 1 | | | | | | | S | 0.150** | 1 | | | | | | pH | -0.345** | -0.063** | 1 | | | | | Corg | 0.379** | -0.038** | -0.749** | 1 | | | | Fe2O3 | 0.382** | -0.059** | -0.522** | 0.454** | 1 | | | Al2O3 | 0.172** | -0.138** | -0.418** | 0.316** | 0.740** | 1 |
|
Correlation analysis of soil Se with other indicators
|
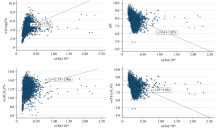
|
Scatter plot of Se and related element content
|

土壤类型
(样本数) | 土壤Se平
均值/10-6 | 土壤类型
(样本数) | 土壤Se平
均值/10-6 | | 沼泽土(n=107) | 0.27±0.10 | 灌淤土(n=118) | 0.14±0.06 | | 山地草甸土(n=1253) | 0.23±0.15 | 高山寒漠土(n=74) | 0.21±0.05 | | 栗钙土(n=2940) | 0.18±0.09 | 高山草原土(n=480) | 0.18±0.10 | | 灰褐土(n=304) | 0.23±0.07 | 高山草甸土(n=1008) | 0.21±0.08 | | 灰钙土(n=364) | 0.20±0.09 | 风沙土(n=74) | 0.06±0.03 | | 黑钙土(n=1539) | 0.20±0.07 | 潮土(n=12) | 0.19±0.02 |
|
Se statistics of different soil types
|
| [1] |
李明龙. 表生环境介质中硒与重金属的地球化学特征及生态效应研究——以湖北省恩施市为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2021.
|
| [1] |
Li M L. Geochemical characteristics and ecological effects of selenium and heavy metals in supergene environmental media—A case study of Enshi City,Hubei Province[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2021.
|
| [2] |
Farooq M R, Zhang Z Z, Yuan L X, et al. Characterization of selenium speciation in Se-enriched crops:Crop selection approach[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2024, 72(7):3388-3396.
|
| [3] |
徐雪生, 骆检兰, 黄逢秋, 等. 富硒耕地质量评价体系构建及其在湖南省新田县新圩镇的应用[J]. 中国地质, 2022, 49(3):789-801.
|
| [3] |
Xu X S, Luo J L, Huang F Q, et al. Construction of the evaluation system for Se-rich arable land and its application in Xinxu Town,Xintian County,Hunan Province[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(3):789-801.
|
| [4] |
Zdziebłowska S, Zajda J, Ruzik L. Microalgae enriched in selenium as a good source of micronutrients[J]. Food Bioscience, 2024,59:103908.
|
| [5] |
朱明勇, 熊永柱, 刘友存, 等. 广东阴那山土壤重金属污染特征、风险评价及源解析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2023, 45(9):1265-1270.
|
| [5] |
Zhu M Y, Xiong Y Z, Liu Y C, et al. Pollution characteristics,risk assessment and source analysis of soil heavy metals in Yinna Mountain of Guangdong[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2023, 45(9):1265-1270.
|
| [6] |
刘金宝, 徐宏国, 袁宏伟, 等. 内蒙古土默特左旗典型草甸土中硒赋存形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(1):245-254.
|
| [6] |
Liu J B, Xu H G, Yuan H W, et al. Speciation of selenium in typical meadow soils in Tumed Left Banner,Inner Mongolia,China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1):245-254.
|
| [7] |
刘熙会, 张小平, 李倩倩, 等. 青藏高原地区大骨节病的流行特征及致病因素探究[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(4):1137-1147.
|
| [7] |
Liu X H, Zhang X P, Li Q Q, et al. Epidemiological trend and pathogenic factors of KBD in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(4):1137-1147.
|
| [8] |
Fordyce F M. Selenium deficiency and toxicity in the environment[J]. Essentials of Medical Geology:Revised Edition,2013:375-416.
|
| [9] |
姬丙艳, 马瑛, 张亚峰, 等. 青藏高原北缘富硒土壤地球化学特征研究及应用[J]. 青海科技, 2018, 25(6):7-10.
|
| [9] |
Ji B Y, Ma Y, Zhang Y F, et al. Study and application of geochemical characteristics of selenium-rich soils in the northern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Qinghai Science and Technology, 2018, 25(6):7-10.
|
| [10] |
刘阳, 姜冰, 张海瑞, 等. 山东省青州市表层土壤硒元素地球化学特征[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(3):933-940.
|
| [10] |
Liu Y, Jiang B, Zhang H R, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in surface soil of Qingzhou,Shandong[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(3):933-940.
|
| [11] |
奚小环, 侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 等. 基于大数据的中国土壤背景值与基准值及其变化特征研究——写在《中国土壤地球化学参数》出版之际[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1095-1108.
|
| [11] |
Xi X H, Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, et al. Big data based studies of the variation features of Chinese soil's background value versus reference value:A paper written on the occasion of Soil Geochemical Parameters of China's publication[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5) :1095-1108.
|
| [12] |
李海蓉, 杨林生, 谭见安, 等. 我国地理环境硒缺乏与健康研究进展[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5):381-386.
|
| [12] |
Li H R, Yang L S, Tan J A, et al. Progress on selenium deficiency in geographical environment and its health impacts in China[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5):381-386.
|
| [13] |
迟凤琴, 徐强, 匡恩俊, 等. 黑龙江省土壤硒分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 土壤学报, 2016, 53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [13] |
Chi F Q, Xu Q, Kuang E J, et al. Distribution of selenium and its infl uencing factors in soils of Heilongjiang Province,China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2016, 53(5):1262-1274.
|
| [14] |
黄春雷. 金衢盆地土壤中硒的富集机理及其生物有效性影响因素研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2022.
|
| [14] |
Huang C L. Study on enrichment mechanism of selenium in soil of jinqu basin and influencing factors of its bioavailability[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2022.
|
| [15] |
陈雪, 杨忠芳, 陈岳龙, 等. 广西中东部9县区农田土壤Cd输入通量研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(2):415-427.
|
| [15] |
Chen X, Yang Z F, Chen Y L, et al. Cadmium input flux in farmland soil of nine counties in middle and east Guangxi[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(2):415-427.
|
| [16] |
廖启林, 崔晓丹, 黄顺生, 等. 江苏富硒土壤元素地球化学特征及主要来源[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [16] |
Liao Q L, Cui X D, Huang S S, et al. Element geochemistry of selenium-enriched soil and its main sources in Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [17] |
李金哲, 龚庆杰, 刘亚轩, 等. 风化过程中硒背景值的定量表征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(5):1031-1041.
|
| [17] |
Li J Z, Gong Q J, Liu Y X, et al. Quantitative description of the geochemical background value of selenium during weathering based on the certified reference materials in China[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(5):1031-1041.
|
| [18] |
鲍丽然, 邓海, 贾中民, 等. 重庆秀山西北部农田土壤重金属生态健康风险评价[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1625-1636.
|
| [18] |
Bao L R, Deng H, Jia Z M, et al. Ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in farmland soil of northwest Xiushan,Chongqing[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1625-1636.
|
| [19] |
严桃桃, 吴轩, 权养科, 等. 从岩石到土壤再到水系沉积物:风化过程的岩性地球化学基因[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3):453-467.
|
| [19] |
Yan T T, Wu X, Quan Y K, et al. Rocks and their weathered products:A geochemical lithogene[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3):453-467.
|
| [20] |
袁宏伟, 陈江均, 郭腾达, 等. 巴彦淖尔市临河区狼山镇和新华镇一带富硒土壤地球化学特征及影响因素[J]. 地质与勘探, 2022, 58(5):1027-1041.
|
| [20] |
Yuan H W, Chen J J, Guo T D, et al. Geochemical characteristics and influencing factors of Se-rich soils in Langshan and Xinhua towns,Linhe district,Bayannur City[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2022, 58(5):1027-1041.
|
| [21] |
马强, 张亚峰, 黄强, 等. 青海省富硒土壤标准探讨[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):772-780.
|
| [21] |
Ma Q, Zhang Y F, Huang Q, et al. Exploring the standard of Se-rich soil in Qinghai province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):772-780.
|
| [22] |
宋礼生. 陕西紫阳焕古滩奥陶纪—志留纪笔石地层[J]. 西北地质科学, 1991(2):87-99.
|
| [22] |
Song L S. Graptolitic strata of Ordovican-Silurian period in Huangutan,Ziyang,Shaanxi[J]. Northwest Geoscience, 1991(2):87-99.
|
| [23] |
付巧玲, 邱顺才. 论土壤硒驱动机制——以河南省崤山地区为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2023, 59(3):580-590.
|
| [23] |
Fu Q L, Qiu S C. On the driving mechanism of soil Se:Taking the Xiaoshan area of Henan Province as an example[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2023, 59(3):580-590.
|
| [24] |
包凤琴, 成杭新, 永胜, 等. 土默特左旗农田土壤环境质量综合评价及特色农业开发建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(2):487-495.
|
| [24] |
Bao F Q, Cheng H X, Yong S, et al. The comprehensive evaluation of farmland soil environmental quality and suggestions on the development of agricultive with distinctive local features in Tumed Left Banner,Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2):487-495.
|
| [1] |
LU Jiang, ZHU Li-Fen, LUO Jian-Lan, LIU Xian-Li. Geochemical background and baseline values of heavy metals in soils in the Xiangjiang River Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2025, 49(3): 687-696. |
| [2] |
XI Xiao-Huan, HOU Qing-Ye, YANG Zhong-Fang, YE Jia-Yu, YU Tao, XIA Xue-Qi, CHENG Hang-Xin, ZHOU Guo-Hua, YAO Lan. Big data based studies of the variation features of Chinese soil’s background value versus reference value: A paper written on the occasion of Soil Geochemical Parameters of China’s publication[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5): 1095-1108. |
|
|
|
|

